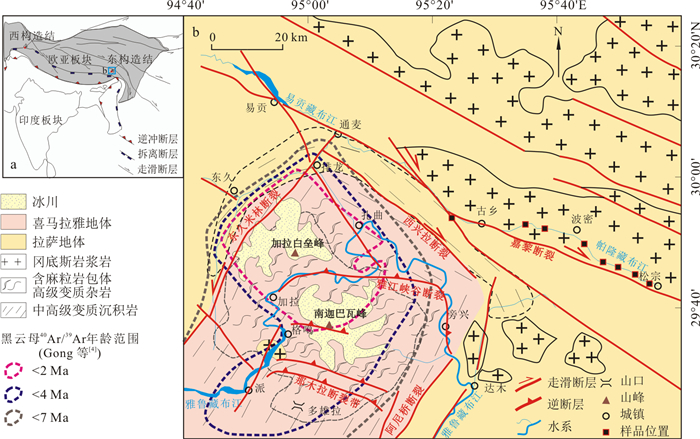
Crust erosion characteristics in the middle reach of the Purlung Tsangpo River
-
摘要:
为揭示东喜马拉雅构造结演化过程, 也为未来可能重大工程建设提供基础地质资料, 对帕隆藏布江中游9块基岩样品进行了黑云母40Ar/39Ar测年, 并利用"Pecube"软件对该地区的地壳剥露速率进行半定量计算。样品黑云母40Ar/39Ar年龄范围为103~12.5 Ma, 对应地壳剥露速率范围为0.068~0.50 km/Ma。帕隆藏布江流域地壳剥露速率具有明显的东西差异特征, 下游(西段)地壳剥露速率显著高于中游(东段)。年龄数据及其模拟计算结果表明, 相对于东喜马拉雅构造结内部, 帕隆藏布江中游流域地壳剥露活动较弱且较稳定。雅鲁藏布江对帕隆藏布江的袭夺, 使得帕隆藏布下游(西段)重新进入河流演化幼年阶段, 河流快速下切剥蚀可能是导致该地区地壳剥露速率东西差异的原因。
-
关键词:
- 东喜马拉雅构造结 /
- 帕隆藏布江 /
- 黑云母40Ar/39Ar /
- 地壳剥露 /
- 河流演化
Abstract:To reveal the tectonic evolution process of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis and provide basic geological data for probable significant engineering construction, this study reports 9 biotite 40Ar/39Ar ages in the middle reach of the Purlung Tsangpo River and semiquantitatively calculates the rock erosion rates represented by these ages using the modeling code "Pecube". The measured biotite 40Ar/39Ar ages range from 103-12.5 Ma, corresponding to erosion rates ranging from 0.068-0.5 km/Ma. The rock erosion rates of the Purlung Tsangpo River have obvious differences between the western and eastern sections, which are characterized by the downstream section (western section) being significantly higher than that of the middle section (eastern section). Ages and simulation results show that in contrast to the eastern Himalayan syntaxis, the crust erosion rate in the middle reach of the Purlung Tsangpo River is lower and stable. The Purlung Tsangpo River was captured by the Yarlung Tsangpo River, which allowed the Purlung Tsangpo River downstream (western section) to change into a youth stage of fluvial geomorphological evolution again.The rapid river incised likely resulted in the erosion rate differences between the western and eastern sections.
-
表 1 样品信息及年龄值
Table 1. Sample information and chronology data
样品名 经度 纬度 海拔/m 岩性 黑云母40Ar/39Ar坪年龄/Ma 2σ误差/Ma MSWD值 11318-01 E96.053° N29.735° 3 067 闪长岩 100.14 0.82 0.32 11318-02 E96.046° N29.731° 3 090 闪长岩 102.57 0.63 0.38 11318-03 E95.985° N29.753° 2 962 闪长岩 76.23 0.40 0.91 11318-04 E95.916° N29.784° 2 896 闪长岩 47.65 0.40 0.17 11318-05 E95.835° N29.811° 2 820 闪长岩 36.61 0.60 0.61 11318-06 E95.788° N29.837° 2 752 闪长岩 20.87 0.22 0.16 11318-07 E95.679° N29.898° 2 716 闪长岩 22.19 0.27 0.82 11318-10 E95.617° N29.907° 2 680 闪长岩 23.25 0.92 1.03 11318-11 E95.401° N29.937° 2 558 片麻岩 12.49 0.69 0.19 表 2 各模拟系列信息及计算结果
Table 2. Information of several simulation series and calculate results
模拟系列 经度范围 纬度范围 对应样品编号 模拟起始时间/Ma 最吻合剥露速率/(km·Ma-1) 最吻合计算年龄/Ma 实测年龄/Ma 1 E96.02°~96.08° N29.6°~29.9° 11318-01, 02 110 0.068 101 100.14,102.57 2 E95.95°~96.02° N29.6°~29.9° 11318-03 90 0.09 76 76.23 3 E95.88°~95.95° N29.6°~29.9° 11318-04 60 0.14 48 47.65 4 E95.81°~95.88° N29.6°~29.9° 11318-05 50 0.18 37 36.61 5 E95.50°~95.81° N29.7°~30.0° 11318-06, 07, 10 30 0.30 22 20.87,22.19,23.25 6 E95.30°~95.50° N29.8°~30.1° 11318-11 20 0.50 12 12.49 -
[1] Burg J P, Nievergelt P, Oberli F, et al. The Namche Barwa syntaxis: Evidence for exhumation related to compressional crusta folding[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1998, 16(2/3): 239-252. [2] Zeitler P K, Meltzer A S, Brown L, et al. Tectonics and topographic evolution of Namche Barwa and the easternmost Lhasa block, Tibet[J]. Special Papers of the Geological Society of America, 2014, 507: 23-58. [3] Tu J Y, Ji J Q, Sun D X, et al. Thermal structure, rock exhumation, and glacial erosion of the Namche Barwa Peak, constraints from thermochronological data[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 105: 223-233. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.035 [4] Gong J F, Ji J Q, Zhou J, et al. Late Miocene thermal evolution of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis as constrained by biotite40Ar/39Ar thermochronology[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2015, 123(4): 369-384. doi: 10.1086/682951 [5] King G E, Herman F, Guralnik B. Northward migration of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis revealed by OSL thermochronometry[J]. Science, 2016, 353: 800-804. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf2637 [6] Yang R, Herman F, Fellin M G, et al. Exhumation and topographic evolution of the Namche Barwa Syntaxis, eastern Himalaya[J]. Tectonophysics, 2018, 722: 43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.10.026 [7] Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic Evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28(1): 211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 [8] Yin A. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Himalayan orogen as constrained byalong-strike variation of structural geometry, exhumation history, and foreland sedimentation[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2006, 76(1): 1-131. [9] Chung S L, Chu M F, Zhang Y Q, et al. Tibetan tectonic evolution inferred from spatial and temporal variations inpost-collisional magmatism[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2005, 68(3): 173-196. [10] Wen D R, Chung S L, Song B, et al. Late Cretaceous Gangdese intrusions of adakitic geochemical characteristics, SE Tibet: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2008, 105(1): 1-11. [11] Wen D R, Liu D, Chung S L, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages of theGangdese Batholith and implications for Neotethyan subduction in southern Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 252(3/4): 191-201. [12] 章振根, 刘玉海, 王天武, 等. 南迦巴瓦峰地区地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1992.Zhang Z G, Liu Y H, Wang T W, et al. Geology of the Namche Barwa region[M]. Beijing: Chinese Science Press, 1992 (in Chinese). [13] Zhang Z, Dong X, Santosh M, et al. Petrology and geochronology of the Namche Barwa complex in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis, Tibet: Constraints on the origin and evolution of the north-eastern margin of the Indian Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 21(1): 123-137. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.02.002 [14] Ding L, Zhong D L, Yin A, et al. Cenozoic structural and metamorphic evolution of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis (Namche Barwa)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 192(3): 423-438. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00463-0 [15] 钟大赉, 丁林. 西藏南迦巴瓦峰地区发现高压麻粒岩[J]. 科学通报, 1995, 40(14): 1343. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.14.029Zhong D L, Ding L. High pressure granulite found in the Namche Barwa region Tibet[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(14): 1343 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.14.029 [16] 丁林, 钟大赉. 西藏南迦巴瓦峰地区高压麻粒岩相变质作用特征及其构造地质意义[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 1999, 29(5): 385-397. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199905000.htmDing L, Zhong D L. High pressure granulite facies metamorphism characteristics and tectonic geological significance in the Namche Barwa region, Tibet[J]. Science in China: Series D, 1999, 29(5): 385-397 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199905000.htm [17] Liu Y, Massonne H J, Siebel W, et al. Geological aspects of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis: New constraints from structural, petrologic and zircon SHRIMP data[M]//Saklani P S E. Himalaya: Geological aspects. New Delhi: Satish Serial Publishing House, 2006. [18] Booth A L, Zeitler P K, Kidd W, et al. U-Pb zircon constraints on the tectonic evolution of southeastern Tibet, Namche Barwa area[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304(10): 889-929. doi: 10.2475/ajs.304.10.889 [19] Zhang J J, Ji J Q, Zhong D L, et al. Structural pattern of eastern Himalayan syntaxis in Namjagbarwa and its formation process[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2004, 47(2): 138-150. doi: 10.1360/02yd0042 [20] 张进江, 季建清, 钟大赉, 等. 东喜马拉雅南迦巴瓦构造结的构造格局及形成过程探讨[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 2003, 33(4): 373-383. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200304009.htmZhang J J, Ji J Q, Zhong D L, et al. Structural pattern of eastern Himalayan syntaxis in Namjagbarwa and its formation process[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2003, 33(4): 373-383 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200304009.htm [21] Lee H Y, Chung S L, Wang J R, et al. Miocene Jiali faulting and its implications for Tibetan tectonic evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 205(3): 185-194. [22] Chiu H Y, Chung S L, Wu F Y, et al. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic constraints from easternTranshimalayan batholiths on the precollisional magmatic and tectonic evolution in southern Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 477: 3-19. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.02.034 [23] 央金拉姆, 季建清, 徐芹芹, 等. 藏东南帕隆藏布现今河流地貌特征及其晚第四纪演化[J]. 地质科学, 2019, 54(4): 1062-1084.Yungchen L, Ji J Q, Xu Q Q, et al. Fluvial geomorphological characteristics and its evolution of the Parlung Zangbo in southeast Tibet[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2019, 54(4): 1062-1084 (in Chinese with English abstract). [24] Baksi A K, Archibald D A, Farrar E. Intercalibration of 40Ar/39Ar dating standards[J]. Chemical Geology, 1996, 129(3): 307-324. [25] Staudacher T, Jessberger E K, Dorflinger D, et al. A refined ultrahigh-vacuum furnace for rare gas analysis[J]. Journal of Physics E: Scientific Instruments, 1978, 11(8): 781. doi: 10.1088/0022-3735/11/8/019 [26] Steiger R H, Jäger E. Subcommission on geochronology: Convention on the use of decay constants in geo-and cosmochronology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1977, 36: 359-362. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(77)90060-7 [27] Braun J. Pecube: A new finite-element code to solve the 3D heat transport equation including the effects of a time-varying, finite amplitude surface topography[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2003, 29(6): 787-794. [28] Braun J, van der Beek P, Valla P, et al. Quantifying rates of landscape evolution and tectonic processes by thermochronology and numerical modeling of crustal heat transport using PECUBE[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 524/525(2): 1-28. [29] Herman F, Copeland P, Avouac J P, et al. Exhumation, crustal deformation, and thermal structure of the Nepal Himalaya derived from the inversion of thermochronological and thermobarometric data and modeling of the topography[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2010, 115(B06407): 1-38. [30] Craw D, Koons P O, Zeitler P K, et al. Fluid evolution and thermal structure in the rapidly exhuming gneiss complex of NamcheBarwa-Gyala Peri, eastern Himalayan syntaxis[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2005, 23(9): 829-845. [31] 田单, 李长安. 清江上游河流发展过程与袭夺模式[J]. 地质科技情报, 2014, 33(1): 80-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201401013.htmTian D, Li C A. River development process and capture model in Upper Qingjiang Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(1): 80-84 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201401013.htm [32] 连志鹏, 徐勇, 付圣, 等. 采用多模型融合方法评价滑坡灾害易发性: 以湖北省五峰县为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 178-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202003022.htmLian Z P, Xu Y, Fu S, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on multi-model fusion method: A case study in Wufeng County, Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 178-186 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202003022.htm [33] 覃瀚萱, 桂蕾, 余玉婷, 等. 基于滑坡灾害预警分级的应急处置措施[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 187-195. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0412Qin H X, Gui L, Yu Y T, et al. Emergency measures based on early warning classification of landslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 187-195 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0412 [34] 黄健, 贺子城, 黄祥, 等. 基于地貌特征的滑坡堰塞坝形成敏感性研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 253-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202105026.htmHuang J, He Z C, Huang X, et al. Formation sensitivity of landslide dam based on geomorphic characteristics[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 253-262 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202105026.htm -





 下载:
下载: