Application of GF-2 remote sensing data for typical Quaternary stratigraphic survey in Gaizi River Basin
-
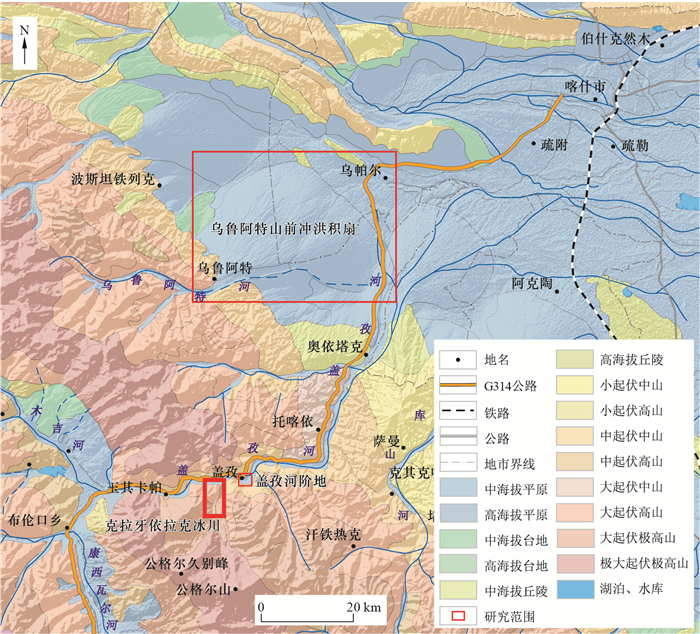
摘要: 国产高分辨率卫星遥感技术的发展为第四系宏观、局部及细部特征调查提供了新的手段。中巴经济走廊东段地区分布较多的冲洪积扇、河谷阶地、冰川堆积等地貌类型,为了研究国产高分数据在该地区第四纪地质调查中的适用性,以高分二号(GF-2)影像为主要数据源,借助数字高程模型构建三维场景,选取中巴公路沿线盖孜河流域乌鲁阿特山前冲洪积扇、盖孜河河谷阶地与克拉牙依拉克冰川堆积物3处典型第四纪地层为研究对象,建立了遥感解译标志,并进行了精细尺度遥感解译;经过野外实地验证,查明了其物质组成与变化规律,修正了前人关于克拉牙依拉克冰川不同期次冰碛物的划分范围;通过对盖孜河河谷阶地分析,盖孜河流域晚更新世以来经历了至少5次阶段性构造抬升,阶地基座冰碛物至少由两期冰川作用形成。研究表明,GF-2影像能快速从宏观尺度上识别地貌、松散堆积物变化特征,能够看到常规方法无法观察到的地质现象;满足大比例尺解译、制图要求,特别是在微地貌识别以及第四纪地层解译中,能够提升精细地质解译水平。研究成果能为盖孜河流域河流、冰川的发展演化过程研究提供基础地质资料,为中巴公路沿线第四纪土体遥感调查提供典型案例。Abstract: The development of domestic high resolution remote sensing satellite technology provides a new means for the investigation of macroscopic, local and detailed characteristics of the Quaternary.Alluvial-diluvial fans, valley terraces, glacial deposits are widely distributed in the eastern section of China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. In order to study the applicability of domestic high-resolution data in the Quaternary geological survey of this region, the alluvial and flood fan in front of Uruat mountain along Gaizi River basin of China-Pakistan highway and three typical Quaternary strata of Gaizi River valley terrace and Kraguirake glacial moraine were selected as the research objects in this study.Using domestic GF-2 images as the main data sources, with the aid of digital elevation model data, the remote sensing interpretation marker was established, and the fine geological interpretation was carried out.The composition and variation were found out through field verification.The previous distribution range of different periods of glacial moraines in Kailaillak was revised.Based on the analysis of the terrace in Gaizi River valley, the study area experienced at least five stages of tectonic uplift since late Epipleistocene, and the terrace base was formed by at least two stages of glaciation.This study shows that GF-2 images can not only quickly identify the change characteristics of landforms and loose deposits at macro scale, but also it can get geological phenomena that cannot be observed by conventional methods.And then it can meet the requirements of large scale interpretation and cartography.Especially in the identification of micro-geomorphology and interpretation of Quaternary strata, it can improve the level of fine geological interpretation.Research results can provide basic geological data for understanding the development and evolution process of fluvial and glaciation in the Gaizi River basin.Besides, this study can provide a typical example for remote sensing investigation of Quaternary soil mass along the China-Pakistan highway.
-
Key words:
- remote sensing /
- Quaternary /
- China-Pakistan highway /
- alluvial and flood fan /
- terrace /
- glacial till
-
图 4 克拉牙依拉克冰碛物解译结果(a)和立体影像(b, c)(图例同图 3)
Figure 4. Interpretation of Clathrate Irak glacial till (a) and three-dimensional images (b, c)
图 5 克拉牙依拉克冰川遗迹分布图(据文献[19])
Figure 5. Remnants of Clathrate Irak glaciation
表 1 GF-2卫星主要技术指标(据文献[27])
Table 1. Technical index of the GF-2 satelite
技术性能 轨道 轨道类型及高度 太阳同步回归轨道,631 km 重访、覆盖特性 无侧摆时,69天可完成全球无缝覆盖观测;侧摆23°时,全球任意地区重访周期不大于5天 观测能力 谱段/μm 全色:0.45~0.90 多光谱:0.45~0.52;0.52~0.59;0.63~0.69;0.77~0.89 星下点地面分辨率/m 全色谱段0.81,多光谱谱段3.24 地面幅宽, 定位精度/km >45, 平面无控制点50 姿态控制 控制方式;姿态指向精度;稳定度 三轴稳定,对地定向;≤0.05°(三轴,3σ);≤5×10-4°/s(三轴,3σ) 惯性空间测量精度 ≤0.003°(三轴,3σ) 姿态机动能力 侧摆±35°,35°范围内侧摆及稳定时间小于180 s 具有每轨侧摆2次的能力 表 2 山前冲洪积扇解译标志
Table 2. Interpretation marks of piedmont alluvial and diluvial fan
标志 描述 分布位置 位于山前河流出山口的广大倾斜平原上 形状 呈扇状 大小 大小不一,通常横向可达数十千米 色调 色调呈现过渡形式,但扇前缘地下水泄出带常出现色调突变 纹理 由扇顶至扇前缘,纹理由粗糙逐渐过渡为平滑 表 3 河流阶地解译标志
Table 3. Interpretation marlcs of river terrace
标志 描述 分布位置 位于河流两侧,高于河漫滩,越老的阶地离河床越远 色调 阶面色调均匀、较浅,阶坎色调较深且有阴影存在 形状 阶地表面较平坦,沿河床呈宽窄不等的条带状展布,组合为阶梯状(据文献[30]) 大小 阶地大小不一,高低不同 阴影 阶坎有阴影存在,阴影深浅、长宽随阶坎高低、倾角变化而变化 表 4 冰川冰碛物解译标志
Table 4. Interpretation marks of glacial drifts
标志 描述 分布位置 位于冰川冰舌的前缘及两侧,古冰川的冰碛物通常在现代冰川前缘及周边,分布范围较广 色调 现代冰川冰碛物多呈灰黑色,古冰川冰碛物由于有现代沉积物覆盖而呈黄色、浅黄色 形状 较新的冰川冰碛物多被保留在冰槽谷的两侧,呈细条带状;古冰川的冰碛物多呈台地、垄岗状 大小 因冰川规模大小及经后期改造的不同而不同 纹理 不同期次的冰碛物纹理不同,较老的冰碛物由于后期风化剥蚀夷平及现代沉积物覆盖,纹理平坦光滑;较新的冰碛物通常表面呈鳞片状,坑坑洼洼,高低不平 -
[1] 贾丽云, 叶培盛, 张绪教, 等. 新构造填图方法探索、应用与实践: 以内蒙古呼勒斯太苏木图幅1: 5万填图试点为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 2017, 23(2): 189-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.02.002Jia L Y, Ye P S, Zhang X J, et al. Application and practice of the neotectonic geological mapping methods: A case study of 1: 50000 mapping pilot in Hulesitai, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(2): 189-205(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.02.002 [2] 李辉, 余忠迪, 蔡晓斌, 等. 基于无人机遥感的河流阶地提取[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5): 734-742. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201705008.htmLi H, Yu Z D, Cai X B, et al. River terrace extraction based on unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(5): 734-742(in chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201705008.htm [3] 迟振卿, 张绪教, 李金洪, 等. 遥感技术在第四纪地质调查中的应用: 以南水北调中线工程天津干渠为例[J]. 第四纪研究, 1999, 19(3): 254-259. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.03.009Chi Z Q, Zhang X J, Li J H, et al. Application of remote sense technique in quaternary geological investigation: A case study in pre-constructing Tianjin trunk canal of northward diversion works from Changjiang River[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1999, 19(3): 254-259(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.03.009 [4] 张微, 杨金中, 王晓红. 基于特征地貌类型的湖州市第四纪地质遥感信息提取方法探讨[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2009, 21(3): 45-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG200903013.htmZhang W, Yang J Z, Wang X H. The remote sensing information extraction of Quaternary sediments based on geomorphologic information: A case study of Huzhou City[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2009, 21(3): 45-48(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG200903013.htm [5] 潘天录. 遥感技术在第四纪地质研究中的应用[J]. 四川地质研究中的应用, 2011, 31(4): 481-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201704117.htmPan T L. The application of remote sensing technology to the study of Quaternary geology[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2011, 31(4): 481-484(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201704117.htm [6] 戴文晗, 刘世丰. 遥感技术在深圳: 大亚湾沿海高速公路工程地质调查及选线中的应用[J]. 国土资源遥感, 1996, 18(2): 51-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG602.007.htmDai W H, Liu S F. The application of remote sensing technology in engineering geological investigation and the route selection of Shenzen: Dayawan coastal highway[J]. Remote sensing for land& resources, 1996, 18(2): 51-56(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG602.007.htm [7] 张绪教, 李团结, 陆平, 等. 卫星遥感在西藏安多幅1: 25万区域第四纪地质调查中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(1): 107-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200801017.htmZhang X J, Li T J, Lu P. et al. Application of satellite remote sensing to 1: 250000 regional Quaternary investigation in Amdo Sheet, Tibet[J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(1): 107-115(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200801017.htm [8] 张艳, 孙杰, 于长春, 等. 基于多源遥感数据的第四系覆盖物分类方法研究: 以内蒙古旗杆甸子幅1: 5万填图试点为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 281-290. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902034.htmZhang Y, Sun J, Yu C C. et al. Classification of quaternary coverings in desert grassland shallow cover area based on multi-source remote sensing data: A case of 1: 50000 pilot geological mapping in Qigandianzi, Inner Mongolia. [J]. Geological Science and Technology information, 2019, 38(2): 281-290(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902034.htm [9] 叶梦旎. 多源遥感数据在河套盆地第四纪地质与土地资源调查中的应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.Ye M N. The application of multi-source remote sensing data in Quaternary geology and tectonic mapping: Taking the 1: 50000 mapping pilot of the Hulesitaiarea, Inner Mongolia as an example[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] Fu B, Lin A, Kano K I, et al. Application of stereoscopic satellite images for studying Quaternary tectonics in arid regions[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2004, 25(3): 537-547(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1080/0143116031000150031 [11] 昝梅. 艾比湖阶地三维反演研究[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2010, 24(4): 126-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG201004027.htmZan M. A three-dimensional inversion study of ebinur terrace[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2010, 24(4): 126-130(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG201004027.htm [12] 秦绪文, 唐壮, 陈伟涛. 基于高分辨率卫星遥感技术的风化层厚度制图方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 195-201. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0321Qin X W, Tang Z, Chen W T. Weathered layer thickness mapping method based on high resolution satellite remote sensing technology[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 195-201(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0321 [13] 梁世川. 盖孜河水源地构造成因"跌水"分析及数值模拟[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2013.Liang S C. The tectonic origin analysis and numerical simulation model of the "head fall" phenomenon in Gaizi river water source[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [14] 刘慧中, 刘斌, 张静, 等. 盖孜河流域地下水水化学特征及生活饮用水分布[J]. 新疆地质, 2014, 32(4): 535-539. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201404025.htmLiu H Z, Liu B, Zhang J, et al. The characteristic of groundwater chemistry migration and the range of domestic drinking water quality distribution in Kashgar[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2014, 32(4): 535-539(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201404025.htm [15] 尚彦军, 李坤, 陈全君, 等. 奥布公路泥石流危险性评价[J]. 新疆地质, 2019, 37(3): 382-388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201903021.htmShang Y J, Li K, Chen Q J, et al. Risk evaluation of debris flow along Ao-Bu section of Karakoram highway[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2019, 37(3): 382-388(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201903021.htm [16] Yasmeen A, Javed I. Spatio temporal change of selected glaciers along Karakoram Highway from 1994-2017 using remote sensing and GIS techniques. ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, [J]. Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2018, 4(3): 7-11. [17] Shangguan D H, Liu S Y, Ding Y J, et al. Characterizing the May 2015 Karayaylak Glacier surge in the eastern Pamir Plateau using remote sensing[J]. Journal of Glaciology, 2016, 62(235): 944-953. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/cbeb/e3c06ee4f2044254032a5738e6b149030ffd.pdf [18] Zhang Z, Xu J L, Liu S Y, et al. Glacier changes since the early 1960s, eastern Pamir, China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2016, 13(2): 276-291. doi: 10.1007/s11629-014-3172-4 [19] 王杰, 周尚哲, 赵井东, 等. 东帕米尔公格尔山地区第四纪冰川地貌与冰期[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41(3): 6-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201103007.htmWang J, Zhou S Z, Zhao J D, et al. Quaternary glacial geomorphology and glaciations of Kongur Mountain, eastern Pamir[J]. China Science(Earth Science), 2011, 41(3): 6-13(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201103007.htm [20] 朱天行. 东帕米尔盖孜河流域地貌特征及区域构造活动关系研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019.Zhu T X. The geomorphology of the Gezi river drainage basin, eastern Pamir, and its relationship with regional tectonics[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [21] Chen S Q, Chen H L. Late Cenozoic activity of the Tashkurgan normal fault and implications for the origin of the Kongur Shan extensional system, Eastern Pamir[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2020, 31(4): 1-12. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/84134X/202004/7102548299.html [22] Yoshiki N, Fu B H. Extracting lithologic information from aster multispechral thermal infrared data in the Northeastern Pamirs[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2003, 21(1): 22-28. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/281162879_Extracting_lithologic_information_from_ASTER_multispectral_thermal_infrared_data_in_the_northeastern_Pamirs [23] Yoshiki N, Fu B H. Wide area lithologic mapping with ASTER thermal infrared data: Case studies for the regions in/around the Pamir Mountains and the Tarim Basin[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2017, 74(1): 1-4. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/74/1/012006/pdf [24] Alexander C, Robinson, An Y, et al. The role of footwall deformation and denudation in controlling cooling age patterns of detachment systems: An application to the Kongur Shan extensional system in the Eastern Pamir, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 496(1): 28-43. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195110004257 [25] 杨栓成, 魏学利, 陈宝成, 等. 中巴公路奥-布段水毁灾害及风险性评价研究[J]. 人民长江, 2019, 50(9): 35-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201909007.htmYang S C, Wei X L, Chen B C, et al. Research on flood damage disaster and risk assessment along Ao-Bu section of Sino-Pakistan Highway[J]. Yangtze River, 2019, 50(9): 35-41(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201909007.htm [26] 中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所. 20170314-T-466地貌类型分类及编码规范[S]. 北京: 国家市场监督管理局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2019.Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research. 20170314-T-466 Specifications of classification and coding of geomorphological types[S]. Beijing: State Administration for Market Supervision, Standardization Administration of China, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [27] 张亮, 那晓东, 刘知, 等. 基于国产GF-2卫星影像的遥感地质解译: 以阿吾拉勒地区为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2): 233-240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802032.htmZhang L, Na X D, Liu Z, et al. Remote sensing geological interpretation based on domestic GF-2 satellite imagery: A case study of the Awulale area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(2): 233-240(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802032.htm [28] 刘肖姬, 梁树能, 吴小娟, 等. "高分二号"卫星数据遥感滑坡灾害识别研究: 以云南东川为例[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2015, 36(4): 93-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HFYG201504019.htmLiu X J, Liang S N, Wu X J, et al. Interpretation of landslide in Dongchuan district of Yunnan province using GF-2 satellite data[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(4): 93-100(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HFYG201504019.htm [29] 胡骁. 基于遥感和高精度DEM数据的鹤庆盆地活动构造识别研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.Hu X. Research on identification of active tectonics in heqing basin based on remote sensing data and high precision DEM data[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [30] 叶梦旎, 张绪教, 叶培盛, 等. SPOT6与无人机航测技术在第四纪地质及活动构造填图中的应用: 以内蒙古1: 50000呼勒斯太苏木等图幅填图试点为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 2016, 22(2): 366-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201602016.htmYe M N, Zhang X J, Ye P S, et al. Application of spot 6 and the UAV aerial technology in Quaternary geology and tectonic mapping: Taking the 1: 50000 mapping pilot of the Hulesitai area, Inner Mongolia as an example[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(2): 366-378(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201602016.htm [31] 陈云芳. 遥感技术在怒江河谷潞江段晚新生代研究中的应用及意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2009.Chen Y F. Application and significance of RS technology during Late Cenozoic studies in Lujiang of Nujiang valley[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2009(in Chinese with English abstract). [32] 魏学利, 陈宝成, 樊圆圆, 等. 中巴公路奥布段冰碛土特征及其路用性能评价[J]. 路基工程, 2019(3): 6-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGC201903002.htmWei X L, Chen B C, Fan Y Y, et al. Characteristics and road performance evaluation of moraine soil in the Aobu Section of the Sino-Pakistan highway[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2019(3): 6-13(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGC201903002.htm [33] 杨金中. 遥感技术在工程地质选址工作中的应用[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2007, 19(4): 90-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG200704021.htmYang J Z. The application of remote sensing to engineering geological site selection[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2007, 19(4): 90-94(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG200704021.htm [34] 谢连文, 黄思静. 甚年轻沉积物的高分辨率遥感定年方法探讨: 以罗布泊盐湖为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2003, 22(3): 83-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200303016.htmXie L W, Huang S J. Discussion of high resolution remote sensing dating method in the youngest sediments: As an example of Luobupo saline[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2003, 22(3): 83-86(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200303016.htm -





 下载:
下载: