Geometry and kinematics of the Aure fold-thrust belt, Papua New Guinea
-
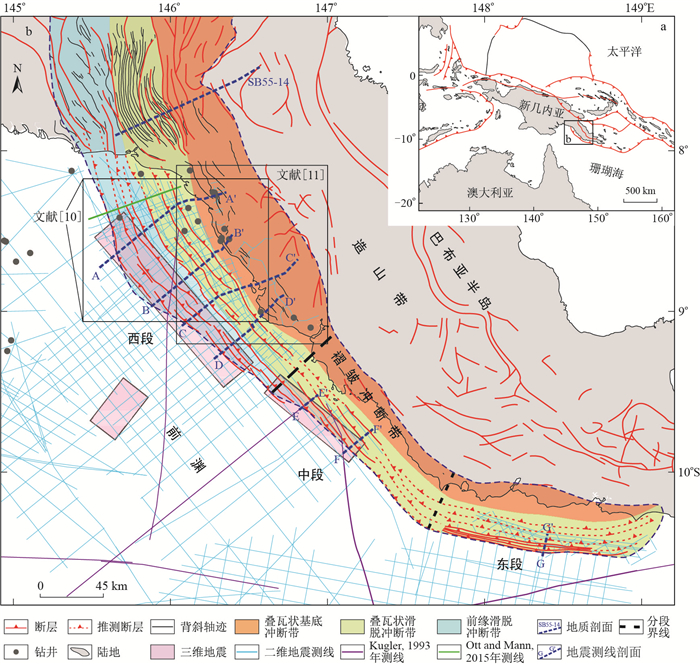
摘要: 奥雷褶皱冲断带是巴布亚新几内亚油气勘探的重要区域,但对褶皱冲断带的构造变形样式与演化认识不清。利用覆盖全区的2D和3D地震资料、钻井和地质信息,结合前人在该地区的地质研究成果,以断层相关褶皱理论为指导,对地震资料进行了闭合解释,系统分析了该区褶皱冲断带的构造几何学与运动学特征。研究结果表明:奥雷褶皱冲断带沿走向可以分为东段、中段和西段3段,其构造变形具有明显的差异性:①沿倾向从NE向SW具有变形层次渐浅、卷入层系渐新、变形程度渐弱的变化特征;②沿走向从NW向SE表现为扩展范围渐小、前陆沉积层系渐新、构造变形时间渐晚、缩短率渐大、缩短量渐小的特征;③西段和中段垂向上分层解体,东段为继承性变形。本次研究将助力巴布亚新几内亚的油气勘探,并为澳大利亚北缘区域构造演化研究提供盆内证据。Abstract: The Aure fold-thrust belt is an important area for oil and gas exploration in Papua New Guinea, but the structural deformation and evolution of the fold-thrust belt are not well understood.In this paper, 2D and 3D seismic data, drilling and geological data covering the structural belt, combined with previous geological research results, were used to identify the structure and kinematics characteristics of the Aure fold-thrust belt.Guided by the theory of fault-related folds, the seismic data are interpretation.The Aure fold-thrust belt can be divided into three sections along the strike, and the structural deformation of the belt has obvious differences, which are mainly reflected in the following aspects: ①In the trend from NE to SW, the deformation level is gradually shallow, the involved strata are gradually new, and the deformation degree is gradually weaker; ②Along the strike from NW to SE, the extension range becomes smaller, the foreland sedimentary strata become newer, the tectonic deformation time becomes later, the shortening rate becomes larger, and the shortening amount becomes smaller; ③The western section and the middle section are disintegrated vertically, and the eastern section is inherited deformation.The results can provide basin evidence for oil and gas exploration in Papua New Guinea and regional tectonic evolution in the northern margin of Australia.
-
Key words:
- geometry /
- kinematics /
- fold-thrust belt /
- foreland basin /
- Aure /
- Papua New Guinea
-
图 2 B-B′测线地震地质综合解释剖面图(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 2. Seismic geological comprehensive interpretation section of B-B′ line
图 3 SB55-14地质构造剖面图(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 3. Geological structure section of SB55-14
图 4 F-F′测线地震地质综合解释剖面图(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 4. Seismic geological comprehensive interpretation section of F-F′ line
图 5 G-G′测线地震地质综合解释剖面图(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 5. Seismic geological comprehensive interpretation section of G-G′ line
表 1 奥雷前陆盆地地震资料解释方案对比
Table 1. Comparison of seismic data interpretation schemes in the Aure foreland basin

表 2 奥雷褶皱冲断带分带分段构造特征对比
Table 2. Comparison of segmented structural characteristics of Aure fold-thrust belt
分带 分段 构造特征 缩短量 构造分层 滑脱层厚度 基底卷入 叠瓦状基底卷入带 西段 断展褶皱、压性断块 较小 继承性 无 中段 断展褶皱、压性断块 较小 继承性 无 东段 断展褶皱、压性断块 较小 继承性 无 盖层滑脱 叠瓦状盖层滑脱带 西段 断展、断弯、叠瓦 较大 上下分层 较厚 中段 断展、断弯、叠瓦 较大 上下分层 较厚 东段 断展、断弯、叠瓦 较大 继承性 较薄 前缘滑脱冲断带 西段 断展、断弯、断滑、叠瓦 较大 上下分层 较厚 表 3 奥雷褶皱冲断带7条测线地震剖面缩短量与缩短率统计
Table 3. Statistics of shortening amount and shortening rate of 7 seismic profiles in Aure fold-thrust belt
剖面 A-A′ B-B′ C-C′ D-D′ E-E′ F-F′ G-G′ 褶皱带长度/km 97.11 72.01 99.78 61.33 9.96 17.76 11.12 原始长度/km 110.72 91.39 110.31 74.30 15.95 26.68 16.63 缩短量/km 13.61 19.38 10.53 12.97 5.99 8.92 5.51 缩短率/% 12.29 21.21 9.55 17.46 37.57 33.44 33.13 表 4 奥雷褶皱冲断带中段和东段测线地震剖面全层系缩短率统计
Table 4. Statistics of shortening rate of the whole strata in the middle and eastern sections of Aure fold-thrust belt
剖面 剖面长度/km 地层 原始长度/km 缩短量/km 缩短率/% E-E′ 9.96 T0 10.20 0.25 2.41 T1 10.15 0.19 1.88 T1″ 14.38 4.40 30.76 T2 15.95 5.99 37.57 Tg 10.30 0.34 3.34 F-F′ 17.76 T0 18.52 0.76 4.11 T1 16.33 T1′ 20.64 4.01 19.43 T1″ 25.86 8.11 31.34 T2 26.68 8.92 33.44 Tg 17.88 0.12 0.67 G-G′ 11.12 T0 11.27 0.16 1.37 T1 11.23 0.11 1.00 T1′ 17.41 6.29 36.15 T1″ 16.63 5.51 33.13 T2 15.90 4.79 30.09 T3 11.69 0.57 4.85 T4 11.56 0.41 3.82 Tg 11.20 0.09 0.76 -
[1] Bulois C, Pubellier M, Chamot-Rooke N, et al. Successive rifting events in marginal basins: The example of the Coral Sea Region (Papua New Guinea)[J/OL]. Tectonics, 2018, 37(1/2): 3-29. doi: 10.1002/2017TC004783. [2] Tregoning P. Evidence for active subduction at the New Guinea Trench[J/OL]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(13): 137-151. doi: 10.1029/2004gl020190. [3] Baldwin S L, Fitzgerald P G, Webb L E. Tectonics of the New Guinea region[J/OL]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 2012, 40(1): 495-520. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-040809-152540. [4] Pigram C J, Davies H L. Terranes and the accretion history of the New Guinea orogen[J]. BMRJ. Aust. Geol. and Geophys, 1987, 10(3): 193-211. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/H_Davies/publication/247713892_Terranes_and_the_accretion_history_of_the_New_Guinea_orogen._B.M.R/links/53e934680cf2dc24b3ca1a3f.pdf [5] Hill K C, Hall R. Mesozoic-Cenozoic evolution of Australia's New Guinea margin in a West Pacific Context. Special Paper 372: Evolution and Dynamics of the Australian Plate[R]. [S.l.]: [s.n.], 2003. [6] van Ufford A Q, Cloos M. Cenozoic tectonics of New Guinea[J/OL]. AAPG Bulletin, 2005, 89(1): 119-140. doi: 10.1306/08300403073. [7] Hall R. Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: Computer-based reconstructions, model and animations[J/OL]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 20(4): 353-431. doi: 10.1016/s1367-9120(01)00069-4. [8] 张洋. 巴布亚盆地巴布亚复杂褶皱带构造综合解释技术及应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1): 29-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901004.htmZhang Y. Structual comprehensive interpretation technology and application in Papuan complex fold belt of Papuan Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(1): 29-34(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901004.htm [9] 尹新义, 胡孝林, 方勇, 等. 印尼-巴新中-古生代盆地群油气地质特征及差异性[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(6): 230-237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201706025.htmYin X Y, Hu X L, Fang Y, et al. Hydrocarbon features of Mesozoic-Paleozoic Basins in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(6): 224-231(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201706025.htm [10] Kugler K A. Detailed analysis from seismic data of the structure within the Aure fold and thrust belt, Gulf of Papua, Papua New Guinea[C]//Anon. Petroleum exploration and development in Papua New Guinea: Proceedings of the 2nd PNG Petroleum Convention. Port Moresby: [s.n.], 1993. [11] Winn Jr R, Pousai P. Synorogenic alluvial-fan-fan-delta deposition in the Papuan Foreland Basin: Plio-Pleistocene Era Formation, Papua New Guinea[J/OL]. Journal of the Geological Society of Australia, 2010, 57(5): 507-523. doi: 10.1080/08120099.2010.492909. [12] Ott B, Mann P. Late Miocene to recent formation of the Aure-Moresby fold-thrust belt and foreland basin as a consequence of Woodlark microplate rotation, Papua New Guinea[J/OL]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2015, 16(6): 1988-2004. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005668. [13] Wpsa B, Gsl A, Vgta C. A Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic reconstruction of the southwest Pacific region: Tectonics controlled by subduction and slab rollback processes[J/OL]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2006, 76(3/4): 191-233. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.01.002. [14] Gaina C, Müller D. Cenozoic tectonic and depth/age evolution of the Indonesian gateway and associated back-arc basins[J/OL]. Earth Science Reviews, 2007, 83(3/4): 177-203. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2007.04.004. [15] Spakman W, Hall R. Surface deformation and slab-mantle interaction during Banda arc subduction rollback[J/OL]. Nature Geoscience, 2010, 3(8): 562-566. doi: 10.1038/ngeo917. [16] Schellart W P, Spakman W. Australian plate motion and topography linked to fossil New Guinea slab below Lake Eyre[J/OL]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 421: 107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.03.036. [17] Harrington L, Zahirovic S, Flament N, et al. The role of deep earth dynamics in driving the flooding and emergence of New Guinea since the Jurassic[J/OL]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 479: 273-283. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.09.039. [18] Pigram C J, Symonds P A. Eastern Papuan Basin: A new model for the tectonic development, and implications for petroleum prospectivity[C]//Anon. Petroleum Exploration and Development in Papua New Guinea: Proceedings of the 2nd PNG Petroleum Convention. Port Moresby: [s.n.], 1993. [19] Pigram C J, Davies P J, Feary D A, et al. Tectonic controls on carbonate platform evolution in southern Papua New Guinea: Passive margin to foreland basin[J/OL]. Geology, 1989, 17(3): 199-202. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1989)0172.3.CO;2 [20] Macedo J, Marshak S. Controls on the geometry offold-thrust belt salient[J/OL]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1999, 111(12): 1808-1822. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1999)1112.3.CO;2 [21] 张连进, 黄家强, 罗强, 等. 川西北前陆双鱼石地区砂箱屋里模拟及其油气地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(2): 156-166. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10126.shtmlZhang L J, Huang J Q, Luo Q, et al. Analogue experiments for the Shuangyushi area in the north western Sichuan Foreland Basin and their implication[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 156-166(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10126.shtml -





 下载:
下载: