Discussion of geological hazard data management and application model in big data era
-
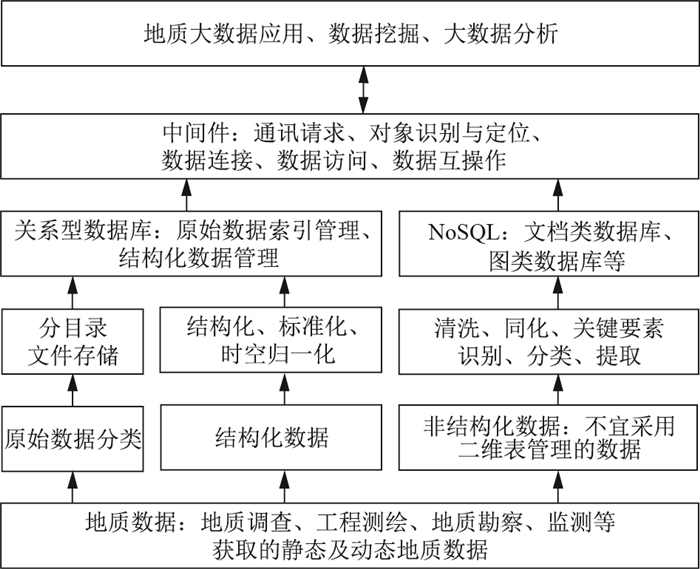
摘要: 地质灾害数据是一种多源异构数据,是典型的大数据。关系型数据库是目前地质灾害数据的主流管理方法。在地质灾害数据中,非结构化数据占有很大的比例。由于关系模型难以有效地管理非结构化数据,因而关系型数据库对地质灾害数据的管理效果并不理想。这种弱点,在大数据时代将会被进一步放大,并对地质数据挖掘和大数据分析造成一定的影响。针对大数据时代地质灾害数据的管理模式,从泛结构化地质数据管理、应用模型和分布式异构系统的集成等方面进行了探讨。认为地质灾害数据的有效管理应该把文件系统、关系型数据库和NoSQL结合起来,并提出了一种基于双C模型和中间件结合的泛结构化地质数据管理与应用模式。这种模式已应用在多个工程中,取得了良好的效果。Abstract: Geological disaster data is a kind of multi-source heterogeneous data with multi-source, large quantity, multi-type, multi-format, multi-scale and multi-precision.It is a typical "big data".Relational database is the mainstream management method of geological disaster data at present.There are a large proportion of unstructured data in geological disaster data.Because it is difficult to manage unstructured data effectively by using relational model, the effect of this management method is not ideal.This weakness will be further amplified in the era of big data, and will have a certain impact on geological data mining and big data analysis.This paper focuses on the management mode of geological disaster data in the era of big data.Discusses the management of pan-structured geological data, application model and integration of distributed heterogeneous system.It is considered that the effective management of geological disaster data should combine file system, relational database and NoSQL, and a pan-structured geological data management and application mode based on the combination of double C model and middleware is proposed.The double C model has an implicit internal data access and management center and an explicit outer analysis and application center.Through the double C model, a variety of work can be integrated into a simple and orderly whole, such as geological data collection, management, statistics, calculation, retrieval, geological map compilation, three dimensional modeling, attribute analysis, spatial analysis and so on.
-
Key words:
- big data /
- pan-structured geological data /
- relational databases /
- NoSQL /
- double C model /
- middleware
-
表 1 钻孔孔径记录表结构示例
Table 1. Structure of borehole aperture record table
序号 字段名称 字段编号 字段类型 字段长度 小数位 1 工程名称 GCEABA 字符型 20 2 勘察阶段 GCJBA 字符型 14 3 钻孔编号 GCJCBN 字符型 10 4 孔径序号 IOTXH 字符型 2 5 钻孔直径/mm SWNCALZ 数值型 4 0 6 终止深度/m MDBWAC 数值型 6 2 注:表中的字段编号是对应字段的标准识别码 -
[1] 吴润泽, 程温鸣, 刘军旗, 等. 三峡库区地质灾害防治信息系统及预警指挥系统数据管理模式探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2018, 29(5): 102-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201805017.htmWu R Z, Chen W M, Liu J Q, et al. Discussion on the data management mode of geologic disaster prevention and control information system and early warning command system in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(5): 102-107(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201805017.htm [2] Viktor M-S, Kenneth C. Big data: A revolution that will transform how we live, work, and think[M]. Eamon Dolan: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2013. [3] Li D R. Towards geo-spatial information science in big data Era[J]. Acta Geodetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2016, 45(4): 379-384. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201604002.htm [4] He F H, Gu L J, Wang T, et al. The synthetic geo-ecological environmental evaluation of a coastal coal-mining city using spatiotemporal big data: A case study in Longkou, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 142(2): 854-866. [5] 刘军旗, 黄长青, 吴冲龙, 等. 工程地质信息处理技术与方法概论[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2015.Liu J Q, Huang C Q, Wu C L, et al. Introduction to engineering geology information processing technology and method[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2015(in Chinese). [6] Baars H, Kemper H G. Management support with structured and unstructured data: An integrated business intelligence framework[J]. Information Systems Management, 2008, 25(2): 132-148. doi: 10.1080/10580530801941058 [7] 陈金水, 王崟. 非结构化数据存储管理的实用化方法[J]. 计算机与现代化, 2006(8): 25-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2475.2006.08.008Chen J S, Wang Y. A method for unstructured data storage management[J]. Computer and Modernization, 2006(8): 25-28(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2475.2006.08.008 [8] Carver T, Berriman M, Tivey A, et al. Artemis and ACT: Viewing, annotating and comparing sequences stored in a relational database[J]. Bioinformatics, 2008, 24(23): 2672-2676. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn529 [9] Sacco G M, Nigrelli G, Bosio A, et al. Dynamic taxonomies applied to a web- based relational database for geo-hydrological risk mitigation[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2012, 39: 182-187. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035031235010_465a.html [10] Chang F, Dean J, Ghemawat S, et al. Big table: A distributed storage system for structured data[J]. Acm Transactions on Computer Systems, 2008, 26(2): 205-218. http://web.stanford.edu/class/cs240/old/sp2014/readings/bigtable-osdi06.pdf [11] 吴广君, 王树鹏, 陈明, 等. 海量结构化数据存储检索系统[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2012, 49(增刊1): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ2012S1004.htmWu G J, Wang S P, Chen M, et al, Massive structured data oriented storageand retrieve system[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2012, 49(S1): 1-5(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ2012S1004.htm [12] Dean J, Ghemawat S. Mapreduce: Simplified data processing on large clusters[J]. Communications of the Acm, 2008, 51(1): 107-113. doi: 10.1145/1327452.1327492 [13] McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, et al. The genome analysis toolkit: A map reduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data[J]. Genome Research, 2010, 20(9): 1297-1303. doi: 10.1101/gr.107524.110 [14] 郎波, 张博宇. 面向大数据的非结构化数据管理平台关键技术[J]. 信息技术与标准化, 2013, 434(10): 53-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-539X.2013.10.013Lang B, Zhang B Y. Key techniques for building big-data-oriented unstructured data management platform[J]. Information Technology and Standardization, 2013, 434(10): 53-56(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-539X.2013.10.013 [15] O'Driscoll A, Daugelaite J, Sleator R D. "Big data", Hadoop and cloud computing in genomics[J]. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2013, 46(5): 774-781. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2013.07.001 [16] 张丰. 面向网格的海量时空数据访问、集成与互操作研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2007.Zhang F. Research on massivespatio-temporal data access, integration and interoperation for grid[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2007(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] Amorim R C, Castro J A, Silva J R, et al. A comparison of research data management platforms: architecture, flexible metadata and interoperability[J]. Universal Access in the Information Society, 2017, 16(4): 851-862. doi: 10.1007/s10209-016-0475-y [18] Heinzelman W B, Murphy A L, Carvalho H S, et al. Middleware to support sensor network applications[J]. Ieee Network, 2004, 18(1): 6-14. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2004.1265828 [19] 罗颖. 针对面向多源异构数据的数据集成中间件的设计与开发[J]. 网络安全技术与应用, 2019(6): 55-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6833.2019.06.032Luo Y. Design and development of data integration middleware for multi-source heterogeneous data[J]. Network Security Technology and Application, 2019, (6): 55-57(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6833.2019.06.032 [20] George G, Haas M, Pentland A. Big data and management[J]. Academy of Management Journal, 2014, 57(2): 321-326. doi: 10.5465/amj.2014.4002 [21] Cattell R. Scalable SQL and NoSQL data stores[J]. Sigmod Record, 2010, 39(4): 12-27. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Rick_Cattell/publication/220415613_Scalable_SQL_and_NoSQL_data_stores/links/568a189608ae1e63f1fabc20.pdf [22] Leavitt N. Will NoSQL databases live up to their promise?[J]. Computer, 2010, 43(2): 12-14. doi: 10.1109/MC.2010.58 [23] 申德荣, 于戈, 王习特, 等. 支持大数据管理的NoSQL系统研究综述[J]. 软件学报, 2013, 24(8): 1786-1803. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJXB201308008.htmShen D R, Yu G, Wang X T, et al. Survey on NoSQL for management of big data[J]. Journal of Software, 2013, 24(8): 1786-1803(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJXB201308008.htm [24] Liu J Q, Mao X P, Wu C L, et al. Study on a computing technique suitable for true 3D modeling of complex geologic bodies[J]. Journal Geological Society of India, 2013, 82: 570-574. doi: 10.1007/s12594-013-0189-1 [25] 刘军旗. 工程地质数据处理方法探讨: 以水利枢纽工程为例[J]. 工程地质学报, 2014, 22(5): 989-996. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201405035.htmLiu J Q. Engineering geological data processing method withwater conservancy hub project, as example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(5): 989-996(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201405035.htm [26] Keim D A, Panse C, Sips M, et al. Pixel based visual data mining of geo-spatial data[J]. Computers & Graphics-UK, 2004, 28(3): 327-344. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f1c5/589138d0b96923417e9be5b5eba0447db4dd.pdf [27] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 周琦, 等. 地质科学大数据统合应用的基本问题[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 1-11. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0401Wu C L, Liu G, Zhou Q, et al. Fundamental problems of integrated application of big data in geoscience[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0401 [28] Fan J Q, Han F, Liu H. Challenges of big data analysis[J]. National Science Review, 2014, 1(2): 293-314. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwt032 [29] 田宜平, 刘维安, 张夏林. 基于等角度变比例投影的矿体轮廓线自动匹配方法研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 175-180. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0119Tian Y P, Liu W A, Zhang X L. Automatic matching of ore body contour line based on equal-angle and variable proportion projection[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 175-180(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0119 [30] Noor A, Shukri M. Java based distributed multimedia data streaming with object request broker[D]. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: IEEE International Symposium on Information Technology, 2008. -





 下载:
下载: