Characteristics of reservoir-source rock and hydrocarbon accumulation model of tight sandstone gas reservoirs in the third Member of Xujiahe Formation in western Sichuan Depression
-
摘要: 川西坳陷须家河组致密气藏已成为拓展油气勘探、发现新储量的重要领域,致密气藏发育特征及其成藏机理成为目前亟需解决的关键科学问题之一。运用地球化学、地球物理和沉积学等分析方法,对须三段源储特征及成藏模式进行了系统分析,对高效烃源岩和优质储层进行了判别和预测,厘定了致密气藏成藏期次和成藏模式。得出以下结论:①须三段发育成熟-高成熟湖相烃源岩,以Ⅲ型干酪根为主,局部偶见Ⅱ2型干酪根。发育于须三下亚段最大湖泛面附近,泥页岩体积分数在65%以上或者单层厚度较大、且1.50% ≤ w(TOC)≤ 10%时,属于高效烃源岩。②基于砂岩粒度中值识别出4期(S1,S2,S3和S4)优质储层,都属于低孔低渗-特低孔特低渗致密储层,中砂-细砂,粒度分布范围为0.5~0.062 5 mm,厚度一般5~10 m。主要发育于三角洲前缘和前三角洲。③烃源岩生排烃时间持续较长,中侏罗世开始生烃,一直持续至晚白垩世;从晚侏罗世开始排烃,早白垩世达到高峰。优质储层经历早期天然气持续充注和晚期凝析气充注,天然气充注时间要早于凝析气充注时间。形成了"断层垂向输导,先聚集后致密,晚期改造调整"的致密气藏成藏模式。Abstract: The tight gas reservoirs of the Xujiahe Formation in western Sichuan Depression have become an important field for expanding oil and gas exploration and discovering new reserves.The development characteristics of tight gas reservoirs and their accumulation mechanism have become one of the key scientific problems that need to be solved urgently. Applied geochemistry, geophysics and sedimentology analysis methods, systematic analysis of the source and reservoir characteristics and accumulation model of the Xu-3 Member was conducted, and the high-efficiency source rocks and high-quality reservoirs were identified and predicted. The accumulation period and accumulation mode were determined.The following conclusions were drawn: ①The lacustrine source rocks in the mature and highly mature stage of the Xu-3 Member in western Sichuan Depression are dominated by type Ⅲ kerogen, and occasionally type Ⅱ2 kerogen.It is developed as a high-efficiency source rock when it is developed near the largest lake flooding surface in the lower sub-segment of Xu-3, with shale content above 65% or a single layer with a large thickness and requiring 1.50% ≤ TOC ≤ 10%.②According to the median value of sandstone grain size, the 4th stage (S1, S2, S3 and S4) high-quality reservoirs were identified, which belonged to low-porosity and ultra-low-permeability-ultra-low-porosity and ultra-low-permeability tight reservoirs. Reservoir space is dominated by secondary pores, micropores and microfractures.Most developed in the front edge of the delta and a small amount developed in the front delta.The particle size distribution range is 0.5-0.062 5 mm, the thickness is generally 5-10 m.③The hydrocarbon generation and expulsion time of the Xu-3 Member source rock in western Sichuan Depression lasted longer, and the Middle Jurassic began to generate hydrocarbons until the end of the Early Cretaceous; the Late Jurassic began to expel hydrocarbons and reached a peak at the end of the Early Cretaceous.High-quality reservoirs experience early natural gas continuous charging and late condensate gas charging.The natural gas charging time is earlier than the condensate gas charging time.The accumulation mode of tight gas reservoirs in the Xu-3 Member is "vertical fault transmission, first gathering and then dense, and later transformation and adjustment".
-
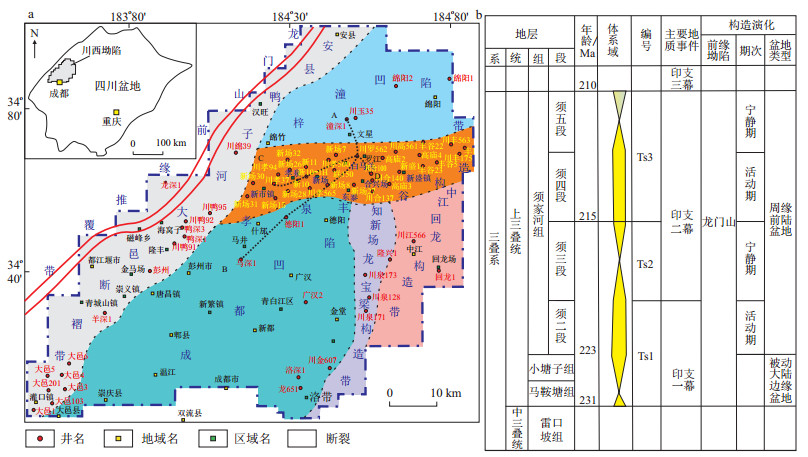
图 1 川西坳陷构造单元划分图(a)[30]和综合柱状图(b)
Figure 1. Structural unit division (a) and comprehensive histogram (b) of western Sichuan Depression
图 2 须三段上、中、下亚段烃源岩样品生烃潜量(a~c)与w(TOC)关系图和烃源岩频率(d~f)与w(TOC)关系图
Figure 2. Relationship between hydrocarbon generation potential and TOC of source rock samples(a-c), relationship between percentage of TOC and TOC of source rock samples (d-f) in the upper, middle and lower sub-segment of the third member of Xujiahe Formation
图 6 科1井-新深1井-川罗562井-川合100井连进对比与优质储层识别剖面(剖面位置见图 1)和过井对应地震剖面
(岩性图例同图 4)
Figure 6. Continuous progression comparison and high-quality reservoir identification section of Well Chuankel-Well Xinshen 1-Well Chuanluo 562-Well Chuanhe 100 (section position is shown in Fig. 1) and seismic section of crossing Wells
图 9 须三段典型样品岩石薄片、阴极发光、铸体薄片和扫面电镜等分析
a.新856井,3 991.8 m,灰白色含灰细砂质中粒岩屑砂岩,薄片鉴定,单偏光,放大倍数5.0×10;b.新856井, 3 991.8 m, 灰白色含灰细砂质中粒岩屑砂岩,薄片鉴定,正交偏光,放大倍数5.0×10;c.绵阳1井,3 998.22 m,灰色泥晶粒屑有孔虫灰岩,薄片鉴定,正交偏光,放大倍数10×10;d.大邑6井,5 560.5 m,中砂岩,铸体薄片;e.川鸭95井,3 671.3 m,含盆屑细砂质极细砂岩,阴极发光鉴定,-1CL,×5;f.川鸭95井,3 671.3 m,含盆屑细砂质极细砂岩,阴极发光鉴定,-1P,×5;g.川孝568井,3 999.5 m,砂岩,扫描电子显微镜(氩离子),×10 000;h.川鸭95井,3 671.3 m,砂岩,扫描电子显微镜(氩离子),×12 000;i.新11井,4 000.12 m,细砂岩,扫描电子显微镜,×2 000;j.川鸭95井,3 671.3 m,中砂岩,扫描电子显微镜,×3 000
Figure 9. Analysis of identification of rock flakes, cathodic luminescence, casting flakes and scanning electron typical samples from the third Member of Xujiahe Formation
图 10 须三段典型样品包裹体识别与均一温度分布图(a)和川西坳陷联150井热演化、温度与埋藏史模拟图(b)
Q.第四系;K.白垩系;J3p.蓬莱镇组;J3s.遂宁组;J2x.沙溪庙组下段;T3x5.须五段;T3x4.须四段;T3x3.须三段;T3x2.须二段
Figure 10. Identification and uniform temperature distribution of typical sample inclusions in the third Member of Xujiahe Formation (a) and simulation diagram of thermal evolution, temperature and burial history of Well Lian 150 in western Sichuan Depression(b)
图 11 须三段致密气藏成藏模式图
(岩性图例同图 4)
Figure 11. Accumulation model of tight gas reservoirs in the third Member of Xujiahe Formation
表 1 川西坳陷各构造单元有机质丰度统计
Table 1. Statistics of organic matter abundance of each structural unit in western Sichuan Depression
评价指标 孝泉丰谷构造带 知新场龙宝梁构造带 成都凹陷 安县鸭子河大邑构造带 梓潼凹陷 w(TOC)/% $\frac{0.39 \sim 7.3406}{1.90(220)}$ $\frac{0.76 \sim 9.19}{3.07(30)}$ $\frac{0.712 \sim 8.13}{2.25(100)}$ $\frac{0.53 \sim 8.2067}{2.70(126)}$ $\frac{0.939 \sim 9.9}{3.19(70)}$ (S1+S2)/(mg·g-1) $\frac{0.01 \sim 28.62}{0.92(164)}$ $\frac{0.51 \sim 11.43}{5.97(2)}$ $\frac{0.1 \sim 21.48}{1.693(52)}$ $\frac{0.06 \sim 4.0318}{1.00(115)}$ $\frac{0.35 \sim 12.76}{3.105(6)}$ 氯仿沥青“A”/% $\frac{0.009 \sim 0.164}{0.052(80)}$ $\frac{0.0158 \sim 0.057}{0.0443(5)}$ $\frac{0.0044 \sim 0.1256}{0.0434(36)}$ $\frac{0.0035 \sim 0.615}{0.061(98)}$ 注:$\frac{{最小值 - 最大值}}{{平均值(样品数)}}$ -
[1] Emre A R, Burak K. Selection of candidate wells for refracturing in tight gas sand reservoirs using fuzzy inference[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2): 413-420. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(20)60058-1 [2] Li C L, Yuan C, Li X, et al. Anisotropy interpretation and the coherence research between resistivity and acoustic anisotropy in tight sands[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2): 463-470. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(20)60063-5 [3] Xu F H, Xu G S, Liu Y, et al. Factors controlling the development of tight sandstone reservoirs in the Huagang Formation of the central inverted structural belt in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(1): 101-113. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(20)60009-X [4] Li X, Li C L, Li B, et al. Response laws of rock electrical property and saturation evaluation method of tight sandstone[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(1): 214-224. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(20)60020-9 [5] Fu J H, Wei X S, Luo S S, et al. Discovery and geological knowledge of the large deep coal-formed Qingyang Gas Field, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(6): 1111-1126. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(19)60267-3 [6] Zhu H H, Zhang T S, Zhong D K, et al. Binary pore structure characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(6): 1297-1306. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(19)60283-1 [7] Feng J, Zhang B W, Feng Z H, et al. Crude oil mobility and its controlling factors in tight sand reservoirs in northern Songliao Basin, East China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(2): 324-334. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(19)60012-1 [8] Xia L, Liu Z, Li W L, et al. Ternary analytic porosity-reduction model of sandstone compaction trend and its significance in petroleum geology: A case study of tight sandstones in Permian Lower Shihezi Formation of Shilijiahan area, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(2): 290-301. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30032-6 [9] Liu H L, Yang Y Y, Wang F Q, et al. Micro pore and throat characteristics and origin of tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Triassic Chang 6 and Chang 8 members in Longdong area, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(2): 239-250. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30027-2 [10] Zhang F D, Li J, Wei G Q, et al. Formation mechanism of tight sandstone gas in areas of low hydrocarbon generation intensity: A case study of the Upper Paleozoic in north Tianhuan Depression in Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(1): 79-87. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30007-7 [11] 王珂, 杨海军, 张惠良, 等. 超深层致密砂岩储层构造裂缝特征与有效性: 以塔里木盆地库车坳陷克深8气藏为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(4): 719-729. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201804010.htmWang K, Yang H J, Zhang H L, et al. Characteristics and effectiveness of structural fractures in ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoir: A case study of Keshen-8 gas pool in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Geology of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2018, 39(4): 719-729(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201804010.htm [12] 康毅力, 张杜杰, 游利军, 等. 塔里木盆地超深致密砂岩气藏储层流体敏感性评价[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(4): 738-748. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201804012.htmKang Y L, Zhang D J, You L J, et al. Fluid sensitivity evaluation of ultra-deep tight sandstone gas reservoirs, Tarim Basin[J]. Geology of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2018, 39(4): 738-748(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201804012.htm [13] 李剑, 姜晓华, 王秀芹, 等. 裂谷盆地致密砂岩气成藏机制与富集规律: 以松辽盆地与渤海湾盆地为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(6): 1005-1018. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201706003.htmLi J, Jiang X H, Wang X Q, et al. Mechanisms for gas accumulation and enrichment in tight sandstone reservoir in rift basins: Cases from the Songliao Basin and the Bohai Bay[J]. Geology of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2017, 38(5): 1005-1018(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201706003.htm [14] 王国亭, 贾爱林, 闫海军, 等. 苏里格致密砂岩气田潜力储层特征及可动用性评价[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(5): 896-904. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201705008.htmWang G T, Jia A L, Yan H J, et al. Characteristics and recoverability evaluation on the potential reservoir in Sulige tight sandstone gas field[J]. Geology of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2017, 38(5): 896-904(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201705008.htm [15] 周翔, 何生, 陈召佑, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地代家坪地区延长组8段低孔渗砂岩成岩作用及成岩相[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(2): 155-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201602003.htmZhou X, He S, Chen Z Y, et al. Diagenesis and diagenetic facies of low porosity and permeability sandstone in Member 8 of the Yanchang Formation in Daijiaping area, Ordos Basin[J]. Geology of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2016, 37(2): 155-164(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201602003.htm [16] 周林, 陈波, 凡睿, 等. 川北地区须四段致密砂岩储层特征及成岩演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(3): 543-550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201703014.htmZhou L, Chen B, Fan R, et al. Characteristics and diagenesis of tight sandstone reservoirs in the 4th Member of Xujiahe Formation, northern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2017, 38(3): 543-550(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201703014.htm [17] 吴小奇, 罗开平, 王萍, 等. 川西坳陷新场气田须家河组五段流体赋存状态[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(6): 1068-1078. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201706009.htmWu X Q, Luo K P, Wang P, et al. Fluid state in the 5th Member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Xinchang Gas Field, western Sichuan Depression in Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2017, 38(6): 1068-1078(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201706009.htm [18] 张有瑜, 陶士振, 刘可禹, 等. 四川盆地须家河组致密砂岩气自生伊利石年龄分布与成藏时代[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(11): 1367-1379. doi: 10.7623/syxb201511006Zhang Y Y, Tao S Z, Liu K Y, et al. Authigenic illite age and hydrocarbon accumulation time in Xujiahe Formation sandstone reservoirs, Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Petroltum, 2015, 36(11): 1367-1379(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7623/syxb201511006 [19] 黄小娟, 李治平, 周光亮, 等. 裂缝性致密砂岩储层裂缝孔隙度建模: 以四川盆地平落坝构造须家河组二段储层为例[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(5): 570-577. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201705010.htmHuang X J, Li Z P, Zhou G L, et al. Fracture porosity modeling of fractured tight sandstone reservoir: A case study of the reservoir in Member 2 of Xujiahe Formatoin, Pingluoba structure, Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Petroltum, 2017, 38(5): 570-577(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201705010.htm [20] 谢升洪, 李伟, 冷福, 等. 致密砂岩储层可动流体赋存规律及制约因素研究: 以鄂尔多斯盆地华庆油田长6段储层为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 105-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905011.htmXie S H, Li W, Leng F, et al. Distribution and controlling factors of movable fluid in tight sandstone reservoir: Taking Chang 6 Formation of Huaqing Oilfield in Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 105-114(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905011.htm [21] 周园园, 杨海风, 刘庆顺, 等. 黄河口凹陷BZ27构造沙河街组砂岩储层致密化与油气充注关系[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1): 168-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901018.htmZhou Y Y, Yang H F, Liu Q S, et al. Relationship between sandstone reservoir densification and hydrocarbon Charging in the Shahejie Formation of the BZ27 Structure in Huanghekou Depression[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(1): 168-175(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901018.htm [22] 杨克明, 朱宏权, 叶军, 等. 川西致密砂岩气藏地质特征[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.Yang K M, Zhu H Q, Ye J, et al. The geological characteristics of tight sandstone gas reservoirs in West Sichuan Basin[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012(in Chinese). [23] 杨克明, 庞雄奇. 致密砂岩气藏形成机制与预测方法: 以川西坳陷为例[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.Yang K M, Pang X Q. The formation mechanism and prediction of tight sandstone gas reservoirs: A case study from western Sichuan Depression[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012(in Chinese). [24] 谢刚平, 朱宏权, 叶素娟, 等. 四川盆地叠覆型致密砂岩气区地质特征与评价方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.Xie G P, Zhu H Q, Ye X J, et al. The geological characteristics and evaluation methods of tight sandstone gas reservoirs in West Sichuan Basin[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018(in Chinese). [25] 张世华, 田军, 叶素娟, 等. 断层输导型天然气成藏模式的动态成藏过程: 以川西坳陷新场构造带上三叠统须二段气藏为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(7): 49-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201907010.htmZhang S H, Tian J, Ye S J, et al. Dynamic accu-mulation process of fault-translocation natural gas accumulation model: A case study on the gas reservoir of the second Member of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Xinchang structural zone of the western Sichuan Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(7): 49-56(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201907010.htm [26] 杨克明, 叶军, 吕正祥. 川西坳陷上三叠统须家河组天然气分布及成藏特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(5): 501-505. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2004.05.005Yang K M, Ye J, Lü Z X. Characteristics of gas distribution and reservoiring in Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in western Sichuan Depression[J]. Geology of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2004, 25(5): 501-505(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2004.05.005 [27] 陈恭洋, 晋静, 罗迎春, 等. 沉积相控制下致密砂岩气藏分布特征: 以四川盆地川西坳陷中段蓬莱镇组为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(3): 467-477. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201703006.htmChen G Y, Jin J, Luo Y C, et al. Characteristics of tight sandstone gas reservoir distribution under control of sedimentary facies: A case study from the Penglaizhen Formation in the central western Sichuan Depression[J]. Geology of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2017, 38(3): 467-477(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201703006.htm [28] 叶素娟, 李嵘, 杨克明, 等. 川西坳陷叠覆型致密砂岩气区储层特征及定量预测评价[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(12): 1484-1494. doi: 10.7623/syxb201512003Ye S J, Li R, Yang K M, et al. Characteristics and quantitative prediction of tight sand gas reservoirs in superimposed tight sandstone gas-bearing area, Western Sichuan depression[J]. Journal of Petroleum, 2015, 36(12): 1484-1494(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7623/syxb201512003 [29] 赵文智, 卞从胜, 徐春春, 等. 四川盆地须家河组须一、三和五段天然气源内成藏潜力与有利区评价[J]. 石油物探与开发, 2011, 38(4): 385-393. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201104002.htmZhao W Z, Bian C S, Xu C C, et al. Assessment on gas accumulation potential and favorable plays within the Xu-1, 3 and 5 Members of Xujiahe Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(4): 385-393. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201104002.htm [30] 林小兵, 刘莉萍, 田景春, 等. 川西坳陷中部须家河组五段致密砂岩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(4): 224-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201402010.htmLin X B, Liu L P, Tian J C, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of tight sandstone reservoirs in the 5th member of Xujiahe Formation in the central of Western Sichuan Depression[J]. Geology of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2014, 35(4): 224-230(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201402010.htm [31] 何生, 叶加仁, 徐思煌, 等. 石油及天然气地质学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2010.He S, Ye J R, Xu S H, et al. Petroleum and gas geology[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2010(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: