Fractal characteristics of pore-throat structure in tight sandstones using high-pressure mercury intrusion porosimetry
-
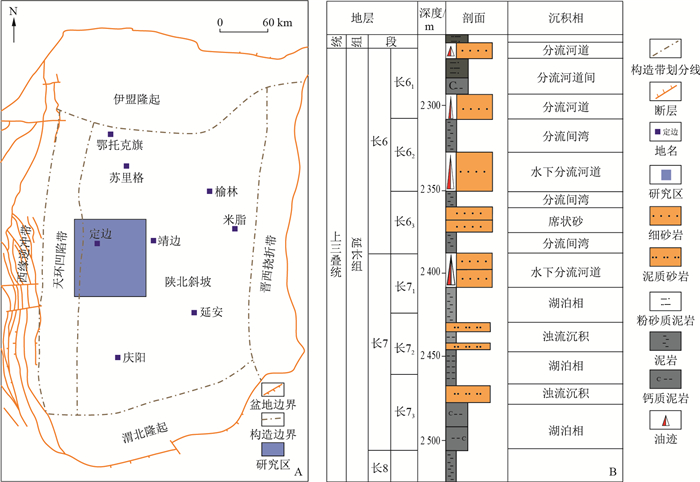
摘要: 微观孔喉结构是影响砂岩油藏特征的重要因素,但致密砂岩孔喉复杂,非均质性强,常规测试难以对其进行有效表征,需要利用分形理论对致密砂岩孔喉结构进行深入研究。以鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区长7段致密砂岩为研究对象,通过高压压汞和分形理论研究了致密砂岩孔喉结构和分形维数特征。讨论了分形曲线转折点与孔喉结构关系,并结合铸体薄片和扫描电镜,分析了孔喉分形特征形成原因。结果表明:致密砂岩分形曲线具有明显转折点。转折点为孔喉分布峰值,代表连通性好的大尺度孔喉向连通性差的小尺度孔喉的转换。致密砂岩小尺度孔喉分形维数平均值为2.24,大尺度孔喉半径分形维数平均值为4.65。大尺度孔喉非均质性明显强于小尺度孔喉。小尺度孔喉分形维数与孔喉结构相关性较好。致密砂岩小尺度孔喉主要为喉道和晶间孔,这部分孔喉连通性差,半径较小,受成岩作用影响微弱,因此分形维数小。致密砂岩大孔喉主要为剩余粒间孔和溶蚀孔隙,该类型孔喉半径较大,受成岩作用改造明显,因此分形维数大。Abstract: Microcosmic pore-throat structure is an important factor affecting the characteristics of sandstone reservoirs.However, the pore-throat of tight sandstone is complex and heterogeneous, which is difficult to be effectively characterized by conventional tests.Therefore, it is necessary to use fractal theory to research the pore-throat structure of tight sandstone.In this study, through high-pressure mercury injection porosimetry and fractal theory, the pore-throat structure and fractal dimension characteristics of the Chang 7 tight sandstones in Jiyuan area of the Ordos Basin are studied, and the relationship between infection points on the fractal curves and pore-throat structure are discussed.And combined with casting thin section and scanning electron microscope, the causes of fractal characteristics from pore-throat are analyzed.The results show that there are obvious infection points on fractal curves, and the infection point is the peak value of pore size distribution, which representes the transition from the large pore-throat with good connectivity to the small pore-throat with poor connectivity.The average fractal dimension of small pore-throat is 2.24, and that of large pore-throat is 4.65.The heterogeneity of large pore-throat is obviously stronger than that of the small pore-throat.And the correlation between fractal dimensions of small pore-throat and pore-throat structure is good.The small pore-throats of tight sandstones mainly consist of intercrystalline pores and throats, which have poor connectivity, small radius and weak influence by diagenesis.Therefore, the fractal dimensions of the small pore-throat are low.The large pore-throats of tight sandstone mainly consist of residual intergranular pores and dissolution pores.The large pore-throat has good connectivity, large radius and obvious transformation by diagenesis.Therefore, the fractal dimension of the large pore-throat is high.
-
Key words:
- tight sandstone /
- Ordos Basin /
- fractal characteristics /
- pore-throat structure /
- diagenesis
-
表 1 致密砂岩孔喉结构和分形特征参数
Table 1. Pore-throat structure and fractal characteristic parameters of tight sandstone samples
井号 深度/m 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 门槛压力/MPa 中值压力/MPa 中值半径/μm 分形维数 转折点 进汞饱和度 孔喉类型 小孔隙 大孔隙 转折点压力/MPa 转折孔喉/μm 大孔喉/% 小孔喉/% 总进汞/% H1 2 554 8.1 0.10 2.91 10.90 0.07 2.25 5.31 7.39 0.10 35.37 54.77 90.14 单峰 H2 2 306 9.2 0.12 1.81 11.15 0.07 2.21 4.62 7.38 0.10 41.02 43.49 84.51 单峰 H3 2 270 9.9 0.14 1.81 10.55 0.07 2.21 4.87 7.39 0.10 39.49 46.68 86.17 单峰 H4 2 170 8.3 0.24 1.14 16.57 0.04 2.29 4.67 4.55 0.16 28.01 59.29 87.30 双峰 H5 2 501 10.3 0.10 0.46 6.86 0.11 2.20 3.78 4.50 0.16 35.92 49.39 85.31 双峰 H6 2 404 10.4 0.32 0.72 4.19 0.18 2.22 5.09 1.81 0.41 28.68 61.85 90.53 双峰 H7 2 620 10.5 0.19 1.17 10.30 0.07 2.26 4.13 4.50 0.16 34.46 57.45 91.91 双峰 H8 2 395 11.5 0.28 1.16 12.63 0.06 2.27 4.71 4.50 0.16 33.95 56.96 90.91 双峰 -
[1] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型, 特征, 机理及展望: 以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2): 173-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201202002.htmZou C N, Zhu R K, Wu S T, et al. Types, characteristics, genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations: Taking tight oil and tight gas in China as an instance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 173-187(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201202002.htm [2] 杨华, 李士祥, 刘显阳. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密油, 页岩油特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301000.htmYang H, Li S X, Liu X Y, et al. Characteristics and resource prospects of tight oil and shale oil in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(1): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301000.htm [3] 姚泾利, 邓秀芹, 赵彦德, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组致密油特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(2): 150-158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201302002.htmYao J L, Deng X X, Zhao Y D, et al. Characteristics of tight oil in Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(2): 150-158(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201302002.htm [4] 王伟, 丁黎, 陈小东, 等. 一种改进的通过压汞来计算致密砂岩渗透率经验方法: 以鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区长7致密砂岩为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(4): 153-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201804021.htmWang W, Ding L, Chen X D, et al. An improved empirical permeability estimator from mercury injection for tight sandstone: A case of Chang 7 tight sandstone in Jiyuan area of Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(4): 153-157(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201804021.htm [5] Wang R, Chi Y, Zhang L, et al. Comparative studies of microscopic pore throat characteristics of unconventional super-low permeability sandstone reservoirs: Examples of Chang 6 and Chang 8 reservoirs of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 160: 72-90. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.10.030 [6] 王伟, 朱玉双, 余彩丽, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密砂岩储层孔喉分布特征及其差异化成因[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(10): 1439-1450. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2019.10.008Wang W, Zhu Y S, Yu C L, et al. Pore size distribution of tight sandstone reservoir and their differential origin in Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(10): 1439-1450(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2019.10.008 [7] 孟子圆, 孙卫, 刘登科, 等. 联合压汞法的致密储层微观孔隙结构及孔径分布特征: 以鄂尔多斯盆地吴起地区长6储层为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 208-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902024.htmMeng Z Y, Sun W, Liu D K, et al. Combined mercury porosimetry to characterize the microscopic pore structure and pore size distribution of tight reservoirs: A case of Chang 6 reservoir in Wuqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 208-216(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902024.htm [8] Lai J, Wang G. Fractal analysis of tight gas sandstones using high-pressure mercury intrusion techniques[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science & Engineering, 2015, 24: 185-96. [9] 陈程, 孙义梅. 砂岩孔隙结构分维及其应用[J]. 沉积学报, 1996, 14(4): 108-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB604.013.htmChen C, Sun Y M. Fractional dimension of the pore-texture in sandstones and its application[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1996, 14(4): 108-113(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB604.013.htm [10] 刘凯, 石万忠, 王任, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区盒1段致密砂岩孔隙结构分形特征及其与储层物性的关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 57-68. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10092.shtmlLiu K, Shi W Z, Wang R, et al. Pore structure fractal characteristics and its relationship with reservoir properties of the first Member of Lower Shihezi Formation tight sandstone in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 57-68(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10092.shtml [11] 冯小哲, 祝海华. 鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格地区下石盒子组致密砂岩储层微观孔隙结构及分形特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 147-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903015.htmFeng X Z, Zhu H H, Micro-pore structure and fractal characteristics of the Xiashihezi Formation tight sandstone reservoirs in Sulige srea, Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 147-156(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903015.htm [12] 吴浩, 刘锐娥, 纪友亮, 等. 致密气储层孔喉分形特征及其与渗流的关系: 以鄂尔多斯盆地下石盒子组盒8段为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(1): 153-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201701015.htmWu H, Liu R E, Ji Y L, et al. Fractal characteristics of pore-throat of tight gas reservoirs and its relation with percolation: A case from He 8 Member of the Permian Xiashihezi Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(1): 153-164(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201701015.htm [13] Zhao P, Wang Z, Sun Z, et al. Investigation on the pore structure and multifractal characteristics of tight oil reservoirs using NMR measurements: Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 86: 1067-1081. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.07.011 [14] Zhao H, Ning Z, Wang Q, et al. Petrophysical characterization of tight oil reservoirs using pressure-controlled porosimetry combined with rate-controlled porosimetry[J]. Fuel, 2015, 154: 233-242. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.03.085 [15] 李相博, 刘化清, 潘树新, 等. 中国湖相沉积物重力流研究的过去, 现在与未来[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(5): 904-921. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201905003.htmLi X B, Liu H Q, Pan S X, et al. The Past, Present and future of research on deep?: Water sedimentary gravity flow in lake basins of China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(5): 904-921(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201905003.htm [16] 付锁堂, 邓秀芹, 庞锦莲. 晚三叠世鄂尔多斯盆地湖盆沉积中心厚层砂体特征及形成机制分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(6): 1081-1089. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201006006.htmFu S T, Deng X X, Pang J L. Characteristics and mechanism of thick sandbody of Yanchang Formation at the Centre of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(6): 1081-1089(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201006006.htm [17] 宋明水, 向奎, 张宇, 等. 泥质重力流沉积研究进展及其页岩油气地质意义: 以东营凹陷古近系沙河街组三段为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(4): 740-751. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201704008.htmSong M S, Xiang K, Zhang Y, et al. Research progresses on muddy gravity flow deposits and their significances on shale oil and gas: A case study from the 3rd oil-member of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation in the Dongying Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(4): 740-751(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201704008.htm [18] Yang Y, Li W, Ma L. Tectonic and stratigraphic controls of hydrocarbon systems in the Ordos Basin: A multicycle cratonic basin in central China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2005, 89(2): 255-269. [19] Wu H, Zhang C, Ji Y, et al. Pore throat characteristics of tight sandstone of Yanchang Formation in eastern Gansu, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Research, 2018, 3(1): 33-43. [20] Washburn E W. The dynamics of capillary flow[J]. Physrevser, 1921, 17(3): 273-283. [21] 解德录, 郭英海, 赵迪斐. 基于低温氮实验的页岩吸附孔分形特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(12): 2466-2472. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201412021.htmXie D L, Guo Y H, Zhao D W. Fractal characteristics of adsorption pore of shale based on low temperature nitrogen experiment[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(12): 2466-2472(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201412021.htm [22] 赵会涛, 郭英海, 杜小伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地高桥地区本溪组砂岩储层微观孔隙多重分形特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 175-184. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10083.shtmlZhao H T, Guo Y H, Du X W, et al. Micro-pore multifractal characteristics of Benxi Formation sandstone reservoirin Gaoqiao area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 175-184(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10083.shtml [23] Xiao D, Jiang S, Thul D, et al. Combining rate-controlled porosimetry and NMR to probe full-range pore throat structures and their evolution features in tight sands: A case study in the Songliao Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 83: 111-123. [24] 尹相东, 蒋恕, 吴鹏, 等. 致密砂岩酸性和碱性成岩环境特征及对储层物性的控制: 以鄂尔多斯盆地临兴和神府地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 142-151. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10100.shtmlYin X D, Jiang S, Wu P, et al. Features of the acid and alkaline diagenetic environment of tigh tsandstones and the control of the reservoir physical properties: A case study of the Linxing and Shenfu district, eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 142-151(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10100.shtml -





 下载:
下载: