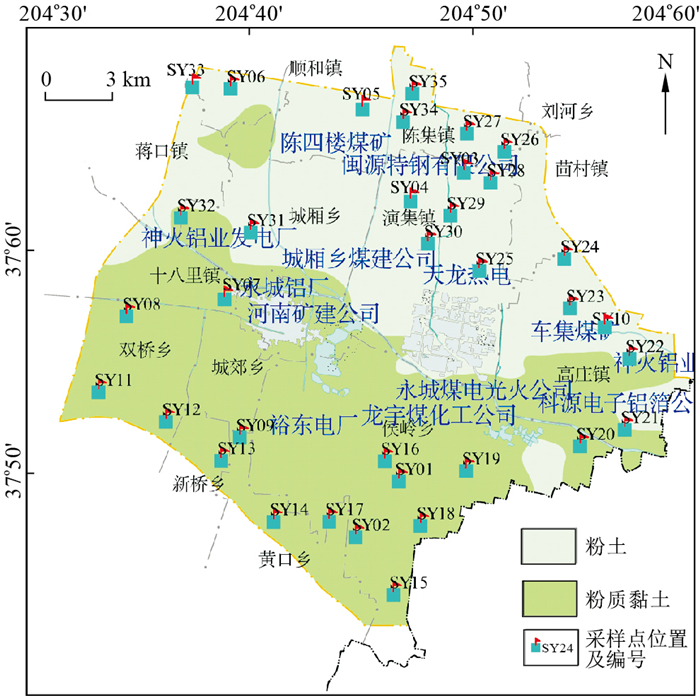
Distribution characteristics and source identification of shallow groundwater pollution in Yongcheng City
-
摘要: 为有效管理和保护永城市浅层地下水资源,维系水资源可续利用,必须查明其污染物的分布特征和来源。在对永城市浅层地下水采样分析的基础上,结合分析城市发展带来产业布局改变及土地利用类型分布对其造成的影响,研究其主要污染组分的来源及分布特征。结果表明:城市第二产业(工矿业)发展,GDP的增长与浅层地下水中ρ(SO42-)、ρ(NO3-)上升存在相关性,城市工业及人口密集区与污染严重区位置趋于一致。浅层地下水污染的最主要来源是SO42-含量的上升,除了直接导致水质变差外,还会间接改变水文地球化学作用的强度,造成原本难溶的碳酸盐和硅酸盐的溶解量增大,使得ρ(TDS)进一步上升而改变水质。其次,NO3-、COD也是浅层地下水主要的污染来源,其部分来源工业废水,部分来源于农业上农药和化肥的过量使用。Abstract: In order to effectively manage and protect the shallow groundwater resource in Yongcheng City and maintain the sustainable utilization of water resource, distribution characteristics and sources of pollutants must be identified.On the basis of sampling and analysis of shallow groundwater, this paper studies the sources and distribution characteristics of main pollution components, combining with the influence of industrial layout change and land use type distribution caused by urban development.The results show that the growth of urban secondary industry (industry and mining) and GDP are correlated with the increase of SO42- and NO3- contents in shallow groundwater, the dense areas of urban industry and population tend to be the same as the seriously polluted areas of shallow groundwater.The main source of shallow groundwater pollution is the increase of SO42- content, in addition to directly causing the deterioration of water quality.It also indirectly changes the intensity of hydrogeochemical action.It leads to an increase in the dissolution of the insoluble carbonate and silicate, which further increases the content of TDS and changes the water quality.In addition, NO3- and COD are also the main pollution sources.It comes partly from industrial waste water and partly from the excessive use of pesticides and fertilizer in agriculture.
-
表 1 浅层地下水化学测试指标及检出限
Table 1. Indicators and detection limits of hydrochemistry of shallow groundwater
测试指标 测试方法 检出限/(mg·L-1) K+和Na+ 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 0.01 Ca2+ 乙二胺四乙酸二钠滴定法 2 Mg2+ 乙二胺四乙酸二钠滴定法 1 Cl- 硝酸银容量法 1 SO42- 硫酸钡比浊法 3 HCO3- 酸碱滴定法 5 F- 分光光度法 0.05 NO3- 分光光度法 0.01 TDS 干燥-重量法 5 COD 酸性高锰酸钾滴定法 0.04 总硬度 乙二胺四乙酸二钠滴定法 3 pH值 玻璃电极法测试 无量纲 表 2 浅层地下水化学统计
Table 2. Statistics of hydrochemical parameters of shallow groundwater
pH K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl- SO42- ρB/(mg·L-1) 极小值 7.2 0.28 8.55 25.25 10.69 3.54 24.02 极大值 8.3 49.94 283.6 206.81 105.58 207.74 453.4 均值 7.56 3.34 94.45 83.88 55.04 57.33 118.09 标准差 0.26 72.40 67.35 40.50 20.16 45.31 83.37 HCO3- F- NO3- NO2- TDS COD 总硬度 ρB/(mg·L-1) 极小值 140.35 0.3 0.02 0 192.24 0.07 138.5 极大值 784.72 2.6 115 1.8 1 235.26 3.67 893.5 均值 510.23 1.22 25.64 0.15 697.96 0.67 435.09 标准差 140.21 0.63 31.35 0.32 232.89 0.77 132.51 表 3 因子分析结果
Table 3. Results of factor analysis
成分 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 SO42- 0.89 0.10 0.20 -0.04 -0.18 Cl- 0.88 0.14 0.01 0.01 0.23 总硬度 0.87 0.07 -0.40 0.08 0.02 TDS 0.78 0.59 0.12 0.09 0.05 Mg2+ 0.64 0.49 -0.01 -0.37 0.15 Ca2+ 0.62 -0.32 -0.52 0.41 -0.10 HCO3- 0.13 0.94 -0.01 0.10 -0.14 Na+ 0.25 0.80 0.43 -0.01 0.02 pH -0.08 0.02 0.89 -0.18 -0.04 K+ 0.10 0.29 0.77 0.42 0.02 F- -0.07 0.16 0.21 -0.89 -0.14 H2SiO3 -0.067 0.35 0.21 0.73 0.03 NO3- 0.06 0.05 -0.13 0.01 0.81 COD 0.08 -0.11 0.12 0.11 0.81 贡献率/% 27.32 17.82 15.57 13.49 10.49 累积贡献率/% 27.32 45.13 60.70 74.19 84.68 -
[1] Simpson T B, Holman I P, Rushton K R. Understanding and modelling spatial drain-aquifer interactions in a low-lying coastal aquifer: The Thurne catchment, Norfolk, UK[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2011, 25(4): 580-592. doi: 10.1002/hyp.7845 [2] Kaushal S S, Duan S, Doody T R, et al. Human-accelerated weathering increases salinization, major ions, and alkalinization in fresh water across land use[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2017, 83: 121-135. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.02.006 [3] Lambán L J, Martos S, Rodríguez-Rodríguez M, et al. Application of groundwater sustainability indicators to the carbonate aquifer of the Sierra de Becerrero (Southern Spain)[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 64(7): 1835-1848. doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-1016-x [4] Anbazhagan S, Jothibasu A. Groundwater sustain ability indicators in parts of Tiruppur and Coimbatore districts[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 2016, 87(2): 161-168. doi: 10.1007/s12594-016-0384-y [5] Alaa A M. Spatio-temporal evaluation of the groundwater quality in Kafr Al-Zayat District, Egypt[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2013, 27: 2987-3002. [6] 刘博, 肖长来, 田浩然, 等. 灰色关联和层次分析法在地下水质评价中的应用: 以吉林市为例[J]. 节水灌溉, 2013, 1(1): 26-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGU201301007.htmLiu B, Xiao C L, Tian H R, et al. Application of method combining grey relation with analytic process for groundwater quality evalution in Jilin City[J]. Water Conservation Irrigation, 2013, 1(1): 26-29(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGU201301007.htm [7] 孙涛, 潘世兵, 李永军. 人工神经网络模型在地下水水质评价分类中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2004, 31(3): 58-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200403013.htmSun T, Pan S B, Li Y J. Application of artificial neural network model to groundwater quality assessment and classification[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2004, 31(3): 58-61(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200403013.htm [8] 金菊良, 魏一鸣, 丁晶. 水质综合评价的投影寻踪模型[J]. 环境科学学报, 2001, 21(4): 431-434. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2001.04.010Jin J L, Wei Y M, Ding J. Projection pursuit model for comprehensive evaluation of water quality[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 2001, 21(4): 431-434(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2001.04.010 [9] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202001004.htmLiang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Scienceand Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202001004.htm [10] 潘欢迎, 邹常健, 毕俊擘, 等. 新疆阿克苏典型山前洪积扇内高氟地下水的化学特征及氟富集机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 194-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202103021.htmPan H Y, Zou C J, Bi J B, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and fluoride enrichment mechanisms of high-fluoride groundwater in a typical piedmont proluvial fan in Aksu area, Xinjiang, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 194-203(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202103021.htm [11] 李琳琳. 太子河流域土地利用对地表地下水水质的影响研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2015.Li L L. The effects of land use on surface and groundwater water quality in Taizi river watershed[D]. Jinan: University of Jinan, 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [12] 巨凡凡, 马腾, 顾栩. 水城盆地空间城镇化对浅层岩溶地下水特征的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2020, 37(1): 123-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHFZ202001017.htmJu F F, Ma T, Gu X. The effect of spatial urbanization on the characteristics of shallow karst groundwater in Shuicheng Basin[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2020, 37(1): 123-134(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHFZ202001017.htm [13] 衡涛, 谢世友. 重庆南川区不同土地利用类型对表层岩溶泉水水质的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(29): 16392-16394. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.29.120Heng T, Xie S Y. Impact of different land use patterns on the quality of surface karst spring in Nanchuan, Chongqing[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(29): 16392-16394(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.29.120 [14] 李绍生, 刘培云, 马勇光, 等. 永城地氟病区氟的地球化学环境研究[J]. 河南科学, 2011, 29(3): 357-361. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKX201103028.htmLi S S, Liu P Y, Ma Y G, et al. Study ongeochemical environment of fluorine in Yongcheng fluorosis areas[J]. Henan Science, 2011, 29(3): 357-361(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKX201103028.htm [15] 赵自建. 河南永城地表水资源质量分析[J]. 黄河水利职业技术学院学报, 2012, 24(4): 8-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHSZ201204007.htmZhao Z J. Analysis on Yongcheng City ground surface water resource quality[J]. Journal of Yellow River Conservancy Technical Institute, 2012, 24(4): 8-10(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHSZ201204007.htm [16] 赵丹, 徐伟攀, 朱文英, 等. 土壤地下水环境损害因果关系判定方法及应用[J]. 环境科学研究, 2016, 29(7): 1059-1066. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201607015.htmZhao D, Xu W P, Zhu W Y, et al, Determining causality of soil and groundwater damage[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 29(7): 1059-1066(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201607015.htm [17] 陈锋, 孟凡生, 王业耀, 等. 多元统计模型在水环境污染物源解析中的应用[J]. 人民黄河, 2016, 38(1): 79-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201601022.htmChen F, Meng F S, Wang Y Y, et al. Application of multivariate statistical analysis in the source apportionment of surface water[J]. Yellow River, 2016, 38(1): 79-84(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201601022.htm [18] 叶慧君, 张瑞雪, 吴攀, 等. 基于主成分分析的岩溶水水化学组成及影响因素研究: 以贵州水城盆地为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(2): 215-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201702009.htmYe H J, Zhang R X, Wu P, et al. Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater and surface water and their influencing factors based on principal component analysis: An example in the Shuicheng Basin of Guizhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(2): 215-225(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201702009.htm [19] Ahmad A, Faramarz D A. R-mod factor analysis, a popular multivariate statistical technique to evaluate water quality in Khaf-Sangan Basin, Mashhad, Northeast of Iran[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2013, 6(3): 893-900. [20] 苏凯峰. 河南永城煤炭矿区环境地质问题及防治对策[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2014, 25(1): 77-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201401019.htmSu K F. Environmental geological problems in the coal mining area and prevention measures of Yongcheng County, Henan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2014, 25(1): 77-81(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201401019.htm [21] 许可, 冯翠红, 魏永霞. 永城市水源地潜水含水层防污性能评价[J]. 人民黄河, 2010, 32(6): 60-62, 65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201006026.htmXu K, Feng C H, Wei Y X. Evaluation on pollution-proof performance of water source region subaqueous aquifer in Yongcheng City[J]. Yellow River, 2010, 32(6): 60-62, 65(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201006026.htm [22] 左俊, 符超峰. 永城市浅层地下水氟化物健康风险评价及其富集原因分析[J]. 地球环境学报, 2015, 6(5): 323-329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHJ201505009.htmZuo J, Fu C F. The fluoride health risk assessment of shallow groundwater and analysis the main reason of fluorine enrichment in Yongcheng[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2015, 6(5): 323-329(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHJ201505009.htm [23] 国家环境保护总局. 地下水环境监测技术规范: HJ/T164-2004[S]. 北京: 国家环境保护总局, 2004.State Environmental Protection Administration. Technical specifications for environmental monitoring of groundwater: HJ/T164-2004[S]. Beijing: State Enviromental Protection Administration, 2004(in Chinese). [24] 王攀, 靳孟贵, 路东臣. 河南省永城市浅层地下水化学特征及形成机制[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(6): 2232-2244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202006033.htmWang P, Jin M G, Lu D C. Hydrogeochemistry characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in Yongcheng City, Henan Province[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(6): 2232-2244(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202006033.htm [25] 贾俊平. 统计学[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2012.Jia J P. Statistics[M]. Beijing: China Renmin University Press, 2012(in Chinese). [26] 李镇镇, 武家玉. 中国主要环境污染物与国内生产总值的相关性分析研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2018, 43(4): 35-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFHJ201804010.htmLi Z Z, Wu J Y. Analysis on correlation between major pollutant emissions and GDP in China[J]. Envronment Science and Management, 2018, 43(4): 35-38(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFHJ201804010.htm [27] 郭芳, 姜光辉, 夏青, 等. 土地利用影响下的岩溶地下水水化学变化特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2007, 26(3): 212-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200703004.htmGuo F, Jiang G H, Xia Q, et al. Hydro-chemical variation of karst groundwater under the impact of land use in Donghe catchment, Hunan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2007, 26(3): 212-218(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200703004.htm [28] 武亚遵, 潘春芳, 林云, 等. 典型华北型煤矿区主要充水含水层水文地球化学特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(5): 191-199.Wu Y Z, Pan C F, Lin Y, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and controlling factors of main water filled aquifers in the typical North China Coalfield[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(5): 191-199(in Chinese with English abstract). [29] Qin T, Yang P, Groves C, et al. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the hydrogeochemistry of the Jialing River and Yangtze River in the Chongqing Main Urban area, SW China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 98: 448-458. [30] 李晓姣, 张岱琼, 乔俊, 等. 基于多元统计方法的某地浅层地下水污染来源分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 2020, 36(1): 88-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB202001015.htmLi X J, Zhang D Q, Qiao J, et al. Analysis of shallow groundwater pollution sources in a certain area based on multivariate statistical approaches[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2020, 36(1): 88-95(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB202001015.htm [31] Rashid A, Guan D X, Farooqi A, et al. Fluorideprevalence in groundwater around a fluorite mining area in the flood plain of the River Swat, Pakistan[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 635: 203-215. [32] 桂和荣. 皖北矿区地下水水文地球化学特征及判别模式研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2005.Gui H R. Study on hydrogeochemical characteristics and discriminant model of groundwater in North Anhui Mining area[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2005(in Chinese with English abstract). [33] 王珺瑜, 王家乐, 靳孟贵. 济南泉域岩溶水水化学特征及其成因[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5): 821-831.Wang J Y, Wang J L, Jin M G. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of karst water in Jinan spring catchment[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(5): 821-831(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: