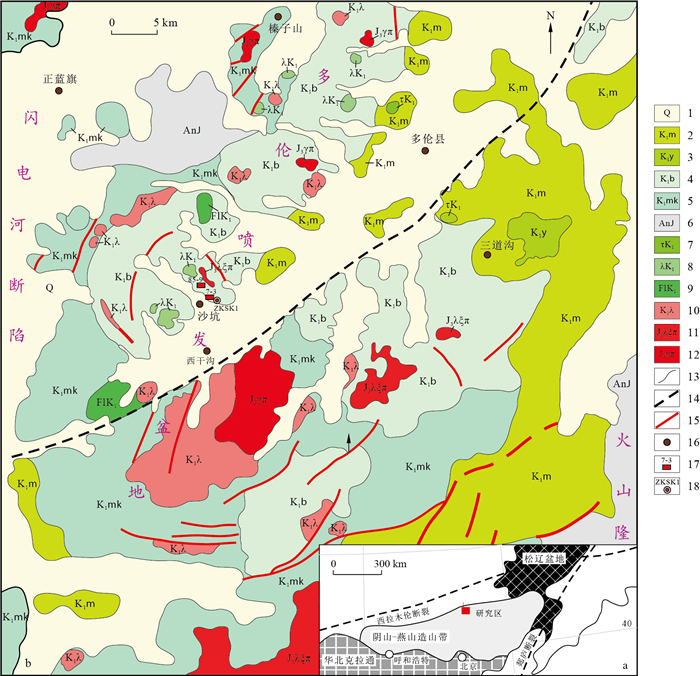
New discovery and prospecting prospect of sandstone type uranium deposits in Duolun Intermountain Basin, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要: 核工业二〇八大队在内蒙古东南部中生代火山岩区多伦山间盆地首次发现了砂岩型工业铀矿化。为了揭示其铀矿化类型、铀成矿条件、成矿作用及找矿前景,在盆地内开展了野外地质、微观特征、岩石学、矿物学、地球化学及矿化规律等方面的研究,并讨论了新发现的砂岩型铀矿化特征及成矿条件。认为多伦盆地中生代强烈的火山活动与基底塌陷为含铀建造的形成提供了良好的构造环境,广泛分布的酸性火山岩提供了充足的铀源,目的层砂体疏松透水、厚度适中(约40 m),利于含氧含铀水的持续渗入,且具有完整的氧化还原分带性,利于铀成矿。根据已有勘查成果,结合盆地演化及区域山间盆地的广泛分布,认为多伦山间盆地具有较好的铀找矿前景,深部可能存在富厚矿体,下一步铀矿勘查应重视多伦古河道两侧的边滩沉积。Abstract: This paper reports the first discovery of sandstone type industrial uranium mineralization in the Duolun Intermountain Basin in the Mesozoic volcanic rock area of Southeast Inner Mongolia by No.208 Geological Party, CNNC.In order to understand the type of uranium mineralization, uranium metallogenic conditions, mineralization and prospecting prospects, the field geological phenomena, microscopic characteristics, petrology, mineralogy, geochemistry and mineralization patterns were studied in the basin.This paper discusses the characteristics and metallogenic conditions of the newly discovered sandstone type uranium mineralization.The strong Mesozoic volcanic activity and basement subsidence in Duolun Basin provided a good tectonic environment for the formation of uranium bearing formations.The widely distributed acidic volcanic rocks provide abundant uranium sources.The sand body of the target layer is loose and permeable, with moderate thickness (about 40 m), which is conducive to the continuous infiltration of oxygen-containing and uranium-containing water, and has complete oxidation-reduction zoning.All these are favorable for uranium mineralization.According to the existing exploration results, combined with the basin evolution and the wide distribution of regional Intermountain Basins, it is considered that the Duolun Intermountain Basin has a good prospecting prospect for uranium, and there may be rich and thick ore bodies in the deep.In the next step of uranium exploration, attention should be paid to the lacustrine deposits and beach deposits on both sides of the Duolun ancient river.
-
Table 1. Uranium and thorium contents of surface rocks in Duolun volcanic basin
盆地 结构 地层 主要岩性 样品/件 w(U)/10-6 w(Th)/10-6 Th/U 多伦火山盆地 基底 P1s2 凝灰岩、安山岩、砂岩 6 2.2 12.0 6.4 P1s1 岩屑晶屑凝灰岩 3 1.1 18.7 17.0 Ar3 片麻岩、变粒岩、片岩 4 1.2 15.0 12.5 盖层 K1m 粗安岩、安山岩 22 2.0 10.5 5.3 K1y 凝灰岩、凝灰质砂岩 11 4.8 20.6 4.3 K1b 岩屑凝灰岩、熔结凝灰岩 40 4.3 26.0 6.0 K1mk 钾质流纹岩、粗面岩 77 3.7 21.5 5.8 注: P1s2/P1s1.下二叠统三面井组二段/一段;Ar3.新太古界;K1m.下白垩统梅勒图组;K1y.下白垩统义县组;K1b.下白垩统白音高老组;K1mk.下白垩统满克头鄂博组 表 2 沙坑地段钻孔中目的层含砾粗砂岩铀镭钍钾分析结果
Table 2. Analysis results of U, Ra, Th and K in target layer sandstone of borehole in Shakeng area
序号 样品编号 w(U)/10-6 w(Ra)/10-11 w(Th)/10-6 w(K)/% Th/U 样品编号 w(U)/10-6 w(Ra)/10-11 w(Th)/10-6 w(K)/% Th/U 1 ZK-1 109 2.808 19.7 1.54 0.18 ZK-19 90 3.870 23.9 2.47 0.27 2 ZK-2 146 4.412 21.6 1.74 0.15 ZK-20 229 6.194 23.8 2.44 0.10 3 ZK-3 246 6.378 16.9 0.99 0.07 ZK-21 376 6.444 21.6 2.29 0.06 4 ZK-4 224 5.924 12.7 0.63 0.06 ZK-22 92 3.094 20.3 2.34 0.22 5 ZK-5 270 7.059 14.3 0.87 0.05 ZK-23 51 1.789 20.4 2.69 0.40 6 ZK-6 163 5.908 18.1 1.27 0.11 ZK-24 288 9.744 14.6 2.23 0.05 7 ZK-7 246 7.836 16.0 1.09 0.07 ZK-25 138 5.899 29.2 2.53 0.21 8 ZK-8 179 5.853 13.6 0.63 0.08 ZK-26 82 2.571 12.5 0.85 0.15 9 ZK-9 178 5.321 13.1 0.82 0.07 ZK-27 101 3.100 18.0 1.66 0.18 10 ZK-10 140 3.746 19.4 1.62 0.14 ZK-28 116 3.744 16.1 1.10 0.14 11 ZK-11 125 5.301 20.3 1.99 0.16 ZK-29 63 1.819 26.3 2.00 0.42 12 ZK-12 197 5.308 12.1 0.99 0.06 ZK-30 103 3.659 13.0 0.97 0.13 13 ZK-13 101 4.431 14.0 1.22 0.14 ZK-31 70 2.381 17.0 1.25 0.24 14 ZK-14 126 3.550 21.9 1.97 0.17 ZK-32 90 3.205 19.9 1.25 0.22 15 ZK-15 88 2.988 23.2 2.00 0.26 ZK-33 98 3.039 14.2 1.18 0.14 16 ZK-16 53 1.346 20.4 2.43 0.38 ZK-34 67 1.743 22.0 1.98 0.33 17 ZK-17 137 3.644 22.8 2.60 0.17 ZK-35 98 3.264 12.7 0.56 0.13 18 ZK-18 247 6.568 20.8 2.56 0.08 注: 数据由包头市分析测试中心使用高纯锗多道γ能谱仪(GMX50P4-83)运用高纯锗多道γ能谱法测定 表 3 沙坑地段钻孔中目的层砂岩主量元素分析结果
Table 3. Analysis results of major elements in target layer sandstone of borehole in Shakeng area
wB/% 样品编号 ZK-1 ZK-2 ZK-8 ZK-21 ZK-24 ZK-26 ZK-33 SiO2 43.51 50.13 32.76 71.46 71.88 36.16 41.11 FeO 0.69 0.67 0.66 1.09 0.77 0.27 0.99 TFe2O3 1.70 1.52 1.28 1.38 1.00 1.03 1.17 Al2O3 10.59 12.86 7.85 13.99 12.89 7.62 8.77 TiO2 0.20 0.20 0.11 0.19 0.22 0.13 0.15 MnO 0.06 0.05 0.08 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.05 CaO 19.69 13.20 28.23 2.10 2.71 26.92 22.21 MgO 0.88 0.95 0.69 0.51 0.46 0.67 0.68 P2O5 0.07 0.06 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.05 0.07 K2O 1.88 2.12 0.88 2.62 2.46 1.05 1.26 Na2O 0.64 0.69 0.25 0.92 0.99 0.41 0.43 烧失量 20.63 17.39 27.59 6.64 6.52 25.12 23.29 总计 99.85 99.18 99.78 99.88 99.23 99.16 99.17 注: 数据由包头市分析测试中心使用X荧光光谱分析仪(AxiosPW4400)运用X荧光光谱分析法测定 -
[1] 孙栋华, 李怀渊, 江民忠, 等. 华北地台北界划分新证据及其找矿意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 25-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902003.htmSun D H, Li H Y, Jiang M Z, et al. New evidence for the boundary of North China Platform' North Margin and its prospecting significance[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 25-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902003.htm [2] 夏毓亮, 林锦荣, 朱杰辰, 等. 沽源-多伦盆地火山岩类和花岗岩类同位素地质年代学及铀成矿条件研究[J]. 铀矿地质, 1998, 14(5): 274-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ199805002.htmXia Y L, Lin J R, Zhu J C, et al. Research on U-metallogenic conditions and isotopic geochronlolgy of volcanic rocks and granitoid in Guyuan-Duolun Basin[J]. Uranium Geology, 1998, 14(5): 274-281(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ199805002.htm [3] Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Capdevila R. Highly evolved juvenile granites with tetrad REE patterns: The Woduhe and Baerzhe granites from the Great Xing'an Mountains in NE China[J]. Lithos, 2001, 59(4): 171-198. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(01)00066-4 [4] 张长厚, 张勇, 李海龙, 等. 燕山西段及北京西山晚中生代逆冲构造格局及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(2): 165-183. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.02.015Zhang C H, Zhang Y, Li H L, et al. Late Mesozoic thrust tectonic framework of western Yanshan and western Beijing and its geological significance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(2): 165-183(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.02.015 [5] 赵国春, 邓晋福, 白志达, 等. 多伦地区晚侏罗世火山活动节律研究[J]. 地质论评, 1999, 45(增刊1): 508-516. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP1999S1070.htmZhao G C, Deng J F, Bai Z D, et al. A study on the rhythm of the Late Jurassic volcanic activities in Duolun region[J]. Geological Review, 1999, 45(S1): 508-516(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP1999S1070.htm [6] 白志达, 顾德林, 徐德斌, 等. 内蒙古多伦环形影像的成因探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2003, 30(3): 261-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200303005.htmBai Z D, Gu D L, Xu D B, et al. Origin of the Duolun ring image, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 2003, 30(3): 261-267(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200303005.htm [7] 吴仁贵, 于振清, 申科峰, 等. 沽源-红山子地区中生代火山作用与铀成矿关系[J]. 铀矿地质, 2011, 27(4): 200-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2011.04.002Wu R G, Yu Z Q, Shen K F, et al. The relational of Mesozoic volcanism to uranium mineralization in Guyuan-Hongshanzi area[J]. Uranium Geology, 2011, 27(4): 200-205(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2011.04.002 [8] 刘哲, 薛怀民, 曹光跃. 内蒙古正蓝旗地区中生代火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄与板内伸展环境成因讨论[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(1): 151-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201701012.htmLiu Z, Xue H M, Cao G Y. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, intraplate extensional environment and genesis of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Zhenglan Banner area, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(1): 151-176(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201701012.htm [9] 王春林, 孟明亮, 陶瑞. 内蒙古多伦中酸性侵入岩岩石地球化学特征及构造环境分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(3): 482-494. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201703008.htmWang C L, Meng M L, Tao R. Geochemical characteristics of intermediate-acid intrusive rocks and tectonic environment in Duolun, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2017, 53(3): 482-494(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201703008.htm [10] 薛伟, 宋卡迪, 刘鑫扬, 等. 内蒙古多伦县三道沟地区中生代火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学研究及其铀成矿意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 69-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906010.htmXue W, Song K D, Liu X Y, et al. Zircon U-Pb chronology of mesozoic volcanic rocks in Sandaogou area, Duolun County, Inner Mongolia and its ore-prospecting significance[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 69-80(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906010.htm [11] 蒋孝君, 彭云彪, 薛伟, 等. 内蒙古正蓝旗丹金地区赋矿火山岩年代学、地球化学特征及铀成矿时代[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(4): 893-907. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202004010.htmJiang X J, Peng Y B, Xue W, et al. Chronology, geochemical characteristics of the host rocks and uranium mineralization age in Danjin area, Zhenglan Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(4): 893-907(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202004010.htm [12] 李亚东, 江小均, 柳永清, 等. 内蒙古正蓝旗钱家营子黑云母二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42(1): 85-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202101009.htmLi Y D, Jiang X J, Liu Y Q, et al. Geochronology and Hf isotopic composition of the biotite monzogranite from the Qianjiayingzi area in Zhenglan Banner of Inner Mongolia and its geological implications[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021, 42(1): 85-97(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202101009.htm [13] 薛伟. 内蒙古镶黄旗-多伦地区铀矿资源调查评价成果报告[R]. 内蒙古包头: 核工业二〇八大队, 2014.Xue W. Investigation and evaluation of uranium resources in Xianghuangqi-Duolun area, Inner Mongolia[R]. Baotou Inner Mongolia: No. 208 Geological Party, CNNC, 2014(in Chinese). [14] 蒋孝君. 内蒙古集宁-多伦地区铀矿资源调查评价成果报告[R]. 内蒙古包头: 核工业二〇八大队, 2019.Jiang X J. Investigation and evaluation of uranium resources in Jining-Duolun area, Inner Mongolia[R]. Baotou Inner Mongolia: No. 208 Geological Party, CNNC, 2019(in Chinese). [15] 白志达. 内蒙古多伦县等5幅1∶5万区域地质调查报告[R]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2000.Bai Z D. 1∶50 000 regional geological survey report of 5 maps, Duolun County, Inner Mongolia[J]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2000(in Chinese). [16] 余达淦, 吴仁贵, 陈培荣, 等. 铀资源地质学[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社, 2005.Yu D G, Wu R G, Chen P R, et al. Uranium geology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University Press, 2005(in Chinese). [17] 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等. 中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景: 来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(2): 339-353.Xu W L, Wang F, Pei F P, et al. Mesozoic tectonic regimes and regional ore-forming background in NE China: Constraints from spatial and temporal variations of Mesozoic volcanic rock associations[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(2): 339-353(in Chinese with English abstract). [18] 吴学鲁. 内蒙古自治区多伦县西大仓煤矿区北段勘探报告[R]. 内蒙古锡林郭勒盟: 内蒙古自治区一一一地质队, 1980.Wu X L. Exploration report on the north section of Xidacang coal mine in Duolun County, Inner Mongolia[R]. Xilin Gol-League, Inner Mongolia: No. 111 Geological Party, Inner Mongolia, 1980(in Chinese). [19] 张宽谋. 对龙首山不同花岗岩体含铀性的探讨[J]. 华东地质学院学报, 1989, 12(2): 63-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ198902007.htmZhang K M. Discussion on uranium bearing properties of different granites in Longshoushan[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Geology, 1989, 12(2): 63-66(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ198902007.htm [20] Cardenas A A, Girty G H, Hanson A D, et al. Assessing differences in composition between low metamorphic grade mudstones and high-grade schists using logratio techniques[J]. Journal of Geology, 1996, 104(3): 279-293. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039025752510_9aad.html [21] 黄广楠, 黄广文, 王伟超, 等. 柴北缘冷湖地区砂岩型铀矿床地质特征及成矿条件分析[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(4): 1200-1211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202104018.htmHuang G L, Huang G W, Wang W C, et al. The geological characteristics and minerogenetic condition of the Lenghu sandstone-type uranium in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin and its implication for uranium mineralization[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(4): 1200-1211(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202104018.htm [22] Hu R Z, Bi X W, Zhou M F. Uranium metallogenesis in South China and its relationship to crustal extension during the cretaceous to tertiary[J]. Economic Geology, 2008, 103(3): 583-598. [23] 张成勇, 聂逢君, 刘庆成, 等. 二连盆地巴彦乌拉地区砂岩型铀矿目的层电测井曲线响应分析[J]. 铀矿地质, 2010, 26(2) : 101-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201002006.htmZhang C Y, Nie F J, Liu Q C, et al. Discussion on electrical logging response of target layer for sandstone-type uranium deposits of Bayanwula area, Erlian basin[J]. Uranium Geology, 2010, 26(2) : 101-107(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201002006.htm -





 下载:
下载: