Constraint of the isotopic age of asphalt Re-Os on the age of hydrocarbon accumulation in Fanjingshan area in Northeast Guizhou
-
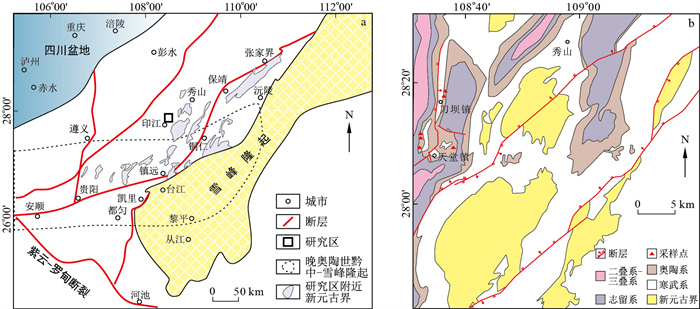
摘要: 黔东北梵净山地区位于雪峰隆起西缘,前寒武纪-早古生代黑色有机质岩系发育,沥青显示广泛。该区在新元古代-中生代经历了晋宁期、加里东期及印支期-燕山期多幕构造变形,前人对后两期构造与油气成藏的响应关系研究较多,而关于晋宁期构造与油气成藏之间的匹配关系则鲜有报道。选取黔东北梵净山地区宝塔组灰岩溶蚀孔、洞内的沥青开展了Re-Os同位素研究,测试结果显示等时线年龄为(915±129)Ma。结合区域地质分析表明,梵净山地区存在晋宁期原生油藏,在加里东期被改造形成次生油藏,古隆起控制了次生油气藏的分布。本研究丰富了雪峰隆起西缘油气成藏期次,同时也促进了复杂构造变形条件下次生油气藏成藏机理研究,对我国南方新元古界油气勘探有重要意义。Abstract: Fanjingshan area in Northeast Guizhou is located at the northern margin of Xuefeng Uplift. The black organic rock series developed from Precambrian to Early Paleozoic, and the asphalt is widely displayed. The Neoproterozoic-Mesozoic period in this area experienced the Jinning period, Caledonian period and Indochina-Yanshan movement multi-stage tectonic deformation. Previous studies mostly focused on the response relationship between the structure and hydrocarbon accumulation in the latter two periods, while the matching relationship between the structure and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Jinning period has not been reported. In this paper, Re-Os isotopic study was carried out on bitumen in limestone dissolution cave of Baota Formation in Fanjingshan area. The isochronal age is (915±129)Ma. Combined with the regional geological analysis, it is concluded that there are primary oil reservoirs of Jinning period in Fanjingshan area, secondary oil reservoirs were formed in Caledonian period, whose distribution was controlled by paleouplift. In summary, this study enriches the oil and gas accumulation stages in the north margin of Xuefeng Uplift, and also promotes the study on the mechanism of secondary reservoir accumulation under complex tectonic deformation. It is of profound significance to the exploration of Neoproterozoic oil and gas in South China.
-
Key words:
- Re-Os isotopic /
- asphalt /
- Jinning Period /
- Baota Formation /
- Xuefeng Uplift
-
表 1 沥青样品Re、Os同位素比值
Table 1. Re and Os isotope ratio of asphalt samples
样品号 Re wB/10-9 Os wB/10-12 187Re wB/10-9 192Os wB/10-12 187Osr wB/10-12 187Osr占比/% 187Re/188Os 187Os/188Os BT1 368.7 4 170.3 231.8 142.7 3 821.3 99.8 5 139.3 84.9 BT2 495.2 6 422.0 311.2 139.2 6 081.6 99.9 7 075.6 138.5 BT3 160.7 1 372.9 101.0 116.4 1 088.2 99.3 2 746.4 29.8 BT4 1 231.2 13 034.4 773.9 252.1 12 417.8 99.9 9 714.0 156.1 BT5 780.2 6 921.2 490.4 257.8 6 290.9 99.7 6 021.1 77.4 BT7 890.5 8 979.7 559.7 228.1 8 421.8 99.8 7 764.9 117.0 -
[1] 沈传波, 葛翔, 白秀娟. 四川盆地震旦系-寒武系油气成藏的Re-Os年代学约束[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3): 713-726. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903003.htmShen C B, Ge X, Bai X J. Re-Os geochronology constraints on the Neoproterozoic-Cambrian hydrocarbon accumulation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(3): 713-726(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903003.htm [2] 王守德, 郑冰, 蔡立国. 中国南方古油藏与油气评价[J]. 海相油气地质, 1997, 2(1): 44-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ199701014.htmWang S D, Zheng B, Cai L G. The destroyed oil pools in South China and hydrocarbon prospecting[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 1997, 2(1): 44-50(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ199701014.htm [3] 向才富, 汤良杰, 李儒峰, 等. 叠合盆地幕式流体活动: 麻江古油藏露头与流体包裹体证据[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 2008, 38(增刊1): 70-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S1009.htmXiang C F, Tang L J, Li R F, et al. Episodic fluid movements in superimposed basin: Combined evidence from outcrop and fluid inclusions of the Majiang ancient oil reservoir, Guizhou Province[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 38(S1): 70-77(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S1009.htm [4] 刘运黎, 沈忠民, 丁道桂, 等. 江南-雪峰山推覆体前缘沥青古油藏及油源对比[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 35(1): 34-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2008.01.006Liu Y L, Shen Z M, Ding D G, et al. The characters of the old asphalt-oil pool in the Jiangnan-Xuefeng thrust nappe front and the correlation of oil sources[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Sciene & Technology Edition, 2008, 35(1): 34-40(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2008.01.006 [5] 梅廉夫, 邓大飞, 沈传波, 等. 江南-雪峰隆起构造动力学与海相油气成藏演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(5): 85-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201205013.htmMei L F, Deng D F, Shen C B, et al. Tectonic dynamics and marine hydrocarbon accumulation of Jiangnan-Xuefeng Uplift[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(5): 85-93(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201205013.htm [6] 邓大飞. 雪峰隆起北缘海相古油气巨量富集的陆内构造研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2014.Deng D F. Study on the intracontinental structure of the enrichment of marine paleo-reservoirs in the northern margin of Jiangnan-Xuefeng Uplift, Southern China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [7] Ge X, Shen C B, Selby D, et al. Apatite fission track and Re-Os geochronology of the Xuefeng Uplift, China: Temporal implications for dry gas associated hydrocarbon systems[J]. Geology, 2016, 44(6): 491-494. doi: 10.1130/G37666.1 [8] 李素梅, 刘洛夫, 王铁冠. 生物标志化合物和含氮化合物作为油气运移指标有效性的对比研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(4): 95-98. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2000.04.023Li S M, Liu L F, Wang T G. A comparison study on the effectiveness of using biomarker and nitrogenous compound as indexes indicating oil and gas migration[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(4): 95-98(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2000.04.023 [9] 李二庭, 靳军, 陈俊, 等. 生物降解稠油沥青质热解产物中生物标志化合物与单体烃碳同位素组成研究[J]. 地球化学, 2019, 48(3): 284-292. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201903006.htmLi E T, Jin J, Chen J, et al. Study on biomarkers and carbon isotopic compositions of monomer hydrocarbons in asphaltene pyrolysis products from biodegraded heavy oil[J]. Geochimica, 2019, 48(3): 284-292(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201903006.htm [10] Smoliar M I, Walker R J, Morgan J W. Re-Os ages of group ⅡA, ⅢA, IVA, and IVB iron meteorites[J]. Science, 1996, 271: 1099-1102. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5252.1099 [11] Creaser R A, Sannigrahi P, Chacko T, et al. Further evaluation of the Re-Os geochronometer in organic sedimentary rock: A test of hydrocarbon maturation effects in the Exshaw Formation, Western Canada Sedimentary Basin[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66(19): 3441-3452. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00939-0 [12] Selby D, Creaser R A, Fowler M G. Re-Os elemental and isotopic systematics in crude oils[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(2): 378-386. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.09.005 [13] 沈传波, 刘泽阳, 肖凡, 等. 石油系统Re-Os同位素体系封闭性研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(2): 187-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201502001.htmShen C B, Liu Z Y, Xiao F, et al. Advancements of the research on Re-Os isotope system in petroleum system[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(2): 187-195(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201502001.htm [14] 陈玲, 马昌前, 凌文黎, 等. 中国南方存在印支期的油气藏: Re-Os同位素体系的制约[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010, 29(2): 95-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2010.02.017Chen L, Ma C Q, Ling W L, et al. Indosinian hydrocarbon accumulation in South China: A Re-Os isotope constrain[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(2): 95-99(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2010.02.017 [15] Li X H. U-Pb zircon ages of granites from the southern margin of the Yangtze Block: Timing of Neoproterozoic Jinning Orogeny in SE China and implications for Rodinia assembly[J]. Precambrian Research, 1999, 97(1/2): 43-57. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926899000200 [16] 贵州省地质矿产局. 1: 20万沿河幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 贵阳: 贵州省地质矿产局, 1970.Guizhou Geology Bureau. 1: 200000 geological survey report of Yanhe[R]. Guiyang: Guizhou Geology Bureau, 1970(in Chinese). [17] 范启超, 张传恒, 游国庆, 等. 梵净山群沉积地质特征与原型盆地分析[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(4): 513-522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201704008.htmFan Q C, Zhang C H, You G Q, et al. Sedimentary features and basin prototype of Fanjingshan Group[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4): 513-522(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201704008.htm [18] 王敏. 黔东北梵净山地区晚元古代岩浆活动及其大地构造意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.Wang M. The Neoproterozoic magamtism and tectonic implcations, the Fanjingshan Mt., Northeast Guizhou Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2012(in Chinese with English abstract). [19] 覃永军. 江南造山带西段新元古代下江群年代地层标定与盆地演化[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2015.Qin Y J. Geochronology calibration and the evolution of the basin in the Neoproterozoic Xiajiang Group on the west Jiangnan Orogen Belt, South China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 江卓斐. 扬子西缘新元古代冰川启动时间、期次及其构造-岩相古地理演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.Jiang Z F. Onset Time and periods of the Neoproterozoic glaciers in western Yangtze Block and the tectonic-lithofacies palaeogeography[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [21] 刘静江, 李伟, 张宝民, 等. 上扬子地区震旦纪沉积古地理[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(6): 735-753. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201506002.htmLiu J J, Li W, Zhang B M, et al. Sedimentary palaeogeography of the Sinian in Upper Yangtze region[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2015, 17(6): 735-753(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201506002.htm [22] 贵州省地质调查院. 贵州省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016.Guizhou Geological Survey Institute. Regional geology of Guizhou Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016(in Chinese). [23] 谢尚克, 汪正江, 王剑. 黔东北地区晚奥陶世岩相古地理[J]. 古地理学报, 2011, 13(5): 539-549. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201105013.htmXie S K, Wang Z J, Wang J. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Late Ordovician in northeastern Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2011, 13(5): 539-549(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201105013.htm [24] 黄福喜. 中上扬子克拉通盆地沉积层序充填过程与演化模式[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2011.Huang F X. Filling process and evolutionary model of sedimentary sequence in Middle-Upper Yangtze Cratonic Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2011(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] 杨坤光, 何良伦, 刘雨, 等. 黔西逆冲滑脱构造及其对铅锌矿床的控制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 149-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202001018.htmYang K G, He L L, Liu Y, et al. The thrust-decollement structure in western Guizhou and its control of Pb-Zn deposit[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 149-156(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202001018.htm [26] 邓新, 杨坤光, 刘彦良, 等. 黔中隆起性质及其构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(3): 79-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201003009.htmDeng X, Yang K G, Liu Y L, et al. Characteristics and tectonic evolution of Qianzhong Uplift[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(3): 79-89(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201003009.htm [27] 吕宝凤. 川东南地区构造变形与下古生界油气成藏研究[D]. 广州: 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所, 2005.Lü B F. The Tectonization and petroleum accumulation in southeast Sichuan Basin[D]. Guangzhou: Gunagzhou Institute of Geochemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005(in Chinese with English abstract). [28] 王泽成, 姜华, 王铜山, 等. 上扬子地区新元古界含油气系统与油气勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(4): 27-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201404006.htmWang Z C, Jiang H, Wang T S, et al. Hydrocarbon systems and exploration potentials of Neoproterozoic in the Upper Yangtze region[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(4): 27-36(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201404006.htm [29] 杨平, 谢渊, 汪正江, 等. 黔北震旦系灯影组流体活动与油气成藏期次[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 313-322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403009.htmYang P, Xie Y, Wang Z J, et al. Fluid activity and hydrocarbon accumulation period of Sinian Dengying Formation in northern Guizhou, South China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 313-322(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403009.htm [30] 周其伟. 贵州松桃地区大塘坡组下段烃源岩地球化学特征研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2016.Zhou Q W. Study on geochemical characteristics of the source rocks of Datangpo Formation Lower Segment in Songtao area of Guizhou Province[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [31] 黄文魁. 贵州松桃大塘坡锰矿中固体沥青的地球化学特征及其成因研究[D]. 武汉: 长江大学, 2016.Huang W K. The geochemical characteristics and genesis study of solid bitumen from Datangpo manganese ore in Songtao, Guizhou[D]. Wuhan: Yangtze University, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [32] 黄乐清, 刘伟, 柏道远, 等. 湘西北奥陶系宝塔组灰岩龟裂纹构造特征、成因及其资源意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(2): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201902005.htmHuang L Q, Liu W, Bai D Y, et al. Characteristics, petrogenesis and resource significance of the limestone with polygonal reticulate structure of Pagoda Formation, in northwestern Hunan Province[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(2): 1-16(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201902005.htm [33] 路远发. GeoKit: 一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J]. 地球化学, 2004, 33(5): 459-464. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2004.05.004Lu Y F. GeoKit: A geochemical toolkit for microsoft excel[J]. Geochimica, 2004, 33(5): 459-464(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2004.05.004 [34] Tripathy G R, Hannah J L, Stein H J, et al. Radiometric dating of marine-influenced coal using Re-Os geochronology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 432: 13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.09.030 [35] 王广利, 李宁熙, 高波, 等. 麻江奥陶系古油藏中的硫酸盐热化学还原反应: 来自分子标志物的证据[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(33): 3450-3457. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201333011.htmWang G L, Li N X, Gao B, et al. Thermochemical sulfate reduction in fossil Ordovician deposits of the Majiang area: Evidence from a molecular-marker investigation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(33): 3450-3457(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201333011.htm [36] Lillis P G, Selby D. Evaluation of the rhenium-osmium geochronometer in the Phosphoria petroleum system, Bighorn Basin of Wyoming and Montana, USA[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 118: 312-330. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.04.021 [37] 李真, 王选策, 刘可禹, 等. 油气藏铼-锇同位素定年的进展与挑战[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(3): 297-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201703006.htmLi Z, Wang X C, Liu X Y, et al. Rhenium-osmium geochronology in dating petroleum systems: Progress and challenges[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(3): 297-306(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201703006.htm [38] 徐思煌, 马永生, 梅廉夫, 等. 中国南方典型气(油)藏控藏模式探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(1): 19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2007.01.004Xu S H, Ma Y S, Mei L F, et al. Natural gas models controlled by graded multi-factors in marine sequences of South China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2007, 29(1): 19-24(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2007.01.004 [39] 赵宗举, 朱琰, 李大成, 等. 中国南方构造形变对油气藏的控制作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002, 23(1): 19-25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.01.004Zhao Z J, Zhu Y, Li D C, et al. Control affect of tectonic deformation to oil-gas pools in southern China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2002, 23(1): 19-25(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.01.004 [40] 梅廉夫, 刘昭茜, 汤济广, 等. 南方多旋回构造作用下的中、古生界海相油气构造-成藏旋回[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2009, 30(5): 589-607. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.05.009Mei L F, Liu Z Q, Tang J G, et al. Tectonic-pooling cycles controlled by polycyclic tectonism in the Mesozoic-Palaeozoic marine strata of South China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2009, 30(5): 589-607(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.05.009 [41] 栾锡武, 鲁银涛, 赵克斌, 等. 东海陆坡及邻近槽底天然气水合物成藏条件分析及前景[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 342-355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.002Luan X W, Lu Y T, Zhao K B, et al. Geological factors for the development and newly advances in exploration of gas hydrate in East China Sea slope and okinawa trough[J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 342-355(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.002 [42] Okui A, Kaneko M, Nakanishi S, et al. An integrated approach to understanding the petroleum system of a frontier deep-water area, offshore Japan[J]. Petroleum Geosciences, 2008, 14(3): 223-233. doi: 10.1144/1354-079308-765 [43] 牟传龙, 葛祥英, 许效松, 等. 中上扬子地区晚奥陶世岩相古地理及其油气地质意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2014, 16(4): 427-440. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201404001.htmMu C L, Ge X Y, Xu X S, et al. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Late Ordovician and its petroleum geological significance in Middle-Upper Yangtze region[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2014, 16(4): 427-440(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201404001.htm [44] 孙冬胜, 李双建, 朱东亚, 等. 四川盆地都匀运动不整合及其油气意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(5): 721-728. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201505003.htmSun D S, Li S J, Zhu D Y, et al. Unconformity of the Duyun Movement in the Sichuan Basin and its significance of petroleum geology[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(5): 721-728(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201505003.htm [45] 李双建, 高波, 沃玉进, 等. 中国南方海相油气藏破坏类型及其时空分布[J]. 石油实验地质, 2011, 33(1): 43-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2011.01.007Li S J, Gao B, Wo Y J, et al. Destruction types and temporal-spatial distribution of marine hydrocarbon reservoirs in South China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2011, 33(1): 43-49(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2011.01.007 [46] Melezhik V A, Fallick A E, Filippov M M, et al. Karelian shungite: An indication of 2.0-Ga-old metamorphosed oil-shale generation of petroleum, geology, lithology and geochemistry[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 1999, 47(1/2): 1-40. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012825299000276 [47] Craig J, Biffi U, Galimberti R F, et al. The palaeobiology and geochemistry of Precambrian hydrocarbon source rocks[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 40: 1-47. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.09.011 [48] Kendall B, Creaser R A, Selby D. Re-Os geochronology of Precambrian organic-rich sedimentary rocks[C]//Craig J, Thurow J, Thusu B. Global neoproterozoic petroleum systems and the emerging potential in North Africa. London: Geological Society, Special Publication, 2009, 326: 83-106. [49] Wang X M, Zhang S C, Wang H J, et al. Significance of source rock heterogeneities: A case study of Mesoproterozoic Xiamaling Formation shale in North China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 32-39. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30005-8 [50] Frolov S V, Akhmanov G G, Bakay E A, et al. Meso-Neoproterozoic petroleum systems of the eastern Siberian Sedimentary Basins[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 259: 95-113. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.11.018 [51] 汪正江, 谢渊, 杨平, 等. 雪峰山西侧震旦纪-早古生代海相盆地演化与油气地质条件[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(11): 1795-1811. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.11.005Wang Z J, Xie Y, Yang P, et al. Marine basin evolution and oil and gas geology of Sinian-Early Paleozoic period on the western side of the Xuefeng Mountain[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31(11): 1795-1811(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.11.005 -





 下载:
下载: