Regeneration of mining wasteland in view of optimization of urban green infrastructure system: A case study of Daye
-
摘要: 完善的绿色基础设施体系在重构矿业城市生态系统,提升矿业城市人居环境品质上作用关键。一方面,经过生态修复后的矿业废弃地是矿业城市绿色基础设施的重要增量,另一方面,以绿色基础设施体系优化为导向的治理是破解当前矿业废弃地治理低效的有效途径。湖北省大冶市是一座典型的资源枯竭型城市,在运用形态学空间格局分析(MSPA)方法评价大冶市绿色基础设施的基础上,结合矿业废弃地空间分布,评价其生态潜力,进而提出生态型、生活型和生产型3种矿业废弃地再生的改造方式。研究结果表明:①大冶市生态基底良好,但是景观破碎化严重,连通性弱;②大部分矿业废弃地生态潜力较高,60%的矿业废弃地可以转化为绿色基础设施;③30%的矿业废弃地适合生态型改造、52%的适合生活型改造、18%的适合生产型改造。
-
关键词:
- 绿色基础设施 /
- 矿业废弃地 /
- 形态学空间格局分析(MSPA) /
- 大冶市
Abstract: The perfect green infrastructure system plays a key role in the reconstruction of the mining city ecosystem and the improvement of the quality of the mining city's living environment.On the one hand, the abandoned mining land after ecological restoration is an important increment of the green infrastructure of mining cities; on the other hand, the optimization of green infrastructure system oriented governance is an effective way to break the current inefficient governance of abandoned mining land.Daye City of Hubei Province is a typical resource-exhausted city.Based on the morphological spatial pattern analysis (MSPA) method to evaluate the green infrastructure in Daye City, combined with the spatial distribution of abandoned mining land, the ecological potential of abandoned mining land was evaluated, and then three reconstruction methods of abandoned mining land regeneration, including ecological type, life type and production type, were put forward.The main conclusions of this paper are as follows: ①The ecological base of Daye City is good, but the landscape fragmentation is serious and the connectivity is weak; ②Most of the abandoned mining areas have high ecological potential, 60% of the abandoned mining areas can be transformed into green infrastructure. ③30% of the abandoned mining lands are suitable for ecological reconstruction, 52% for life reconstruction, and 18% for production reconstruction. -
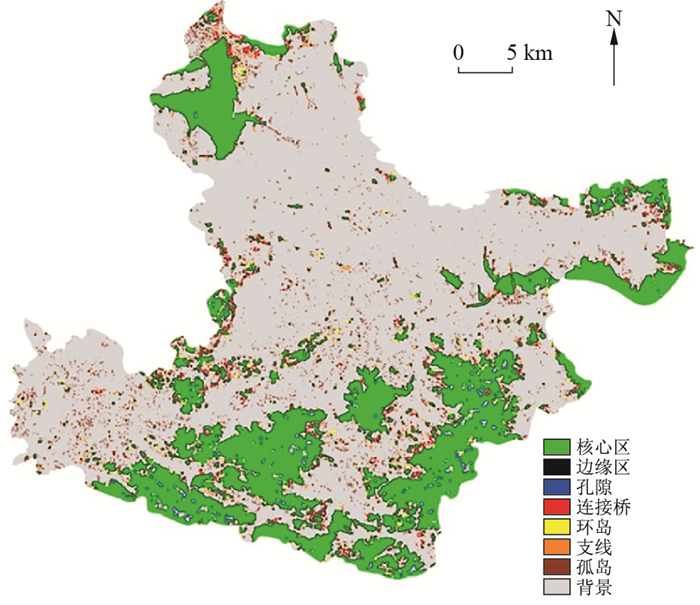
表 1 MSPA的景观类型及生态学含义
Table 1. Landscape types and ecological implications of MSPA
景观类型 生态学含义 核心区 前景中像元较大的生境斑块,能够提供栖息地和维护生物多样性 边缘区 核心与外围非绿色景观斑块的过渡地带,具有边缘效应 孔隙 核心与内部非绿色景观斑块的过渡地带,具有边缘效应 连接桥 连接不同核心区的狭长区域,代表生态网络中斑块连接的廊道 环岛 连接同一核心区的内部廊道 支线 只有一端与边缘、连接桥、环或孔隙相连的区域 孤岛 彼此不相连的孤立、破碎的小斑块 表 2 矿业废弃地生态潜力等级划分标准
Table 2. Classification criteria for ecological potential of mining wasteland
评价因子 景观连接度等级 斑块面积等级 生态潜力等级 1 1 Ⅰ 2 3 4 2 1 2 Ⅱ 3 4 3 1 2 Ⅲ 3 4 Ⅳ 4 1 2 3 4 注:1~4分别代表景观连接度和斑块面积的等级,值越大景观连接度越高、斑块面积越大; Ⅰ~Ⅳ代表生态潜力的等级,值越大生态潜力越大) 表 3 土地利用的类别及定义
Table 3. Category and definition of land use in Daye
类型 定义 采矿用地 采矿、采石、砂(砂)田、盐田、砖窑等地面生产用地和尾矿堆 耕地 水田、旱地、水浇地等 建设用地 住宅、工业、商业、交通等用地 林地 乔木林地、竹林地、灌木林地等 水域 河流、湖泊、水库、坑塘等水面 表 4 斑块面积统计与等级划分
Table 4. Statistics and classification of patoh areas
面积范围/
hm2斑块数/个 所占比例/% 斑块总面积/hm2 所占比例/% 等级 0.08~17.39 76 65.52 530.98 18.58 1 17.40~40.70 23 19.83 622.66 21.79 2 40.71~70.25 10 8.62 566.21 19.82 3 70.26~212.53 7 6.03 1137.30 39.81 4 表 5 斑块重要性等级划分及面积统计
Table 5. The importance of phaque classification and area statistics
斑块重要性 斑块数/个 所占比例/% 斑块总面积/hm2 所占比例/% 等级 0.000 015~0.008 017 38 32.76 307.54 10.76 1 0.008 018~0.071 435 52 44.83 779.66 27.29 2 0.071 436~0.697 482 22 18.97 1 140.34 39.91 3 0.697 483~3.032 285 4 3.45 629.59 22.04 4 -
[1] 中国地质调查局. 全国矿产资源开发环境遥感监测项目[R]. 北京: 中国地质调查局, 2016.China Geological Survey. National mineral resources development environment remote sensing monitoring project[R]. Beijing: China Geological Survey, 2016(in Chinese). [2] Weber T, Wolf J, Blank P, et al. Restoration targeting in Maryland's green infrastructure[R]. Maryland: Maryland Department of Natural Resources, 2004. [3] Davies A M. Nature after minerals: How mineral site restoration can benefit people and wildlife[R]. Sandy: RSPB, 2006. [4] 冯姗姗, 常江. 矿业废弃地: 完善绿色基础设施的契机[J]. 中国园林, 2017, 33(5): 24-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYL201705006.htmFeng S S, Chang J. Mining wasteland: An opportunity to improve green infrastructure[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2017, 33(5): 24-28(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYL201705006.htm [5] Hu T, Jiang C, Liu X, et al. Integrated methods for determining restoration priorities of coal mining subsidence areas based on green infrastructure: A case study in the Xuzhou urban area of China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 94(11): 164-174. [6] Pfenning B, Hovestadt T, Poethke H J. The effect of patch constellation on the exchange of individuals between habitatislands[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2004, 180(4): 515-522. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2004.04.035 [7] Vergara P M, Hahn I. Linking edge effects and patch size effects: Importance of matrix nest predators[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2009, 220: 1189-1196. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.02.015 [8] Clergeau P, Burel F. The role of spatio-temporal patch connectivity at the landscape level: An example in a bird distribution[J]. Landscape & Urban Planning, 1997, 38: 37-43. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169204697000170 [9] Taylor P D, Fahrig L, Henein K, et al. Connectivity is a vital element of landscape structure[J]. Oikos, 1993, 68(3): 571-573. doi: 10.2307/3544927 [10] Turner M G, Gardner R H, O'neill R V, et al. Landscape ecology in theory and practice[M]. New York: Springer, 2015. [11] Linehan J, Gross M, Finn J. Greenway planning: Developing a landscape ecological network approach[J]. Landscape & Urban Planning, 1995, 33: 179-193. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/016920469402017A [12] Zetterberg A, M rtberg U M, Balfors B. Making graph theory operational for landscape ecological assessments, planning, and design[J]. Landscape & Urban Planning, 2010, 95: 181-191. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169204610000204 [13] 王越, 林箐. 基于MSPA的城市绿地生态网络规划思路的转变与规划方法探究[J]. 中国园林, 2017, 33(5): 68-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYL201705014.htmWang Y, Lin J. The transformation of planning ideas and the exploration of planning methods of urban green space ecological network based on MSPA[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2017, 33(5): 68-73(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYL201705014.htm [14] Sun J, Southworth J. Indicating structural connectivity in Amazonian rainforests from 1986 to 2010 using morphological image processing analysis[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2013, 34(14): 5187-5200. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2013.788800 [15] 刘颂, 何蓓. 基于MSPA的区域绿色基础设施构建: 以苏锡常地区为例[J]. 风景园林, 2017(8): 98-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJYL201708013.htmLiu S, He B. Construction of regional green infrastructure based on MSPA: Case study on Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou area[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2017(8): 98-104(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJYL201708013.htm [16] 裴丹. 绿色基础设施构建方法研究述评[J]. 城市规划, 2012, 36(5): 84-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8985.2012.05.019Pei D. Review of green infrastructure planning methods[J]. City Planning Review, 2012, 36(5): 84-90(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8985.2012.05.019 [17] Wickham J D, Riitters K H, Wade T G, et al. A national assessment of green infrastructure and change for the conterminous United States using morphological image processing[J]. Landscape & Urban Planning 2010, 94: 186-195. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169204609002011 [18] Saura S, Vogt P, Velazquez J, et al. Key structural forest connectors can be identified by combining landscape spatial pattern and network analyses[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 2011, 262(2): 150-160. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20113189008.html [19] Carlier J, Moran J. Landscape typology and ecological connectivity assessment to in form greenway design[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 651(2): 3241-3252. [20] 于亚平, 尹海伟, 孔繁花, 等. 基于MSPA的南京市绿色基础设施网络格局时空变化分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(6): 1608-1616. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201606030.htmYu Y P, Yin H W, Kong F H, et al. Analysis of the temporal and spatial pattern of the green infrastructure network in Nanjing, based on MSPA[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(6): 1608-1616(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201606030.htm [21] Soille P, Vogt P. Morphological segmentation of binary patterns[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2008, 30(4): 456-459. [22] Gurrutxaga M, Lozano P J, del Barrio G. GIS-based approach for incorporating the connectivity of ecological networks into regional planning[J]. Journal for Nature Conservation, 2010, 18: 318-326. doi: 10.1016/j.jnc.2010.01.005 [23] 廖启鹏, 陈茹, 黄士真. 基于模糊综合评判与GIS方法的废弃矿区景观评价[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 241-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906029.htmLiao Q P, Chen R, Huang S Z. Study on landscape evaluation of abandoned mining area based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation and GIS[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 241-250(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906029.htm -





 下载:
下载: