Experimental study on solid-free anti-sloughing drilling fluid suitable for deep core drilling projects
-
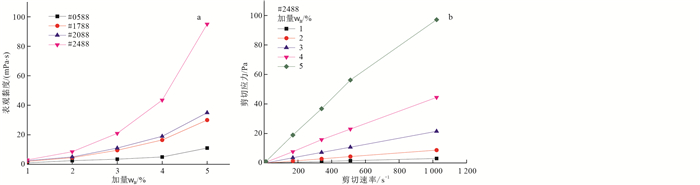
摘要: 为应对金刚石绳索取心钻进普遍发生的垮塌、造浆、钻杆内壁结泥皮等问题,完成了基于聚乙烯醇(PVA)为抑制剂的无固相防塌钻井液室内研究。通过泥页岩滚动回收试验、膨润土临界加量试验、泥球浸泡试验以及电动电位测试等对比了常用抑制剂的抑制效果;通过配伍性试验确定了增黏剂及降失水剂的种类和加量;对比了不同种类的污染物对所获配方钻井液综合性能的影响。结果表明,相比于NaCl、KCl等常规无机盐抑制剂,聚乙烯醇具有较强的抑制性,且抑制性与聚合度呈正相关;黄原胶(XC)、磺化褐煤树脂(SPNH)、磺化沥青(FT-1)可用作配制该钻井液的增黏提切剂和降失水剂;该配方钻井液可抗35% NaCl、4% CaCl2以及12%钙土的污染,能满足110℃温度范围内的使用要求,可在3 000 m深度范围内的强造浆地层、破碎地层、盐膏层等复杂地层中使用。Abstract: To deal with the problems of wellbore collapse, mud making and mud lining in drilling strings, a solid-free anti-collapse drilling fluid with polyvinyl alcohol as inhibitor was developed. The inhibition effect of commonly used inhibitors was studied by shale hot rolling recovery test, critical addition of bentonite test, and mud boulder soaking test. The types and dosage of viscosifiers and water loss reducers were determined by compatibility test, and the influence of different pollutants on the comprehensive properties of the formulated drilling fluid were compared. Experimental results showed that compared with the conventional inorganic salt such as NaCl and KCl, polyvinyl alcohol had a stronger inhibition effect which was positively correlated with polymerization degree. XC, SPNH and FT-1 could be used as viscosifier and water loss reducers to prepare the drilling fluid, respectively. The performance of formula drilling fluid under the pollution of 35%NaCl, 4% CaCl2 and 12% calcium bentonite can be stable in the temperature of 110 ℃, indicating that the prepared drilling fluid can be used in the strong mud making strata, fractured strata, salt bed and other complex strata in the depth of 3 000 m.
-
Key words:
- core drilling /
- solid-free drilling fluid /
- anti-sloughing /
- polyvinyl alcohol /
- pseudoplastic
-
表 1 污染物对钻井液性能的影响
Table 1. Influence of pollutants on drilling fluid performance
钻井液 加量wB/% 稠度系数K/(Pa·s n) 流型指数n 切力τ/Pa 失水量/mL 基浆 - 0.21 0.64 0 7.2 基浆+NaCl 5 0.04 0.84 0 5.6 15 0.11 0.69 0.61 6.8 25 0.11 0.69 0.61 7.6 35 0.13 0.68 0.77 7.6 基浆+CaCl2 0.5 0.13 0.68 0 5.6 1.0 0.13 0.67 0 6.0 2.0 0.07 0.77 0.19 6.0 4.0 0.07 0.77 0.19 6.4 基浆+钙基膨润土 4 0.21 0.67 0.29 8.0 8 0.31 0.63 0.36 8.8 12 0.34 0.64 0.53 9.6 表 2 老化温度对钻井液性能的影响
Table 2. Influence of aging temperature on drilling fluid performance
钻井液 温度/℃ K/(Pa·s n) n 切力τ/Pa 失水量/mL 基浆 50 0.14 0.68 0.66 7.4 80 0.12 0.69 0.42 8.4 110 0.02 0.81 0 8.6 基浆+35% NaCl 50 0.16 0.64 0.68 9.6 80 0.10 0.69 0.81 11.2 110 0.13 0.67 0.76 28.0 基浆+4% CaCl2 50 0.16 0.67 0 5.6 80 0.15 0.68 0 6.2 110 0.11 0.71 0 7.2 基浆+12%钙基膨润土 50 0.58 0.53 1.13 7.6 80 0.28 0.64 0.25 8.8 110 0.56 0.52 0.19 11.6 -
[1] 曾祥熹. 金刚石钻进的特点和对泥浆的要求[J]. 中南矿冶学院学报, 1980, 11(1): 55-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD198001005.htm [2] 姜桂春. 聚丙烯酰胺无固相冲洗液在复杂地层中的应用研究[J]. 探矿工程: 岩土钻掘工程, 2015, 42(1): 34-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7428.2015.01.007 [3] 李生海, 马智跃, 邓先明, 等. 高分子聚合物无固相冲洗液在牛头山深钻CUSD3孔的应用研究[J]. 探矿工程: 岩土钻掘工程, 2017, 44(1): 29-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7428.2017.01.007 [4] 李攀义, 单文军, 徐兆刚, 等. 成膜防塌无固相钻井液体系在金鹰矿区ZK1146井中的应用研究[J]. 探矿工程: 岩土钻掘工程, 2015, 42(10): 26-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7428.2015.10.007 [5] 张翼, 方俊伟, 于培志, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北一区柯吐尔组失稳特征及钻井液技术研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 281-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904030.htm [6] Deville J P, Livanec P W, Zhou Hui. Polyvinyl alcohol-based shale inhibitor[P]. US: 2017/0218251A1, 2017-08-03. [7] Dardir M M, Farag Ab, Ramdan M A, et al. Activation of Egyptian bentonite to improve their drilling fluids properties[J]. International Journal of Current Research, 2014, 6(5): 6772-6780. http://www.journalcra.com/sites/default/files/5479.pdf [8] Zhao Xin, Qiu Zhengsong, Huang Weian, et al. Multifunctional properties of polyglycol in deepwater drilling fluids[J]. Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils, 2014, 50(4): 362-362. doi: 10.1007/s10553-014-0533-1 [9] 方俊伟, 苏晓明, 熊汉桥, 等. 塔中区块成膜封缝堵气钻井液体系[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 297-302. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902036.htm [10] Huang Weian, Lan Qiang, Qiu Zhengsong, et al. Colloidal properties and clay inhibition of sodium silicate in solution and montmorillonite suspension[J]. Silicon, 2016, 8(1): 111-122. doi: 10.1007/s12633-015-9351-2 [11] Guo Jiankang, Yan Jienian, Fan Weiwang, et al. Applications of strongly inhibitive silicate-based drilling fluids in troublesome shale formations in Sudan[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2006, 50(3/4): 195-203. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920410505002147 [12] McDonald M J. A novel potassium silicate for use in drilling fluids targeting unconventional hydrocarbons[C]//Paper 162180-MS presented at the SPE Canadian Unconventional Resources Conference, 30 October-1 November 2012, Calgary, Alberta, Canada, 2012. [13] 翟育峰, 王鲁朝, 丁昌盛, 等. 西藏罗布莎科学钻孔冲洗液技术[J]. 探矿工程: 岩土钻掘工程, 2014, 41(4): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TKGC201404001.htm [14] 张红红. 油页岩勘探无固相聚合物钻井液研究与应用[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2007. [15] 郑克清. 复杂地层钻探护壁堵漏工艺研究与应用[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012. [16] API Recommended Practice 13B-1. Recommended practice for field testing water-based drilling fluids[S]. Washington, DC: American Petroleum Institute, 2009. [17] API Recommended Practice 13I. Recommended Practice for standard procedure for laboratory testing drilling fluids[S]. Washington, DC: American Petroleum Institute, 2006. [18] 北京有机化工厂研究所. 聚乙烯醇的性质和应用[M]. 北京: 纺织工业出版社, 1979. [19] İşçi S, Ünlü C H, Atici O, et al. Rheology and structure of aqueous bentonite-polyvinyl alcohol dispersions[J]. Bulletin of Materials Science, 2006, 29(5): 449-456. doi: 10.1007/BF02914075 [20] 裴向军. PAA无固相冲洗液在水敏岩层钻进中的应用[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2001, 16(02): 140-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK200102012.htm [21] Mohamed N, Nadji M M, Jean P C, et al. Investigation of combined effects of xanthan gum, sodium dodecyl sulphate, and salt on some physicochemical properties of their mixtures using a response surface method[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 2009, 30(9): 1333-1341. doi: 10.1080/01932690902735538 [22] 王世高. 黄原胶的化学改性及其性能和结构的研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2011. -





 下载:
下载: