Analysis of deformation and stress evolution of thrust structure: A case of Jurassic in east Kuqa Subbasin
-
摘要: 逆冲构造是较为常见的构造形式,其由弱到强的变形过程及应力定量分布状态目前还不是很清楚。以库车前陆盆地东部逆冲构造为例,基于构造剖面的解析,将逆冲构造活动分为4个阶段:初始期、发展期、成熟期和改造期,并运用有限元计算分析方法对不同阶段剖面进行了精细数值模拟计算。研究表明:逆冲构造的扩展并不是一个简单线性发展的过程,而是前翼、后翼不断往复迁移推进的历程。简单的逆冲断褶带发育于逆冲构造初始期,应力主要集中在后翼;变形向后翼扩展,转折端范围不断增加对应逆冲构造发展期,应力主要集中于转折端;变形向前翼扩展,前翼范围开始增大对应逆冲构造成熟期,应力主要集中于转折端和前翼靠近转折端区域;后翼掀斜,前翼竖直,前翼前缘大量新的逆冲断层发育对应逆冲构造改造期,应力主要集中于前翼前缘。理清逆冲构造变形过程及应力集中分布范围的差异,可为后期指导裂缝发育部位以及超压异常发育带的预测奠定较好的基础。Abstract: Thrust structure is a relatively common structural form, and its deformation process from weak to strong and the quantitative distribution of stress are not very clear. This study analyzes the tectonic profile in the eastern part of Kuqa Subbasin, and according to the complexity of deformation, the thrust tectonic activity can be divided into four stages: initial stage, development stage, mature stage, and reformation stage. And it uses the finite element calculation and analysis method to carry out detailed numerical simulation calculation on the different stages of the section. Research suggests that the expansion of the thrust structure is not a simple linear development process, but a process of continuous migration and advancement of the front and rear wings. A simple thrust fold is the initial stage of the thrust structure, and the stress is mainly concentrated on the rear wing; after deformation, it expands to the rear wing and the end area increasing continuously is the development period of the thrust structure, and the stress is mainly concentrated on the end; it expands to the front wing after deformation and the wing range beginning to increase is the mature stage of the thrust structure, and the stress is mainly concentrated on the end and the front wing near the end; the rear wing is tilted, the front wing is vertical, and a large number of new thrust faults developed at the front edge of the front wing are thrust structures; it is the period of thrust structural transformation, and the stress is mainly concentrated on the front edge of the front wing. To clarify the difference in the deformation process of the thrust structure and the distribution range of the stress concentration will lay a good foundation for the prediction of the fracture development position and the abnormal development zone of overpressure in the later stage.
-
Key words:
- thrust structure /
- extended form /
- stress distribution /
- difference
-
逆冲构造变形一般分为两类:盖层逆冲构造和造山带内基底逆冲构造。前者表现为脆性逆冲推覆,主要遵循薄皮构造变形规则,伴随形成断弯褶皱、断展褶皱、滑脱褶皱以及多种断层组合形式;后者表现为脆-韧性过渡环境,主要遵循厚皮构造变形规律,伴随形成大型平卧或斜歪褶皱,倒转一翼的韧性变形明显强于正常翼。沉积盖层中的逆冲构造变形影响着油气成藏,引起了大量石油地质学者的关注。目前,盖层逆冲构造几何学[1-5]、运动学[6-8]、动力学机制[9-14]逐渐完善,并在构造物理[15-16]、地震解释[17-19]和几何学[20-21]方面取得了较为丰富的成果。但这些研究不能较好地描述盖层逆冲过程及应力分布的变化:地震解释、几何学均是对目前构造状态的静态解译,物理模拟则是建立在不确切的假设条件的正演而获得相似结果的一种状态[22],均很难体现盖层逆冲构造变形过程中应力分布状态[23]以及扩展方式[24];而盖层逆冲变形演化正是油气构造圈闭定型过程的反映,对于油气藏形成与改造过程的解剖有重要的意义。
近东西向展布的依奇克里克、吐格尔明构造是库车前陆盆地东部较为重要的含油气构造,本次研究以库车东部6条构造剖面为研究对象,在地震解释、平衡剖面分析的基础上,阐述盖层逆冲构造变形特征和变形过程,然后运用数值模拟的方法展现逆冲断层不断扩展变形过程中的变化状态,明确不同逆冲变形阶段应力集中分布范围的差异,为裂缝发育部位以及超压异常发育带的预测奠定基础。
1. 区域地质背景
库车坳陷发育于塔里木盆地北缘富含油气的前陆冲断带,该坳陷中发现了丰富的油气资源,Chen等[25]、Jia等[26]、Jin等[27]对克拉苏构造带、依奇克里克构造带、秋里塔格构造带和南部斜坡带做过大量的研究,在盐下地层中发现了多个大中型油、气田,如克拉2、迪那2、大北1、大北3等。库车坳陷是形成于天山南侧的中新生代陆相沉积坳陷[28],主要地层为中、新生界。其经历了晚二叠世-三叠纪的前陆盆地、侏罗纪-古近纪造山期轻微调整的伸展坳陷盆地以及新近纪-第四纪的陆内前陆盆地的再生演化过程[29-30],沉积中心逐渐由北向南迁移[31],说明坳陷内的构造变形时间也是由北向南逐渐推进的。北部单斜带形成于早中新世,克拉苏-依奇克里克构造带主要形成于中晚中新世,秋里塔格构造带主要形成于上新世晚期[27, 32]。褶皱冲断带发育多个主滑脱面,导致不同范围的构造变形有较大的差异,纵向构造变形丰富而复杂,记录了南天山新生代构造演化的复杂性。
库车褶皱冲断带发育近东西向延伸的断层相关褶皱以及由北向南冲断的逆断层[33]。卷入逆冲变形的岩层有:①中侏罗统、白垩系的砂岩和夹有煤层的暗色泥岩;②古近系的砾岩、砂岩和夹有膏泥岩的泥岩,古近系膏泥岩是库车逆冲褶皱冲断构造的主要滑脱层,导致地表构造与地下构造呈现出较大的差异;③新近系、第四系的砂岩和砾岩,由山前向坳陷出露地层逐渐变新。
2. 逆冲构造变形特征及差异性分析
库车褶皱冲断带东部由东至西依次发育:吐格尔明构造、依奇克里克构造、巴什基奇克构造。在变形较强烈的区域表现为断层传播褶皱,研究区多见在断层传播褶皱的前翼发育突破断层,偶在局部可见反冲断层发育。这些断层在走向上具有不连续性,位移规模较小,沿着走向断层产状有时发生变化,有些区域呈反向突破,有些区域呈正向突破。由于南天山边界断层的不同地段向库车盆地逆冲的速率有差异,逆冲的位移量大小不同,导致构造组合形式、构造线走向在空间上有较大的变化。同一背斜构造的不同地段隆升的高度在走向上差异较大,主要受断层的数量、断层的倾角、断距的大小及断层发育的层位等因素的共同控制,也反映了构造样式在空间上的变化和变形的不均匀性。
2.1 逆冲构造变形特征
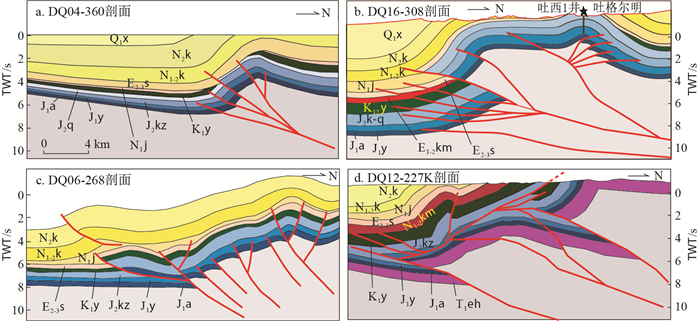
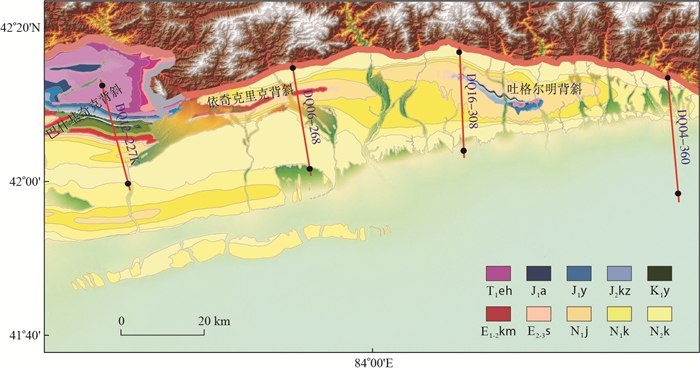
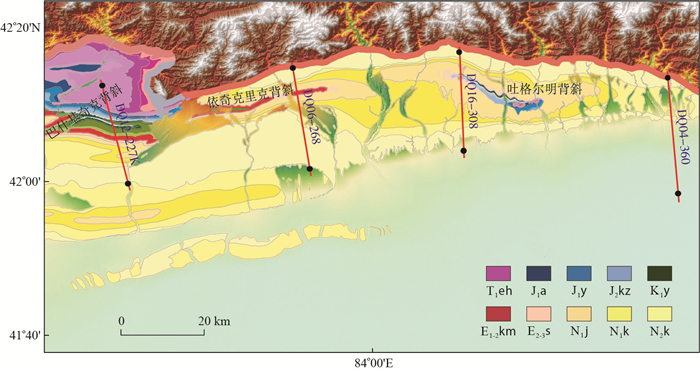
新近纪以来,印度板块与欧亚大陆碰撞的远程效应影响到天山,导致天山急剧隆升,并向坳陷内部逆冲推覆。库车坳陷东部逆冲构造变形就是在该背景下形成的,并以褶皱冲断薄皮构造为主,地层产状变化剧烈。但不同部位,变形程度有较大的差异。为了探讨逆冲构造变形差异,本次研究选择库车东部4条剖面进行详细解剖(图 1)。其中吐格尔明背斜两条(DQ04-360、DQ16-308)、依奇克里克背斜一条(DQ06-268)、巴什基奇克背斜一条(DQ12-227K)。
 图 1 库车东北部4条地震剖面的位置图(地层代号对应的地层组名称见图 4)Figure 1. Location map of the four seismic sections in the northeast of Kuqa
图 1 库车东北部4条地震剖面的位置图(地层代号对应的地层组名称见图 4)Figure 1. Location map of the four seismic sections in the northeast of Kuqa(1) DQ04-360剖面
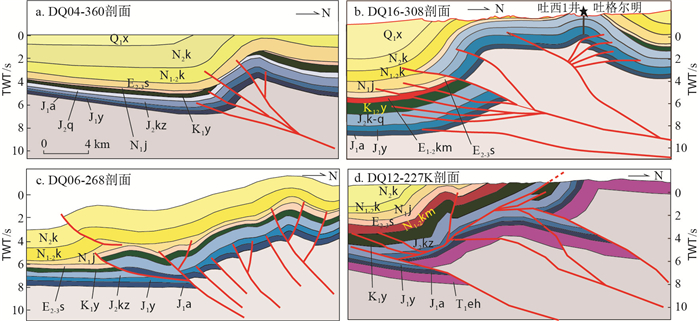
背斜南侧深部多条基底断裂发育,与反冲断层联合控制了吐格尔明背斜的活动。整体上主控断层是一条高角度基底卷入断层,断层向上尖灭,未断穿地表。背斜南翼中生界顶部缺失下白垩统和上侏罗统,克孜勒努尔组(J2kz)直接与新近系中新统的吉迪克组(N1j)不整合接触,所缺失的下白垩统和上侏罗统在背斜的两翼被保留下来,说明吐格尔明背斜东部的深层存在一期古构造事件,通过古近纪地层的沉积分析,确定了这一古构造事件发生在古近纪古新世的库姆格列木组(E1-2km)沉积期。新近系中新统的吉迪克组(N1j)和康村组(N1k)在剖面范围内均匀覆盖,同时,新近纪上新统库车组(N2k)沉积后期出现生长地层,晚期的构造事件基本上可以限定在上新统沉积后期。同时也表明背斜核部的断层和主控断层在新生代一起活动,控制了背斜构造高点由南向北迁移(早期背斜构造高点在现今构造南翼,早期背斜构造北翼成为现今构造高点),呈现向后扩展的特征(图 2-a)。
 图 2 库车坳陷东部构造剖面图(地层代号对应的地层组名称见图 4)Figure 2. Structural profile of the eastern part of Kuqa Depression
图 2 库车坳陷东部构造剖面图(地层代号对应的地层组名称见图 4)Figure 2. Structural profile of the eastern part of Kuqa Depression(2) DQ16-308剖面
不同于东侧DQ04-360剖面,DQ16-308剖面背斜南侧深部多条基底断裂发育,控制了吐孜洛克断层上盘吐孜-迪北“平台区”的发育。吐西1井下部向南逆冲断层及其反冲断层控制了吐格尔明背斜西段的活动,尤其是反冲断层控制了吐格尔明背斜西段的发育,使得断层上盘中生界出露地表,出露地层产状较陡,构造变形更为强烈,形成目前吐格尔明背斜转折端。该剖面非常好地解释了吐孜-迪北基底冲断的大型箱状褶皱的成因,也解决了阳霞背斜的形成及与南侧平台的分异问题。南翼控制了吐孜-迪北平台褶皱的基底逆冲断层,控制了早新生代的古构造,造成白垩系、古新统库姆格列木组(E1-2km)和始新统苏维依组(E2-3s)地层的缺失。两期构造事件和两个不同的基底构造导致了剖面的结构差异。该剖面显示古近纪的古构造事件一直延伸到吐格尔明背斜西段地区,通过古近纪地层的沉积分析,确定了这一古构造事件发生在古新世库姆格列木组(E1-2km)沉积期。现今框架下的结构形态属于上新世库车组(N2k)沉积期以后的构造活动所致(图 2-b)。
(3) DQ06-268剖面
DQ06-268剖面北部依奇克里克背斜表现为南翼较陡、北翼较缓的高陡紧闭背斜。背斜南翼发育7条北倾逆断层,形成叠瓦状构造。迪那2井北部断层以及控制依奇克里克背斜的基底断层均表现为下部断距相对较大,往上地层断距迅速减小,有可能是侏罗系煤层发生塑性变形,导致煤层厚薄不均,影响上覆岩层断开岩层间距有差异(图 2-c)。
与吐格尔明背斜剖面不同,过依奇克里克背斜剖面缺乏早新生代古构造活动的记录,古近系与下白垩统之间的不整合属于区域性质的,反映了晚新生代的一期构造活动事件。新生界有一个大的变化,中新统吉迪克组发现有膏岩塑性流动形成的低幅度盐构造,造成迪那背斜带顶部的吉迪克组(N1j)厚度变化较大,同时膏岩地层的存在,导致上下构造滑脱,形成两套不同的褶皱和冲断构造。依奇克里克背斜与南侧的迪北单斜带从成因上是一个大型基底冲断的褶皱,迪那属于该冲断带南侧伴生的小型滑脱褶皱,因为膏岩的赋存,导致深浅层变形的差异,使该区的构造复杂化。
(4) DQ12-227K剖面
该剖面同时切过了巴什基奇克和依奇克里克2个构造带,与东部3条剖面相比,该剖面揭示的变形记录要复杂得多。剖面显示由于中侏罗统克孜勒努尔组的泥岩、含煤泥岩滑脱层的存在,致使上下岩层构造变形差异较大。下构造层基底卷入断层向上在中侏罗统克孜勒努尔组泥岩、含煤泥岩滑脱层顶板的滑脱,形成背驮式构造,导致山前中新生界大幅度抬升,形成倾向南的斜坡,北部地层大范围的剥蚀夷平。上构造层中发育的反冲断层控制形成了吉迪克背斜。
该区发育两种体系的断裂系统:一是深部的基底断裂,其中有2条比较重要的断层,分别为控制巴什北部的大型基底褶皱(低幅度构造带与南侧的迪北2-巴什2单斜带)的深部断裂和控制迪北2构造的深部断裂,它们的活动结果是形成了深部的迪北2号褶皱体系以及浅层的北部褶皱体系;另外一个断裂系统是与深部基底冲断相关联的浅层滑脱反向冲断系统,其中也有2条断裂带,一条是与北部单斜伴生的滑脱冲断,造成侏罗系和白垩系之间的反向冲断以及地层重复,另外一条是控制吉迪克背斜的滑脱断层,该断层源于侏罗系内部,向浅层切入到新生界,具有左旋斜向冲断的运动学特征(图 2-d)。
与东部的依奇克里克背斜相比,复杂的深部结构、多基底断层的活动、两个基底冲断褶皱的叠加以及多套浅层反向滑脱构造的发育是库车坳陷东部地区的特点。
2.2 构造差异变形分析
吐格尔明背斜为基底冲断的褶皱,这类构造广泛发育于盆地边缘[35],基底卷入式构造通常受一条主要的逆冲基底断层影响,而主逆冲基底断层可能消失在盖层中;当主断层上盘抬升时,在基底错断边缘的沉积盖层形成前翼,整体表现为单斜构造,这类构造一般显示了轻缓的后翼(0°~20°)和一个相对短而产状中度变形甚至陡立的前翼(30°-直立)。通常基底卷入型断层导致基底和沉积盖层发生不同方式的变形,在褶皱的前翼,三角剪切变形带内的基底主要发生剪切变形,而上部沉积盖层发生弯曲,发育褶皱和单斜构造;在褶皱顶部,高角度断层上盘的基底整体抬升,发育断块构造,形成平顶的基底抬升断块。可能主要有两个原因:①基底缺乏古生界(目前只是该地区中生界直接覆盖在元古宙花岗岩体之上),元古宙花岗岩的阻挡导致横向变形弱;②缺乏深部的滑脱层导致吐格尔明向南的扩展量变小,这主要受晚白垩世、古新世和上新世构造活动的影响。
依奇克里克背斜为基底卷入的冲断构造,褶皱的南翼相对简单,少有伴生的构造,为迪北斜坡带,受到由南天山古生界组成的冲断楔的影响,背斜的北翼低角度北倾。中新统吉迪克组膏岩塑性流动形成了低幅度盐构造,导致上下构造滑脱,形成2套不同的褶皱和冲断构造。因为膏岩的赋存导致深浅层变形的差异,以及该区构造的复杂化。这主要受上新世构造活动的影响。
巴什基奇克背斜为多个基底卷入的冲断褶皱的叠加,包括巴什北部的大型基底卷入的褶皱和深部迪北2构造的褶皱在空间上的叠置,组成了一个复杂的基底冲断系统。这一区域基底断裂具有较大的向南扩展的水平矢量,区域性的剖面水平缩短量达到21.7 km,强烈的水平挤压导致深部发育多个基底褶皱的叠加,垂直隆升量远远超过东部的垂直隆升量。南翼发育反向滑脱褶皱和逆冲断层,巴什基奇克背斜、吉迪克背斜和单斜带南翼的南倾逆冲断层均为与深层双重冲断相关的浅层伴生和调节构造,这些浅层构造与主逆冲断层相互伴生,如深部的迪北2号基底冲断构造与吉迪克构造组成一个构造楔,位于迪北2号构造北翼的基底断裂与单斜带上的反向冲断层组成了浅层的另外一个构造楔,主要受上新世构造活动的影响(表 1)。
表 1 逆冲构造差异变形分析Table 1. Differential deformation analysis of thrust structure区域 期次 变形模式 复杂程度 滑脱分层 应力方位 垂直隆升量/km 水平缩短量/km 东部 多期 继承性基底冲断 单-基底冲断,以隆升为主 无 北北东-南南西 3~5 8.8 中部 一期 简单性基底冲断 盐构造影响大,浅层变形复杂化 有 北北西-南南东 4~7 13.5 西部 一期 多层次、被改造和复杂化 浅层横向缩短量大,变形强烈 有 北北西-南南东 >10 21.7 2.3 逆冲构造变形阶段划分
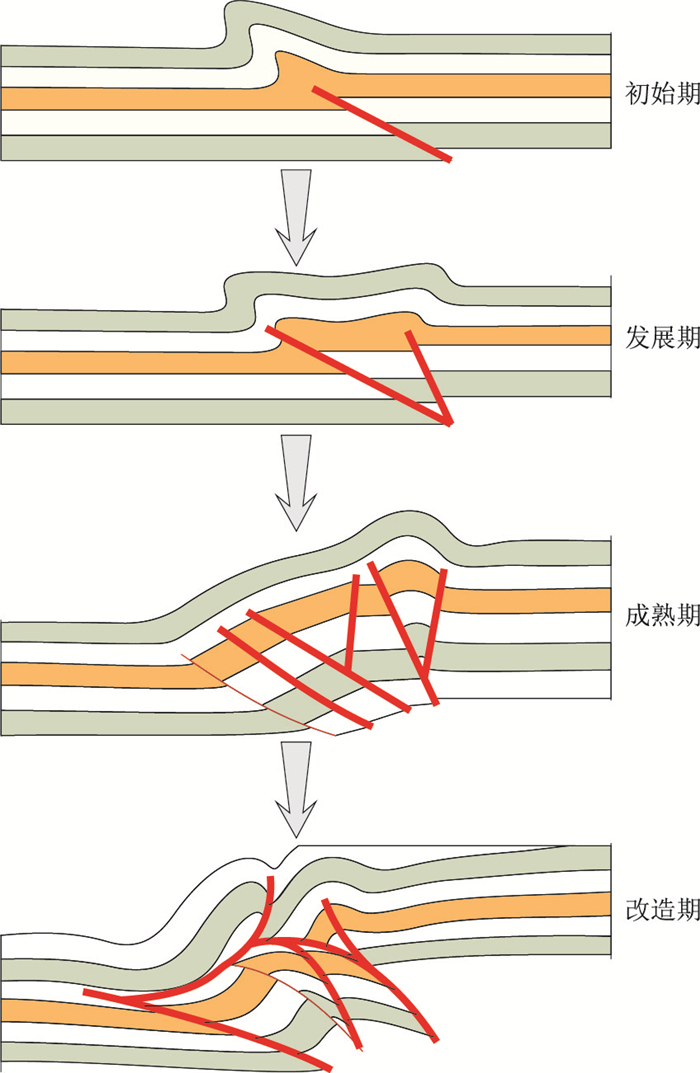
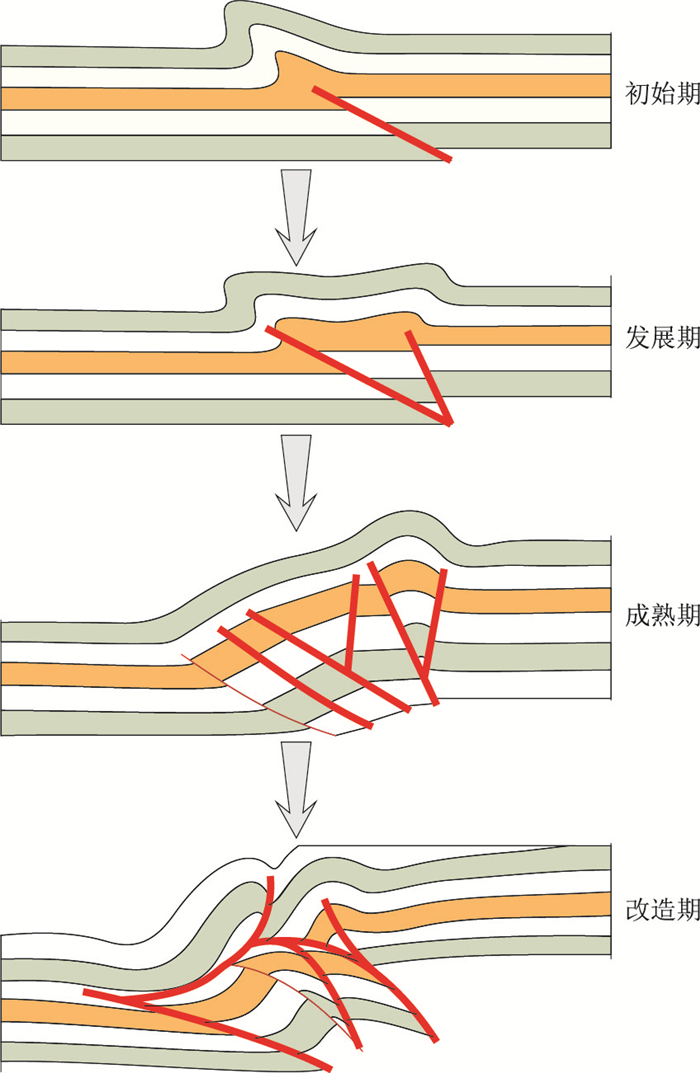
通过前面分析可知,虽然在不同的区域有着不同的变形强度,但整个库车坳陷东部构造主要受逆冲断层控制。由东至西整个变形由断展褶皱变化为断弯褶皱,由简单的冲起构造变化为叠瓦状和堆垛状。这种变化主要是逆冲断层变形强度的不同所导致,不同的变形强度反映了逆冲构造发展的不同阶段。按照变形强弱可以将逆冲构造活动划分为4个阶段:逆冲构造初始期(DQ04-360剖面)、逆冲构造发展期(DQ16-308剖面)、逆冲构造成熟期(DQ06-268剖面)、逆冲构造改造期(DQ12-227K剖面)。①逆冲构造初始期,发育一条逆断层及其所控制的断展褶皱,逆断层断距较小,逆冲所导致的隆升量相对较小,地层变形范围也相对较小;②逆冲构造发展期,在初始期的基础上进一步活动,发育了1条倾角相对较陡的逆断层,断距相对早期逆断层要小,两条逆断层的活动导致隆升范围扩大了约3倍,形成了一个近似箱状褶皱的平台,但垂向上隆升量增幅不是很大;③逆冲构造成熟期,逆断层大量发育,呈叠瓦状,整个断展背斜的后翼急剧抬升,背斜的前翼随着构造活动强度的增大,不断向逆冲方向拓展,导致前翼的影响范围要远远大于后翼的影响范围,同时背斜的转折端范围大大缩小;④逆冲构造改造期,逆冲推覆进一步加强,出现多条断层叠覆相交,呈现为背驮状,同时在背斜前翼发育一条反向逆断层,改造了整个逆冲构造的面貌,并在上覆岩层中派生出新的小规模断展褶皱,同时背斜后翼大范围地抬升剥蚀(图 3)。由东至西4条剖面的解译较好地展现了逆冲构造活动不同发展阶段的状态。
3. 逆冲构造应力场数值模拟
为了进一步弄清楚逆冲构造扩展的过程,针对库车坳陷东部由东至西的4个逆冲阶段进行了应力场数值模拟。
3.1 垂向目的层段的粗化与归并
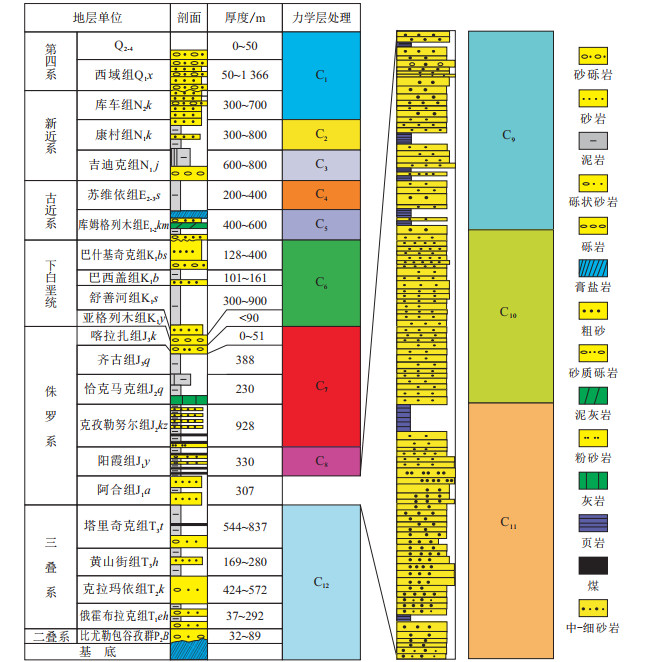
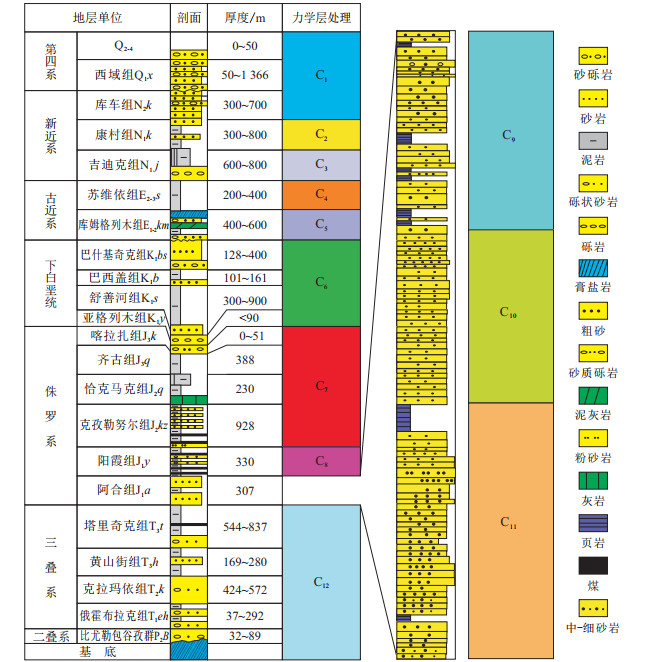
由于目的层段较厚,且垂向上发育的岩石类型变化较为频繁。为了提高计算速度和模拟结果的精度,按照岩性特征将整个目的层段进行了粗化合并。所遵循的原则:每个小层以体积分数大于70%的岩石类型的物理力学性质为主,且为主要的计算参数,其他岩石类型力学性质作为参考,为后期模型的微调服务;若一个力学层中多种岩石类型的体积分数相差不大,则模型的计算参数为这几种岩石力学数据的平均值。依据这一原则将整个层段进行了力学性质的归并,其结果见图 4。
本次研究将其大致划分为12个力学层,从上向下为:①C1层,主要包括地表至库车组(N2k),岩性横向变化较大,发育一套灰色、褐色砾岩、砂岩及粉砂岩;②C2层,呈灰黄色,主要为砂岩、粉砂岩、砾岩互层,厚度变化大,局部最厚可达到800 m,由康村组构成;③C3层,由黄红色砂岩、泥岩、膏盐层互层的吉迪克组组成。对于这种间互的杂岩性段,考虑到具体细化该层段的复杂性和计算的简捷性,将其整体考虑,并在后面的力学处理过程中将岩石力学参数取泥岩、砂岩和膏盐层的平均值;④C4层,由苏维依组构成,主要为红色泥岩、粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩,岩性变化较为频繁,总体上表现为泥多砂少;⑤C5层,该力学层厚度极不均衡,变化较大,下部为灰褐色粉砂岩、砂砾岩,中部为膏盐岩,上部为灰白色盐岩夹灰褐色泥岩,并且该层岩性在平面上变化也较为迅速,由库姆格列木组构成;⑥C6层,由厚度200~1 600 m的白垩系构成,岩性主要为黄色、紫红色泥岩、砂岩,局部可见红色块状的砾石,包含亚格列木组、舒善河组、巴西盖组和巴什基奇克组;⑦C7层,由厚度为200~1 400 m的齐古组、恰克马克组和克孜勒努尔组构成,岩性主要为黄色、紫红色砂岩夹泥岩、泥质砂岩,局部可见红色块状的砾石;⑧C8层,主体为一套黑色煤层,其间可见薄层砂岩层和厚度与煤层相当的泥岩,整体为安静水体的沼泽沉积环境,力学性质偏弱;⑨C9层,主要发育一套灰白色、灰绿色砂岩及极薄层黑色碳质页岩,中间夹薄层泥岩,厚度变化较大,主要有阿合组上部构造,其力学属性变化相对频繁;⑩C10层,灰白色、浅绿灰色-灰色粉砂岩和灰色-深灰色泥岩、碳质泥岩,局部可见厚度变化较大的砾岩层,整体以长石石英砂岩为主,颗粒分选、磨圆程度较均匀,力学性质稳定;B11 C11层,以灰白色、灰色砂岩为主,其间夹多套粗砂和砾岩旋回出现,该层的上部和下部均发育厚度稳定的泥岩层,整体上粗粒含量相对较高;B12 C12层,由三叠系、二叠系和下伏的基底构成,其中三叠系顶部为煤层,中下部以火山岩为主,二叠系比尤勒包谷孜群发育紫红色泥岩、浅绿灰色-灰色粉砂岩和灰色-深灰色泥岩、碳质泥岩,下伏则为强烈变形和动力变质的碎屑岩和火山碎屑岩。
3.2 物理模型建立
(1) 材料属性的确定
本次研究的材料力学参数主体根据钻井所获得的三轴岩石力学实验结果,考虑各个力学层的厚度,以及不同构造形态和构造部位,运用加权平均的方式和类比法,综合分析而获得的,同时还参考了张凤奇等[36]以及塔里木油田研究院分析计算时的数据。为了使模拟结果能较好地反映研究层段的应力状态,将研究区中断裂两侧适当范围内的岩石力学参数按照一定比例降低,具体的数据可以根据研究区实际的岩性组合以及断层规模予以适当的调整(表 2)。
表 2 库车坳陷力学物理模型材料参数值Table 2. Material parameter value of mechanical and physical model in Kuqa Depression层位 密度/(g·cm-3) 杨氏模量/GPa 泊松比 岩盐发育 岩盐不发育 Q1x 施加重力 N2k 2.10 15 15 0.26 N1k 2.20 20 20 0.25 N1j 2.16 5 20 0.42 E2-3s 2.21 20 20 0.30 E1-2km 2.01 6 21 0.35 K 2.34 25 25 0.23 J2k 2.36 30 30 0.25 J1y 2.13 6 6 0.41 J1a 2.38 34 34 0.24 Pre-J1a 2.48 39 39 0.25 断裂带 2.00 8 8 0.32 注:数据主要来自西南石油大学岩石力学实验室三轴应力实验,结合岩层的厚度和岩性的组合加以类比修正;地层代号见图 4 (2) 网格单元划分
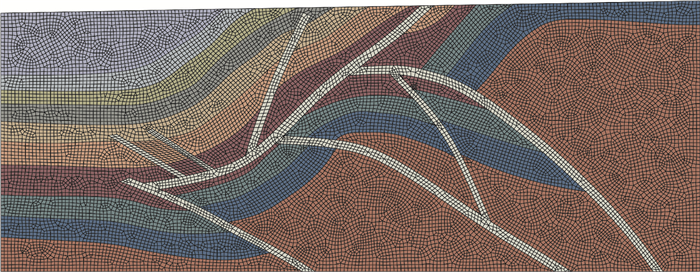
库车坳陷受到不同期次、不同强度构造活动的影响,致使整个构造形态较为复杂,因此对模型自动网格化相对较为困难,为了突显重点区块的应力特征并减少人为误差,采用人工控制与自动相结合的方法,对研究区进行了网格化。研究区依据CPS8R单元,兼顾计算机容量和复杂程度,从地质模型中抽象出力学模型,划分出由多节点构成的多类型单元(图 5)。
(3) 边界条件确定
库车坳陷东部在新近纪以来的近南北向构造挤压作用下,构造变形时间由北而南逐渐变新是不争的事实。库车坳陷东部新生代地层的构造变形是在吉迪克组沉积开始的,强烈变形发生于库车组、西域组沉积时期。依据这一认识,研究过程中对模型进行了大量的试算。其中模型Ⅴ:模型右侧施加向x负方向的梯度位移量(由底至顶逐渐减小,随着深度变化而变化,即受埋藏深度的控制),左侧将x方向约束,y方向自由;顶面施加向y负方向且由左至右渐渐变小的梯度负载量(由坳陷向褶皱冲断带逐渐减小,即上覆沉积物负载只作用于坳陷内部,褶皱冲断带受到的影响相对较小),底面将y方向约束,x方向自由,与库车坳陷实际的构造作用类似,并且计算结果与这2阶段的构造应力分布、大小等特征较为吻合。由此选择模型Ⅴ的边界条件作为最终的计算约束条件(表 3)。
表 3 库车坳陷东部区域构造模型边界条件的选择Table 3. Selection of boundary conditions for the structural model in the eastern part of the Kuqa Depression时期 方案 垂直x轴的面 垂直y轴的面 备注 x正方向 x负方向 y正方向 y负方向 N2k→Q Ⅰ 施加向x负方向的位移量,y方向约束 全约束 自由 x方向自由
y方向约束经过试算,方案Ⅴ结果最佳,后面所有的计算均按方案Ⅴ进行计算。由于是二维平面模型,无z方向上的边界条件 Ⅱ 施加向x负方向的位移量 y方向自由
x方向约束自由 x方向自由y方向约束 Ⅲ 施加向x负方向的位移量, y方向约束 y方向自由
x方向约束施加沿y负方向的应力 x方向自由y方向约束 Ⅳ 施加向x负方向的位移量 全约束 施加沿y负方向的应力 x方向自由y方向约束 Ⅴ 施加向x负方向的梯度位移量 全约束 施加沿y负方向的梯度应力 x方向自由y方向约束 3.3 应力数值模拟结果
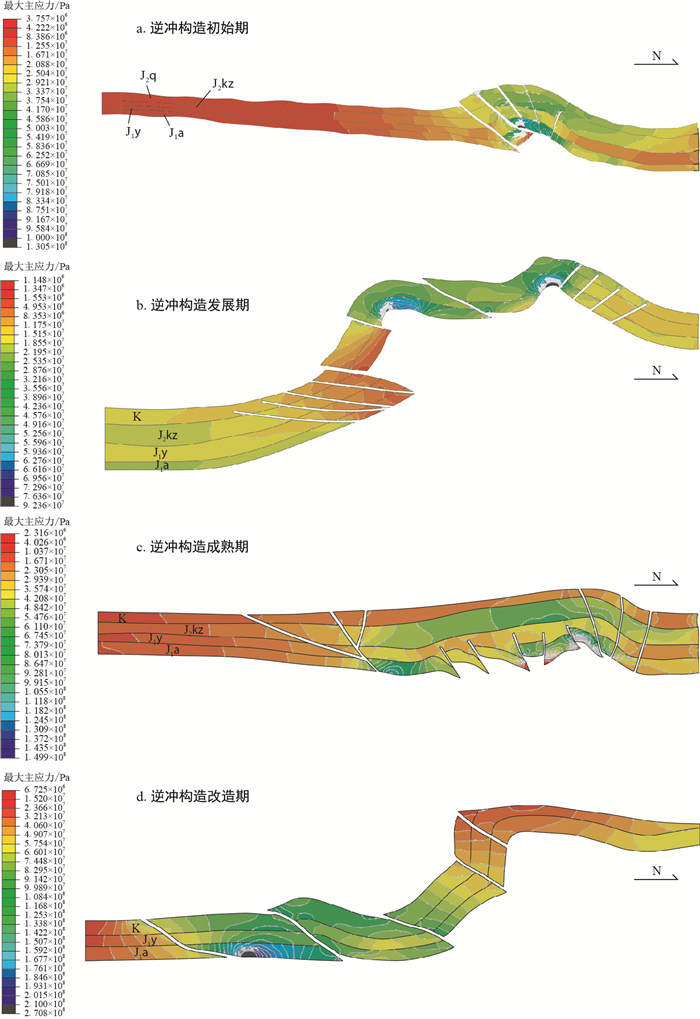
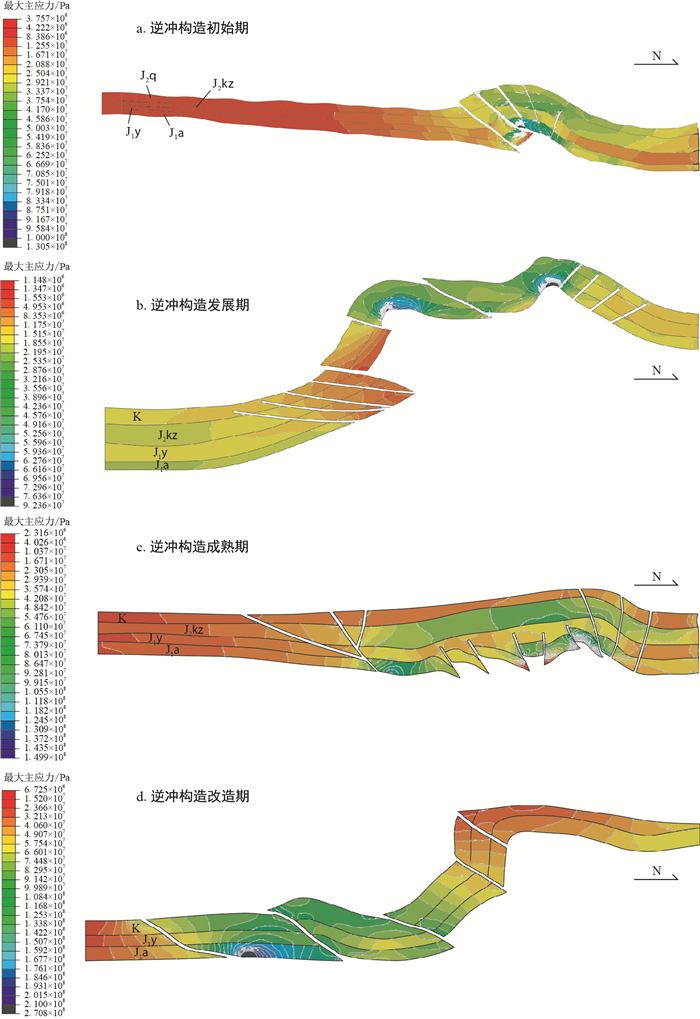
(1) 逆冲构造初始期
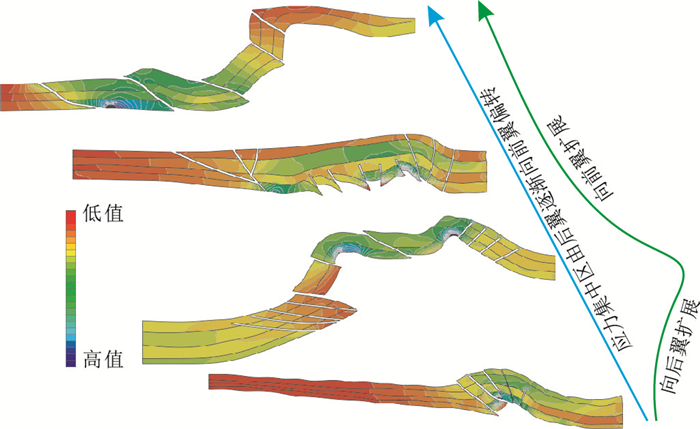
整体上,由北至南最大主应力的变化趋势为北翼最大→转折端居中→南翼最小,呈逐渐减小的趋势,整个构造变形表现为后展趋势,与前面构造分析变形量最大的为褶皱核心带的结论相吻合。由底-顶其中阳霞组塑性煤层、泥岩层段呈现为明显的力学软弱层,其最大主应力值位于褶皱核部,也仅仅介于25~33.37 MPa之间,构造变形较弱的南部区域为整个剖面最大主应力低值分布区域,高应力主要分布于靠近北部褶皱冲断带断裂汇聚区域的下部地层(侏罗系)。聚焦到目的层段(侏罗系阿合组)最大主应力由北向南逐渐减小,其最大值位于整个剖面断裂和褶皱区域,可达75.01 MPa,最小主应力分布区位于剖面南部,为3.757 MPa左右,整个剖面应力分布由北至南,断裂、褶皱控制程度较大,逆冲断层以南最大主应力急剧减小,集中于8~29.21 MPa,断裂、褶皱发育的北部最大主应力明显集中于33~75.01 MPa之间,其中目的层段阿合组最大主应力的90%分布于49~54 MPa之间。断层活动的过程或者局部断层形态的变化导致应力的释放,致使最大主应力很难向剖面的南部区域扩展集中(图 6-a)。剖面最大主应变量高值区主要发育于中北段,最高可达1.92×10-3,是整个剖面应变量最大的区域,最后也导致了断层和褶皱的发育。整体上北部的应变强度要比南部的应变强度高5~10倍,这也很好地说明北部变形要比南部强很多。
剖面隆升量的对比显示,断褶带隆升量最大,核心区可达4.13×10-3,北部区域隆升量较南部要高1~2个数量级,其中剖面南部区域由于挤压逆冲挠曲也在一定范围内下沉,但下沉量较小,挠曲下沉的范围也非常有限。
(2) 逆冲构造发展期
断褶带核部由顶至底,最大主应力场逐渐增大,但在褶皱南翼则呈现相反的格局,由顶至底逐渐减小。整体上,由北至南最大主应力的变化趋势为北翼小→转折端最大→南翼小,呈中间高值,往两翼逐渐减小,整个构造呈现断展褶皱发育核心期。相对于逆冲构造初始期,逆冲构造尤其在向南扩展的过程中,应力集中程度及范围由北翼向转折端转移,导致断褶核心隆升量大幅增大,而褶皱转折端断裂区表现为应力极大的集中区。由底-顶其中阳霞组塑性煤层、泥岩层段呈现为明显的力学软弱层,其最大主应力值位于褶皱核部,也仅仅介于21~38.96 MPa之间,构造变形较弱的南部区域为整个剖面最大主应力低值分布区域,高应力主要分布于靠近褶皱变形带。聚焦到目的层段(侏罗系阿合组)最大主应力由北向南逐渐减小,其最大值位于整个剖面断裂和褶皱区域,平均为76.36 MPa,局部点最大值可高达92.36 MPa。整个剖面应力分布由北至南,断裂、褶皱控制程度较大,逆冲断层以南最大主应力呈现突变的特征。在断裂、褶皱发育的北部最大主应力明显集中于38~76 MPa之间,其中目的层段阿合组最大主应力的90%分布于45~76 MPa之间。断层活动的过程或者局部断层形态的变化导致应力的释放,致使最大主应力很难向剖面的南部区域扩展集中(图 6-b)。剖面最大主应变量高值区主要发育于中北段,以及向前扩展带,最高可达1.8×10-3,是整个剖面应变量最大的区域,最后也导致了断层和褶皱的发育。整体上北部的应变强度要比南部的应变强度高6~8倍,这也很好地说明北部变形要比南部强很多。
剖面隆升量的对比显示,断褶转折端隆升量最大,核心区可达4.837×10-3,尤其是在褶皱转折端靠北翼的范围达到极大隆升量,其中剖面南部区域由于挤压逆冲也表现出极小范围的隆升。
(3) 逆冲构造成熟期
相比前2个剖面,该期剖面构造变形也复杂了很多,尤其是在向前扩展的过程中,应力集中程度及范围也在向南扩展,由北至南最大主应力的变化趋势为北翼小→转折端居中→南翼最大,呈现应力值向南翼偏移的状态,并且褶皱南翼范围有较大程度的扩张,北翼范围减小。由底-顶其中阳霞组塑性煤层、泥岩层段呈现为明显的力学软弱层,其最大主应力值位于褶皱核部,也仅仅介于23~42.08 MPa之间,构造变形较弱的南部区域为整个剖面最大主应力低值分布区域,高应力主要分布于靠近褶皱变形带。聚焦到目的层段(侏罗系阿合组)最大主应力由北向南逐渐减小,其最大值位于整个剖面的断裂和褶皱区域,可达137.2 MPa,局部点最大值可高达149.9 MPa。整个剖面应力分布由北至南,断裂、褶皱控制程度较大,逆冲断层以南最大主应力呈现突变的特征。断裂、褶皱发育的北部最大主应力明显集中于48.42~124.5 MPa之间,其中目的层段阿合组最大主应力的90%分布于61~105.5 MPa之间(图 6-c)。剖面最大主应变量高值区主要发育于南翼,并逐渐向南扩展,最高可达3.287×10-3,是整个剖面应变量最大的区域,最后也导致了断层和褶皱的发育。
剖面隆升量的对比显示,整个南翼开始大范围的隆升,但隆升量还不是很大,呈现向南转移的态势。最大值还是位于褶皱转折端,可达5.826×10-3。
(4) 逆冲构造改造期
结果显示:整个剖面最大主应力主要集中于褶皱南翼,高值为210 MPa,而最南端则相对较低,主要集中于6.725~74.48 MPa之间(图 6-d)。最大主应变量分布格局与最大主应力分布较为类似,但区别在于断层交汇区域(特别是多条断裂交汇处)和边界条件施加处有一定的应变强度高值区,也是裂缝极易发育的区域。剖面隆升量主要集中于褶皱南翼扩展带,北翼和转折端隆升量次之,最南部隆升量最小。最大主应力由水平方向转向上部逆冲,尤其是断裂发育处展现得极为明显。
4. 讨论
受喜山期构造活动的影响,南天山向库车坳陷北部逆冲推覆。由于受古近系和新近系膏岩层分布不均匀性以及构造应力作用非均质性的影响[20, 37-38],导致南天山向坳陷推覆过程中呈现挤压速度不均,造成变形差异较大。由逆冲变形初始期(DQ04-360剖面)→逆冲构造发展期(DQ16-308剖面)→逆冲构造成熟期(DQ06-268剖面)→逆冲构造改造期(DQ12-227K剖面)缩短量由初始期的5.97%逐渐增加到改造期的17.61%(表 4),表明南天山对库车北部的改造是逐渐加强的,模拟结果很好地展现了逆冲构造渐变的过程,是很好地剖析从初始断裂开始到逐步发展再一直到后期浅部岩层反冲改造的一个完整逆冲构造形成发展的平台。
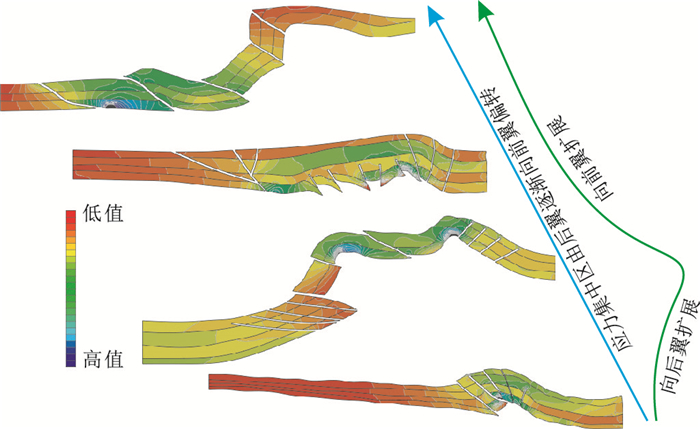
表 4 逆冲构造不同阶段表现形式分析Table 4. Analysis of the manifestation of the thrust structure at different stages逆冲构造不同阶段 侏罗系阿合组(众数) 应力集中区域 变形方式 应力/MPa 缩短量/% 隆升量/10-4 南翼 转折端 北翼 初始期 8~29.21 25.16~50.37 49~54 5.97 1.3~4.13 北翼 隆升 发展期 18.88~32.16 67.63~71.7 24.48~46.96 8.24 2.223~4.837 转折端 后展 成熟期 64.76~87.13 86.59~91.89 23.5~61.1 10.55 2.11~5.826 南翼 前展 改造期 144.54~153.39 6.72~40.60 15.2~57.4 17.61 35.2~71.8 前缘 前展 逆冲构造初始期,构造变形程度相对较弱,以断褶隆升为主,但隆升程度相对较小;同时最大主应力计算显示高值区集中于褶皱北翼,这也为构造变形向北翼扩展奠定了基础。随着南天山挤压作用的加强,逆冲构造活动进一步加强,进入发展期,变形以向后翼扩展为主,在褶皱的北翼形成晚期的高角度逆断层,将断褶变形的横向扩展范围进一步扩大,褶皱的转折端范围较逆冲构造初始期扩大了近3倍,顶部形成近箱状褶皱;相比于构造变形初始期,逆冲构造发展期最大主应力高值区集中于褶皱转折端,表明最大主应力向褶皱转折端偏移。随后构造运动持续加强,构造变形复杂化,整个逆冲构造进入成熟期,在褶皱南翼形成大量逆断层,并且南翼范围大大增加,较逆冲构造发展期前翼扩展了近3倍,而转折端影响范围已经大大减小,最终与逆冲构造初始期的转折端范围相同;最大主应力高值区集中在转折端偏南翼和转折端范围,同时整个南翼的最大主应力绝对值逐渐增大,已经整体高于北翼,并且接近于转折端最大主应力,表明成熟期最大主应力已经开始向南翼偏移。逆冲构造改造期,构造变形程度最强,北翼在逆冲作用的影响下发生掀斜并大量剥蚀,而南翼则近竖直,南翼前缘持续发育逆断层,并不断向南扩展;最大主应力值则主要集中于南翼前缘,为天山向库车坳陷的扩展奠定了力学基础(图 7)。
逆冲构造变形研究目前较为成熟,中西部各大盆地均有学者进行了细致研究,如四川盆地的川东北大巴山、米仓山[39]、川西龙门山[40]、塔里木盆地塔西南[41]、鄂尔多斯盆地西缘[42],均认为逆冲构造变形是由造山带逐渐向盆地内部递进扩展。但针对逆冲构造变形是否有一个完整发育过程以及发育过程是否是简单的线性扩展(单纯的前展、单纯的后展)则讨论的较少。本次研究表明逆冲构造变形是一个完整的往复扩展的过程,早期向后翼扩展、中晚期向前翼扩展,主要是由抬升量的差异以及断层影响范围这两个因素所决定的。逆冲构造早期由于后翼与前翼埋藏深度相同,抬升量均较小,断层影响的范围较小,应力释放方式较少,故应力在靠近力源的后翼集中,由此导致整个逆冲构造向后翼扩展,发展的过程中断层影响的范围开始增加,并且前后翼的隆升量逐渐产生差异,整个逆冲构造变形逐渐向中期过渡。逆冲构造中晚期,由于构造活动逐渐增强,后翼靠近力源方向,抬升幅度逐渐增大,断层发育程度增强,导致后翼应力快速释放。前翼由于埋藏深度保持不同,隆升量小,同时前翼断层滑移的幅度较后翼小太多,由此应力开始在前翼集中,导致前翼不断向前扩展变形。
5. 结论
(1) 南天山对库车东部的构造作用存在一定的差异性,库车东部北缘由东至西,构造缩短量、隆升量均逐渐增加。这种差异导致了断层发育程度和地层抬升有一定程度的变化,进而控制库车东部北缘构造应力集中区域和绝对值大小的变化。
(2) 库车东部北缘的逆冲构造发育可以分为4个阶段:初始期、发展期、成熟期和改造期。逆冲构造的扩展并不是一个简单线性发展的过程,而是前翼、后翼不断往复迁移推进的历程。简单的逆冲断褶带发育于逆冲构造初始期,应力主要集中于后翼;变形向后翼扩展,转折端范围不断增加对应逆冲构造发展期,应力主要集中于转折端;变形向前翼扩展,前翼范围开始增大对应逆冲构造成熟期,应力主要集中于转折端和前翼靠近转折端区域;后翼掀斜,前翼竖直,前翼前缘发育大量新的逆冲断层对应逆冲构造改造期,应力主要集中于前翼前缘。由此可以预测库车东部油气勘探重点区由东至西应由山前断褶高点向断褶南翼前缘转移,不同部位侧重点区域应差别对待。
-
图 1 库车东北部4条地震剖面的位置图(地层代号对应的地层组名称见图 4)
Figure 1. Location map of the four seismic sections in the northeast of Kuqa
图 2 库车坳陷东部构造剖面图(地层代号对应的地层组名称见图 4)
Figure 2. Structural profile of the eastern part of Kuqa Depression
表 1 逆冲构造差异变形分析
Table 1. Differential deformation analysis of thrust structure
区域 期次 变形模式 复杂程度 滑脱分层 应力方位 垂直隆升量/km 水平缩短量/km 东部 多期 继承性基底冲断 单-基底冲断,以隆升为主 无 北北东-南南西 3~5 8.8 中部 一期 简单性基底冲断 盐构造影响大,浅层变形复杂化 有 北北西-南南东 4~7 13.5 西部 一期 多层次、被改造和复杂化 浅层横向缩短量大,变形强烈 有 北北西-南南东 >10 21.7 表 2 库车坳陷力学物理模型材料参数值
Table 2. Material parameter value of mechanical and physical model in Kuqa Depression
层位 密度/(g·cm-3) 杨氏模量/GPa 泊松比 岩盐发育 岩盐不发育 Q1x 施加重力 N2k 2.10 15 15 0.26 N1k 2.20 20 20 0.25 N1j 2.16 5 20 0.42 E2-3s 2.21 20 20 0.30 E1-2km 2.01 6 21 0.35 K 2.34 25 25 0.23 J2k 2.36 30 30 0.25 J1y 2.13 6 6 0.41 J1a 2.38 34 34 0.24 Pre-J1a 2.48 39 39 0.25 断裂带 2.00 8 8 0.32 注:数据主要来自西南石油大学岩石力学实验室三轴应力实验,结合岩层的厚度和岩性的组合加以类比修正;地层代号见图 4 表 3 库车坳陷东部区域构造模型边界条件的选择
Table 3. Selection of boundary conditions for the structural model in the eastern part of the Kuqa Depression
时期 方案 垂直x轴的面 垂直y轴的面 备注 x正方向 x负方向 y正方向 y负方向 N2k→Q Ⅰ 施加向x负方向的位移量,y方向约束 全约束 自由 x方向自由
y方向约束经过试算,方案Ⅴ结果最佳,后面所有的计算均按方案Ⅴ进行计算。由于是二维平面模型,无z方向上的边界条件 Ⅱ 施加向x负方向的位移量 y方向自由
x方向约束自由 x方向自由y方向约束 Ⅲ 施加向x负方向的位移量, y方向约束 y方向自由
x方向约束施加沿y负方向的应力 x方向自由y方向约束 Ⅳ 施加向x负方向的位移量 全约束 施加沿y负方向的应力 x方向自由y方向约束 Ⅴ 施加向x负方向的梯度位移量 全约束 施加沿y负方向的梯度应力 x方向自由y方向约束 表 4 逆冲构造不同阶段表现形式分析
Table 4. Analysis of the manifestation of the thrust structure at different stages
逆冲构造不同阶段 侏罗系阿合组(众数) 应力集中区域 变形方式 应力/MPa 缩短量/% 隆升量/10-4 南翼 转折端 北翼 初始期 8~29.21 25.16~50.37 49~54 5.97 1.3~4.13 北翼 隆升 发展期 18.88~32.16 67.63~71.7 24.48~46.96 8.24 2.223~4.837 转折端 后展 成熟期 64.76~87.13 86.59~91.89 23.5~61.1 10.55 2.11~5.826 南翼 前展 改造期 144.54~153.39 6.72~40.60 15.2~57.4 17.61 35.2~71.8 前缘 前展 -
[1] 裴振洪. 南大巴山构造带中新生代构造变形特征研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2007, 29(3): 269-274.Pei Z H. Research on Mesozoic and Cenozoic structural deformation characteristics of south Dabashan structural belt[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2007, 29(3): 269-274(in Chinese with English abstract). [2] 胡健民, 施炜, 渠洪杰, 等. 秦岭造山带大巴山弧形构造带中生代构造变形[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(3): 49-68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.03.003Hu J M, Shi W, Qu H J, et al. Mesozoic deformation of Dabashan curvilinear structural belt of Qinling orogen[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(3): 49-68(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.03.003 [3] 刘重庆, 周建勋, 郎建. 多层滑脱条件下褶皱-冲断带形成制约因素研究: 以川东-雪峰构造带为例[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2013, 35(2): 45-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.02.005Liu C Q, Zhou j X, Lang J. Study on restrictive factor of fold-thrust belt formation with multiple decollements: Taking eastern Sichuan-Xuefeng tectonic belt as an example[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2013, 35(2): 45-55(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.02.005 [4] 谢国爱, 贾东, 张庆龙, 等. 川东侏罗山式褶皱构造带的物理模拟研究[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(6): 773-778. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.06.003Xie G A, Jia D, Zhang Q L, et al. Physical modeling of the Jura-type folds in eastern Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(6) 773-778(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.06.003 [5] 张旭亮. 鄂西-渝东地区构造演化及成因机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019: 9-11.Zhang X L. Tectonic evolution and genetic mechanism of western Hubei and eastern Chongqingarea[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019: 9-11(in Chinese with English abstract). [6] 沈传波, 梅廉夫, 徐振平, 等. 四川盆地复合盆山体系的结构构造和演化[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 31(3): 288-299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2007.03.004Shen C B, Mei L F, Xu Z P, et al. Architecture and tectonic evolution of composite basin-mountain system in Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2007, 31(3): 288-299(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2007.03.004 [7] 梅廉夫, 刘昭茜, 汤济广, 等. 湘鄂西-川东中生代陆内递进扩展变形: 来自裂变径迹和平衡剖面的证据[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(2): 161-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2010.02.008Mei L F, Liu Z Q, Tang J G, et al. Mesozoic intra-continental progressive deformation in western Hunan-Hubei-eastern Sichuan Provinces of China: Evidence from apatite fission track and balanced cross-section[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 35(2): 161-174(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2010.02.008 [8] 李三忠, 王涛, 金宠, 等. 雪峰山基底隆升带及其邻区印支期陆内构造特征与成因[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2011, 41(1): 93-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201101013.htmLi S Z, Wang T, Jin C, et al. Features and causes of indosinian intracontinental structures in the Xuefengshan PreCambrian basement and its neighboring regions[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(1): 93-105(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201101013.htm [9] 朱志澄. 逆冲推覆构造研究进展和今后探索趋向[J]. 地学前缘, 1995, 2(1/2): 51-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY501.009.htmZhu Z C. Progress and trends of researches on thrust-nappe tectonics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1995, 2(1/2): 51-58(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY501.009.htm [10] 金宠, 李三忠, 王岳军, 等. 雪峰山陆内复合构造系统印支-燕山期构造穿时递进特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2009, 30(5): 598-607. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.05.010Jin C, Li S Z, Wang Y J, et al. Diachronous and progressive deformation during the Indosinian-Yanshanian movements of the Xuefeng Mountain intracontinental composite tectonic system[J]. Oll and Gas Geology, 2009, 30(5): 598-607(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.05.010 [11] 何登发, 李德生, 张国伟, 等. 四川多旋回叠合盆地的形成与演化[J]. 地质科学, 2011, 46(3): 589-606. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2011.03.001He D F, Li D S, Zhang G W, et al. Formation and evolution of multi-cycle superposed Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2011, 46(3): 589-606(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2011.03.001 [12] 张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等. 中生代多向挤压构造作用与四川盆地的形成和改造[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(2): 233-250. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.02.001Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Li J H, et al. Mesozoic multi-directional compressional tectonics and formation-reformation of Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2011, 38(2): 233-250(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.02.001 [13] 万天丰. 论构造地质学和大地构造学的几个重要问题[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(1): 132-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201401015.htmWan T F. Discussion on some important problems in structural geology and tectonics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(1): 132-149(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201401015.htm [14] 李锦轶, 张进, 刘建峰, 等. 中国地壳结构构造与形成过程: 来自构造变形的约束[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(5): 678-698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201905006.htmLi J Y, Zhang J, Liu J F, et al. Crustal tectonic framework of China and its formation processes: Constraints from stuctural deformation[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(5): 678-698(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201905006.htm [15] 周建勋. 断裂系统形成机制: 来自物理模拟实验的新启示[J]. 自然杂志, 2011, 33(5): 260-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZZ201105004.htmZhou J X. Formation mechanisms of fault systems: Some new insights from physical modeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2011, 33(5): 260-265(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZZ201105004.htm [16] He W G, Zhou J X, Yuan K. Deformation evolution of eastern Sichuan-Xuefeng fold-thrust belt in South China: Insights from analogue modelling[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2018, 109: 74-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2018.01.002 [17] 汪新, 唐鹏程, 谢会文, 等. 库车坳陷西段新生代盐构造特征及演化[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(1): 57-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.008Wang X, Tang P C, Xie H W, et al. Cenozoic salt structures and evolution in the western Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2009, 33(1): 57-65(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.008 [18] 张玮, 徐振平, 赵凤全, 等. 库车坳陷东部构造变形样式及演化特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(1): 48-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201901008.htmZhang W, Xu Z P, Zhao F Q, et al. Structural deformation styles and tectonic evolution characteristics in eastern Kuqa Depression[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(1): 48-83(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201901008.htm [19] 成亚. 库车坳陷东部构造分析: 先存断裂与膏盐岩发育对构造变形的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020: 18-21.Cheng Y. Structural analysis in the eastern Kuqa Depression: Influence of pre-existing faults and gypsum salt deposits on structural deformation[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020: 18-21(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 张仲培, 王清晨. 断层滑动分析与古应力恢复研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(4): 605-613 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.04.018Zhang Z P, Wang Q C. The summary and comment on fault-slip analysis and palaeostress reconstruction[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2004, 19(4): 605-613(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.04.018 [21] 汤双立, 颜丹平, 汪昌亮, 等. 华南雪峰山薄皮-厚皮构造转换过程: 来自桑植-安化剖面的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(1): 22-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.01.003Tang S L, Yan D P, Wang C L, et al. Deformational process from thick-skinned to thin-skinned thrust in Xuefeng Mountain, South China: Evidence from Sangzhi-Anhua tectonic section[J]. Geoscience, 2011, 25(1): 22-30(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.01.003 [22] 邓宾, 何宇, 黄家强, 等. 前陆盆地形成与演化砂箱物理模拟启示: 以四川盆地西部龙门山为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(2): 401-415. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202102012.htmDeng B, He Yu, Huang J Q, et al. Analogue modeling insights to foreland basin growth: A case study on the Longmengshan thrust belt in western Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2021, 42(2): 401-415(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202102012.htm [23] 黄光明, 李忠海, 周永智. 塔西南甫沙地区被动顶板双重构造和乌泊尔地区背驮盆地的数值模拟[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(8): 1674-1693. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.08.002Huang G M, Li Z H, Zhou Y Z. The different origins between passive-roof duplex in the Fusha area and Piggyback Basin in the Wupoer area in southwestern Tarim Basin based on numerical modelling study[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(8): 1674-1693(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.08.002 [24] 杨庚, 王晓波. 川西龙门山逆冲带北段多断层同时逆冲几何学证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(6): 1027-1045. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202006001.htmYang G, Wang X B. Geometric evidence for synchronous thrusting and folding of the northern Longmengshan thrust-fold belt, West China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2020, 44(6): 1027-1045(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202006001.htm [25] Chen J, Wang S L, Shang Y J. Geometric tests and their application to fault-related folds in Kuqa[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2005, 25(3): 473-480. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.04.008 [26] Jia C Z, Li Q M. Petroleum geology of Kela-2, the most productive gas field in China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2008, 25(4/5): 335-343. [27] Jin Z J, Yang M H, Lü X X, et al. The tectonics and petroleum system of the Qiulitagh fold and thrust belt, northern Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2008, 25(8): 767-777. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.01.011 [28] 贾承造. 环青藏高原巨型盆山体系构造与塔里木盆地油气分布规律[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.001Jia C Z. The structures of basin and range system around the Tibtan Plateau and the distribution of oil and gas in the Tarim Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2009, 33(1): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.001 [29] 卢华复, 贾东, 陈楚铭, 等. 库车新生代构造性质和变形时间[J]. 地学前缘, 1999, 6(4): 215-221. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.04.003Lu H F, Jia D, Chen C M, et al. Nature and timing of the Kuqa Cenozoic structures[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1999, 6(4): 215-221(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.04.003 [30] 何登发, 周新源, 杨海军, 等. 库车坳陷的地质结构及其对大油气田的控制作用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(1): 19-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.003He D F, Zhou X Y, Yang H J, et al. Geological structure and its controls on giant oil and gas fields in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin: A clue from new shot seismic data[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2009, 33(1): 19-32(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.01.003 [31] Li Z, Song W J, Peng S T, et al. Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic relationships between the Kuqa subbasin and Tianshan, northwest China: Constraints from depositional records[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2004, 172(3/4): 223-249. [32] Chen S P, Tang L J, Jin Z J, et al. Thrust and fold tectonics and the role of evaporites in deformation in the western Kuqa foreland of Tarim Basin, northweast China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(8): 1027-1042. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.01.008 [33] 贾承造. 塔里木盆地构造特征与油气聚集规律[J]. 新疆石油地质, 1999, 20(3): 177-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD903.000.htmJia C Z. Structural characteristics and oil and gas accumulation rules in Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 1999, 20(3): 177-183(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD903.000.htm [34] 曹婷. 库车坳陷东部碎屑岩层新生代断层传播褶皱过程中的裂缝发育模式[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018: 65-66.Cao T. Fracture patterns during the Cenozoic fault-propagation folding process: Insights from the clastic rock of eastern Kuqa Depression[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018: 65-66(in Chinese with English abstract). [35] Mitra S. Falit-propagation folds: Geometry, kinematic evolution, and hydrocarbon traps[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(6): 621-645. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/249895964_Fault_Propagation_Folds_Geometry_Kinematic_Evolution_and_Hydrocarbon_Traps_ABSTRACT [36] 张凤奇, 王震亮, 赵雪娇, 等. 库车坳陷迪那2气田异常高压成因机制及其油气成藏的关系[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(5): 739-845. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2012.05.006Zhang F Q, Wang Z L, Zhao X J, et al. Genetic mechanism of overpressure and its relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation in Dina-2 Gasfield, Kuqa Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(5): 739-845(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2012.05.006 [37] 詹彦, 侯贵廷, 孙雄伟, 等. 库车坳陷东部侏罗系砂岩构造裂缝定量预测[J]. 高校地质学报, 2014, 20(2): 294-302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.02.014Zhan Y, Hou G T, Sun X W, et al. Quantitative prediction of tectonic fractures of Jurassic sandstones in the eastern Kuche Depression[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2014, 20(2): 294-302(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.02.014 [38] 郑淳芳, 侯贵廷, 詹彦, 等. 库车坳陷新生代构造应力场恢复[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(1): 130-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201601012.htmZheng C F, Hou G T, Zhan Y, et al. An analysis of Cenozoic tectonic stress fields in the Kuqa Depression[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(1): 130-139(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201601012.htm [39] 刘昭茜, 罗开平, 唐永, 等. 四川盆地元坝-通南巴地区关键构造期构造特征及陆相致密砂岩天然气成藏响应[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3): 756-772. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903006.htmLiu Z Q, Luo K P, Tang Y, et al. Critical tectonic periods and the response of gas accumulation in Non-Marine tight sandstone reservoir in Yuanba-Tongnanba area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(3): 756-772(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903006.htm [40] 刘树根, 罗志立, 赵锡奎, 等. 中国西部盆山系统的耦合关系及其动力学模式: 以龙门山造山带-川西前陆盆地系统为例[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 77(2): 177-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200302007.htmLiu S G, Luo Z L, Zhao X K, et al. Coupling relationships of sedimentary basin-orogenic belt systems and their dynamic models in West China: A case study of the Longmenshan orogenic belt -west Sichuan Foreland Basin system[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science and Technology Edition, 2003, 77(2): 177-186(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200302007.htm [41] 王春阳. 塔西南褶皱-冲断带变形控制因素物理模拟研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2014: 79-81.Wang C Y. The deformation controlling factors of fold-and-thrust belt in SW Tarim Basin: Physical analogue modeling study[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014: 79-81(in Chinese with English abstract). [42] 赵红格. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部构造特征及演化[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2003: 18-32.Zhao H G. Structural characteristics and the evolution in western Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern University, 2003: 18-32(in Chinese with English abstract). 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 曹自成,唐大卿,骆满嵩,姜忠正,洪才均,夏永涛,魏华. 塔里木盆地顺北地区中新生界断裂构造特征及演化. 地质科技通报. 2023(01): 226-238 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载: