Cenozoic stratigraphic correlation and the lower limit of Quaternary in Guanzhong Basin
-
摘要: 关中盆地巨厚的新生代沉积为研究区域构造、沉积环境演变与古气候变化研究提供了良好的地质记录,但目前对新生界地层划分和第四纪下限问题仍存在争论。基于钻孔和剖面资料,结合古地磁和生物地层,对关中盆地新生界地层进行了梳理和修订,就第四纪下限和新生界地层划分与对比问题进行了探讨。岩性地层、磁性地层、生物地层证据以及气候变化特征等都支持将第四纪下限定在传统三门组的黄三门与绿三门的交界处或风成黄土与红黏土的界线之处,即松山负极性向高斯正极性转换处(M/G),古地磁年龄为2.6 Ma。基于关中盆地钻孔和剖面的古地磁数据及前人资料,划分了新生界地层,重新厘定了各沉积地层的沉积年代,将新近纪和第四纪沉积分为风成相和河湖相两套同期异相沉积地层序列,风成红黏土的年代延伸到中中新世,建议将中新世的风成堆积命名为段家坡组。这对关中盆地沉积环境形成演化与古气候变化研究、盆地资源开发以及地质工程建设具有重要意义。Abstract: Thick Cenozoic sediments in Guanzhong Basin provide excellent geological records for the study of the regional tectonics, sediment environment evolution and paleoclimate change.However, there are still controversies about the Cenozoic stratigraphic division and the lower boundary of Quaternary in Guanzhou Basin.Based on paleomagnetism and paleontology strata from drilling cores and outcrop sections, we reappraise and reestablish the Cenozoic strata framework in Guanzhong Basin.According to fluvial-lacustrine deposits and eolian red clay-loess sequences, the authors discuss the lower limit of Quaternary in Guanzhong Basin. Evidence from lithology, magnetostratigraphy, biostratigraphy and climate change supporting the lower limit of Quaternary strata should be confined to the boundary of "Yellow Sanmen" and "Green Sanmen" in the traditional Sanmen Formation or the boundary of eolian loess and red clay sediments around M/G boundary, and the paleomagnetic age is 2.6 Ma.Based on palaeomagnetic data of drilling cores, outcrops and previous literature, we revise the Cenozoic chronostratigraphic chart in Guanzhong Basin and amend or reallocate the ages of different strata from Eocene to Holocene.We propose that Neogene and Quaternary deposits in the Guanzhong Basin can be generally classified into two sets of different genesis sediments e.g.eolian and fluvial-lacustrine sequences.The eolian deposits can be extended to the Miocene period, which is older than previous conventional knowledge, and this Miocene eolian red clay sequences can be named as Duangjiapo Formation.This study is helpful to understand the formation and evolution of the sedimentary environment, paleoclimatic change, basin resource exploitation and geological engineering construction in Guanzhong Basin.
-
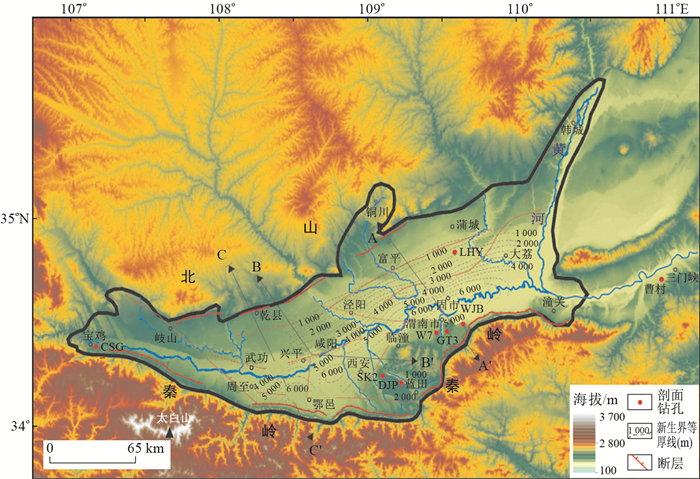
图 1 关中盆地地形与新生界沉积厚度图(新生界沉积厚度(m)数据引自文献[33])
CSG.宝鸡长寿沟剖面;SK2.西安白鹿塬SK2钻孔;DJP.蓝田段家坡剖面;W7.渭南W7钻孔;GT3.渭南GT3钻孔;WJB.渭南武家堡剖面;LYH.渭南卤阳湖钻孔
Figure 1. Topography and isopach map of Cenozoic deposits in Guanzhong Basin
图 3 关中盆地构造单元划分图(据文献[33]修改)
Figure 3. Tectonic units in Guanzhong Basin
表 1 关中盆地新生界地层划分历史与方案
Table 1. Stratigraphic division history and scheme of Cenozoic sediments in Guanzhong Basin

表 2 关中盆地新生界地层岩性、古地磁年代与动、植物类型对比
Table 2. Correlation of stratigraphic lithology, paleomagnetic age and animal and plant types in Cenozoic in Guanzhong Basin

-
[1] Wang P, Huang Z, Mi N, et al. Crustal structure beneath the Weihe Graben in central China: Evidence for the tectonic regime transformation in the Cenozoic[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 81: 105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.11.010 [2] Tang Y, Zhou S, Chen Y J, et al. Crustal structures across the western Weihe Graben, North China: Implications for extrusion tectonics at the northeast margin of Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 2015, 120(7): 5070-5081. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011210 [3] 韩恒悦, 张逸, 袁志祥. 渭河断陷盆地带的形成演化及断块运动[J]. 地震研究, 2002, 54(4): 362-368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2002.04.010 [4] Rao G, Lin A, Yan B, et al. Tectonic activity and structural features of active intracontinental normal faults in the Weihe Graben, central China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 636(24): 270-285. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195114004776 [5] 扈桂让, 李自红, 闫小兵, 等. 韩城断裂西庄村-西南村一带断裂展布及晚第四纪剖面[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(4): 36-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201704005.htm [6] 张伯声, 王战. "汾渭地堑"的发展及其地震活动性[J]. 西安地质学院学报, 1982, 4(1): 24-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX198201007.htm [7] 李高阳, 李陈侠, 李晓妮, 等. 渭南塬前断裂晚第四纪古地震研究[J]. 华南地震, 2019, 39(3): 65-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDI201903009.htm [8] 彭建兵. 渭河盆地活动断裂与地质灾害[M]. 西安: 西北大学出版社, 1992: 1-233. [9] 张勤, 瞿伟, 彭建兵, 等. 渭河盆地地裂缝群发机理及东、西部地裂缝分布不均衡构造成因研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(8): 2589-2597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201208011.htm [10] 刘建朝, 李荣西, 魏刚峰, 等. 渭河盆地地热水水溶氦气成因与来源研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2009, 28(6): 84-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2009.06.013 [11] 刘东生, 丁梦麟, 高福清. 西安蓝田间新生界地层剖面[J]. 地质科学, 1960, 3(4): 199-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX196004007.htm [12] 陕西省地质矿产局. 陕西省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989: 243-265. [13] 张云翔, 薛祥煦. 陕西蓝田地区新第三纪地层划分的几点讨论[J]. 西北地质科学, 1996, 17(1): 59-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBFK601.001.htm [14] 李智超, 李文厚, 李永项, 等. 渭河盆地新生代沉积相研究[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(4): 529-540. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201504009.htm [15] 王斌, 郑洪波, 王平, 等. 渭河盆地新生代地层与沉积演化研究: 现状和问题[J]. 地球科学进展, 2013, 28(10): 1126-1135. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2013.10.1126 [16] 鹿化煜, 张瀚之, 王逸超, 等. 渭河盆地新生代沉积序列与亚洲季风气候起源演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(5): 1057-1067. [17] 蔡鑫磊. 渭河盆地一热两气资源勘探开发研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 1-218. [18] 张茂省, 董英, 刘洁. 论新型城镇化中的城市地质工作[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 50(5): 581-587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK201405003.htm [19] 张文, 李玉宏, 王利, 等. 渭河盆地氦气成藏条件分析及资源量预测[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(2): 236-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201802009.htm [20] 周静静, 张晓敏, 赵法锁, 等. 陕西秦巴山区地质灾害危险性评价研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(4): 544-553. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201904011.htm [21] 李峰峰, 郭睿, 余义常. 层序地层划分方法进展及展望[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 215-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904022.htm [22] 张文彪, 段太忠, 刘彦锋, 等. 定量地质建模技术应用现状与发展趋势[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 264-275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903029.htm [23] 贾兰坡, 张玉萍, 黄万波, 等. 陕西蓝田新生界[C]//中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所. 陕西蓝田新生界现场会议论文集. 北京: 科学出版社, 1966: 1-31. [24] 地矿部第三普查勘探大队. 汾渭盆地石油普查阶段地质成果报告[R]. 西安: 地矿部第三普查勘探大队, 1977: 1-253. [25] 刘护军, 薛祥煦. 对渭河盆地新生界及其年代的讨论[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2004, 26(4): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2004.04.001 [26] 李智超, 李文厚, 李永项, 等. 陕西渭河地区新生代地层及沉积环境演化[J]. 地层学杂志, 2016, 40(2): 168-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201602006.htm [27] 张梦婷, 李红, 李文厚, 等. 渭河盆地新生代沉积速率特征与主控因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(4): 74-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201804010.htm [28] 薛祥煦. 陕西渭南早更新世哺乳动物群及其层位[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1981, 19(1): 35-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZD198101007.htm [29] 何培元, 刘兰锁, 于清河. 从三门峡东坡沟剖面探讨"三门系"的时代及其环境演变[J]. 地质论评, 1984, 32(2): 161-169. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1984.02.008 [30] 王书兵, 蒋复初, 吴锡浩, 等. 三门组的内涵及其意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 45(1): 116-123. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.01.016 [31] 孙建中. 关于"黄三门"与"绿三门"[J]. 西安地质学院学报, 1986, 8(4): 42-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX198604006.htm [32] Wang B, Zheng H B, He Z, et al. Middle Miocene eolian sediments on the southern Chinese Loess Plateau dated bymagnetostratigraphy[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 411: 257-266. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.07.007 [33] 王建强, 刘池洋, 高飞, 等. 陕西渭河盆地前新生界地质特征及其油气意义[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(10): 1981-1991. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.10.024 [34] 李智超. 渭河盆地新生代岩相古地理及环境演化[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2017. [35] Rits D S, Prins M A, Troelstra S R, et al. Facies analysis of the Middle and Late Quaternary sediment infill of the northern Weihe Basin, Central China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2016, 31(2): 152-165. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2853 [36] Li Z C, Li W H, Li Y X. The lithofacies paleogeography and paleoenvironmental evolution of the Cenozoic in the Weihe Basin, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica: English Edition, 2017, 91(S1): 132-133. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13222 [37] Shi W, Chen L, Chen X, et al. The Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the faulted basins in the northern margin of the Eastern Qinling Mountains, Central China: Constraints from fault kinematic analysis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 173: 204-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.01.018 [38] Sun J M. Long-term fluvial archives in the Fenwei Graben, central China, and their bearing on the tectonic history of the India-Asia collision system during the Quaternary[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2005, 24(10/11): 1279-1286. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379104002665 [39] Fan S H, Chen S E, Li R X. Combined effects of the subductions of the Pacific Plate and Indian Plate in Central China in the Cenozoic: Recorded from the Wei River Basin[J]. Geological Journal, 2018, 53(S1): 266-273. [40] 王斌. 渭河盆地新生代沉积演化盆山耦合与风尘沉积[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2014. [41] Yang P, Ren Z, Zhang J, et al. Discussion of the coupling relationships between the Cenozoic sedimentary-tectonic migration of the Weihe Basin and the uplift of the Weibei and East Qinling areas[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 2018, 53(3): 876-892. [42] Pillans B, Naish T. Defining the Quaternary[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2004, 23(23/24): 2271-2282. [43] 安芷生, 艾莉. 尚未完成的地质年代表: 第四纪悬而未决的前程[J]. 地层学杂志, 2005, 29(2): 99-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2005.02.003 [44] Gibbard P L, Head M J, Walker M J C, et al. Formal ratification of the Quaternary System/Period and the Pleistocene Series/Epoch with a base at 2.58 Ma[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2010, 25(2): 96-102. doi: 10.1002/jqs.1338 [45] Deng C L, Hao Q Z, Guo Z T, et al. Quaternary integrative stratigraphy and timescale of China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(1): 324-348. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9195-4 [46] 王永焱, 滕志宏. 中国黄土区第四系下限问题[J]. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版, 1987, 17(1): 15-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ198701004.htm [47] An Z S. A study on the Lower Boundary of Quaternary in North China: Stratigraphic significance of the Matuyama/Gauss boundary[C]//Anon. Developments in Geoscience-Contribution to 27th International Geological Congress. Moscow. Beijing: Science Press, 1984: 149-157. [48] 张宗祜, 邵时雄, 刘海坤. 中国第四纪地层[M]. 北京: 中国海洋出版社, 1991: 77-121. [49] 曹照垣, 于清河, 刘兰锁, 等. 试论中国第四纪下界问题[J]. 地质学报, 1983, 57(1): 96-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE198301009.htm [50] 李秉成. 第四系下界问题[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2002, 22(5): 55-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-8879.2002.05.016 [51] 岳乐平. 蓝田段家坡黄土剖面磁性地层研究[J]. 地质论评, 1989, 35(5): 479-488. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1989.05.012 [52] 赵志中, 吴锡浩, 蒋复初, 等. 三门峡地区黄土与古季风[J]. 地质力学学报, 2000, 6(4): 19-26, 66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2000.04.003 [53] Zhu Z Y, Dennell R, Huang W W, et al. Hominin occupation of the Chinese Loess Plateau since about 2.1 million years ago[J]. Nature, 2018, 559: 608-612. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0299-4 [54] Sun D H, Liu D S, Chen M Y, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and palaeoclimate of red clay sequences from Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 1997, 40(4): 337-343. [55] 孙建中, 赵景波, 魏明建, 等. 武家堡剖面古地磁新资料[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1988, 32(5): 44-48, 36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG198805013.htm [56] 蒋复初, 傅建利, 王书兵, 等. 关于黄河贯通三门峡的时代[J]. 地质力学学报, 2005, 25(4): 293-301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2005.04.001 [57] 方甲炳, 杨飞, 岳乐平. 宝鸡长寿沟渭河五级阶地磁性地层学研究[J]. 陕西地质, 1992, 10(1): 53-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXDY199201005.htm [58] Yan Y H, Zhou J, He Z, et al. Evolution of Luyang Lake since the last 34, 000 years: Climatic changes and anthropogenic impacts[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 440: 90-98. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.06.009 [59] Zheng H B, An Z S, Shaw J. New contributions to Chinese Plio-pleistocene magnetostratigraphy[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1992, 70(3/4): 146-153. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/003192019290177W [60] Wang H, Lu H, Zhao L, et al. Asian monsoon rainfall variation during the Pliocene forced by global temperature change[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 5272. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13338-4 [61] 童国榜, 张俊牌, 刘明建, 等. 渭河盆地距今200~300万年古植被及第四纪下限的讨论[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1989, 9(4): 86-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198904011.htm [62] 童国榜, 吴锡浩, 陈云, 等. 渭河谷地晚新生代地表环境巨变的孢粉记录[J]. 地质力学学报, 2000, 6(4): 11-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2000.04.002 [63] 赵琳, 鹿化煜, 唐领余. 渭河盆地新生代孢粉组合与植被演化特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(5): 1083-1093. [64] Zhao L, Lu H, Wang H, et al. Vegetation dynamics in response to evolution of the Asian Monsoon in a warm world: Pollen evidence from the Weihe Basin, central China[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2020, 193: 103-269. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921818120301600 [65] Song Y G, Fang X M, Chen X L, et al. Rock magnetic record of Late Neogene red clay sediments from the Chinese Loess Plateau and its implications for East Asian monsoon evolution[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 510: 109-123. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.09.025 [66] 袁凤钿. 渭河地区新生界及第四系下界的讨论[J]. 陕甘宁石油普查通讯, 1976, 2(1): 22-32. [67] 胡惠民, 王淑芳. 鄂尔多斯及其周围地区第四纪下限问题的讨论[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1989, 9(2): 79-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198902012.htm [68] Li B, Feng Z, Wang W P. Characteristics of the Sanmen Formation clays and their relationship with loess landslides in the Guanzhong area, Shaanxi, China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2015, 8(10): 7831-7843. doi: 10.1007/s12517-015-1822-7 [69] 董英, 宋友桂, 张茂省, 等. 关中盆地城市群发展中几个关键基础地质问题[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(2): 12-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201902004.htm [70] 胡巍, 岳乐平, 田新红. 渭南沋河宋家北沟剖面磁性地层学研究[J]. 陕西地质, 1993, 11(2): 26-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXDY199302004.htm [71] 王焯, 王平, 王曦. 陕西渭南宋家北沟新近纪/第四纪三门组介形类化石研究[J]. 西安石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 25(1): 35-40, 44, 110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201001010.htm [72] 周明镇. 陕西蓝田地区第三纪哺乳类动物群[C]//中国地质科学院地层古生物论文集编委会. 地层古生物论文集: 第7辑. 北京: 地质出版社, 1978: 98-108. [73] 孙文峰, 鹿化煜, 王逸超, 等. 渭河盆地蓝田始新世红河组沉积物特征和古环境记录[J]. 高校地质学报, 2017, 23(3): 533-544. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201703015.htm [74] 张玉萍, 黄万波, 汤英俊, 等. 陕西蓝田地区新生界[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1978: 1-60. [75] Zhang Z, Gentry W A. Land mammal faunal sequence of the Late Miocene of China: New evidence from Lantian, Shaanxi Province[J]. Vertebrata Pal Asiatica, 2002, 40(3): 165-176. http://europepmc.org/abstract/CBA/374620 [76] Kaakinen A, Lunkka J P. Sedimentation of the Late Miocene Bahe Formation and its implications for stable environments adjacent to Qinling Mountains in Shaanxi, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2003, 22(1): 67-78. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00044-0 [77] Zhang Z Q, Kaakinen A, Liu L P, et al. Mammalian biochronology of the Late Miocene Bahe Formation[M]//Anon. Fossil mammals of Asia: Neogene biostratigraphy and chronology. New York: Columbia University Press, 2013: 187-202. [78] 谢青, 曾忠诚, 张若愚, 等. 关中盆地上新世地层形成时代、层序划分及沉积相特征研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2018, 33(3): 434-440. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201803014.htm [79] Kang S G, Lu Y C, Wang X L. Closely-spaced recuperated OSL dating of the last interglacial paleosol in the southeastern margin of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2011, 6(5): 480-490. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2011.04.004 [80] Kang S G, Wang X L, Lu Y C. Quartz OSL chronology and dust accumulation rate changes since the Last Glacial at Weinan on the southeastern Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Boreas, 2013, 42(4): 815-829. doi: 10.1111/bor.12005/references [81] 贾兰坡. 蓝田猿人头骨发现经过及地层概况[J]. 科学通报, 1965, 16(6): 477-481. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB196506002.htm -





 下载:
下载: