Using compaction simulation experiment to recover burial history: Taking the fourth Member of Shahejie Formation in Leijia area, Western Depression of Liaohe River as an example
-
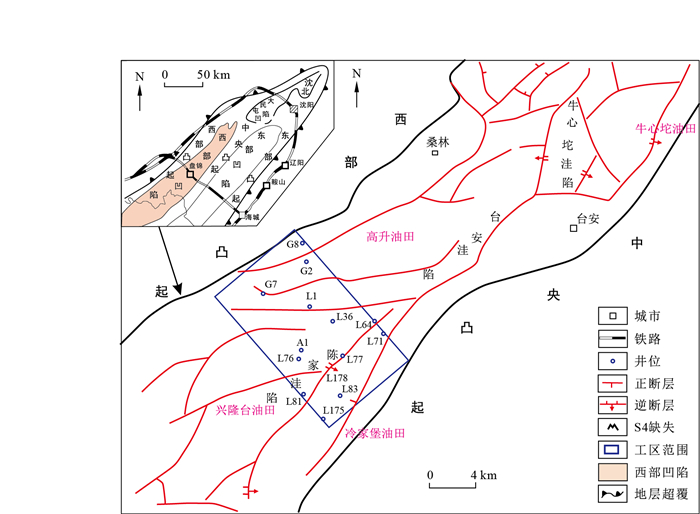
摘要: 辽河西部凹陷雷家地区具有良好的油气勘探开发潜力,但目前对该地区的埋藏史分析缺乏清晰的认识。运用沉降史的恢复原理对研究区残余地层进行原始厚度的恢复,首先利用声波曲线法和邻层对比方法恢复地层的剥蚀厚度,然后配比5个实验样品(含砾细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、泥质灰岩、灰质泥岩、泥岩)进行压实模拟实验,根据实验得出样品的孔隙度-深度曲线。利用现有的埋藏资料进行地层骨架厚度计算,并根据骨架体积不变公式,以每个单一岩性分层作为最小单位逐一进行回剥计算,得到各组、段地层在不同地质时期的沉积厚度以及埋藏深度。通过埋藏史分析认为雷家地区新生界地层埋藏过程中,古近系沙河街组时期地层的沉积速率较大,沉积地层较厚,但在沙河街组二段地层抬升遭受剥蚀,地层较薄;东营组时期,地层沉积变缓,末期地层遭受抬升剥蚀;在新近系、第四系时期,地层沉积速率小,沉积的地层厚度不大。Abstract: The Leijia area in the Western Depression of the Liaohe River has good oil and gas exploration and development potential, but the current analysis of the burial history in this area lacks a clear understanding.This paper uses the recovery principle of subsidence history to restore the original thickness of the remaining stratum in the study area.Firstly, the sonic curve method and the adjacent layer comparison method are used to restore the denuded thickness of the stratum.Sandstone, argillaceous limestone, limestone mudstone, mudstone) were subjected to compaction simulation experiments, and the porosity-depth curve of the sample was obtained according to the experiment.Use the existing burial data to calculate the thickness of the stratum framework, and according to the constant volume formula of the framework, use each single lithological layer as the smallest unit to carry out the backstripping calculation one by one to obtain the sedimentary thickness of each group and section in different geological periods and the depth of burial.According to the analysis of burial history, during the burial process of the Cenozoic strata in Leijia area, the sedimentation rate of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation was higher and the sedimentary strata was thicker, but the second Member of Shahejie Formation was uplifted and eroded and the strata was thin; During the Dongying Formation, the stratum deposition slowed down, and the stratum was uplifted and eroded at the end; in the Neogene and Quaternary, the stratum deposition rate was low, and the thickness of the deposited stratum was not large.
-
Key words:
- Leijia area /
- burial history /
- stratum thickness /
- Paleogene
-
图 3 邻层地层对比法求取剥蚀厚度示意图[32]
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the denudation thickness obtained by the adjacent layer stratum comparison method
图 13 研究区典型井埋藏史图(地层代号同表 7)
Figure 13. Burial history of typical wells at the study area
表 1 声波测井曲线法恢复剥蚀量
Table 1. Recovery denudation by the sonic logging curve
井名 沙三段剥蚀厚度/m 井名 东营组剥蚀厚度/m L7 60 L7 151 G17 94 G17 129 G63 50 G63 130 G1003 64 G1003 171 G1007 64 G1007 148 L173 72 L173 237 G1221 173 G1221 85 G33 25 G33 171 G39 142 G39 110 Gg29 71 Gg29 25 Gg5 65 Gg5 130 Gg29 80 Gg29 60 G61 68 G61 92 L3 58 L3 146 表 2 邻层地层对比法恢复剥蚀量
Table 2. Recovery of denudation by the adjacent layer stratum comparison method
井号 沙三段剥蚀厚度/m 东营组剥蚀厚度/m L81 无剥蚀 74 L163 无剥蚀 43 L169 无剥蚀 84 L193 无剥蚀 45 L195 无剥蚀 65 L181 无剥蚀 70 表 3 实验样品成分
Table 3. Composition of experimental sample
编号 岩性 成分 样品1 含砾细砂岩 泥10%;砾20%;细砂70% 样品2 泥质粉砂岩 泥30%;粉砂70% 样品3 泥质灰岩 泥28%;碳酸钙粉末67%;粉砂5% 样品4 灰质泥岩 碳酸钙粉末30%;泥65%;粉砂5% 样品5 泥岩 泥100% 表 4 实验模拟条件
Table 4. Experimental simulation conditions
深度/m 承载压强/MPa 骨架压强/MPa 流体压强/MPa 温度/℃ 0 0.00 0.0 0.00 18.0 100 2.18 1.2 0.98 21.5 200 4.36 2.4 1.96 25.0 400 8.72 4.8 3.92 32.0 600 13.08 7.2 5.88 39.0 800 17.44 9.6 7.84 46.0 1 000 21.80 12.0 9.80 53.0 1 200 26.16 14.4 11.76 60.0 1 400 30.52 16.8 13.72 67.0 1 600 34.88 19.2 15.68 74.0 1 800 39.24 21.6 17.64 81.0 2 000 43.60 24.0 19.60 88.0 2 200 47.96 26.4 21.56 95.0 2 400 52.32 28.8 23.52 102.0 2 600 56.68 31.2 25.48 109.0 2 800 61.04 33.6 27.44 116.0 3 000 65.40 36.0 29.40 123.0 表 5 新生界地层分层数据(L73井)
Table 5. Stratigraphic data of the Cenozoic(Well L73)
分层 顶深/m 底深/m 馆陶组-平原组 0 762 东营组 762 959 沙一二段 959 1 218 沙三段 1 218 2 383 沙四段 2 383 2 704 表 6 各地质时期地层初始沉积厚度(L73井)
Table 6. Initial deposition thickness of the strata in each geological period(Well L73)
地层 Es4/m Es3/m Es1+2/m Ed/m Ng-Qp/m 馆陶组-平原组 - - - - 762.0 东营组 - - - 202.1 197.0 沙一二段 - - 271.5 269.6 259.0 沙三段 - 1 222.0 1 207.2 1 196.7 1 165.0 沙四段 353.8 335.1 331.8 329.4 321.0 表 7 辽河西部凹陷地层时代与绝对年龄
Table 7. Stratigraphic age and absolute age in the Western Depression of Liaohe River
地层 绝对年龄/Ma 平原组(Qp) 1.6 明化镇组(Nm) 12.0 馆陶组(Ng) 24.6 东营组(Ed) 36.0 沙一段(Es1) 37.5 沙二段(Es2) 38.0 沙三段(Es3) 43.0 沙四段(Es4) 45.5 -
[1] 程顶胜, 韩慧, 李永铁, 等. 藏北比如盆地油气地表地球化学勘探[J]. 石油勘探与开发. 2001, 28(1): 45-47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2001.01.015Cheng D S, Han H, Li Y T, et al. Surface geochemical exploration for oil and gas in the Ru Basin, northern Tibet[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2001, 28(1): 45-47(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2001.01.015 [2] 叶加仁, 陆明德. 盆地地史模拟述评[J]. 地质科技情报, 1995, 14(2): 45-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ502.007.htmYe J R, Lu M D. A review of basin geological history simulation[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1995, 14(2): 45-51(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ502.007.htm [3] Wang W, Lin C, Zhang X, et al. Effect of burial history on diagenetic and reservoir-forming process of the Oligocene sandstone in Xihu sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 112(10): 34-40. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817219304544 [4] 谭开俊, 卫平生, 吕锡敏, 等. 地层古厚度定量恢复方法研究及应用: 以准噶尔盆地陆东地区为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2005, 25(10): 24-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2005.10.008Tan K J, Wei P S, Lu X M, et al. Research on quantitative resumption method of stratum paleothickness and it's application: Taking Ludong area in ZHUNGE'ER Basin as an example[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2005, 25(10): 24-26(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2005.10.008 [5] 秦承志, 王先彬, 林锡祥, 等. 辽河盆地埋藏史及烃源岩成熟度演化史的数值模拟[J]. 沉积学报, 2002, 20(3): 493-498. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.03.021Qin C Z, Wang X B, Lin X X, et al. Basin modeling of buried history and maturity history of source rock in Liaohe Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(3): 493-498(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.03.021 [6] 魏巍. 西部凹陷南部沙河街组储层孔隙度计算与有利区预测[D]. 黑龙江大庆: 东北石油大学, 2013.Wei W. Reservoir porosity calculation and favorable area prediction of Shahejie Formation in the southern part of Western Depression[D]. Daqing Helongjiang: Northeast Petroleum University, 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [7] 秦承志, 王先彬, 林锡祥, 等. 辽河盆地埋藏史及烃源岩成熟度演化史的数值模拟[J]. 沉积学报, 2002, 20(3): 493-498. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.03.021Qin C Z, Wang X B, Lin X X, et al. Basin modeling of buried history and maturity history of source rock in Liaohe Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(3): 493-498(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.03.021 [8] 寿建峰, 张惠良, 沈扬, 等. 中国油气盆地砂岩储层的成岩压实机制分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(8): 2165-2170. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200608005.htmShou J F, Zhang H L, Shen Y, et al. Diagenetic mechanisms of sandstone reservoirs in China oil and gas-bearing basins[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(8): 2165-2170(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200608005.htm [9] 刘琳琳, 张金功, 吴春燕. 砂泥岩埋藏过程孔隙度演化特征探讨[J]. 地下水, 2016, 38(1): 186-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2016.01.068Liu L L, Zhang J G, Wu C Y. Discussion on porosity evolution characteristics of sand-shale burial process[J]. Groundwater, 2016, 38(1): 186-189(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2016.01.068 [10] 关振良. 利用压实模拟计算地层古厚度及差异压实量的尝试[J]. 石油实验地质, 1992, 14(2): 152-158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD199202006.htmGuan Z L. Anattempt simulation to calculate the paleo-thickness and the amount of differential compaction in a formation with an application of compaction simulations[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 1992, 14(2): 152-158(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD199202006.htm [11] 赵帅, 解习农, 刘中戎, 等. 古地貌对断陷盆地沉积体系的控制作用: 以青藏高原伦坡拉盆地始新统牛堡组为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 53-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902007.htmZhao S, Xie X N, Liu Z R, et al. Control of tectonic-paleogeomorphology on deposition system of faulting-subsiding Basin: A case from the eocene Niubao Formation in Lunpola Basin, Central Tibet[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 53-64(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902007.htm [12] 陈林, 李珊珊, 游君君, 等. 文昌B凹陷古近系低渗储层物性影响因素定量评价与应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 165-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903017.htmChen L, Li S S, You J J, et al. Quantitative evaluation and application of factors affecting the properties of low permeability reservoirs from the Paleogene in Wenchang B Sag[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 165-173(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903017.htm [13] 刘国勇, 金之钧, 张刘平. 碎屑岩成岩压实作用模拟实验研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 21(3): 407-413. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.03.013Liu G Y, Jin Z J, Zhang L P. Simulation study on clastic rock diagenetic compaction[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 21(3): 407-413(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.03.013 [14] 纪天亮. 辽河坳陷雷家地区致密油成藏特征研究[D]. 山东青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2016.Ji T L. Study on forming characteristics of tight oil reservoirs in Leijia area, Liaohe Depression[D]. Qingdao Shandong: China University of Petroleum(East China), 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [15] 白东昆. 辽河西部凹陷雷家地区沙三段层序地层及沉积微相研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2017.Bai D K. Research on sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary microfacies of the third Member of Shahejie Formation in Leijia area, Western Depression of Liaohe River[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] 安欣. 雷家地区致密油综合研究与勘探目标优选[D]. 黑龙江大庆: 东北石油大学, 2017.An X. Comprehensive study of tight oil and optimization of exploration targets in Leijia area[D]. Daqing Heilongjiang: Northeast Petroleum University, 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] 黄蕾. 湖相碳酸盐岩储层及成因机理研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2016.Huang L. Research on lacustrine carbonate reservoir and its genetic mechanism[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [18] Sumit K, Keka O. Reaction kinetic, maturity, burial and thermal histories modelling of cambay shale source rocks, Cambay Basin, Western India[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 202(2): 437-442. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920410521002035 [19] 姜正龙, 邓宏文, 林会喜, 等. 古地貌恢复方法及应用: 以济阳坳陷桩西地区沙二段为例[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(5): 865-871. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.05.015Jiang Z L, Deng H W, Lin H X, et al. Methods and application of paleo-geomorphologies rebuildingan example of the second member of ShaHeJie Formation Zhuangxi area, Jiyang Depression[J]. Modern Geology, 2009, 23(5): 865-871(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.05.015 [20] 吴智平, 韩文功. 济阳坳陷早晚第三纪沉积间断地层剥蚀量研究[J]. 中国海上油气: 地质, 2000, 14(5): 320-323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200005004.htmWu Z P, Han W G. Erosiveness under the hiatus between Paleogene and Neogene in Jiyang Depression[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas: Geology, 2000, 14(5): 320-323(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200005004.htm [21] 刘玉瑞. 声波时差法计算地层剥蚀量问题的斧正[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2015, 7(2): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ201502002.htmLiu Y R. Correction of erosion thickness of strata calculated by acoustic time difference[J]. Complicated Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2015, 7(2): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ201502002.htm [22] 杨雪, 杨桥, 于福生. 辽河盆地西部凹陷北部地区古近系地层剥蚀量恢复[J]. 西安石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 21(5): 34-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2006.05.007Yang X, Yang Q, Yu F S. Calculation of the denudation amount of the Paleogene in the north part of the West Depression, Liaohe Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University: Natural Science Edition, 2006, 21(5): 34-37(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2006.05.007 [23] 史长林, 纪友亮, 李清山, 等. 包裹体测温恢复剥蚀厚度新方法在准噶尔盆地车莫古隆起的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2011, 41(1): 64-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201101009.htmShi C L, Ji Y L, Li Q S, et al. Using a new method based on homogeneity temperature of fluid inclusion to restore the thickness of eroded strata of Chemo Paleo-Uplift in Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(1): 64-70(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201101009.htm [24] 曹强, 叶加仁, 王巍. 沉积盆地地层剥蚀厚度恢复方法及进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2007, 12(6): 41-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2007.06.009Cao Q, Ye J R, Wang W. Methods and progress in restoration of stratum denudation thickness in sedimentary basins[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2007, 12(6): 41-46(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2007.06.009 [25] 王传远, 段毅, 杜建国, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长9油层组流体包裹体特征与油气成藏期次分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2009, 28(4): 47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2009.04.008Wang C Y, Duan Y, Du J G, et al. Hydrocarbon migration stages in chang 9 formation in Ordos Basin by fluid inclusion analysis[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2009, 28(4): 47-50(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2009.04.008 [26] 刘建, 任莹, 王丹蕾, 等. 蠡县斜坡北段储层流体包裹体特征及成藏时期[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(1): 53-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201601008.htmLiu J, Ren Y, Wang D L, et al. Fluid inclusions characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation period of the reservoir in the Northern Section, Lixian Slope[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(1): 53-58(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201601008.htm [27] Liu J Y, Steel R J, Lin C Y, et al. Geomorphology control on the development of reservoir depositional systems, Devonian Donghetang Formation in the Tabei Uplift of the Tarim Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 38(1): 177-194. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.06.009 [28] Magara K. Thickness of removed sedimentary rocks, paleopore pressure, and paleotemperature, southwestern part of Western Canada Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1976, 60(4): 554-565. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040489567210_f29a.html [29] Hinte J. Geohistory analysis: Application of micropaleontology in exploration geology[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1978, 62(2): 201-222. http://aapgbull.geoscienceworld.org/content/62/2/201 [30] 陈荷立. 泥岩压实资料在油气勘探构造研究中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1980, 7(5): 18-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK198005001.htmChen H L. Application of mudstone compaction data in the study of oil and gas exploration structures[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1980, 7(5): 18-26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK198005001.htm [31] 刘玉瑞. 声波时差法计算地层剥蚀量问题的斧正[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2015, 7(2): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ201502002.htmLiu Y R. Correction of erosion thickness of strata calculated by acoustic time difference[J]. Complicated Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2015, 7(2): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ201502002.htm [32] 牟中海, 唐勇, 崔炳富, 等. 塔西南地区地层剥蚀厚度恢复研究[J]. 石油学报, 2002, 23(1): 40-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2002.01.009Mu Z H, Tang Y, Cui B F, et al. Erosion thickness restoration in southwest Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2002, 23(1): 40-44(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2002.01.009 [33] 石广仁, 郭秋麟. 盆地综合模拟系统BASIMS[J]. 石油学报, 1996, 17(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB601.000.htmShi G R, Guo Q L. Basin integrated simulation system "BASIMS"[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1996, 17(1): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB601.000.htm [34] 陆江, 赵彦璞, 朱沛苑, 等. 孔隙度反演回剥法在储层物性定量预测中的应用: 以珠Ⅲ坳陷文昌区为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(6): 105-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806013.htmLu J, Zhao Y P, Zhu P Y, et al. Application of porosity inversion method to reservoir quantitative prediction: Taking Wenchang Aarea of Zhu Ⅲ Depression as an example[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(6): 105-114(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806013.htm [35] 温凯, 何蕾, 虞维超, 等. 枯竭油气藏型储气库地层压力的计算方法[J]. 油气储运, 2017, 36(7): 781-788. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY201707008.htmWen K, He L, Yu W C, et al. Calculation methods on formation pressure of underground gas storage rebuilt from depleted oil and gas reservoir[J]. Petroleum Storage and Transportation, 2017, 36(7): 781-788(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY201707008.htm [36] 蒋有录, 吴松涛, 翟秀芬, 等. 沾化凹陷四扣地区沙四段礁灰岩油藏成藏动力探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(3): 15-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201103003.htmJiang Y L, Wu S T, Zhai X F, et al. Accumulation dynamic of reef limestone reservoirs from Member 4 of Shahejie Formation in Sikou District, Zhanhua Depression, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(3): 15-22(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201103003.htm [37] 孟凡晋. 辽河西部凹陷南段沙三段成岩作用数值模拟与优质储层预测[D]. 黑龙江大庆: 东北石油大学, 2013.Meng F J. Giagenetic numerical modeling and favorable reservoirs prediction in the third Member of Shehajie formation, southern of the Western Sag of Liaohe Depression[D]. Daqing Heilongjiang: Northeast Petroleum University, 2013(in Chinese). [38] Jon Gluyas, 王菁. 压实砂的孔隙度预测[J]. 国外油气勘探, 1999, 11(4): 408-416. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWQY199904002.htmJon G, Wang J. Porosity prediction of compacted sand[J]. Foreign oil and gas exploration, 1999, 11(4): 408-416(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWQY199904002.htm -





 下载:
下载: