Deformation characteristics of building foundation under different action modes of landslide
-
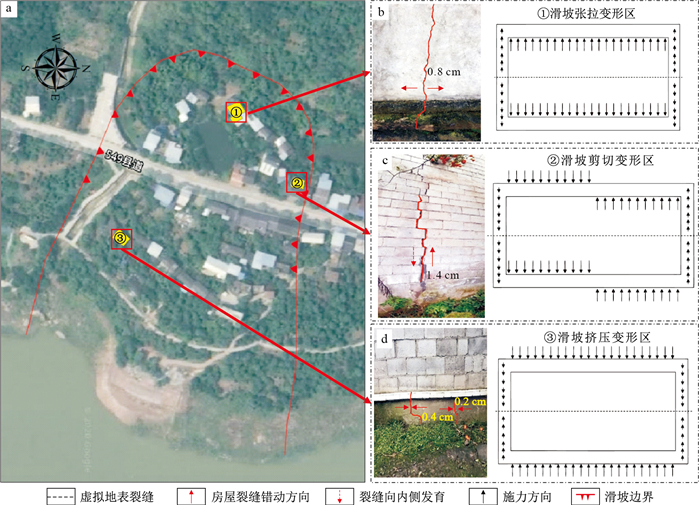
摘要: 受地形条件限制,我国西南山区大量房屋修建在滑坡上,存在安全隐患。探明滑坡对其上房屋的作用机理,科学指导滑坡上房屋设计和防护,对保障居民生命财产安全、促进人地和谐发展具有重要意义。基础是滑坡对其上房屋作用的直接对象,因此,以砌体结构房屋基础为研究对象,采用室内物理实验和数值模拟相结合的方法,对比分析试验与模拟中基础的变形特征,验证数值模型边界设置的可靠性,开展房屋基础在滑坡不同作用模式下变形破坏特征的研究。结果表明:建筑物基础在滑坡缓慢变形作用下的破坏模式可归纳为3种:张拉、剪切和挤压模式;房屋裂缝发育的位置与滑坡地表裂缝位置关系密切,随着滑坡主滑方向与房屋基础夹角的增大,房屋基础破坏越严重。因此,在房屋的选址和设计时,应优先利用滑坡挤压区或减小房屋长边中轴线与滑坡主滑方向的夹角。Abstract: Due to the topographic conditions, a large number of houses are built on the landslide in the southwest mountainous area, which have potential safety hazard. It is of great significance to explore the action mechanism between landslide and buildings and scientifically guide the design and protection of houses on landslide, so as to ensure the safety of residents' lives and property and promote the harmonious development of people and land. The foundation is the direct object of the landslide on the house. Therefore, taking the masonry structure house foundation as the research object, the deformation characteristics of the foundation in the test and simulation are compared and analyzed by using the method of physical experiment and numerical simulation, the reliability of the boundary setting of the numerical model is verified, and the deformation and failure characteristics of the house foundation under different landslide action modes are studied. The results show that the failure modes of building foundation under the slow deformation of landslide can be summarized into three modes: tension, shear and compression; The location of house crack development is closely related to the location of landslide surface crack. With the increase of the included angle between the main sliding direction of landslide and house foundation, the house foundation damage becomes more and more serious. Therefore, in the site selection and design of houses, priority should be given to the use of landslide extrusion area or reducing the included angle between the central axis of the long side of the house and the main sliding direction of the landslide.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- foundation /
- failure modes
-
表 1 实验方案设计
Table 1. Design of the experimental scheme
方案 模型大小/m 荷载/Pa 物理模型实验参数 数值模型试验参数 材料配比(水泥∶河沙∶碎石∶水)质量比 弹性模量/(N·mm-2) 泊松比 1 1.2×0.6×0.06 13 162 1∶1.6∶3.1∶0.5 2 200 0.2 2 1∶1.6∶3.0∶0.5 2 180 3 1∶1.6∶3.2∶0.5 2 220 表 2 房屋基础在不同作用模式下的变形特征
Table 2. Deformation characteristics of foundation under different action
作用模式 角度α/(°) 最大主应力/Pa 最大位移/mm 破坏影响范围 最大应变με 应变集中点 变形特征 张拉作用 0 80 283.0 7.00 基础长边右侧 0.306 00 基础长边中部 裂缝发育从基础长边中部开始,基础长短边转角处破坏最严重 剪切作用 45 77 082.0 2.66 基础长边3/4 0.120 99 距基础短边固定端1/4处 裂缝在错断面处开始发育,随着角度的增加,错断面向基础长边受力端一侧移动,且位移传递的影响范围变小 60 27 602.9 2.50 基础长边5/8 0.109 80 距基础短边固定端3/8处 75 28 917.0 2.79 基础长边3/5 0.112 70 距基础短边固定端2/5处 90 8 807.0 3.80 基础长边右侧 0.118 40 基础长边中部 挤压作用 180 59 350.0 3.40 基础长边右侧 0.170 00 基础长边中部 基础整体位移偏小,基本无破坏 -
[1] Matteo D S, Diego D M, Silvia B, et al. Assessment of landslide-induced damage to structures: The agnone landslide case study (Southern Italy)[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2019, 78(4): 2387-2408. doi: 10.1007/s10064-018-1303-9 [2] Li G R, Lei Y L, Yao H J, et al. The influence of land urbanization on landslides: An empirical estimation based on Chinese provincial panel data[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 595: 681-690. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.258 [3] Xu D D, Peng L, Liu S Q, et al. Influences of risk perception and sense of place on landslide disaster preparedness in southwestern China[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science, 2018, 9(2): 167-180. doi: 10.1007/s13753-018-0170-0 [4] 黄发明, 陈佳武, 唐志鹏, 等. 不同空间分辨率和训练测试集比例下的滑坡易发性预测不确定性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(6): 1155-1169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202106008.htmHuang F M, Chen J W, Tang Z P, et al. Uncertainty of landslide susceptibility prediction with different spatial resolutions and training test set ratios[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(6): 1155-1169 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202106008.htm [5] Luigi B, Gianfranco N, Settimio F, et al. Geology, slow-moving landslides, and damages to buildings in the Verbicaro area (north-western Calabria region, southern Italy)[J]. Journal of Maps, 2018, 14(2): 32-44. doi: 10.1080/17445647.2018.1425164 [6] 杨永刚, 殷坤龙, 赵海燕, 等. 基于C5.0决策树-快速聚类模型的万州区库岸段乡镇滑坡易发性区划[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 189-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906023.htmYang Y G, Yin K L, Zhao H Y, et al. Landslide susceptibility zoning of townships in the reservoir bank section of Wanzhou District based on C5.0 decision tree-fast clustering model[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 189-197 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906023.htm [7] 覃瀚萱, 桂蕾, 余玉婷, 等. 基于滑坡灾害预警分级的应急处置措施[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 187-195. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0412Qin H X, Gui L, Yu Y T, et al. Emergency disposal measures based on landslide hazard warning classification[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 187-195 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0412 [8] 张望喜, 段连蕊, 廖莎, 等. 基于ABAQUS的砌体结构动力弹塑性时程分析[J]. 建筑结构, 2016, 46(1): 64-70, 86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCJG201601011.htmZhang W X, Duan L R, Liao S, et al. ABAQUS-based dynamic elastoplastic time analysis of masonry structures[J]. Building Structure, 2016, 46(1): 64-70, 86(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCJG201601011.htm [9] Varum H, Costa A, Fonseca J, et al. Behaviour characterization and rehabilitation of adobe construction[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015, 114: 714-721. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.08.015 [10] 郑妮娜, 李英民, 潘毅. 心柱式构造柱约束的低层砌体结构抗震性能[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2011, 46(1): 24-29, 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2011.01.004Zheng N N, Li Y M, Pan Y. Seismic performance of low-rise masonry structures restrained by core-column type structural columns[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011, 46(1): 24-29, 55(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2011.01.004 [11] Papathoma-Kohle M, Gems B, Sturm M, et al. Matrices, curves and indicators: A review of approaches to assess physical vulnerability to debris flows[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 171: 272-288. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.06.007 [12] 陈伟涛, 和海霞, 杨思全, 等. 重大自然灾害房屋倒塌程度高分辨率遥感识别方法: 以舟曲特大泥石流灾害为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2014, 33(6): 197-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201406029.htmChen W T, He H X, Yang S Q, et al. A high-resolution remote sensing identification method for house collapse degree of major natural disasters: An example of Zhouqu mudslide disaster[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(6): 197-202(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201406029.htm [13] 吴越, 刘东升, 李明军. 滑体下滑及冲击受灾体过程中的能耗规律模型试验[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(4): 693-701. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201104008.htmWu Y, Liu D S, Li M J. Modeling the energy consumption law during slide slide and impact impact[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(4): 693-701(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201104008.htm [14] 吴越, 刘东升, 张小飞, 等. 滑坡灾害易损性定量评估模型应用与比较[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2012, 8(5): 916-921. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE201205004.htmWu Y, Liu D S, Zhang X F, et al. Application and comparison of quantitative assessment models for landslide hazard vulnerability[J]. Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2012, 8(5): 916-921(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE201205004.htm [15] Luo H Y, Zhang L L, Zhang L M. Progressive failure of buildings under landslide impact[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16(7): 1327-1340. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01164-0 [16] Chen Q, Chen L X, Gui L, et al. Assessment of the physical vulnerability of buildings affected by slow-moving landslides[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2020, 20(9): 2547-2565. doi: 10.5194/nhess-20-2547-2020 [17] Kappes M S, Papathoma-Köhle M, Keiler M. Assessing physical vulnerability for multi-hazards using an indicator-based methodology[J]. Applied Geography, 2012, 32(2): 577-590. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2011.07.002 [18] Peduto D, Ferlisi S, Nicodemo G, et al. Empirical fragility and vulnerability curves for buildings exposed to slow-moving landslides at medium and large scales[J]. Landslides, 2017, 14(6): 1993-2007. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0826-7 [19] Aditi S D P, Kanungo S P. A modified approach for semi-quantitative estimation of physical vulnerability of buildings exposed to different landslide intensity scenarios[J]. Georisk: Assessment and Management of Risk for Engineered Systems and Geohazards, 2019, 13(1): 66-81. doi: 10.1080/17499518.2018.1501076 [20] Fotopoulou S D, Pitilakis K D. Vulnerability assessment of reinforced concrete buildings subjected to seismically triggered slow-moving earth slides[J]. Landslides, 2013, 10(5): 563-582. doi: 10.1007/s10346-012-0345-5 [21] Negulescu C, Foerster E. Parametric studies and quantitative assessment of the vulnerability of a RC frame building exposed to differential settlements[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Science, 2010, 10(9): 1781-1792. doi: 10.5194/nhess-10-1781-2010 [22] 秦杰, 朱炯, 黄达海, 等. 砌体房屋受地表变形的有限元分析[J]. 工业建筑, 2002, 32(5): 41-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8993.2002.05.012Qin J, Zhu J, Huang D H, et al. Finite element analysis of masonry houses subjected to ground deformation[J]. Industrial Building, 2002, 32(5): 41-44(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8993.2002.05.012 [23] 梁为民, 李想, 乔俊凤. 受采动曲率变形影响的地基对建筑物基础的力学作用[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2012, 32(4): 93-96, 104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYK201204030.htmLiang W M, Li X, Qiao J F. Mechanical effect of foundation on building foundation affected by mining curvature deformation[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2012, 32(4): 93-96, 104(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYK201204030.htm [24] 由丽雯, 刘文生. 考虑附加应力的采动沉陷区建筑物设计[J]. 辽宁科技大学学报, 2011, 34(3): 264-270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1048.2011.03.010You L W, Liu W S. Design of buildings in mining subsidence areas considering additional stresses[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Science and Technology, 2011, 34(3): 264-270(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1048.2011.03.010 [25] 吴一川. 采动区新建抗变形房屋基础圈梁的设计问题[J]. 矿山测量, 1987(4): 39-44, 63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KSCL198704009.htmWu Y C. Design of foundation ring beams for new deformation-resistant houses in mining areas[J]. Mine Survey, 1987(4): 39-44, 63(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KSCL198704009.htm [26] 曹文贵, 袁青松, 胡卫东. 临坡矩形浅基础地基极限承载力的上限分析[J]. 湖南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 43(11): 86-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2974.2016.11.013Cao W G, Yuan Q S, Hu W D. Upper limit analysis of ultimate bearing capacity of slope facing rectangular shallow foundation foundation[J]. Journal of Hunan University : Natural Science Edition, 2016, 43(11): 86-94 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2974.2016.11.013 [27] 梁海洋. 西安地裂缝调查: 对房屋条形基础破坏机理研究[D]. 西安: 西安工业大学, 2017.Liang H Y. Investigation of ground cracks in Xi'an: Study on the damage mechanism of house strip foundation[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [28] 王腾飞, 李远耀, 曹颖, 等. 降雨型浅层土质滑坡非饱和土-水作用特征试验研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 181-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906022.htmWang T F, Li Y Y, Cao Y, et al. Experimental study on unsaturated soil-water interaction characteristics of rainfall-type shallow soil landslide[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 181-188 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906022.htm -





 下载:
下载: