Distribution and influencing factors of soil selenium and iodine in Limushan-Wanling, Qiongzhong area
-
摘要: 琼中黎母山-湾岭地区位于海南岛中部,调查发现该地区土壤同时具有富硒、富碘的特征。以研究区表层(0~20 cm)、中层(80~100 cm)、深层(180~200 cm)土壤样品分析结果为基础,探讨了土壤硒、碘的分布特征及其影响因素。结果显示,表层土壤中Se、I质量分数具有高正相关性,并与高程为正相关关系,结合已有研究成果,推断在研究区范围内降雨作用是研究区表层土壤Se、I质量分数空间分布格局的关键影响因素。通过分析表层、中层、深层土壤Se、I质量分数与土壤pH值、总有机碳(TOC)、Al2O3、Fe2O3质量分数的相关关系和变化规律,总结了研究区Se、I在土壤垂向剖面上的赋存、迁移规律。这些结果可为当地优质土地资源的高效利用提供科学依据,也可为土壤Se来源、迁移研究提供新的证据。Abstract: Qiongzhong Limushan-Wanling area is located in the middle of Hainan Island, where has an abundance of selenium-rich and iodine-rich soil resources.The distribution characteristics of Se and I contents were analyzed based on the analysis results of soil samples in the topsoil (0-20 cm), middle-layer-soil(80-100 cm), and deep-soil (180-200 cm) of the study area.The correlation characteristics of Se and I in soil and their relationship with elevation potentially indicate that the input of rainfall to soil Se and I is a key factor leading to the enrichment of Se and I.By analyzing the correlation and change law between the contents of Se, I and the contents of pH, soil organic matter, Al2O3 and Fe2O3 in top, middle and deep layer soil, the enrichment and migration of Se and I in the vertical section of soil in the study area was summarized.These results can provide scientific basis for the efficient use of local high-quality land resources and provide new evidence for the study of soil Se source and migration.
-
Key words:
- Qiongzhong area /
- soil /
- Se /
- I /
- precipitation
-
图 3 研究区表层(a, b)-中层(c, d)-深层(e, f)土壤Se、I质量分数分布图
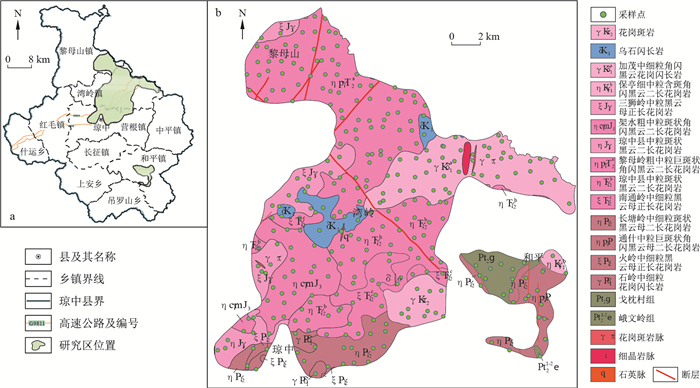
γπK.中白垩世花岗斑岩;ηγJ3.晚侏罗世二长花岗岩;γδP1.早二叠世花岗闪长岩;δK1.早白垩世闪长岩;γδK1.早白垩世黑云花岗闪长岩;ηγK1.早白垩世二长花岗岩;ξγJ3.晚侏罗世正长花岗岩;ηγT2.中三叠世二长花岗岩;ξγT2.中三叠世正长花岗岩;ηγP2.中二叠世二长花岗岩;ξγP2.中二叠世正长花岗岩;Pt2g.戈枕村组黑云斜长片麻岩;Pt21-2e.峨文岭组石英云母片岩;l.细晶岩脉
Figure 3. Se and I content distribution in the top (a, b), middle (c, d) and deep (e, f) soil of the study area
图 4 不同成壤母岩形成的土壤Se、I平均质量分数柱状图(地质体代号同图 3)
Figure 4. Bar graph of soil selenium and iodine contents by different soil parent rocks
表 1 各指标分析方法及检出限
Table 1. Analytical methods and detection limits of various indicators
指标 分析方法 检出限 单位 Se AFS 0.010 0 mg/kg I COL 0.350 0 mg/kg pH ISE 0.100 0 无量纲 TOC VOL 0.030 0 % Hg AFS 0.000 5 mg/kg Al2O3 XRF 0.050 0 % Fe2O3 ICP-AES 0.050 0 % 表 2 研究区土壤Se、I丰缺划分界线及特征
Table 2. Abundance and deficiency demarcation value of soil selenium and iodine
全量w(Se)/
(mg·kg-1)硒效应 样品数(占比/%) 全量w(I)/
(mg·kg-1)碘效应 样品数(占比/%) 表层 中层 深层 表层 中层 深层 < 0.125 硒不足 20(6.6) 57(18.8) 113(37.2) < 1 碘不足 40(13.2) 67(22.0) 100(32.9) [0.125, 0.175) 硒潜在不足 11(3.6) 37(12.2) 37(12.2) [1, 1.5) 碘潜在不足 27(8.9) 23(7.6) 34(11.2) [0.175, 0.4) 足硒 140(46.1) 127(41.8) 114(37.5) [1.5, 5) 足碘 80(26.3) 106(34.9) 120(39.5) [0.4, 3) 富硒 133(43.8) 83(27.3) 40(13.2) [5, 100) 富碘 157(51.6) 108(35.5) 50(16.4) ≥3 硒中毒 0 0 0 ≥100 碘中毒 0 0 0 表 3 不同成壤母岩形成的土壤Se、I平均质量分数
Table 3. Comparison of soil selenium and iodine contents by different soil parent rocks
地质体 数量/
个w(Se)/(mg·kg-1) w(I)/(mg·kg-1) 表层 中层 深层 表层/深层 表层 中层 深层 表层/深层 ξγT2 18 0.39 0.27 0.18 2.17 5.61 4.04 2.67 2.10 ξγJ3 22 0.37 0.30 0.21 1.78 5.65 4.93 3.34 1.69 ηγT2 129 0.44 0.34 0.24 1.86 6.51 5.24 3.14 2.07 ηγP2 30 0.40 0.30 0.21 1.89 5.92 4.15 2.67 2.21 ηγJ3 23 0.35 0.23 0.18 1.89 5.28 3.57 3.26 1.62 γπK2 10 0.50 0.27 0.22 2.23 6.05 2.68 2.06 2.93 δK1 8 0.39 0.28 0.19 2.05 6.65 5.12 3.56 1.87 γδK1 45 0.37 0.31 0.22 1.69 4.46 3.61 2.24 2.00 Pt2g 9 0.41 0.43 0.26 1.58 6.03 6.52 3.58 1.60 注:地质体代号同图 1 表 4 不同土壤发生类型中Se、I质量分数与其他指标相关性
Table 4. Correlation between soil selenium, iodine contents and other indicators in various soil types
其他指标 砖红壤(n=274) 水稻土(n=30) 表层 中层 深层 表层 中层 深层 Se I Se I Se I Se I Se I Se I Se 0.855** 0.781** 0.720** 0.647** -0.042 -0.052 I 0.855** 0.781** 0.720** 0.647** -0.042 -0.052 pH -0.556** -0.476** -0.448** -0.353** -0.404** -0.327** -0.362* -0.163 -0.281* 0.235 -0.389* 0.242 TOC 0.350** 0.177** 0.323** 0.194** 0.307** 0.145** 0.513** 0.333* 0.643** 0.027 0.737** 0.005 Fe2O3 0.281** 0.330** 0.176** 0.369** 0.172** 0.420** 0.491** 0.411* 0.327 0.244 0.074 0.247 Al2O3 0.470** 0.480** 0.329** 0.432** 0.302** 0.436** 0.410* 0.346 0.017 0.203 -0.161 0.265 Hg 0.499** 0.312** 0.488** 0.407** 0.753** 0.595** 0.600** 0.311 0.682** 0.046 0.721** 0.078 注:n为样品数量;**表示在0.01级别相关性显著;*表示在0.05级别相关性显著;统计过程中,删除了表层砖红壤TOC离群数据点1个,删除了表层、中层砖红壤Hg离群数据点各4个 表 5 高程与土壤中Se、I、TOC质量分数以及pH值的相关性
Table 5. Correlation between elevation and soil selenium, iodine contents, TOC, pH
高程-Se质量分数 高程-I质量分数 高程-TOC质量分数 高程-pH值 相关系数 P 相关系数 P 相关系数 P 相关系数 P 表层 0.302 < 0.01 0.309 < 0.01 0.086 0.135 -0.146 0.011 < 0.05 中层 0.105 0.069 0.087 0.129 0.058 0.312 -0.116 0.043 < 0.05 深层 0.040 0.492 0.065 0.257 0.005 0.925 -0.134 0.020 < 0.05 表 6 不同类型岩石中Se的质量分数
Table 6. Selenium contents in various rock types
表 7 不同高程范围内样品土壤发生类型分布
Table 7. Distribution of soil types in various elevation ranges
高程/m [50, 100] (100, 150] (150, 200] (200, 250] (250, 300] (300, 350] (350, 400] (400, 450] 水稻土 数量/个 1 3 11 3 7 4 1 0 占比/% 50.0 15.8 15.9 3.2 8.3 16.0 11.1 0.0 砖红壤 数量/个 1 16 58 91 77 21 8 2 占比/% 50.0 84.2 84.1 96.8 91.7 84.0 88.9 100.0 -
[1] Fordyce F M, Guangdi Z, Green K, et al. Soil, grain and water chemistry in relation to human selenium-responsive diseases in Enshi District, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(1): 117-132. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00035-9 [2] Johnson C C, Fordyce F M, Rayman M P. Symposium on "geographical and geological influences on nutrition" factors controlling the distribution of selenium in the environment and their impact on health and nutrition[J]. Proc. Nutr. Soc., 2010, 69(1): 119-132. doi: 10.1017/S0029665109991807 [3] Huang Y, Wang Q X, Gao J, et al. Daily dietary selenium intake in a high selenium area of Enshi, China[J]. Nutrients, 2013, 5(3): 700-710. doi: 10.3390/nu5030700 [4] Dinh Q T, Cui Z W, Huang J, et al. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: A review[J]. Environment International, 2018, 112: 294-309. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.035 [5] Jones G D, Droz B, Greve P, et al. Selenium deficiency risk predicted to increase under future climate change[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2017, 114(11): 2848-2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611576114 [6] Liu H L, Wang X Q, Zhang B M, et al. Concentration and distribution of selenium in soils of mainland China, and implications for human health[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 220: 106654. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106654 [7] 周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 319-336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS202003002.htmZhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 319-336(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS202003002.htm [8] Matos R P, Lima V M P, Windmöller C C, et al. Correlation between the natural levels of selenium and soil physicochemical characteristics from the Jequitinhonha Valley (MG), Brazil[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 172: 195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.11.001 [9] Ni R X, Luo K L, Tian X L, et al. Distribution and geological sources of selenium in environmental materials in Taoyuan County, Hunan Province, China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2016, 38(3): 927-938. doi: 10.1007/s10653-015-9772-2 [10] 程湘, 李福林, 王成刚, 等. 鄂西地层硒的分布、富硒岩石成因及硒的来源[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 45-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902006.htmCheng X, Li F L, Wang C G, et al. Distribution and source of selenium in western Hubei and the genesis of the rocks rich in selenium[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 45-52(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902006.htm [11] Lei W S, Cicchella D, Liu T, et al. Origin, distribution and enrichment of selenium in oasis farmland of Aksu, Xinjiang, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2021: 106723. [12] Li M L, Yang B Y, Xu K Y, et al. Distribution of Se in the rocks, soil, water and crops in Enshi County, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2020, 122: 104707. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104707 [13] 陈锦平, 刘永贤, 曾成城, 等. 降雨对土壤硒迁移转化的影响研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志. 2019, 38(6): 1909-1915. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201906035.htmChen J P, Liu Y X, Zeng C C, et al. Research advances in the effects of rainfall on soil selenium migration and transformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(6): 1909-1915(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201906035.htm [14] Sun G X, Meharg A A, Li G, et al. Distribution of soil selenium in China is potentially controlled by deposition and volatilization?[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 20953. doi: 10.1038/srep20953 [15] 田欢. 典型富硒区岩石-土壤-植物中硒的赋存状态及环境行为研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2017.Tian H. The occurrence state and speciation of selenium and its environmental behaviors in rock-soil-plant from typical high-Se areas[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] Yu T, Yang Z, Lü Y, et al. The origin and geochemical cycle of soil selenium in a Se-rich area of China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 139: 97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.09.006 [17] Blazina T, Sun Y, Voegelin A, et al. Terrestrial selenium distribution in China is potentially linked to monsoonal climate[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 4717. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5717 [18] 杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等. 海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 837-849. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.001Yang Z F, Yu T, Hou Q Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5): 837-849(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.001 [19] 傅杨荣. 海南岛土壤地球化学与优质农业研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2014.Fu Y R. Studies on soil geochemistry and high-quality agriculture in Hainan Island[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 张黎明, 魏志远, 漆智平. 近30年海南不同地区降雨量和蒸发量分布特征研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(4): 403-407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2006.04.108Zhang L M, Wei Z Y, Qi Z P. Characteristics of rainfall and evaporation of different region in recent 30 years in Hainan Province[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2006, 22(4): 403-407(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2006.04.108 [21] 谭见安. 中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989.Tan J A. The atlas of endemic diseases and their environment in the People's Republic of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989(in Chinese). [22] 中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990.China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Press, 1990(in Chinese). [23] 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.Chi Q H, Yan M C. Handbook of elemental abundance for applied geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007(in Chinese). [24] 鄢明才, 迟清华. 中国东部地壳与岩石的化学组成[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997.Yan M C, Chi Q H. The chemical compositions of crust and rocks in the eastern part of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997(in Chinese). [25] 郭跃品, 杨奕, 张固城, 等. 海南省土地质量地球化学评估[R]. 海口: 海南省地质调查院, 2011.Guo Y P, Yang Y, Zhang G C, et al. Geochemical assessment of land quality in Hainan Province[R]. Haikou: Hainan Geological Survey, 2011(in Chinese). [26] Whitehead D C. The distribution and transformations of iodine in the environment[J]. Environment International, 1984, 10(4): 321-339. doi: 10.1016/0160-4120(84)90139-9 [27] Johanson K J. Iodine in soil[J]. Technical Report, 2000, 1(21): 42-48. [28] 朱发庆, 谭见安. 我国降水、降尘中硒、碘、氟的研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 1988, 8(4): 428-437. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX198804005.htmZhu F Q, Tan J A. Selenium, iodine and fluorine in rainwater and dustfall in China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1988, 8(4): 428-437(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX198804005.htm [29] Wen H J, Carignan J. Reviews on atmospheric selenium: Emissions, speciation and fate[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 41(34): 7151-7165. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.07.035 [30] Blazina T, Läderach A, Jones G D, et al. Marine primary productivity as a potential indirect source of selenium and other trace elements in atmospheric deposition[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 51(1): 108-118. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27959548 [31] Suess E, Aemisegger F, Sonke J E, et al. Marine versus continental sources of iodine and selenium in rainfall at two european high-altitude locations[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(4): 1905-1917. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000041599120999_b7c1.html [32] 温新平, 陈永祥, 王三祥, 等. 山西省水土含硒量及大骨节病区的海拔分布[J]. 广东微量元素科学, 1996, 3(2): 61-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYS602.017.htmWen X P, Chen Y X, Wang S X, et al. Selenium content in water, soil of Shanxi Province and effects of sea-level elevation on Kaschin-Beck disease endemic areas[J]. Guangdong Trace Elements Science, 1996, 3(2): 61-64(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYS602.017.htm [33] 张晓平, 张玉霞. 西藏土壤中硒的含量及分布[J]. 土壤学报, 2000, 37(4): 558-562. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2000.04.018Zhang X P, Zhang Y X. Content and distribution of selenium in soils of Tibet[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2000, 37(4): 558-562(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2000.04.018 [34] 章海波, 骆永明, 吴龙华, 等. 香港土壤研究: Ⅱ. 土壤硒的含量、分布及其影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2005, 42(3): 404-410. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2005.03.009Zhang H B, Luo Y M, Wu L H, et al. Hong Kong soil researches: Ⅱ. Distribution and content of selenium in soils[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2005, 42(3): 404-410(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2005.03.009 [35] 王晓杰, 孟凡乔, 吴文良. 内蒙古武川县土壤硒分布特性研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(3): 624-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201603018.htmWang X J, Meng F Q, Wu W L. Distribution patterns of soil Se in Wuchuan County, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(3): 624-629(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201603018.htm [36] Xu Y F, Li Y H, Li H R, et al. Effects of topography and soil properties on soil selenium distribution and bioavailability (phosphate extraction): A case study in Yongjia County, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 633: 240-248. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.190 [37] 邵亚. 桂林富硒长寿区小流域地理环境中硒分布特征、控制因素及其生态效应[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2019.Shao Y. Distribution characteristics, controlling factors and ecological effects of Se in the geographical environment of small watershed in Guilin Se-enriched longevity area[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [38] 廖金凤. 海南岛生态环境中的硒[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版, 1992, 31(3): 110-116. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.1992.03.001Liao J F. Selenium in the ecological environment of Hainan Island[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 1992, 31(3): 110-116(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.1992.03.001 [39] 傅抱璞. 地形和海拔高度对降水的影响[J]. 地理学报, 1992, 47(4): 302-314. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1992.04.003Fu B P. The effects of topography and elevation on precipitation[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1992, 47(4): 302-314(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1992.04.003 [40] Germann U, Joss J. Spatial continuity of alpine precipitation[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part B: Hydrology, Oceans and Atmosphere, 2000, 25(10): 903-908. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S1464190900001234&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1414134409&md5=e4a928332576c1ebe0b82c5aeb6fa2f3 [41] Sevruk B, Nevenic M. The geography and topography effects on the areal pattern of precipitation in a small prealpine basin[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1998, 37(11): 163-170. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0273122398003291 [42] 丁昌璞, 保学明, 潘淑贞, 等. 土壤氧化还原状况的空间分异和特征[J]. 土壤学报, 1993, 30(3): 289-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB199303007.htmDing C P, Bao X M, Pan S Z, et al. Spatial variation and characteristics of oxidation-reduction regime in soils[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1993, 30(3): 289-296(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB199303007.htm [43] 丁昌璞. 中国自然土壤、旱作土壤、水稻土的氧化还原状况和特点[J]. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(1): 66-75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2008.01.009Ding C P. Oxidation-reduction regimes and characteristics of natural soil, upland soil and paddy soil in China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008, 45(1): 66-75(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2008.01.009 [44] Fordyce F M. Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment[M]. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2012. [45] Yuita K. Dynamics of iodine, bromine, and chlorine in soil: Ⅱ. Chemical forms of iodine in soil solutions[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 1992, 38(2): 281-287. doi: 10.1080/00380768.1992.10416491 [46] 武少兴, 龚子同, 黄标. 土壤中的碘与人类健康[J]. 土壤通报, 1998, 29(3): 44-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB803.015.htmWu S X, Gong Z T, Huang B. Iodine in the soil and human health[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1998, 29(3): 44-47(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB803.015.htm [47] Whitehead D C. The sorption of iodide by soil components[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 1974, 25(1): 73-79. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740250109 [48] Dai J L, Zhang M, Zhu Y G. Adsorption and desorption of iodine by various Chinese soils[J]. Environment International, 2004, 30(4): 525-530. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2003.10.007 [49] 付中彪, 何宁洁, 鲍征宇, 等. 赣南地区水稻-根系土系统中硒含量影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 220-229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905024.htmFu Z B, He N J, Bao Z Y, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of selenium content in rice-root soil system in southern Jiangxi[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 220-229(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905024.htm [50] Liu Y L, Tian X L, Liu R, et al. Key driving factors of selenium-enriched soil in the low-Se geological belt: A case study in Red Beds of Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Catena, 2021, 196: 104926. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104926 [51] Fordyce F. Selenium geochemistry and health[J]. Ambio., 2007, 36(1): 94-97. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[94:SGAH]2.0.CO;2 -





 下载:
下载: