Visualization of geological spatial distributing information in regional geochemical exploration data based on t-SNE algorithm: A case study of SW England
-
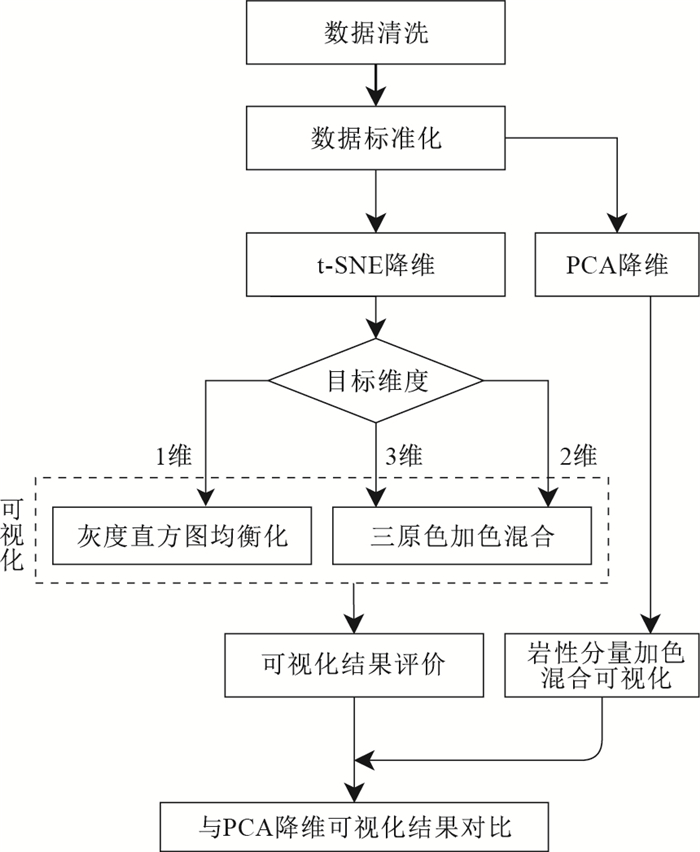
摘要: 区域化探数据中包含了丰富的地质信息,提取出蕴含在这些数据中的地质体空间分布信息,对于区域地质研究和找矿勘查具有重要意义。区域化探数据通常包括数十个元素,属于高维数据,隐藏在这些高维数据中的地质体空间分布信息无法直接从数据中观察到。针对这个问题,构建了一个基于t分布随机近邻嵌入(t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding,简称t-SNE)算法的高维区域化探数据降维可视化模型。t-SNE算法是一种非线性降维方法,特别适用于高维数据集的降维和可视化。选择对岩性鉴定比较稳定的元素,通过t-SNE算法将高维化探数据降维到人眼可观察的一、二、三维,把降维之后的变量表达为栅格图,通过三原色混合等方法进行可视化,从而把隐藏在高维化探数据中的地质体空间分布信息可视化表达出来。以英格兰西南部某地区水系沉积物区域化探数据为例进行研究来检验t-SNE算法在高维化探数据可视化上的实际应用效果。结果显示:①通过t-SNE算法对高维化探数据进行可视化得到的结果能够很好地反映研究区的地质体空间分布情况;②可视化的效果与t-SNE算法的目标维度和复杂度两个参数密切相关。在t-SNE算法中设定要降维到的目标维度越高,所显示的地质体信息越详细。③基于t-SNE算法的化探数据降维可视化效果比基于主成分分析(PCA)的化探数据降维可视化效果更好。本文研究表明基于t-SNE算法的化探数据降维可视化方法能够很好地将地质体空间分布信息可视化表达出来,对于推断地质体的空间分布有一定的指导意义。Abstract: Regional geochemical prospecting data contains a lot of geological information. Extracting the geological spatial distributing information contained in these data is of great significance for regional geological research and mineral prospecting. Regional geochemical data usually includes dozens of elements, which belong to high-dimensional data. Geological spatial distributing information hidden in these high-dimensional data cannot be observed directly from the data. In order to solve this problem, we constructed a dimensionality reduction and visualization model of high-dimensional regional geochemical exploration data based on the t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) algorithm. t-SNE algorithm is a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method, which is especially suitable for dimensionality reduction and visualization of high-dimensional data. Select the elements that are sufficiently stable in lithology identification. Reduce the dimension of high-dimensional geochemical exploration data to 1D, 2D or 3D through the t-SNE algorithm, because the low-dimensional data less than 3D can be observed by human eyes easily. Express the output variables of dimension reduction algorithm as raster files, and visualize them by RGB color mixing and other methods, thus the spatial distribution information of geological bodies hidden in high-dimensional geochemical exploration data can be observed directly. The regional geochemical exploration data of stream sediments in a region of southwest England are taken as an example to evaluate the t-SNE algorithm in visualization of high-dimensional geochemical exploration data. The case study shows that: (1) The high-dimensional geochemical exploration data visualization results through t-SNE algorithm can represent the spatial distribution of geological bodies in the study area very well; (2) The visualization results are tightly related to two parameters: target dimension and perplexity of the t-SNE algorithm. The higher the target dimension was be reduced in the t-SNE algorithm, the more detailed the geological spatial information displayed. (3) The results of dimension reduction and visualization of geochemical exploration data based on the t-SNE algorithm are better than those based on principal component analysis (PCA). The research in this paper shows that the high-dimensional geochemical exploration data visualization method based on the t-SNE algorithm can display the spatial distribution information of geological bodies, which has certain guiding significance for inferring the spatial distribution of geological bodies.
-
图 5 降维到2维时的低维分量RGB颜色混合结果
由两个图层RGB合成: 红色图层(R).d2-1(降低到2维时的低维分量1);绿色图层(G).d2-2(降低到2维时的低维分量2);其余地质单元代号同图 2。颜色越偏绿说明d2-2的值越大,颜色越红说明d2-1的值越大
Figure 5. RGB color mixing result of low-dimension components when reduced to 2D
图 6 降维到3维时的低维分量RGB颜色混合结果
由3个图层RGB合成:红色图层(R).d3-2(降低到3维时的低维分量2);绿色图层(G).d3-3(降低到3维时的低维分量3);蓝色图层(B).d3-1(降低到3维时的低维分量1);其余地质单元代号同图 2。颜色越蓝表示d3-1的值越大,颜色越红表示d3-2的值越大,颜色越绿表示d3-3的值越大
Figure 6. RGB color mixing result of low-dimension components when reduced to 3D
图 7 低维分量及元素聚类分析谱系图(代号同图 3)
Figure 7. Cluster dendrogram of low-dimensional components and elements
图 8 主成分分量PC1、PC2、PC4颜色混合结果
由3个图层RGB合成: 红色图层(R).PC1(主成分分量1);绿色图层(G).PC2(主成分分量2);蓝色图层(B).PC4(主成分分量4);其余地质单元代号同图 2。颜色越偏红表示PC1的值越大,颜色越绿表示PC2的值越大,颜色越蓝表示PC4的值越大
Figure 8. RGB color mixing result of PCA components PC1, PC2, PC4
表 1 元素数据列表
Table 1. Elements list
类型 个数 元素 本论文中采用的元素 17 Ce, Ca, Ba, Fe, Hf, Cr, Ni, Mo, Mn, Sm, K, Sr, Si, Se, U, Th, Zr 受矿化影响大的元素 8 As, Cu, Pb, Sb, Sn, Ti, W, Zn 无效数据过多的元素 2 Ag, Cd -
[1] Rose A W, Hawkes H E, Webb J S. Geochemistry in mineral exploration, second edition[M]. London: Academic Press, 1979. [2] 严桃桃, 吴轩, 权养科, 等从岩石到土壤再到水系沉积物: 风化过程的岩性地球化学基因[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(3): 453-467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201803004.htm [3] Gong Q, Deng J, Jia Y, et al. Empirical equations to describe trace element behaviors due to rock weathering in China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 152: 110-117. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.02.004 [4] Ma L, Cheng Z, Fan G, et al. Weathering of granodiorite crust, long-term storage of elements in weathering profiles, and petrogenesis of siliciclastic sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(8): 1653-1670. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00031-8 [5] Duzgorenaydin N, Aydin A, Malpas J. Re-assessment of chemical weathering indices: Case study on pyroclastic rocks of Hong Kong[J]. Engineering Geology, 2002, 63: 99-119. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00073-4 [6] Green P M. Digital image-processing of integrated geochemical and geological information[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1984, 141(9): 941-949. [7] Steenfelt A. Geochemical mapping and prospecting in Greenland: A review of results and experience[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1987, 29: 183-205. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(87)90077-X [8] Shepherd A, Harvey P K, Leake R C. The geochemistry of residual soils as an aid to geological mapping: A statistical approach[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1987, 29: 317-331. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(87)90084-7 [9] Steenfelt A. Geochemical patterns related to major tectono-stratigraphic units in the Precambrian of northern Scandinavia and Greenland[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1990, 39: 35-48. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(90)90068-L [10] 刘德鹏, 丁峰, 汤正江. 区域化探在森林沼泽区地质填图应用初探[J]. 物探与化探, 2004, 28(3): 209-212. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8918.2004.03.006 [11] 马晓阳, 白显清, 臧晓凡, 等. 黑龙江沙兰站幅森林沼泽区基础地质调查中的区域化探新方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2005, 29(2): 108-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8918.2005.02.004 [12] 史长义, 任院生. 区域化探资料研究基础地质问题[J]. 地质与勘探, 2005, 41(3): 53-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2005.03.011 [13] 郝立波, 陆继龙, 马力. 浅覆盖区土壤化学成分与基岩化学成分的关系及其意义: 以大兴安岭北部地区为例[J]. 中国地质, 2005, 32(3): 477-482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2005.03.018 [14] 郝立波, 陆继龙, 李龙, 等. 区域化探数据在浅覆盖区地质填图中的应用方法研究[J]. 中国地质, 2007, 34(4): 710-715. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.04.022 [15] 时艳香, 郝立波, 陆继龙, 等. 因子分类法在黑龙江塔河地区地质填图中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2008, 38(5): 899-903. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200805032.htm [16] Barnett C T, Williams P M. Using geochemistry and neural networks to map geology under glacial cover[J]. Geoscience BC, Report, 2009, 3: 26. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/262635689_Using_Geochemistry_and_Neural_Networks_to_Map_Geology_under_Glacial_Cover/download [17] 向运川, 龚庆杰, 刘荣梅, 等. 区域地球化学推断地质体模型与应用: 以花岗岩类侵入体为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2609-2618. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409012.htm [18] Sadeghi M, Billay A, Carranza E J M. Analysis and mapping of soil geochemical anomalies: Implications for bedrock mapping and gold exploration in Giyani area, South Africa[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 154: 180-193. [19] 高洪生, 张全, 曹淑萍, 等. 区域化探中利用三元图进行地质体划分及异常评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(2): 377-384. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201402031.htm [20] 徐国志, 徐锦鹏, 段玲玲. 化探资料在地质填图中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(3): 450-455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201503003.htm [21] 陈军林, 彭润民, 李帅值, 等. 利用自组织特征映射神经网络和K-means聚类算法挖掘区域化探数据中的地质信息[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(5): 919-927. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201705019.htm [22] Xie X, Cheng H. Sixty years of exploration geochemistry in China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 139: 4-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.06.013 [23] 石文杰, 魏俊浩, 谭俊, 等. 基于滑动窗口对数标准离差法的地球化学异常识别: 以青海多彩地区1∶5万水系沉积物地球化学测量为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 81-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905008.htm [24] 贾琳, 石文杰, 魏俊浩, 等. 水平总梯度法在化探异常圈定中的应用: 以青海省某地区1∶5万水系沉积物的测量为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 71-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905007.htm [25] 黄文斌, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 等. 青海省石灰沟地区水系沉积物测量地球化学特征及找矿预测[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 150-159. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10032.shtml [26] van der Maaten L, Hinton G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9: 2579-2605. http://www.mendeley.com/catalog/visualizing-data-using-tsne/ [27] Li W, Cerise J E, Yang Y, et al. Application of t-SNE to human genetic data[J]. Journal of Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, 2017, 15(4): 1750017. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28718343 [28] Shail R K, Leveridge B E. The Rhenohercynian passive margin of SW England: Development, inversion and extensional reactivation[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2009, 341: 140-155. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2008.11.002 [29] Simons B, Shail R K, Andersen J C Ø. The petrogenesis of the Early Permian Variscan granites of the Cornubian Batholith: Lower plate post-collisional peraluminous magmatism in the Rhenohercynian Zone of SW England[J]. Lithos, 2016, 260: 76-94. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.05.010 [30] Franke W. The Mid-European segment of the Variscides: Tectonostratigraphic units, terrane boundaries and plate tectonic evolution[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 2000, 179(1): 35-61. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.179.01.05 [31] Edwards R A, Warrington G, Scrivener R C, et al. The Exeter Group, south Devon, England: A contribution to the early post-Variscan stratigraphy of northwest Europe[J]. Geological Magazine, 1997, 134(2): 177-197. doi: 10.1017/S001675689700664X [32] Chen Y, Clark A H, Farrar E, et al. Diachronous and independent histories of plutonism and mineralization in the Cornubian Batholith, southwest England[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1993, 150(6): 1183-1191. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.150.6.1183 [33] Chesley J T, Halliday A N, Snee L W, et al. Thermochronology of the Cornubian Batholith in Southwest England: Implications for pluton emplacement and protracted hydrothermal mineralization[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(8): 1817-1835. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90115-D [34] Kirkwood C, Everett P, Ferreira A, et al. Stream sediment geochemistry as a tool for enhancing geological understanding: An overview of new data from southwest England[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 163: 28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.01.010 [35] Krijthe J H. Rtsne: T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding using Barnes-Hut implementation[EB/OL]. (2019-02-08)[2019-05-03]. https://github.com/jkrijthe/Rtsne -





 下载:
下载: