Structural characteristics of the Western Branch of the Tanlu fault in Bohai Sea and its control on the formation of buried hills
-
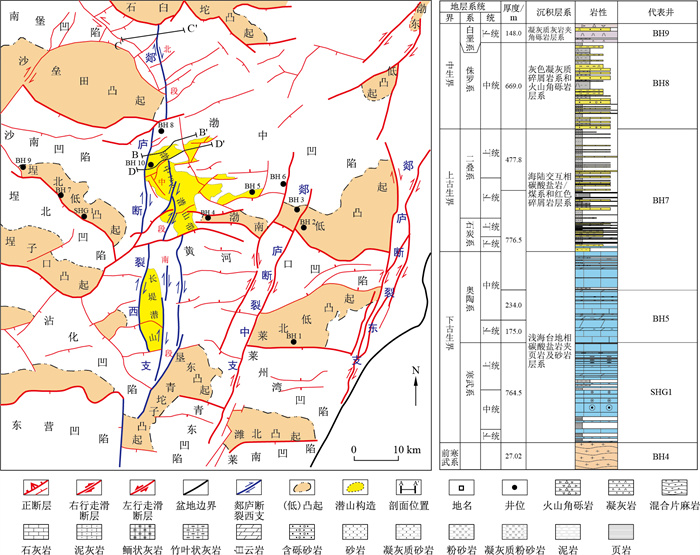
摘要: 渤海郯庐断裂西支是指郯庐断裂渤海段西侧分支断层,其形成演化对前新生代地层展布和潜山构造发育具有重要控制作用。基于三维地震、钻井、分析化验等资料,对渤海郯庐断裂西支构造特征、成因演化模式,以及对潜山形成的控制作用进行了分析。研究表明:①渤海郯庐断裂西支具有印支期、燕山早期、燕山中期、喜山早期多期叠加活动的特征,喜山晚期活化作用弱,整体隐伏于新生代沉积物之下;②渤海郯庐断裂西支具有显著的分段性,被近东西向断裂分割成北、中、南3段,各段在关键地质时期构造变形型式和强度存在一定差异;③印支期不均一南北向挤压所导致的走滑转换是渤海郯庐断裂西支的启动机制;④渤海郯庐断裂西支在印支期-燕山早期走滑逆冲活动及伴生褶皱是控制潜山地层展布及渤中19-6等潜山构造形成的关键因素。研究成果可以为渤海海域的油气勘探提供基础。Abstract: The Western Branch of the Tanlu fault in Bohai Sea refers to the Western Branch fault of Bohai segment of the Tanlu fault, the formation and evolution of which plays an important role in controlling the distribution of pre Cenozoic strata and the development of the structure of buried hills.Based on the data of 3D seismic, drilling and experimental data, the structural characteristics, genetic evolution model of the Western Branch of the Tanlu fault in Bohai Sea and its control on the formation of buried hills are analyzed.The results show that: ①the Western Branch of Tanlu fault in Bohai Sea is characterized by multi-stage superimposed activities in Indosinian, Yanshanian and Himalayan.The activation of late Himalayan is weak, and it is concealed under Cenozoic sediments.②The Western Branch of the Tanlu fault in Bohai Sea is divided into three segments: north, middle and south by nearly EW trending fault.There are some differences in the structural deformation patterns and strength of each segment in the key geological period.③The Western Branch of the Tanlu fault in Bohai Sea was originated from strike slip transition caused by uneven N-S compression in Indosinian.④Indosinian-Yanshanian strike slip thrust and associated folds in the Western Branch of the Tanlu fault in Bohai Sea are the key factors controlling the distribution of strata buried hills and the formation 19-6 buried hill structures of Bozhong.The research results can provide a basis for oil and gas exploration in Bohai Sea.
-
Key words:
- Bohai Sea /
- Tanlu strike slip fault zone /
- Indosinian /
- Yanshanian /
- buried hill /
- tectonic evolution
-
图 2 郯庐断裂西支南段构造特征(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 2. Structural characteristics of the southern part of the Western Branch of the Tanlu fault
图 3 郯庐走滑断裂西支中段构造特征(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 3. Structural characteristics of the middle of Western Branch of Tanlu strike-slip fault
图 4 郯庐断裂西支北段构造特征(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 4. Structural characteristics of the northern section of Western Branch of Tanlu strike-slip fault
图 6 郯庐断裂西支中段构造演化特征(剖面位置见图 1中D-D′)
Figure 6. Structural evolution of the middle segment of the Western Branch of the Tanlu fault
图 9 渤海西南部地区潜山地层对比图(据文献[28]修改)
Figure 9. Stratigraphic correlation map of buried hill in southwest Bohai Sea
-
[1] 侯贵廷, 钱祥麟, 蔡东升. 渤海湾盆地中、新生代构造演化研究[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2001, 37(6): 845-851. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2001.06.016Hou G T, Qian X L, Cai D S. The tectonic evolution of Bohai Basin in Mesozoic and Cenozoic time[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2001, 37(6): 845-851(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2001.06.016 [2] 李三忠, 吴奇, 焦倩, 等. 华北克拉通内部的拉分盆地: 渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷结构构造与演化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2011, 41(5): 1362-1379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201105011.htmLi S Z, Wu Q, Jiao Q, et al. Pull-apart basins within the North China Craton: Structural pattern and evolution of Huanghua Depression in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(5): 1362-1379(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201105011.htm [3] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 嵇少丞, 等. 中国大陆构造及动力学若干问题的认识[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(1): 3-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201001000.htmXu Z Q, Yang J S, Ji S C, et al. On the continental tectonics and dynamics of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(1): 3-31(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201001000.htm [4] 万天丰. 中国东部中新生代板内变形构造应力场及其应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993.Wan T F. Meso Cenozoic intraplate deformation tectonic stress field and its application in eastern China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993(in Chinese). [5] 乔秀夫, 高林志, 彭阳. 古郯庐带新元古界[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001.Qiao X F, Gao L L, Peng Y. Neoproterozoic ancient Tanlu belt[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2001(in Chinese). [6] 乔秀夫, 张安棣. 华北块体、胶辽朝块体与郯庐断裂[J]. 中国地质, 2002, 29(4): 337-345. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2002.04.001Qiao X F, Zhang A L. North China block, Jiao-Liao-Korea block and Tanlu fault[J]. Geology in China, 2002, 29(4): 337-345(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2002.04.001 [7] 张家声. 沂沭断裂带中段基底韧性剪切带[J]. 地震地质, 1983, 5(2): 11-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ198302001.htmZhang J S. Basement ductile shear zone in the middle of Yishu fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1983, 5(2): 11-23(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ198302001.htm [8] 张家声. 郯庐剪切带的性质与意义[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 1992, 17(4): 363-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199204000.htmZhang J S. Properties and significance of Tanlu shear zone[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1992, 17(4): 363-371(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199204000.htm [9] 徐嘉炜. 郯-庐断裂带巨大的左行平移运动[J]. 合肥工业大学学报, 1980, 1(1): 4-29, 130-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEFE198001000.htmXu J W. Huge sinistral translational movement in Tanlu fault zone[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology, 1980, 1(1): 4-29, 130-131(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEFE198001000.htm [10] 万天丰, 朱鸿. 郯庐断裂带的最大左行走滑断距及其形成时期[J]. 高校地质学报, 1996, 2(1): 14-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX601.001.htmWan T F, Zhu H. The maximum sinistral strike-slip and its forming age of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 1996, 2(1): 14-27(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX601.001.htm [11] 王小凤, 李中坚, 陈柏林, 等. 郯庐断裂带[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005.Wang X F, Li Z J, Chen B L, et al. Tanlu fault zone[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2005(in Chinese). [12] 朱光, 刘国生, Dunlap W J, 等. 郯庐断裂带同造山走滑运动的40Ar/39Ar年代学证据[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(2): 190-198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.02.015Zhu G, Liu G S, Dunlap W J, et al. 40Ar/39Ar chronological evidence of syn-orogenic strike slip movement in the Tanlu fault zone[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(2): 190-198(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.02.015 [13] 徐嘉炜, 马国烽. 郯庐断裂带研究的十年回顾[J]. 地质论评, 1992, 38(4): 316-324. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1992.04.004Xu J W, Ma G F. Review of ten years (1981-1991) of research on the Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone[J]. Geological Review, 1992, 38(4): 316-324(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1992.04.004 [14] 陈丕基. 郯庐断裂巨大平移的时代与格局[J]. 科学通报, 1988, 33(4): 289-293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198804013.htmChen P J. The era and pattern of the great translation of the Tanlu fault[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1988, 33(4): 289-293(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198804013.htm [15] 万天丰, 朱鸿, 赵磊, 等. 郯庐断裂带的形成与演化: 综述[J]. 现代地质, 1996, 10(2): 159-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ602.002.htmWan T F, Zhu H, Zhao L, et al. Formation and evolution of Tanlu fault zone: A review[J]. Geoscience, 1996, 10(2): 159-168(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ602.002.htm [16] 朱光, 王薇, 顾承串, 等. 郯庐断裂带晚中生代演化历史及其对华北克拉通破坏过程的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(4): 935-949. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201604001.htmZhu G, Wang W, Gu C C, et al. Late Mesozoic evolution history of the Tan-Lu fault zone and its indication to destruction processes of the North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(4): 935-949(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201604001.htm [17] 张岳桥, 董树文. 郯庐断裂带中生代构造演化史: 进展与新认识[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(9): 1371-1390. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.09.002Zhang Y Q, Dong S W. Mesozoic tectonic evolution history of the Tan-Lu fault zone, China: Advances and new understanding[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(9): 1371-1390(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.09.002 [18] 龚再升, 蔡东升, 张功成. 郯庐断裂对渤海海域东部油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(4): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200704000.htmGong Z S, Cai D S, Zhang G C. Dominating action of tanlu fault on hydrocarbon accumulation in eastern Bohai Sea area[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(4): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200704000.htm [19] 邓运华. 郯庐断裂带新构造运动对渤海东部油气聚集的控制作用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2001, 15(5): 301-305. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200105000.htmDeng Y H. Control of the Neotectonism along Tancheng-Lujiang fracture zone on hydrocarbon accumulation in the eastern Bohai Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2001, 15(5): 301-305(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200105000.htm [20] 姜丽娜, 邹华耀. 郯庐断裂带渤中-渤南段新构造运动期断层活动与油气运聚[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2009, 30(4): 462-468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.04.012Jiang L N, Zou H Y. Fault activities and hydrocarbon migration and accumulation during the Neotectonic period in the Bozhong-Bonan segment of the Tanlu fault zone[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2009, 30(4): 462-468(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.04.012 [21] 韩国猛, 牟连刚, 董越崎, 等. 歧口凹陷板桥斜坡区新生代断裂特征及油气地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202006001.htmHan G M, Mou L G, Dong Y Q, et al. Cenozoic fault characteristics and petroleum geological significance in Banqiao slope area of Qikou Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202006001.htm [22] 李浩, 吴金涛, 黄建廷, 等. 断层垂向封闭性定量分析及其在渤海湾盆地A油田中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 125-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202004016.htmLi H, Wu J T, Huang J T, et al. Quantitative analysis of fault vertical sealing ability and its application in A Oilfield of Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 125-131(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202004016.htm [23] 刘德良, 杨强, 吴小奇, 等. 郯庐断裂安徽段桴槎山韧性剪切带的形成时限初探[J]. 地质科学, 2006, 41(2): 333-343. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.02.013Liu D L, Yang Q, Wu X Q, et al. Duration of structural deformation of ductile shear zone in Fuchashan Hill, Anhui sector of the Tan-Lu fault[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2006, 41(2): 333-343(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.02.013 [24] 任纪舜. 中国大陆的组成、结构、演化和动力学[J]. 地球学报, 1994, 15(3/4): 5-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB4Z2.002.htmRen J S. Composition, structure, evolution and dynamics of the Chinese mainland[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 1994, 15(3/4): 5-13(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB4Z2.002.htm [25] 邵济安, 牟保磊, 何国琦, 等. 华北北部在古亚洲域与古太平洋域构造叠加过程中的地质作用[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 1997, 27(5): 390-394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199705001.htmShao J A, Mou B L, He G J, et al. Geological process of northern North China in the process of tectonic superposition of paleo Asian domain and paleo Pacific domain[J]. Science in China: Series D, 1997, 27(5): 390-394(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199705001.htm [26] 翟明国, 朱日祥, 刘建明, 等. 华北东部中生代构造体制转折的关键时限[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2003, 33(10): 913-920. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200310000.htmZhai M G, Zhu R X, Liu J M, et al. Key time limit of Mesozoic tectonic regime transition in eastern North China[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2003, 33(10): 913-920(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200310000.htm [27] 肖述光, 韦阿娟, 王粤川, 等. 郯庐断裂渤南段各分支新生代构造特征及其对油气聚集的控制作用[J]. 地质科学, 2017, 52(2): 375-389.Xiao S G, Wei A J, Wang Y C, et al. Structural characteristics of the various branches of Bonan segment, Tanlu fault belt and their controlling effects of hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2017, 52(2): 375-389(in Chinese with English abstract). [28] 吴庆勋, 韦阿娟, 王粤川, 等. 渤海南部地区潜山构造差异与成因机制[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(10): 3698-3708. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201810029.htmWu Q X, Wei A J, Wang Y C, et al. Tectonic difference and genetic mechanism of buried hill in southern Bohai Area[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(10): 3698-3708(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201810029.htm [29] 张捷, 刘廷海, 张京思, 等. 渤海海域428东潜山结构特征及勘探潜力分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 219-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903023.htmZhang J, Liu T H, Zhang J S, et al. Structural feature and exploration potential analysis of 428 east buried hill, Bohai Sea[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 219-226(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903023.htm [30] 于福生, 漆家福, 王春英. 华北东部印支期构造变形研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2002, 31(4): 402-406. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2002.04.017Yu F S, Qi J F, Wang C Y. Tectonic deformation of indosinian period in eastern part of North China[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2002, 31(4): 402-406(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2002.04.017 [31] 李勇, 钟建华, 温志峰, 等. 印支运动对济阳坳陷构造形态形成演化的影响[J]. 地质论评, 2006, 52(3): 321-330. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.03.013Li Y, Zhong J H, Wen Z F, et al. Effects of Indosinian Movements on tectonic formation and evolution, Jiyang Depression[J]. Geological Review, 2006, 52(3): 321-330(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.03.013 -





 下载:
下载: