Discovery and geological significance of gas-liquid spouting expulsion and effusion depositional structures at Xialei manganese deposit in Guangxi
-
摘要: 广西大新下雷泥盆纪锰矿床是我国首个超大型锰矿床。通过对矿床含锰岩系、矿石组合、矿石成分、矿石结构构造综合分析研究,在锰矿体中发现了可能为气液喷溢沉积成因的角砾状、脉状以及网脉状构造的锰矿石。同时在矿石中普遍见热液成因的含锰硅酸盐矿物和硫化物,如蔷薇辉石、锰铁叶蛇纹石、黄铁矿、黄铜矿、锰帘石等。通过对矿区钻孔原始编录资料综合分析,在控制该锰矿床形成分布的泥盆纪晚期的下雷-土湖Ⅳ级地堑盆地中,成功恢复识别出3条锰矿成矿期同沉积断层。发现角砾状锰矿石等在空间上集中成群分布,应是导致锰矿形成的古气液喷溢口的分布位置,空间分布受锰矿成矿期同沉积断层的控制。通过与贵州松桃南华纪"大塘坡式"气液喷溢沉积型锰矿床进行对比,发现二者气液喷溢沉积构造等特征较为相似,故认为广西大新下雷泥盆纪锰矿床的成因类型可能与南华纪"大塘坡式"锰矿相似,具有气液喷溢沉积型锰矿床的一些典型特征,这为"下雷式"锰矿成矿研究与找矿预测提供了新的思路。Abstract: The Daxin Xialei Devonian manganese deposit in Guangxi is the first super-massive manganese ore deposit ever discovered in China. Here we conducted detailed petrographic studies on manganese-bearing sequence, ore mineral assemblages and their textures and structures. Our work reveal that the brecciated, vein-bearing and stockwork manganese ore minerals may form correspondingly to the expulsion and effusion of the gas and liquid-rich fluid. In addition, prevailing manganese-bearing silicate and sulfide minerals (rhodonite, manganese-iron chlorophyllite, pyrite, chalcopyrite, manganite, etc.) of hydrothermal origin are observed among the ores. Further comprehensive examinations of the original borehole data of the mining area lead to two major outcomes.First, three syndepositional faults are successfully recovered and identified in Late Devonian Xialei-Tuhu Ⅳ-graben basins, which controls the formation and spatial distribution of the manganese ore deposit.Second, brecciated manganese ore minerals appear to be clustered in space, and the localities of which may correspond to the locations of the ancient gas-liquid expulsion and effusion centers that give rise to the formation of manganese ore. Notably, the spatial distribution of the fossilized gas-liquid centers is controlled by the syndepositional faults developed during the formation of manganese ore deposit. Given the observation that Xalei Devonian manganese ore deposit shares comparable expulsion and effusion depositional features to Nanhua Datangpo gas-liquid depositional manganese ore deposit at Songtao of Guizhou Province, it is therefore argued that both Xialei and Datangpo manganese ore developed by similar mechanisms. This study sheds light on a better understanding of the metallogenic mechanism(s) and will place better constraints on the future explorations of Xialei manganese ore deposit.
-
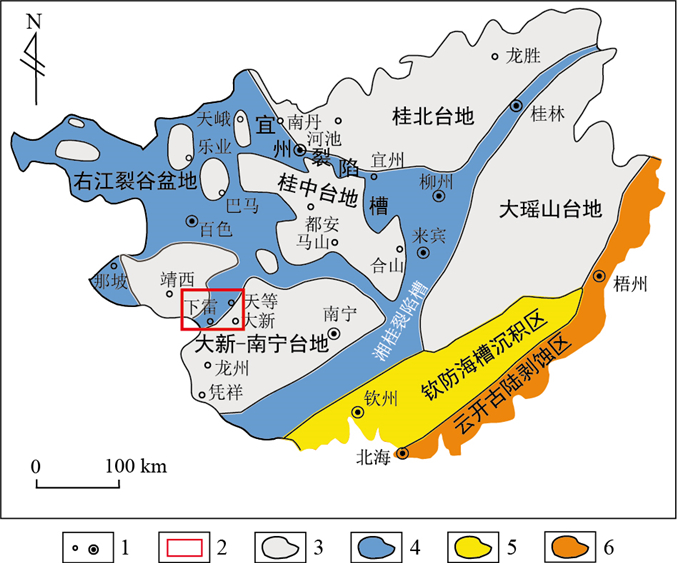
图 1 广西早石炭世沉积-构造古地理图(据文献[35])
1.地名;2.研究区;3.碳酸盐岩台地;4.深水盆地;5.海槽;6.古陆
Figure 1. Sedimentary and tectonic palaeogeography map of the Early Carboniferous in Guangxi
图 3 下雷锰矿床含锰岩系柱状剖面对比图
1.锰矿体;2.次级盆地中半局限台地相;3.斜坡相;4.盆地相;5.条带状锰矿石;6.豆状锰矿石;7.角砾状锰矿石;8.钻孔编号;9.地层厚度;10.锰矿体厚度及品位;11.上泥盆统五指山组第一段;12.上泥盆统五指山组第二段;13.上泥盆统五指山组第三段;14.泥质灰岩;15.泥质硅质岩;16.钙质硅质岩;17.含碳硅质岩;18.含泥质钙质硅质岩;19.硅质岩;20.碳质硅质岩;21.含碳灰岩;22.见矿钻孔;23.未见矿钻孔;24.地层剖面位置;25.盆地结构与沉积相界线;26.钻孔(剖面)间距离;27.次级盆地
Figure 3. Comparison of columnar sections of manganese-bearing rock series in Xialei-Longbang graben basin
图 5 下雷锰矿床矿区地质图及10号勘探线剖面图
1.倒转背斜;2.倒转向斜;3.背斜轴;4.向斜轴;5.倾伏方向;6.断层及编号;7.矿体露头线;8.勘探线及编号;9.中泥盆统东岗岭组;10.辉绿岩体;11.下石炭统;12.上泥盆统;13.上泥盆统五指山组;14.下石炭统大塘阶硅质灰岩;15.下石炭统岩观阶第二段泥质硅质岩;16.下石炭统岩观阶第一段含碳含生物碎屑硅质灰岩;17.上泥盆统五指山组第四段泥质硅质岩;18.上泥盆统五指山组第三段钙质硅质岩;19.上泥盆统五指山组第二段硅质岩;20.锰矿体;21.钻孔;22.钻孔编号;23.孔深;24.地层界线;25.断层
Figure 5. Geological map of Xialei manganese deposit and No.10 exploration line profile
表 1 晚泥盆纪右江盆地靖西-天等次级盆地结构划分
Table 1. The structure division of Jinxi-Tiandeng graben basin in Late Devonian
Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅲ级 Ⅳ级 备注 右江盆地
(深水盆地+浅水台地)靖西-天等次级盆地
(半局限台地)下雷-龙邦地堑盆地 下雷-土湖地堑盆地
依屯-含香地堑盆地
龙邦-地州地堑盆地
壬庄地堑盆地Ⅳ级地堑盆地沉积相均为盆地相 -
[1] 莫斯霖. 广西晚泥盆世沉积锰矿的矿质来源及成矿作用[J]. 地质与勘探, 1985, 21(11): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT198511000.htmMo S L. Mineral sources and mineralization of manganese deposits in the Late Devonian in Guangxi[J]. Geology and Exploration, 1985, 21(11): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT198511000.htm [2] 汪金榜. 下雷碳酸锰矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 1987, 23(8): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT198708000.htmWang J B. features and origin of the Xialei carbonate manganese ore deposit[J]. Geology and Exploration, 1987, 23(8): 1-5(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT198708000.htm [3] 曾友寅. 桂西南晚泥盆世锰矿床锰质豆鲕粒类型及其成因探讨[J]. 广西地质, 1989, 2(3): 63-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ198903008.htmZeng Y Y. Discussion on the genesis of the manganese pisolite and lite of the Late Devonian manganese deposits in southwestern Guangxi[J]. Geology of Guangxi, 1989, 2(3): 63-70(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ198903008.htm [4] 祝寿泉. 广西下雷碳酸锰矿风暴成因[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 1991, 6(4): 63-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK199104006.htmZhou S Q. On the origin of storm of the Xialei carbonate manganese ore deposit[J]. Contributions to geology and mineral resources research, 1991, 6(4): 63-71(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK199104006.htm [5] 曾友寅. 广西下雷锰矿床沉积学研究[J]. 沉积学报, 1991, 9(1): 73-78.Zeng Y Y. Study on the sedimentology of Late Devonian manganese ore deposit in Xialei[J]. Acta Minalogica Sinica, 1991, 9(1): 73-78(in Chinese with English abstract). [6] 郝瑞霞, 关广岳. 广西下雷-湖润锰矿带原生碳酸锰矿床的沉积机制[J]. 地质地球化学, 1994, 22(1): 57-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ199402012.htmHao R X, Guan G Y. Sedimentary mechanism of primary manganese carbonate deposit in Xialei-Hurun manganese ore belt in Guangxi[J]. Geology and Geochemistry, 1994, 22(1): 57-61(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ199402012.htm [7] 李毅. 广西热水沉积矿床成矿规律及找矿方向研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2007.Li Y. Research on metallogenic law and prospecting direction of Guangxi hydrothermal sedimentary deposit[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2007 (in Chinese with English abstract). [8] 李升福, 王泽华, 李朗田, 等. 桂西南优质锰矿成矿机理分析[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2009, 23(2): 364-370. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK200904001.htmLi S F, Wang Z H, Li L T, et al. Analysis on metallogenic mechanism of high-quality manganese deposits in Southwest Guangxi[J]. Resources Environment and Engineering, 2009, 23(2): 364-370(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK200904001.htm [9] 和平贤. 广西大新锰矿区矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 中国锰业, 2012, 30(3): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201203004.htmHe P X. A discussion on the geological features and causes of manganese ore deposit of Daxin County in Guangxi[J]. China's Manganese Industry, 2012, 30(3): 8-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201203004.htm [10] 王荣庚. 广西大新下雷锰矿沉积环境特征及成矿物质来源分析[J]. 中国锰业, 2012, 30(4): 8-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4336.2012.04.004Wang R G. An elementary analysis of Xialei Mn-ore with the sedimentary features and material sources of ore-forming[J]. China's Manganese Industry, 2012, 30(4): 8-21(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4336.2012.04.004 [11] 欧莉华. 桂西南地区上泥盆统锰矿沉积特征与成矿机理[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013.Ou L H. Sedimentary characteristics and metallogenic mechanism of Upper Devonian manganese deposits in southwestern Guangxi[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2013 (in Chinese with English abstract). [12] 夏静柳. 广西大新县下雷锰矿成因新认识[J]. 矿床地质, 2014, 33(增刊): 758-759.Xia J L. New understanding of the genesis of Xialei manganese deposit in Daxin County, Guangxi[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2014, 33 (S): 758-759(in Chinese with English abstract). [13] 黄明富, 杨妍. 浅谈广西大新下雷锰矿沉积环境特征及成矿物质来源分析[J]. 能源环境, 2015, 24(9): 147-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201204004.htmHang M F, Yang Y. A brief talk on the characteristics of sedimentary environment and the source of minerals in Daxin Xialei manganese deposit in Guangxi[J]. Energy Environment, 2015, 24(9): 147-148 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201204004.htm [14] 杨威, 周永章, 何俊国, 等. 钦杭成矿带南段广西下雷锰矿的热水沉积成因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2015, 45(增刊1): 1514. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD201506004053.htmYang W, Zhou Y Z, He J G, et al. An analysis of the causes of hydrothermal sedimentation of Xialei manganese deposit in Guangxi in the southern section of Qinhang metallogenic belt[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2015, 45(S1): 1514. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD201506004053.htm [15] 朱建德, 朱恺军, 周尚国, 等. 下雷-东平锰矿带矿床特征和成因探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 2016, 52(5): 846-853. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201605005.htmZhu J D, Zhu K J, Zhou S G, et al. Characteristics and genesis of deposits in the Xialei-Dongping manganese ore belt of Guangxi Province[J], Geology and Exploration, 2016, 52(5): 846-853(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201605005.htm [16] 金玺, 陈显锋. 广西大新县下雷锰矿地质特征与矿床成因探讨[J]. 矿产与地质, 2018, 32(3): 404-408. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2018.03.004Jin X, Chen X F. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Xialei Mn deposit in Daxin County, Guangxi[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2018, 32(3): 404-408 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2018.03.004 [17] Hao Y, Dao H P, Shao Y J, et al. Hydrothermally induced 34S enrichment in pyrite as an alternative explanation of the Late Devonian sulfur isotope excursion in South China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2020, 283: 1-21. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2020.05.017 [18] 周琦, 杜远生, 袁良军, 等. 黔湘渝毗邻区南华纪武陵裂谷盆地结构及其对锰矿的控制作用[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(2): 177-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201602001.htmZhou Q, Du Y S, Yuan L J, et al. The structure of the wining rift basin and its control on the manganese deposit during the nanhua period in Guizhou-Hunan-Chongqing border area, South China[J], Earth Science, 2016, 41(2): 177-188 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201602001.htm [19] 周琦, 杜远生, 覃英. 古天然气渗漏沉积型锰矿床成矿系统与成矿模式: 以黔湘渝毗邻区南华纪"大塘坡式"锰矿为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(3): 457-466. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.03.001Zhou Q, Du Y S, Qin Y. Ancient natural gas seepage sedimentary-type manganese metallogenic system and ore-forming model: A case study of "Datangpo type" manganese deposits formed in rift basin of Nanhua Period along Guizhou-Hunan-Chongqing border area[J]. Deposit Geology, 2013, 32(3): 457-466(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.03.001 [20] 周琦, 杜远生, 王家生, 等. 黔东北地区南华系大塘坡组冷泉碳酸盐岩及其意义[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2007, 32(3): 339-346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200703005.htmZhou Q, Du Y S, Wang J S, et al. Characteristics and significance of the cold seep carbonates from the Datangpo Formation of the Nanhua series in the Northeast Guizhou[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2007, 32(3): 339-346 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200703005.htm [21] 周琦, 杜远生, 颜佳新, 等. 贵州松桃大塘坡地区南华纪早期冷泉碳酸盐岩地质地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2007, 32(6): 845-852. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2007.06.015Zhou Q, Du Y S, Yan J X, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the cold seep carbonates in the early Nanhua system in Datangpo, Songtao, Guizhou Province[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2007, 32(6): 845-852 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2007.06.015 [22] 周琦, 杜远生, 袁良军, 等. 古天然气渗漏沉积型锰矿床找矿模型: 以黔湘渝毗邻区南华纪"大塘坡式"锰矿为例[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(10): 2285-2298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.10.010Zhou Q, Du Y S, Yuan L J, et al. Prospecting model of ancient natural gas seepage sedimentary manganese deposits: Taking Nanhua "Datangpo" manganese deposits in the adjacent areas of Guizhou, Xiangyu and Chongqing as an example[J]. Acta Geology, 2017, 91(10): 2285-2298 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.10.010 [23] 周琦, 杜远生, 覃英, 等. 贵州省松桃县大塘坡南华纪早期古天然气渗漏构造的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2007, 32(增刊): 33-40.Zhou Q, Du Y S, Qin Y. Discovery of ancient natural gas seepage structures in the Early Nanhua Period in Datangpo, Songtao County, Guizhou Province and their geological significance[J]. Earth Science, 2007, 32(S): 33-40 (in Chinese with English abstract). [24] 周琦, 杜远生. 古天然气渗漏与锰矿成矿: 以黔东地区南华纪"大塘坡式"锰矿为例[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012.Zhou Q, Du Y S. Ancient natural gas seepage and manganese mineralization: A case of Nanhua "Datangpo" manganese deposit in eastern Guizhou[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2012(in Chinese). [25] 周琦, 杜远生, 袁良军, 等. 贵州铜仁松桃锰矿国家整装勘查区地质找矿主要进展及潜力预测[J]. 贵州地质, 2016, 33(4): 237-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ201604001.htmZhou Q, Du Y S, Yuan L J, et al. Major progress and potential prediction of geologic exploration in Songtao manganese national fully equipped exploration district in Tongren, Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2016, 33(4): 237-244 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ201604001.htm [26] 周琦, 杜远生, 袁良军, 等. 黔东及毗邻区南华纪"大塘坡式"锰矿研究历史、主要进展及展望[J]. 贵州地质, 2018, 5(4): 270-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ201804003.htmZhou Q, Du Y S, Yuan L J, et al. Research history, manganese geposit major progress and outlook of Datangpo Type in Nanhua Period of East Guizhou and nearby area[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2018, 5(4): 270-281(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ201804003.htm [27] 李建威, 赵新福, 邓晓东, 等. 新中国成立以来中国矿床学研究若干重要进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 49(11): 1720-1771. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201911003.htmLi J W, Zhao X F, Deng X D, et al. An overview of the advance on the study of China's ore deposits during the last seventy years, in China[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2019, 49(11): 1720-1771(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201911003.htm [28] 毛景文, 袁顺达, 谢桂青, 等. 21世纪以来中国关键金属矿产找矿勘查与研究新进展[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(5): 935-969. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201905001.htmMao J W, Yuan S D, Xie G Q, et al. New advances on metallogenic studies and exploration on critical minerals of China in 21st century[J]. Mineral Deposit, 2019, 38(5): 935-969 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201905001.htm [29] 侯明才, 陈洪德, 田景春. 泥盆纪右江盆地演化与层序充填响应[J]. 地层学杂志, 2005, 29(1): 62-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200501011.htmHou M C, Chen H D, Tian J C. Devonion sequence filling response to the evolution of the Youjiang Basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2005, 29(1): 62-70 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200501011.htm [30] 陈洪德, 侯明才, 林良彪, 等. 不同尺度构造-层序岩相古地理研究思路与实践[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(5): 894-905. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201005008.htmChen H D, Hou M C, Lin L B, et al. Different scale structure-sequence lithofacies paleogeography research ideas and practice[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(5): 894-905 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201005008.htm [31] 吴诒, 周怀玲, 蒋廷操. 广西泥盆纪沉积相古地理及矿产[M]. 南宁: 广西人民出版社, 1987.Wu Y, Zhou H L, Jiang T C. Paleogeography and mineral resources of Devonian sedimentary facies in Guangxi[M]. Nangning: Guangxi People's Publishing House, 1987 (in Chinese). [32] 冯增昭, 杨玉卿, 金振奎, 等. 从岩相古地理论中国南方石炭系油气潜景[J]. 古地理学报, 1999, 1(4): 86-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX199904011.htmFeng Z Z, Yang Y Q, Jin Z G, et al. Theory of petroleum potential of Carboniferous in southern China based on lithofacies and paleogeography[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 1999, 1(4): 86-92 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX199904011.htm [33] 梅冥相, 马永生, 邓军, 等. 加里东运动构造古地理及滇黔桂盆地的形成: 兼论滇黔桂盆地深层油气勘探潜力[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(3): 227-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200503031.htmMei M X, Ma Y S, Deng J, et al. Tectonic palaeogeographic changes resulting from the Caledonian movement and the formation of the Dianqiangui Basin: Discussion on the deep exploration potential of oil and gas in the Dianqiangui Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(3): 227-236(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200503031.htm [34] 罗胜元, 王传尚, 彭中勤. 桂中坳陷下石炭统鹿寨组页岩气研究[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2016, 32(2): 180-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC201602012.htmLou S Y, Wang C S, Peng Z Q. Study on the shale gas of the stone village group in Guizhong Depression[J]. South China Geology and Minerals, 2016, 32(2): 180-190(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC201602012.htm [35] 黄恒, 颜佳新, 余文超. 广西宜州裂陷槽晚古生代演化与早石炭世沉积锰矿分布[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(5): 1001-1011. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202005015.htmHuang H, Yan J X, Yu W C. Evolution of Yizhou aulacogen in Guangxi during Late Palozoic and distriution of manganese deposits in Early Carboniferous[J]. Ancient Geography, 2020, 22(5): 1001-1011(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202005015.htm [36] 张伯友, 杨树锋. 古特提斯造山带在华南两广交界地区的新证据[J]. 地质论评, 1995, 41(1): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199501000.htmZhang B Y, Yang S F. New evidence of the paleoteetehyan orogenic belt on the Guangdong-Guangxi border region, South China[J]. Geological Review, 1995, 41(1): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199501000.htm [37] 吴根耀, 吴浩若, 钟大赉, 等. 滇桂交界处古特提斯的洋岛和岛弧火山岩[J]. 现代地质, 2000, 14(4): 393-400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200004002.htmWu G Y, Wu H R, Zhong D L, et al. Volcanic rochs of paleotethyan oceanic island and island-arc bordering Yunnan and Guangxi, China[J]. Geoscience, 2000, 14(4): 393-400(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200004002.htm [38] 殷鸿福, 吴顺宝, 杜远生, 等. 华南是特提斯多岛洋体系的一部分[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 1995, 24(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX901.000.htmYin H F, Wu S B, Du Y S, et al. South China defined aspart of Tethyan archi pelagic ocean system[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1995, 24(1): 1-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX901.000.htm [39] 马文璞. 华南陆域内古特提斯形迹: 二叠纪造山作用和互换构造域的东延[J]. 地质科学, 1996, 31(2): 105-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX602.000.htmMa W P. Paleotethys in South China, Permian orogeny and the eastwards extension of interchange domain[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 1996, 31(2): 105-113(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX602.000.htm [40] Chen D, Tucker M E, Zhu J, et al. Carbonate sedimentation in astarved pullapart basin, Middle to Late Devonian, southern Guilin, South China[J]. Basin Research, 2001, 13(2): 141-167. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2117.2001.00148.x/pdf [41] 杜远生, 黄虎, 杨江海, 等. 晚古生代-中三叠世右江盆地的格局和转换[J]. 地质论评, 2013, 59(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201301002.htmDu Y S, Huang H, Yang J H, et al. The basin translation from Late Paleozoic to Triassic of the Youjiang Basin and its tectonic signification[J]. Geologica Review, 2013, 59(1): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201301002.htm [42] 侯宗林, 薛友智, 黄金水, 等. 扬子地台周边锰矿[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1997.Hou Z L, Xue Y Z, Huang J S, et al. Manganese mineral[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1997(in Chinese). [43] 刘建明, 叶杰, 刘家军, 等. 盆地流体中有机组分的成矿效应[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2000, 19(3): 141-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200003000.htmLiu J M, Ye J, Liu J J, et al. On ore-forming effect of organic compounds in basin fluids[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemisty, 2000, 19(3): 141-147(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200003000.htm [44] 叶杰, 刘建明, 张安立, 等. 沉积喷流型矿化的岩石学证据: 以大兴安岭南段黄岗和大井矿床为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2002, 18(4): 585-592. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200204017.htmYe J, Liu J M, Zhang A L, et al. Petrological evidence for exhalative mineralization: Case studies of Huanggang and Dajing deposits in the the southern segment of the Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2002, 18(4): 585-592(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200204017.htm [45] 熊永柱, 夏斌, 林丽, 等. 热水沉积成矿研究现状与展望[J]. 矿产与地质, 2005, 19(3): 233-238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200503004.htmXiong Y Z, Xia B, Lin L, et al. Advances in the research on hydrothermal sedimementary mineralization[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2005, 19(3): 233-238(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200503004.htm [46] 王长明, 邓军, 张寿庭, 等. 内蒙古小坝梁铜金矿床的地质特征与喷流沉积成因[J]. 黄金, 2007, 28(6): 9-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ200706002.htmWang C M, Deng J, Zhang S T, et al. Geological characteristics and exhalative sedmientation genesis of Xiaobaliang Cu-Au deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Gold Geology, 2007, 28(6): 9-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ200706002.htm [47] 王玉奇. Sedex型矿床与VMS型矿床对比研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2009, 23(3): 259-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK200903010.htmWang Y Q. Comparative study on Sedex deposits and VMS deposits[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2009, 23(3): 259-262(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK200903010.htm [48] 薛静, 戴塔根, 付松武, 等. 广西武宣盘龙铅锌矿喷流沉积成矿作用: 稀土元素和硫同位素证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 35(3): 394-403. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201103010.htmXue J, Dai T G, Fu S W, et al. SEDEX origin of the Panlong lead-zinc deposit, Wuxuan, Guangxi: REE and S isotope evidences[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2011, 35(3): 394-403(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201103010.htm [49] 赵静, 梁金龙, 韩波. 海底喷流成矿作用研究现状及展望[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2015, 37(14): 236-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC201504008.htmZhao J, Liang J L, Han B. A review and prospect of research on sedimentary exhalative deposits[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2015, 37(14): 236-244(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC201504008.htm [50] Gao J B, Yang R D, Xu H, et al. Genesis of Permian sedimentary manganese deposits in Zunyi, Guizhou Province, SW China: Constraints from geology and elemental geochemistry[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 192: 142-154. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S0375674216302904&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1530343236&md5=c4c583361ec8d900f6bfaf692a598651 [51] Joseph M, Carles C, Eduardo G P, et al. Geochemical constraints on the genesis of the "Montaña de Manganeso" vein-type Mn deposit, Mexican Plateau[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 125: 1-16. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136819309977 [52] 刘雨, 周琦, 袁良军, 等. 黔东大塘坡锰矿区古天然气渗漏喷溢口群发现及地质意义[J]. 贵州地质, 2015, 32(4): 250-255. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ201504002.htmLiu Y, Zhou Q, Yuan L J, et al. The found of the ancient natural gas leakage spray overflow port group and its geological significant in Datangpo Mining of East Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2015, 32(4): 250-255(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ201504002.htm [53] 翟裕生, 张湖, 宋鸿林, 等. 大型构造与超大型矿床[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997.Zhai Y S, Zhang H, Song H L, et al. Type structure and super large deposit[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1997(in Chinese). [54] 张义勋, 李光岑, 肖庆辉, 等. 地球科学大辞典[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006.Zhang Y X, Li G C, Xiao Q H, et al. Earth science dictionary[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006(in Chinese). [55] Carne R C, Cathro R J. Sedimentary exhalative (SEDEX) zinc-lead-silver deposits, Northern Canadian cordillera[J]. Cim Bulletin, 1982, 75: 66-78. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279893534_Sedimentary_exhalative_SEDEX_zinc-lead-silver_deposits_Northern_Canadian_Cordillera [56] Leach D L, Bradley D C, Huston D, et al. Sediment-hosted leadZinc deposits in earth history[J]. Economic Geology, 2010, 105: 593-625. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034834688510_71be.html [57] Farquhar J, Wu N, Canfield D E, et al. Connection between sulfur cycle evolution, sulfur isotopes, sediments, and base metal sulfide deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 2010, 105: 509-533. [58] 詹涵钰, 李占轲, 武文辉, 等. 陕西大西沟喷流沉积型菱铁矿矿床地质特征及矿床成因[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(1): 1-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201901001.htmZhan H Y, Li Z K, Wu W H, et al. Geological characteristics and origin of Daxigou SEDEX siderite deposit in Shaanxi Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(1): 1-20(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201901001.htm [59] 丛源, 董庆吉, 肖克炎, 等. 中国锰矿资源特征及潜力预测[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(3): 118-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201803013.htmCong Y, Dong Q J, Xiao K Y, et al. Characteristics and predicted potential of Mn resources in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(3): 118-136(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201803013.htm [60] 臧忠江. 西昆仑与西南天山结合部晚古生代沉积型锰矿床成矿规律与成矿预测[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2020.Zang Z J. Study on metallogenic regularity and prediction of Late Paleozoic sedimentary manganese deposits near the junction of West Kunlun tectonic belt and southwest Tianshan tectonic belt[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2020 (in Chinese with English abstract). [61] Hu R Z, Burnard P, Bi X W, et al. Helium and argon isotope geochemistry of alkaline intrusion-associated gold and copper deposits along the Red River-Jinshajiang fault belt, SW China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 203(3): 305-317. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254103003188 [62] Xu W Y, Hou Z Q, Yang Z S, et al. Numerical simulation of fluid migration during ore formation of Carboniferous exhalation-sedimentary massive sulfide deposits in the Tongling District, Anhui Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(1): 98-105. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=12213040 [63] Bischoff J L, Roserbauser R J. Salinity variations in submarine hydrothermal system by layered double-diffusive convection[J]. Journal of Geology, 1989, 97: 613-623. [64] Herzig P M, Becker K P, Stoffers P, et al. Hydrothermal silica chimney fields in the galapagos spreading center at 86W[J]. Earth and Plantary Science Letter, 1998, 89(1): 281-320. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X8890115X [65] Peng R M, Zhai Y S, Xiao R G, et al. Ore-forming response to syndepositional submarine volcanism in Langshan-Zhaertai mesoproterozoic SEDEX ore belt, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2000, 11(3): 302-307. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=4000690419 [66] Zarasvandi A, Samet M, Sadeghi M, et al. The Gol-Zard Zn-Pb deposit, Lorestan Province, Iran: A metamorphosed SEDEX deposit[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica: English Edition, 2014, 88(1): 142-153. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12188 [67] 刘雨, 周琦, 袁良军, 等. 黔东松桃大塘坡地区南华系大塘坡组锰矿相带及分布规律[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(6): 40-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201506006.htmLiu Y, Zhou Q, Yuan L J, et al. Manganese ore phase and distribution of Nanhua Datangpo Formation in Datangpo area, Songtao, East Guizhou[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(6): 40-46(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201506006.htm [68] 陈多福, 陈先沛. 贵州省松桃热水沉积锰矿的地质地球化学特征[J]. 沉积学报, 1992, 12(1): 169-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199204003.htmChen D F, Chen X P. Geological and geochemical characteristices hydrothermal sedimentary mangenes deposits, of Songtao Guizhuo[J]. Acth Sedimentologica Sinfca, 1992, 12(1): 169-179(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199204003.htm -





 下载:
下载: