Cenozoic tectonic subsidence characteristics of Albert Lake Depression in East African Rift System
-
摘要: 新生代形成的东非裂谷是威尔逊旋回萌芽阶段的典型陆内裂谷,长期以来备受国内外地质学家关注。Albert湖凹陷位于东非裂谷系的西支最北端,整体呈北西向带状展布的不对称(半)地堑。目前,该区已有较好的工业性油气发现,分析其沉降演化规律对进一步揭示该凹陷的构造沉降特征及其油气勘探潜力具有重要的意义。基于钻井资料,结合地震资料解释、沉降史、埋藏史与断层活动性分析,重新划分了构造单元,总结了构造沉降特征,探讨了沉降与断裂的关系、沉降中心迁移的规律及其对油气勘探的指示意义。研究表明:Albert湖凹陷东部的次级构造单元主要受到东部边界断裂的控制,F1、F2断层对东部陡断带、东部断阶带以及三个构造调节带的沉降变化及其形成起主要控制作用;南部次凹在早期沉降速率较大,有利于晚中新世形成巨厚的烃源岩,随着沉降中心向北迁移,北部次凹发育了上中新统和下上新统烃源岩;沉降中心周缘的构造带是油气运聚的有利指向区。研究成果为东非裂谷系Albert湖凹陷油气进一步勘探提供了新的依据。Abstract: The Cenozoic East African Rift is a typical intracontinental rift at the germination stage of the Wilson cycle, which has long attracted the attention of geologists at home and overseas. The Albert Lake Depression is located at the northern most end of the west branch of the East African Rift System.It is an asymmetric (half) graben with a NW orientation. At present, good industrial oil and gas have been discovered in this area.The analysis of the subsidence evolution is of great significance to further reveal the tectonic subsidence characteristics and petroleum exploration potential of this depression.Based on drilling data, combined with seismic interpretation, and analysis of subsidence history, burial history and fault activities, this paper reclassifies tectonic units, and summarizes the characteristics of tectonic subsidence. The relationship between subsidence and fault activities, the law of subsidence center migration and its indicating significance for petroleum exploration were discussed in this study. The results show that the secondary structural units in the east of the Albert Lake Depression are mainly controlled by the eastern boundary faults, and the F1 and F2 faults play a major role in controlling the subsidence and formation of the eastern steep fault belt, the eastern fault terrace zone and the three structural adjustment belts. The subsidence rate of the southern sub sag was large in the early stage, which was conducive to the formation of extremely thick source rocks in Late Miocene.With the northward migration of the subsidence center, the Upper Miocene and Lower Pliocene source rocks were developed in the northern sub sag.The structural belt around the subsidence center is the favorable direction area for hydrocarbon migration and accumulation. This study provides a new basis for further petroleum in Albert Lake Depression of the East African Rift System.
-
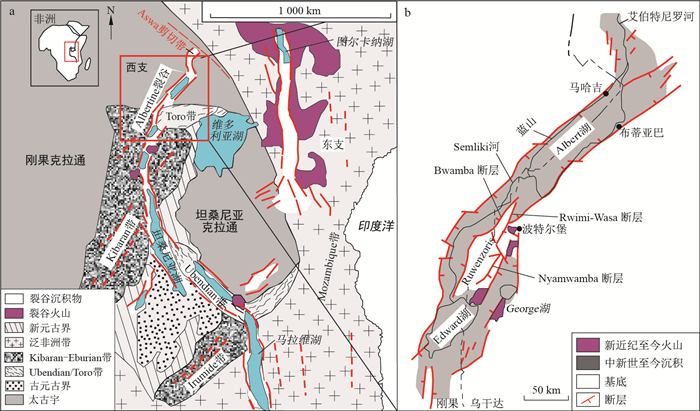
图 1 东非裂谷简要地质图(a)和Albertine裂谷简要地质图(b)(据文献[20]修改)
Figure 1. Simplified structural map of the East African Rift (a), regional geological map of the Albertine Rift (b)
图 4 Albert湖凹陷结构剖面图(剖面图位置见图 3)
Figure 4. Structural profile of the Albert Lake Depression
图 8 F1、F2断裂活动速率图(断层位置见图 3)
Figure 8. Activity rate of F1 and F2 faults
图 9 Albert湖凹陷埋藏史及生烃史图(Well 32、Well 35位置见图 3)
Figure 9. Burial history and hydrocarbon generation history of Albert Lake Depression
-
[1] Ebinger C J. Tectonic development of the western branch of the East African Rift System[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101: 885-903. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0885:TDOTWB>2.3.CO;2 [2] Pouclet A, Bellon H, Bram K. The Cenozoic volcanism in the Kivu Rift: Assessment of the tectonic setting, geochemistry, and geochronology of the volcanic activity in the South-Kivu and Virunga regions[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2016, 121: 219-246. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.05.026 [3] Abeinomugisha D, Kasande R. Tectonic control on hydrocarbon accumulation in the intracontinental albertine graben of the East African Rift System[J]. AAPG Memoir, 2012, 100(9): 14-21. http://www.oilfield.searchanddiscovery.com/documents/2009/10183abeinomugisha/images/abeinomugisha.pdf [4] 张兴, 童晓光. 艾伯特裂谷盆地含油气远景评价: 极低勘探程度盆地评价实例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2001, 28(2): 102-106. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2001.02.030Zhang X, Tong X G. Hydrocarbon prospective evalution of Albert Rift Basin: An example of evalution about least explored basins[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2001, 28(2): 102-106(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2001.02.030 [5] 孙和风, 姜雪, 钟锴. 阿尔伯特盆地沉降-热史演化特征分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(5): 63-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201805008.htmSun H F, Jiang X, Zhong K, et al. Analysis on subsidence-thermal history evolution characteristics of Albert Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(5): 63-70(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201805008.htm [6] Chorowicz J. The East African Rift System[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2005, 43: 379-410. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.07.019 [7] 张可宝, 史卜庆, 徐志强, 等. 东非地区沉积盆地油气潜力浅析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2007, 18(6): 869-874. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2007.06.018Zhang K B, Shi B Q, Xu Z Q, et al. A study on petroleum geology and hydrocarbon potential in Eastern Africa[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2007, 18(6): 869-874(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2007.06.018 [8] 温志新, 童晓光, 张光亚, 等. 东非裂谷系盆地群石油地质特征及勘探潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2012, 17(4): 60-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2012.04.010Wen Z X, Tong X G, Zhang G Y, et al. Petroleum geology features and exploration potential of basin group in East African Rift System[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2012, 17(4): 60-65(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2012.04.010 [9] 于水, 韩文明, 赵伟, 等. 裂谷盆地陡断带三角洲沉积特征与成因模式: 以东非裂谷Albertine地堑为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2013, 25(6): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201306005.htmYu S, Han W M, Zhao W, et al. Delta sedimentation and origin model within steep faulted zones in rift basins: A case of Albertine graben in East African Rift Valley[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2013, 25(6): 31-35(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201306005.htm [10] 蔡文杰, 韩文明, 许志刚, 等. 东非Lake Albert盆地构造调节带特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(4): 119-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201504017.htmCai W J, Han W M, Xu Z G, et al. Geological character of accommodation zone and its importance in controlling accumulation of oil and gas in Lake Albert Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(4): 119-123(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201504017.htm [11] 韩文明, 赵伟. 试论火山活动对东非裂谷系油气成藏的作用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(4): 20-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201804003.htmHan W M, Zhao W. Discussion on effect of volcanic activities on hydrocarbon accumulation in East African Rift System[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(4): 20-26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201804003.htm [12] 李智, 张志业, 何登发, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷与南阳凹陷油气地质特征类比及勘探启示[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 74-84. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9976.shtmlLi Z, Zhang Z Y, He D F, et al. Comparison in petroleum geology between Biyang Depression and Nanyang Depression in Nanxiang Basin and its exploration significance[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 74-84(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9976.shtml [13] 顾家伟. 上新世以来苏北盆地与长江三角洲构造沉降史分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(1): 95-99, 106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201501015.htmGu J W. Tectonic subsidence analysis of Subei Basin and Yangtze Delta from the Pliocene[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(1): 95-99, 106(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201501015.htm [14] 李向东, 陈刚, 李玖勇, 等. 沉降史分析方法及研究现状[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2010, 32(5): 199-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201005048.htmLi X D, Chen G, Li J Y, et al. Analysis methods and research status of subsidence history[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2010, 32(5): 199-203(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201005048.htm [15] Zhao R, Chen S, Wang H, et al. Intense faulting and downwarping of Nanpu Sag in the Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China: Response to the Cenozoic Stagnant Pacific Slab[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 109: 819-838. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.06.034 [16] Ma M, Liu C Y, Qi J F, et al. Cenozoic subsidence history of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 750-770. doi: 10.1002/gj.3439 [17] 陈懋弘, 梁金城, 张桂林, 等. 桂北-桂东加里东期盆地构造沉降史分析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2006, 30(1): 9-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2006.01.002Chen M H, Liang J C, Zhang G L, et al. Tectonic subsidence history of the Caledonian Basin in northeast Guangxi[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2006, 30(1): 9-17(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2006.01.002 [18] 何玉光, 卢华复, 杨树锋, 等. 库车中新生代盆地沉降特征[J]. 浙江大学学报: 理学版, 2004, 31(1): 110-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZDX200401024.htmHe Y G, Lu H F, Yang S F, et al. Subsiding features of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic Kuqa Basin, northwestern China[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Natural Science, 2004, 31(1): 110-113(in Chinese with English abstract). . https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZDX200401024.htm [19] Roberts E M, Stevens N J, O'Connor P M, et al. Initiation of the western branch of the East African Rift coeval with the eastern branch[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5: 289-294. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1432 [20] Bauer F U, Glasmacher U A, Ring U, et al. Long-term cooling history of the Albertine Rift: New evidence from the western rift shoulder, D.R. Congo[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2016, 105(6): 1707-1728. doi: 10.1007/s00531-015-1146-6 [21] Morley C K. Stress re-orientation along zones of weak fabrics in rifts: An explanation for pure extension in "oblique" rift segments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 297: 667-673. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.07.022 [22] Purcell P G. Re-imagining and re-imaging the development of the East African Rift[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2018, 24: 21-40. doi: 10.1144/petgeo2017-036 [23] Bauer F U, Karl M, Glasmacher U A, et al. The Rwenzori Mountains of western Uganda-Aspects on the evolution of their remarkable morphology within the Albertine Rift[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2012, 73: 44-56. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035399356610_0e78.html [24] Delvaux D, Barth A. African stress pattern from formal inversion of focal mechanism data[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 482: 105-128. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.05.009 [25] Stamps D S, Flesch L M, Calais E, et al. Current kinematics and dynamics of Africa and the East African Rift System[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2014, 119(6): 5161-5186. doi: 10.1002/2013JB010717 [26] Sachau T, Koehn D, Stamps D, et al. Fault kinematics and stress fields in the Rwenzori Mountains, Uganda[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2016, 105: 1729-1740. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000037616492410_4048.html [27] Koehn D, Link K, Sachau T, et al. The Rwenzori Mountains, a Palaeoproterozoic crustal shear belt crossing the Albertine Rift System[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2016, 105: 1693-1705. doi: 10.1007%2Fs00531-015-1167-1.pdf [28] Simon B, Guillocheau F, Robin C, et al. Deformation and sedimentary evolution of the Lake Albert Rift (Uganda, East African Rift System)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 86: 17-37. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.05.006 [29] 赵伟, 韩文明, 胡滨, 等. 东非裂谷Albertine地堑石油地质条件和成藏规律[J]. 四川地质学报, 2016, 36(2): 275-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2016.02.023Zhao W, Han W M, Hu B, et al. Petroleum geology and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Albertine Graben, East Africa Rift[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2016, 36(2): 275-279(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2016.02.023 [30] 于彪, 刘建良, 杨贵丽, 等. 渤海海域东部不同富油凹陷烃源岩生烃特征差异及意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 104-114, 130. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10165.shtmlYu B, Liu J L, Yang G L, et al. Hydrocarbon generation characteristics and signification of source rock in different oil-rich depressions in the eastern part of the Bohai Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 104-114, 130. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10165.shtml [31] 王敏芳, 焦养泉, 任建业, 等. 准噶尔盆地侏罗纪沉降特征及其与构造演化的关系[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(1): 27-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200701004.htmWang M F, Jiao Y Q, Ren J Y, et al. Characteristics of Jurassic subsidence and its relation with tectonic evolution in Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(1): 27-32(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200701004.htm [32] 崔哿, 金爱民, 邬长武, 等. 东非裂谷阿尔伯特盆地石油地质特征及成藏模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(4): 514-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201804009.htmCui G, Jin A M, Wu C W, et al. Petroleum geology and hydrocarbon accumulation pattern in the Lake Albert Basin of East African Rift System[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2018, 40(4): 514-518(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201804009.htm [33] 张燕, 田作基, 温志新, 等. 东非裂谷系东支油气成藏主控因素及勘探潜力[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(1): 79-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201701012.htmZhang Y, Tian Z J, Wen Z X, et al. Controlling factors for petroleum accumulation and exploration potential of the eastern branch of East African Rift System[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2017, 39(1): 79-85(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201701012.htm -





 下载:
下载: