Application of high pressure mercury injection and nuclear magnetic resonance in analysis of the pore structure of dense sandstone: A case study of the Heshui area, Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
孔隙结构制约着油气在储层中的储集能力和流动能力, 是研究致密砂岩储层的关键要素, 也是当前研究的重点和难点问题。以鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区上三叠统延长组长7致密储层为例, 结合高压压汞、核磁共振等分析技术, 对储层孔隙结构、可动流体参数之间的关系进行了深入研究, 主要取得以下认识: ①利用常规方法, 线性最小二乘法将核磁共振
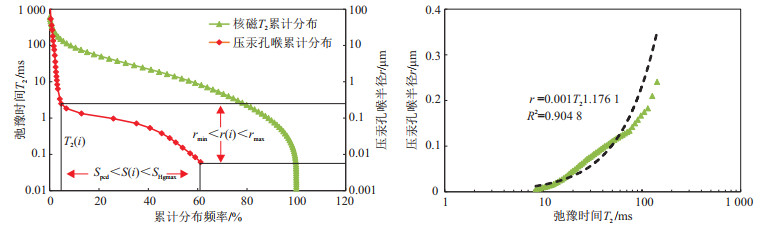
T 2谱转换孔隙半径时, 这种通过线性关系得到的结果精度较低, 相关系数为(0.87~0.98)/0.92, 通过分形理论, 计算出压汞曲线对应的拐点, 进行分段换算出对应的T 2, 以此为界限将核磁共振T 2谱分段转换, 结果显示转化后曲线叠合程度高, 相关系数(0.97~0.99)/0.98;②通过分析流体可动性的影响因素, 岩石的物性具有直接的关系, 其中孔隙度更适合表征储层的储集空间大小, 相关性为0.9, 和可动流体饱和度的相关性更好; 孔隙结构特征参数与可动流体参数相关性较好, 致密的孔隙结构制约着流体的可动性。Abstract:Pore structure restricts the reservoir capacity and flow capacity of oil and gas in the reservoir, which is the key factor of studying tight sandstone reservoir, and also the key and difficult problem of current research. Taking the Chang 7 tight reservoir of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Heshui area of Ordos Basin as an example, the relationship between pore structure and movable fluid parameters was studied by combining high-pressure mercury injection and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis techniques. The main results are as follows: ① when using the conventional method and linear least square method to convert the NMR T2 spectrum into pore radius, the pore structure can be divided into two parts, The correlation coefficient is (0.87-0.98)/0.92. The inflection point of the mercury injection curve is calculated by fractal theory, and the corresponding T2 is converted. The T2 spectrum is converted by segments. After the conversion, the curve has a high degree of overlap, and the number of phase relations is (0.97-0.99)/0.98. ② By analyzing the influencing factors of fluid mobility, it is found that there is a direct relationship between rock physical properties, in which porosity is more suitable to characterize the size of reservoir space, the correlation is 0.9, and the correlation with movable fluid saturation is better; The characteristic parameters of pore structure have a good correlation with the parameters of movable fluid, and the tight pore structure restricts the mobility of fluid. The proportion of dead pores is related to SMFS φ The negative correlation coefficients of MFS were 0.5371 and 0.3775, respectively φ MFS has little effect, but it has no effect φ MFS is more suitable to characterize the micro pore structure.
-
Key words:
- dense sandstone /
- NMR /
- high pressure mercury injection /
- mercury compression fractal /
- pore structure /
- movable fluid
-
表 1 岩样基本物性参数
Table 1. Basic physical parameters of rock samples
岩样编号 深度/m 压汞测试样品 核磁测试样品 直径/cm 长度/cm 压汞孔隙度/% 压汞渗透率/10-3 μm2 直径/cm 长度/cm 核磁孔隙度/% 气测孔隙度/% 气测渗透率/10-3 μm2 L23_1 1 645.4 2.52 2.32 10.3 0.156 2.52 3.29 11.83 11.8 0.150 L23_2 1 672.0 2.51 2.35 7.6 0.055 2.51 3.35 8.55 7.9 0.024 L205_1 1 636.9 2.52 2.30 9.1 0.049 2.52 3.50 10.57 10.0 0.050 Z143_1 1 842.7 2.53 2.32 6.8 0.028 2.53 3.73 12.20 7.9 0.024 N181_1 1 613.6 2.53 2.27 3.5 0.017 2.53 3.20 5.50 4.9 0.088 N181_2 1 659.7 2.52 2.42 2.6 0.011 2.52 3.31 5.85 4.4 0.005 表 2 合水地区不同岩心转化系数
Table 2. Conversion coefficients of different cores in Heshui Area
样品编号 气测孔隙度/% 气测渗透率/10-3 μm2 最大进汞饱和度/% C $ \frac{1}{n}$ R2 L23-1 0.156 10.3 68.302 0.007 2 0.851 8 0.93 L23-2 0.055 7.6 62.615 0.001 7 0.487 5 0.92 L205-1 0.049 9.1 66.904 0.007 9 0.779 9 0.90 Z143-1 0.028 6.8 61.204 0.000 8 1.241 7 0.90 N181-1 0.017 3.5 53.509 0.010 2 0.871 7 0.87 N181-2 0.011 2.6 52.459 0.002 5 1.014 3 0.98 表 3 合水地区样品分形计算结果和转化系数计算结果
Table 3. Fractal calculation results and conversion coefficient calculation results of samples in the Heshui area
样品编号 大孔 小孔 拐点半径ra/μm R2 Dp-1 C 1/n Dp-2 C 1/n L23_1 2.598 7 0.015 9 0.642 8 2.830 8 0.000 7 2.191 3 0.050 0 0.99 L23_2 2.687 5 0.019 3 0.366 3 2.787 6 0.002 3 1.852 1 0.039 0 0.99 L205_1 2.606 8 0.015 2 0.571 3 2.773 3 0.000 9 2.420 7 0.039 0 0.99 Z143_1 2.614 5 0.007 5 0.678 7 2.810 8 0.000 05 2.290 5 0.053 7 0.99 N181_1 2.670 5 0.016 4 0.584 6 2.826 0 0.003 1 2.611 6 0.022 0 0.97 N181_2 2.822 5 0.000 9 1.355 5 2.678 3 0.002 7 0.981 2 0.026 0 0.98 表 4 束缚孔隙度和死孔隙占比计算结果
Table 4. Calculation results of bound porosity and dead porosity
样品编号 气测 核磁测试 束缚孔隙度/% 死孔隙(含水)/% 有效孔隙度/% 核磁孔隙度/% 离心孔隙度/% 可动流体孔隙度/% 可动流体饱和度/% L23-1 11.82 11.83 6.22 5.61 47.38 6.21 0.01 L23-2 7.87 8.55 5.20 3.35 39.25 4.52 0.68 L205-1 10.04 10.57 5.90 4.67 44.16 5.37 0.53 Z143-1 7.87 12.20 7.43 4.77 39.13 3.10 4.33 N181-1 4.87 5.50 3.16 2.34 42.51 2.53 0.63 N181-2 4.38 5.85 4.03 1.82 31.03 2.56 1.47 表 5 合水地区长7储层可动流体参数与孔喉结构参数数据
Table 5. Movable fluid parameters and pore throat structure parameters of Chang 7 reservoir inHeshui Area
样品编号 可动流体参数 孔喉结构参数 孔喉连通特征 孔喉大小特征 孔喉分布特征 可动流体饱和度Smfs/% 可动流体孔隙度φmfs/% 最大进汞饱和度SHgmax/% 退汞饱和度/% 排驱压力/MPa 最大孔隙半径/μm 中值孔隙半径/μm 平均孔隙半径/μm 分选系数 歪度 L23-1 47.38 5.61 68.30 17.72 1.148 0.640 0.067 0.130 1.563 0.28 L23-2 39.25 3.35 62.62 15.86 3.983 0.185 0.029 0.059 1.494 0.102 L205-1 44.16 4.67 66.90 19.27 3.977 0.185 0.036 0.059 1.837 0.038 Z143-1 39.13 4.77 61.20 17.05 2.947 0.249 0.01 0.075 2.361 0.032 N181-1 42.51 2.34 53.51 15.14 7.573 0.097 0.01 0.031 3.269 0.612 N181-2 31.03 1.82 52.46 12.72 7.571 0.097 0.007 0.024 2.369 0.402 表 6 死孔隙占比计算结果
Table 6. Calculation results of dead pore proportion
样品编号 核磁孔隙度/% 可动流体孔隙度/% 束缚孔隙度/% 死孔隙(含水)/% 死孔隙占比/% L23-1 11.83 5.61 6.21 0.01 0.08 L23-2 8.55 3.35 4.52 0.68 7.95 L205-1 10.57 4.67 5.37 0.53 5.01 Z143-1 12.20 4.77 3.10 4.33 35.49 N181-1 5.50 2.34 2.53 0.63 11.45 N181-2 5.85 1.82 2.56 1.47 25.13 -
[1] 马洪, 李建忠, 杨涛, 等. 中国陆相湖盆致密油成藏主控因素综述[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(6): 668-677. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201406004.htmMa H, Li J Z, Yang T, et al. Main controlling factors of tight oil accumulation in continental lacustrine basins in China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(6): 668-677(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201406004.htm [2] 邹才能, 杨智, 陶士振, 等. 纳米油气与源储共生型油气聚集[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(1): 13-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201201003.htmZou C N, Yang Z, Tao S Z, et al. Nano-hydrocarbon and the accumulation in coexisting and reservoir[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(1): 13-26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201201003.htm [3] 邓秀芹, 付金华, 姚泾利, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中及上三叠统延长组沉积相与油气勘探的突破[J]. 古地理学报, 2011, 13(4): 443-455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201104011.htmDeng X Q, Fu J H, Yao J L, et al. Sedimentary facies of the Middle-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin and breakthrough in the petroleum exploration[J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 2011, 13(4): 443-455(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201104011.htm [4] 张浩, 陈刚, 朱玉双, 等. 致密油储层微观孔隙结构定量表征: 以鄂尔多斯盆地新安边油田长7储层为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(1): 112-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201701017.htmZhang H, Chen G, Zhu Y S, et al. Quantitative characterization of micro pore structure of tight Oil reservoir: A case study of Chang 7 reservoir in Xin'anbian oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(1): 112-119(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201701017.htm [5] 王崇孝, 罗群, 宋岩, 等. 纳米石油地质学: 非常规油气地质理论与研究方法探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(6): 659-667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201406003.htmWang C X, Luo Q, Song Y, et al. Nano-meterpetroleum geology: Discussion about geology and research method of unconventional petroleum[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(6): 659-667(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201406003.htm [6] 王磊, 李克文, 赵楠, 等. 致密油储层孔隙度测定方法[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2015, 22(4): 49-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.04.009Wang L, Li K W, Zhao N, et al. Methods research of porosity determination for tight oil reservoir[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2015, 22(4): 49-53(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.04.009 [7] 王振华, 陈刚, 李书恒, 等. 核磁共振岩心实验分析在低孔渗储层评价中的应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(6): 773-779. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201406019.htmWang Z H, Chen G, Li S H, et al. Application of NMR core experimental analysis inevaluation of low-porosity and low-permeability sandstone reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(6): 773-779(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201406019.htm [8] 赵靖舟, 吴少波, 武富礼. 论低渗透储层的分类与评价标准: 以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(3): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.03.005Zhao J Z, Wu S B, Wu F L. The classification and evaluation criteria of low permeability reservoir: An example from Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 19(3): 28-31(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.03.005 [9] 李留仁, 赵艳艳, 李忠兴, 等. 多孔介质微观孔隙结构分形特征及分形系数的意义[J]. 石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 28(3): 105-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200403028.htmLi L R, Zhao Y Y, Li Z X, et al. Fractal characteristics of micropore structure in porous media and the meaning of fractal coefficient[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2004, 28(3): 105-107(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200403028.htm [10] Mandelbrot B B. On the geometry of homogeneous turbulence, with stress on the fractal dimension of the iso-surfaces of scalars[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2006, 72(3): 401-416. [11] 黄延章, 杨正明, 何英, 等. 低渗透多孔介质中的非线性渗流理论[J]. 力学与实践, 2013, 35(5): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXYS201305001.htmHuang Y Z, Yang Z M, He Y, et al. Nonlinear porous flow in low permeability porous media[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 2013, 35(5): 1-8(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXYS201305001.htm [12] 齐亚东, 雷群, 于荣泽, 等. 影响特低-超低渗透砂岩油藏开发效果的因素分析[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 37(2): 89-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2013.02.015Qi Y D, Lei Q, Yu R Z, et al. Analysis of factors influencing development effect of extra-ultralow permeability sandstone reservoirs[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2013, 37(2): 89-94(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2013.02.015 [13] 刘堂宴, 马在田, 傅容珊. 核磁共振谱的岩石孔喉结构分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2003, 18(3): 737-742. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200304026.htmLiu T Y, Ma Z T, Fu R S. Analysis of rock pore structure with NMR spectra[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2003, 18(3): 737-742(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200304026.htm [14] 阙洪培, 雷卞军. 核磁共振T2谱法估算毛管压力曲线综述[J]. 西南石油学院学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 25(6): 9-11. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2003.06.003Que H P, Lei B J. Deriving capillary presure curves from NMR T2 spectra[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Science & Technology Edition, 2003, 25(6): 9-11(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2003.06.003 [15] 何雨丹, 毛志强, 肖立志, 等. 核磁共振T2分布评价岩石孔径分布的改进方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2005, 48(2): 373-378. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2005.02.020He Y D, Mao Z Q, Xiao L Z, et al. An improved method of using NMR T2 distribution to ecaluate pore size distribution[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48(2): 373-378(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2005.02.020 [16] 李海波, 朱巨义, 郭和坤. 核磁共振T2谱换算孔隙半径分布方法研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2008, 25(2): 273-280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4556.2008.02.016Li H B, Zhu J Y, Guo H K. Methods for calculating pore radius distribution in rock from NMR T2 spectra[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2008, 25(2): 273-280(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4556.2008.02.016 [17] 李爱芬, 任晓霞, 王桂娟, 等. 核磁共振研究致密砂岩孔隙结构的方法及应用[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 39(6): 92-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2015.06.012Li A F, Ren X X, Wang G J, et al. Characterization of pore structure of low permeability reservoirs using a nuclear magnetic resonance method[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2015, 39(6): 92-98(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2015.06.012 [18] 王学武, 杨正明, 李海波, 等. 核磁共振研究低渗透储层孔隙结构方法[J]. 西南石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 32(2): 69-72. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2010.02.013Wang X W, Yang Z M, Li H B, et al. Experimental study on pore structure of flow permeability core with NMR spectra[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Science & Technology Edition, 2010, 32(2): 69-72(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2010.02.013 [19] 李艳, 范宜仁, 邓少贵, 等. 核磁共振岩心实验研究储层孔隙结构[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2008, 31(2): 129-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ200802009.htmLi Y, Fan Y R, Deng S G, et al. Expermental study of pore structure with nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2008, 31(2): 129-132(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ200802009.htm [20] 王克文, 李宁. 储层特性与饱和度对核磁T2谱影响的数值模拟[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(3): 422-426. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.03.019Wang K W, Li N. Numerical simulation on effects of reservoir characteristics and saturation on T2 spectra of nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(3): 422-426(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.03.019 [21] Mao Z Q, He Y D, et al. An improved method of using NMR T2 distribution to evaluate pore size distribution[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48(2): 412-418. doi: 10.1002/cjg2.668 [22] Sing S W K. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984)[J]. Pure & Applied Chemistry, 1985, 57(4): 603-619. [23] 何琰, 吴念胜. 确定孔隙结构分形维数的新方法[J]. 石油实验地质, 1999, 21(4): 372-375. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.1999.04.018He Y, Wu N S. A new method for determining fractal dimensionof pore structure[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 1999, 21(4): 372-375(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.1999.04.018 [24] 卢晨刚, 张遂安, 毛潇潇, 等. 致密砂岩微观孔隙非均质性定量表征及储层意义: 以鄂尔多斯盆地X地区山西组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(4): 556-561. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201704017.htmLu C G, Zhang S A, Mao X X, et al. Quantitative characterization of micro pore heterogeneity of tight sandstone and it's reservoir significance: Taking Shanxi Formation in X area of Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(4): 556-561(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201704017.htm [25] 周江羽, 袁艳斌, 李星. 地学分形研究中值得注意的几个问题[J]. 地质科技情报, 1999, 18(2): 93-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ902.027.htmZhou J Y, Yuan Y B, Li X. Some noticeable problems in the study of geoscience fractal[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1999, 18(2): 93-96 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ902.027.htm [26] Zhang Z, Weller A, Kruschwitz S. Pore radius distribution and fractal dimension derived from spectral induced polarisation[J]. Near Surface Geophysics, 2017, 15(6): 625-632. doi: 10.3997/1873-0604.2017035 [27] Jin L, Wang G, Song W, et al. Review of diagenetic facies in tight sandstones: Diagenesis, diagenetic minerals, and prediction via well logs[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 185: 234-258. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.06.009 [28] 蔡建超, 赵春明, 谭吕, 等. 低渗储层多孔介质渗吸系数的分形分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2011, 30(5): 54-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201105011.htmCai J C, Zhao C M, Tan L, et al. Fractal analysis of permeability coefficient of porous media in low permeability reservoir[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2011, 30(5): 54-59(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201105011.htm [29] 王欣, 齐梅, 胡永乐, 等. 高压压汞法结合分形理论分析页岩孔隙结构[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2015, 34(2): 165-169. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-3754.2015.02.033Wang X, Qi M, Hu Y L, et al. Analysis of shale pore structure by high pressure mercury injection combined with fractal theory[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2015, 34(2): 165-169(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-3754.2015.02.033 [30] 纪发华, 张一伟. 分形几何学在储层非均质性描述中的应用[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 1994, 18(5): 161-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX405.030.htmJi F H, Zhang Y W. Application of fractal geometry in reservoir heterogeneity description[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 1994, 18(5): 161-168 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX405.030.htm [31] 贺伟钟, 孚勋, 贺承祖, 等. 储层岩石孔隙的分形结构研究和应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2000, 20(2): 67-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200002024.htmHe W Z, Fu X, He C Z, et al. Fractal texture research on the pores in reservoir rocks and it's application[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2000, 20(2): 67-70(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200002024.htm [32] 王伟, 宋渊娟, 黄静, 等. 利用高压压汞实验研究致密砂岩孔喉结构分形特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 22-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202104003.htmWang W, Song Y J, Huang J, et al. Study on fractal characteristics of pore throat structure of tight sandstone by high pressure mercury injection experiment[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 22-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202104003.htm [33] 马新仿, 张士诚, 郎兆新. 储层岩石孔隙结构的分形研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2003, 12(9): 47-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA200309013.htmMa X F, Zhang S C, Lang Z X. Fractal research on pore structure in reservoir rock[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2003, 12(9): 47-49(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA200309013.htm [34] 赵会涛, 郭英海, 杜小伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地高桥地区本溪组砂岩储层微观孔隙多重分形特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 175-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202006019.htmZhao H T, Guo Y H, Du X W, et al. Multifractal characteristics of micro pores of sandstone reservoirs of Benxi Formation in Gaoqiao area, Ordos Basin[J]Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 175-184(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202006019.htm [35] 刘凯, 石万忠, 王任, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区盒1段致密砂岩孔隙结构分形特征及其与储层物性的关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 57-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101006.htmLiu K, Shi W Z, Wang R, et al. Fractal characteristics of pore structure of tight sandstone in He 1 Member in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin and its relationship with reservoir physical properties[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 57-68(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101006.htm [36] 尹志军, 盛国君, 王春光. 基于压汞法的煤岩各段孔隙的分形特征[J]. 金属矿山, 2011(9): 54-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201109018.htmYin Z J, Sheng G J, Wang C G. Fractal characteristics of pores in coal and rock sections based on mercury injection method[J]. Metal Mines, 2011(9): 54-57(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201109018.htm [37] 王伟, 牛小兵, 梁晓伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密砂岩储层可动流体特征: 以姬塬地区延长组长7段油层组为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(1): 183-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201701022.htmWang W, Niu X B, Liang X W, et al. Movable fluid characteristics of tight sandstone reservoir in Ordos Basin: A case study of Chang 7 oil formation in Yanchang Formation in Jiyuan area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(1): 183-187(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201701022.htm [38] 欧阳思琪, 孙卫, 吴育平, 等. 低渗-特低渗油藏渗流特征及影响因素: 以鄂尔多斯盆地安塞油田侯市-杏河地区长6油藏为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38, 185(2): 199-207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902023.htmOuyang S Q, Sun W, Wu Y P, et al. Seepage characteristics and influencing factors of low permeability ultra-low permeability reservoir: Taking Chang 6 reservoir in Houshi-Xinghe area of Ansai Oilfield in Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 199-207(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902023.htm -





 下载:
下载: