Analogue experiments for the Shuangyushi area in the north western Sichuan Foreland Basin and their implications
-
摘要: 基于川西北前陆双鱼石地区地震构造解释和砂箱物理模拟实验等,揭示川西北前陆盆地构造变形特征、过程与形成演化机制。标准模型、标准地层模型和断坪-断坡结构模型物理模拟实验揭示出川西北双鱼石地区具有双重构造扩展变形特征,受底部滑脱层系和断坡结构带联合控制,其深部物质变形形成典型冲起构造。断坡结构带对上覆下古生界构造变形及其断裂发育具有重要控制作用,部分断裂体系易于形成高效的下寒武统筇竹寺组源岩-古生界储层“源-储”输导体系。前陆扩展变形带逆断层与相关冲起构造易于形成深部隐伏的双重构造,前陆盆地隐伏构造由新生代晚期构造扩展变形形成,但其构造变形相对较弱,因而具有较佳的晚期油气保存富集条件。“自然界原型到实验模型”的砂箱物理模拟为解译前陆盆地演化过程及其油气富集等提供了独立有效的手段。Abstract: In this study, we conducted three sets of analouge experiments, i.e., the pilot experiment with homogeneous quartz sand with frontal ramp, scaled experiments with embedded layer of silicone and/or frontal ramp, for the Shuangyushi area in the north western Sichuan Foreland Basin.It suggests that the north western Sichuan Foreland Basin is dominated with two-layer style of deformation, in particular, with pop-up in deep strata which is controlled by the basal decollement and frontal ramp.It should be noted that the frontal ramp has significant influence on the undistributed deformation and related fault-style occurred at the overlying sequences, which are in favor of formation for a pathway system between Lower Cambrian Qiongzhushi Formation and Mesozoic carbonate/dolomite reservoir.In contrast to duplex as a result of multistage deformation in the thrust-and-fold-belt, the north western Sichuan Foreland Basin is characterized with gentle deformation, as a result of forelandward propagation deformation in Cenozoic, and thus with a better quality of hydrocarbon preservation.Analogue experiments have been a powerful and indispensable tool to help us understand the thrust-fold-belt and foreland basin, as well as their hydrocarbon accumulation, from nature to models.
-
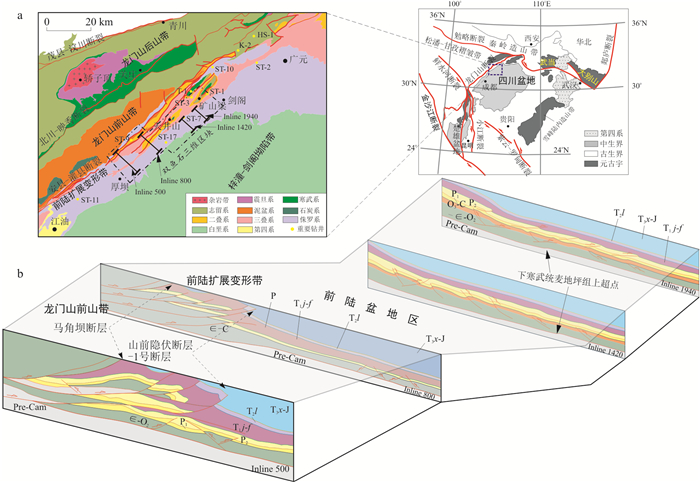
图 6 双鱼石地区典型剖面构造解释及其变形模型对比图
a.Inline-1260测线构造解释及其变形模式图;b.Inline-1940测线构造解释及其变形模式图;P1l.下二叠统梁山组;P2w.上二叠统吴家坪组;其他地层代号说明同图 1
Figure 6. Diagram of typical section structure explanation and comparison of its deformation model in the Shuangyushi area
-
[1] Chapple W M. Mechanics of thin-skinned fold and thrust belts[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1978, 89(8): 1189-1198. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1978)89<1189:MOTFB>2.0.CO;2 [2] Dahlen F A, Suppe J, Davis D. Mechanics of fold-and-thrust belts and accretionary wedges: Cohesive coulomb theory[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1984, 89(B12): 10087-10101. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB12p10087 [3] Beaumont C, Fullsack P, Hamilton J. Erosional control of active compressional orogens[M]//McClay K R. Thrust tectonics. London: Chapman and Hall, 1992: 1-18. [4] Willett S D, Beaumont C, Fullsack P. Mechanical model for the tectonics of doubly vergent compressional orogens[J]. Geology, 1993, 21(4): 371-374. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0371:MMFTTO>2.3.CO;2 [5] Bonnet C, Malavieille J, Mosar J. Interactions between tectonics, erosion, and sedimentation during the recent evolution of the Alpine orogen: Analogue modeling insights[J/OL]. Tectonics, 2007, 26(6). doi: 10.1029/2006TC002048. [6] Graveleau F, Malavieille J, Dominguez S. Experimental modelling of orogenic wedges: A review[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 538/540: 1-66. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.01.027 [7] 赖东, 范彩伟, 罗强, 等. 砂箱物理模型浅表底辟构造研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 103-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903010.htm [8] 刘树根, 罗志立, 赵锡奎, 等. 试论中国西部陆内俯冲型前陆盆地的基本特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(1): 37-48, 56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.01.007 [9] 王鹏, 朱童, 徐邱康, 等. 川西坳陷中段雷口坡组烃源岩评价及气源分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 180-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903019.htm [10] 刘树根, 孙玮, 王国芝, 等. 四川叠合盆地油气富集原因剖析[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 40(5): 481-497. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2013.05.01 [11] 张本健, 谢继容, 尹宏, 等. 四川盆地西部龙门山地区中二叠统碳酸盐岩储层特征及勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(2): 33-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201802006.htm [12] 刘树根, 李智武, 曹俊兴, 等. 龙门山陆内复合造山带的四维结构构造特征[J]. 地质科学, 2009, 44(4): 1151-1180. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2009.04.010 [13] 何鲤, 刘莉萍, 罗潇, 等. 川西龙门山推覆构造特征及有利油气勘探区块预测[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(3): 247-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2007.03.005 [14] 陈竹新, 贾东, 魏国齐, 等. 龙门山北段冲断前锋构造带特征[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(5): 657-662, 668. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.05.005 [15] Liu Shugen, Deng Bin, Jansa L, et al. The early Cambrian Mianyang-Changning intracratonic sag and its control on petroleum accumulation in the Sichuan Basin, China[J/OL]. Geofluids, 2017. doi: org/10.1155/2017/6740892. [16] 罗强, 何宇, 黄家强, 等. 川西北前陆扩展砂箱物理模拟及其深层晚期扩展变形特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(6): 1031-1040. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202006021.htm [17] Deng B, Fan C W, He Y, et al. Low basal friction-controlled geometry and kinematics of accretionary wedges from analogue experiments[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 3821-3836. doi: 10.1002/gj.3642 [18] Bonanno E, Bonini L, Basili R, et al. How do horizontal, frictional discontinuities affect reverse fault-propagation folding?[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2017, 102: 147-167. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2017.08.001 [19] Johnson K M. Growth of fault-cored anticlines by flexural slip folding: Analysis by boundary element modeling[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2018, 123(3): 2426-2447. doi: 10.1002/2017JB014867 [20] Knipe R J. Footwall geometry and the rheology of thrust sheets[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1985, 7(1): 147-167. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0191814185901105 [21] Strayer L M, Hudleston P J. Numerical modeling of fold initiation at thrust ramps[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1997, 19(3/4): 551-566. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0191814196001095 [22] Erickson S G, Strayer L M, Suppe J. Numerical modeling of hinge-zone migration in fault-bend folds[M]//McClay K R. Thrust tectonics and hydrocarbon systems. AAPG Memoir 82, 2004: 438-452. [23] Wibberley C A J. Three-dimensionalgeometry, strain rates and basement deformation mechanisms of thrust-bend folding[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1997, 19(3/4): 535-550. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0191814196000995 [24] 范昌育, 王震亮, 张晓强. 断裂活动中的瞬时流场及断裂的输导性研究: 以库车前陆盆地克拉苏冲断带为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(6): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201606002.htm [25] 王国芝, 刘树根, 赵锡奎. 龙门山中段川西前陆盆地初始盆山边界及其变迁[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 35(4): 431-439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2008.04.013 [26] 戴鸿鸣, 刘文龙, 杨跃明, 等. 龙门山北段山前带侏罗系油砂岩成因研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(6): 604-608. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2007.06.014 [27] 刘光祥, 王守德, 潘文蕾, 等. 四川广元天井山古油藏剖析[J]. 海相油气地质, 2003, 8(1/2): 103-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ2003Z1024.htm [28] 黄第藩, 王兰生. 川西北矿山梁地区沥青脉地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(1): 23-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200801005.htm [29] 罗茂, 耿安松, 廖泽文, 等. 四川盆地江油厚坝油砂有机地球化学特征与成因研究[J]. 地球化学, 2011, 40(3): 280-288. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201103008.htm -





 下载:
下载: