Experiments on the bearing capacity of aeolian sand stabilized by cement stabilizers
-
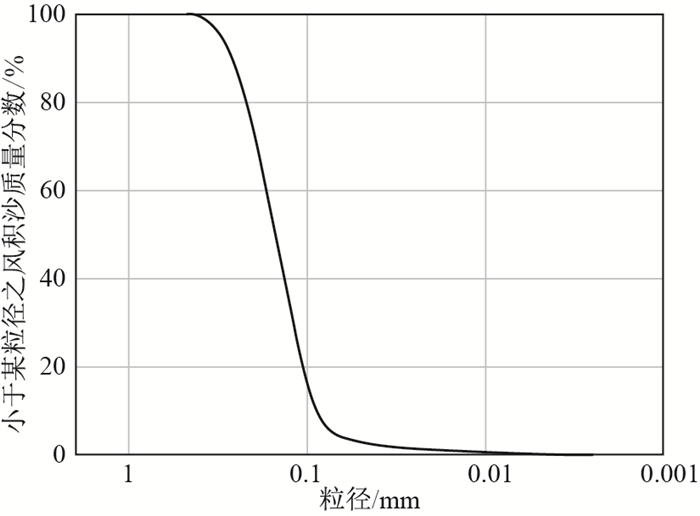
摘要: 沙漠风积沙稳定性差, 采用水泥作为固化剂进行风积沙固化, 是改善风积沙性质和实现风积沙资源化利用的有效手段。以取自内蒙古库布齐沙漠的风积沙为材料, 制备3%含水量的重塑风积沙, 掺入水泥固化剂并充分拌匀而形成固化风积沙, 开展水泥固化风积沙的抗剪、抗压和抗拔承载性能试验。结果表明, 水泥掺量对固化风积沙黏聚强度的提高程度要大于内摩擦角。含水量3%的风积沙掺入6%的水泥经28 d常温养护的固化风积沙无侧限抗压强度平均值为0.156 MPa。固化风积沙扩展基础抗拔荷载-位移曲线呈现初始弹性段至峰值荷载以及峰值荷载后破坏的两阶段脆性破坏特征。水泥固化提高风积沙抗拔承载性能效果显著, 且与基础底板尺寸、抗拔埋深及基础深宽比等因素有关。Abstract: Aeolian sands are inherently very low in strength and very poor in stability. By using local sources according to local conditions, aeolian sand stabilization with cement may be an alternative method to improve the mechanical characteristics of aeolian sand in desert areas. In this study, shear, compression and uplift bearing capacity tests were carried out on the cement-stabilized aeolian sand with 3% water content by using aeolian sand collected from the Kubuqi Desert of Inner Mongolia. The results show that cement stabilization has a much greater enhancement on the cohesive strength than that of the inner frictional angle. After 28 days of normal temperature curing, the average unconfined compressive strength of the stabilized aeolian sand with 3% water content and 6% cement content is 0.156 MPa. The uplift load-displacement curve of stabilized aeolian sand shows a two-stage change law from the initial elastic section to the peak load and failure after the peak load, which has obvious brittle failure characteristics. The results show that the uplift capacity of aeolian sand stabilized by cement is related to the foundation slab size, uplift embedment, and the ratio of uplift embedment to foundation slab width.
-
表 1 风积沙和固化风积沙抗拔性能试验概况与结果
Table 1. Overview and results of uplift load test for model spread foundations embedded in aeolian sand and cement-stabilized aeolian sand
回填料 D/m ht/m ht/D Tu/kN su/mm λu 风积沙 0.30 0.30 1.00 2.58 1.03 6.59 0.30 0.60 2.00 7.09 1.57 9.05 0.30 0.90 3.00 12.40 8.45 10.56 0.30 1.20 4.00 20.50 12.81 13.09 0.30 1.50 5.00 29.20 19.84 14.92 0.60 0.30 0.50 5.52 0.70 3.52 0.60 0.60 1.00 11.97 1.90 3.82 0.60 0.90 1.50 18.90 5.77 4.02 0.60 1.20 2.00 29.50 10.73 4.71 0.60 1.50 2.50 45.00 13.71 5.75 0.90 0.60 0.67 21.60 1.40 3.07 0.90 0.90 1.00 32.40 7.13 3.07 0.90 1.20 1.33 47.80 7.62 3.39 0.90 1.50 1.67 67.00 8.58 3.80 固化风积沙 0.10 0.15 1.50 8.44 1.58 380.18 0.10 0.25 2.50 10.86 2.13 293.51 0.10 0.35 3.50 12.10 0.14 233.59 0.20 0.30 1.50 22.18 1.44 124.89 0.20 0.50 2.50 25.60 1.10 86.49 0.20 0.70 3.50 27.64 6.53 66.70 0.30 0.45 1.50 20.15 4.04 33.62 0.30 0.75 2.50 39.47 1.64 39.51 0.30 1.05 3.50 44.60 1.67 31.89 注:D.基础底板边长;ht.抗拔埋深;ht/D.深宽比;Tu.抗拔基础的极限承载力;su.与Tu对应的位移;λu.抗拔因子 -
[1] 乔建伟, 郑建国, 刘争宏. "一带一路"沿线特殊岩土分布与主要工程问题[J]. 灾害学, 2019, 34(增刊1): 65-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU2019S1012.htmQiao J W, Zheng J G, Liu Z H. Distribution of special rock one along "The belt and road initiative" and major engineering problems[J]. Disaster Science, 2019, 34(S1): 65-71(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU2019S1012.htm [2] 杜德斌, 马亚华. "一带一路": 中华民族复兴的地缘大战略[J]. 地理研究, 2015, 34(6): 1005-1014. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ201506002.htmDu D B, Ma Y H. "The belt and road initiative": The geostrategy of the rejuvenation of the Chinese Nation[J]. Geographical Research, 2015, 34(6): 1005-1014(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ201506002.htm [3] 陈正汉, 郭楠. 非饱和土与特殊土力学及工程应用研究的新进展[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(1): 1-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201901002.htmChen Z H, Guo N. Recent progress in mechanics and engineering application of unsaturated soil and special soil[J]. Geotechnical Mechanics, 2019, 40(1): 1-54(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201901002.htm [4] 詹金林, 水伟厚, 梁永辉. 强夯法加固沙漠土地基处理试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 30(增刊2): 489-493. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2009S2106.htmZhan J L, Shui W H, Liang Y H, et al. Experimental study on strengthening desert soil foundation by dynamic compaction[J]. Geotechnical Mechanics, 2013, 30(S2): 489-493(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2009S2106.htm [5] Elipe M G M, López-Querol S. Aeolian sands: Characterization, options of improvement and possible employment in construction-The state-of-the-art[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 73: 728-739. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.10.008 [6] 刘文白, 周健, 苏跃宏, 等. 加筋风积砂扩展基础的抗拔试验与位移控制计算[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2003, 25(5): 562-566.Liu W B, Zhou J, Su Y H, et al. Uplift test and displacement control calculation of reinforced aeolian sand spread foundation[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2003, 25(5): 562-566(in Chinese with English abstract). [7] 乾增珍, 鲁先龙, 丁士君. 加筋风积沙地基直柱扩展基础抗拔试验[J]. 土木工程学报, 2011, 44(增刊): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC2011S2008.htmQian Z Z, Lu X L, Ding S J. Uplift test of straight column spread foundation on reinforced aeolian sand foundation[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering, 2011, 44(S): 29-32(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC2011S2008.htm [8] 盛明强, 乾增珍, 田开平. 土体固化/稳定技术与固化土性质研究综述[J]. 江西水利科技, 2017, 10(5): 313-317. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXSK201705001.htmSheng M Q, Qian Z Z, Tian K P. Review on soil solidification / stabilization technology and properties of solidified soil[J]. Jiangxi Hydraulic Science & Technology, 2017, 10(5): 313-317 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXSK201705001.htm [9] 王忠凯, 徐光黎. 盾构施工对既有建(构)筑地基承载力影响及加固土体稳定性分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 38(4): 109-116. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0414Wang Z K, Xu G L. Influence of shield construction on bearing capacity of existing building (structure) foundation and stability analysis of reinforced soil[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 38(4): 109-116(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0414 [10] 盛明强, 乾增珍, 鲁先龙. 水泥固化的风积沙地基扩展基础抗拔试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(12): 2261-2267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201712018.htmSheng M Q, Qian Z Z, Lu X L. Experimental study on uplift resistance of expanded foundation of cement solidified aeolian sand foundation[J]. Geotechnical Mechanics, 2017, 39(12): 2261-2267(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201712018.htm [11] Mohamedzein Y E A, Al-Aghbari M Y. The use of municipal solid waste incinerator ash to stabilize dune sands[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2012, 30(6): 1335-1344. [12] 李维生, 张雁. 风积沙路用性能初探[J]. 交通科技, 2008, 26(1): 71-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKQB200801026.htmLi W S, Zhang Y. Preliminary study on road performance of aeolian sand[J]. Transportation Technology, 2008, 26(1): 71-73 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKQB200801026.htm [13] 王朝辉, 王选仓, 谭雪琴. 路用风积沙固化剂配制及其混合料性能[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(1): 192-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201101033.htmWang C H, Wang X C, Tan X Q. Preparation of road aeolian sand curing agent and its mixture properties[J]. Journal of Central South University: Natural Science Edition, 2011, 42(1): 192-198(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201101033.htm [14] 冉武平, 赵杰, 黄文薏, 等. 无机处治风积沙强度特性及工程应用研究[J]. 大连理工大学学报, 2018, 58(2): 141-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLLG201802005.htmRan W P, Zhao J, Huang W Y, et al. Study on strength characteristics and engineering application of inorganic treatment of aeolian sand[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2018, 58(2): 141-146(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLLG201802005.htm [15] 张彩利, 孟庆营, 韩森. 聚丙烯纤维在风积沙基层材料中的应用研究[J]. 中外公路, 2007, 27(2): 154-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWGL200702040.htmZhang C L, Meng Q Y, Han S. Application of polypropylene fiber in aeolian sand base material[J]. China and Foreign Highway, 2007, 27(2): 154-157(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWGL200702040.htm [16] Asi I M, Al-Abdul W H I, Al-Amoudi O S B, et. al. Stabilization of dune sand using foamed asphalt[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2002, 25(2): 168-176. [17] Homauoni Z J, Yasrobi S S. Stabilization of dune sand with poly (methylmethacrylate) and polyvinyl acetate using dry and wet processing[J]. Geotechnical & Geological Engineering, 2011, 29(4): 571-579. [18] 鲁先龙, 程永锋, 丁士君. 风积沙地基工程性质及其输电线路基础抗拔设计[J]. 电力建设, 2010, 31(7): 46-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLJS201007011.htmLu X L, Cheng Y F, Ding S J. Engineering properties of aeolian sand foundation and uplift design of transmission line foundation[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2010, 31(7): 46-50(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLJS201007011.htm [19] 张晓奇, 胡新丽, 刘忠绪, 等. 呷爬滑坡滑带土蠕变特性及其稳定性[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 145-153. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0604Zhang X Q, Hu X L, Liu Z X, et al. Creep properties and stability of sliding zone soil in Gapa landslid[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 145-153(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0604 [20] 楚纯洁, 赵景波, 吴楠楠, 等. 毛乌素沙地晚第四纪地层特征与沙漠化研究综述[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36 (5): 14-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705003.htmChu C J, Zhao J B, Wu N N, et al. Review on Late Quaternary stratigraphic characteristics and desertification in Maowusu Sandy Land[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(5): 14-21(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705003.htm [21] 王旋, 胡新丽, 周昌, 等. 基于物理模型试验的滑坡-抗滑桩位移场变化特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 103-108. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0413Wang X, Hu X L, Zhou C, et al. Model test on the displacement field characteristics of the landslide stabilizing piles[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 103-108(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0413 [22] 邢康宇, 陆洪智, 陈耀春, 等. 成层土中轴横向受荷桩水平响应的非线性解[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 166-174. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0112Xing K Y, Lu H Z, Chen Y C, et al. Nonlinear solutions of lateral response for piles under axial and lateral load embedded in layered soils[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 166-174(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0112 [23] Consoli N C, Dalla R F, Fonini A. Plate load tests on cemented soil layers overlaying weaker soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnieal and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2009, 135(12): 1846-1856. [24] Rattley M J, Lehane B M, Consoli N C, et al. Uplift of shallow foundations with cement-stabilised backfill[J]. Proceedings of the Institute of Civil Engineers-Geotechnical Engineering-Ground Improvement, 2008, 161(2): 103-110. [25] Consoli N C, Ruver C A, Schnaid F. Uplift performance of anchor plates embedded in cement-stabilized backfill[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2013, 139(3): 511-517. -





 下载:
下载: