Regional groundwater flow pattern in Beishan, Hexi Corridor and Qilian Mountain
-
摘要: 山区地下水流动受到区域气候条件、地形地貌、地质构造等因素共同控制,限于资料有限,其流动模式与控制机理尚不清晰。特别是地处甘肃北山的高放废物地质处置库预选区、河西走廊以及祁连山北麓区域地下水的流动模式,直接决定了处置库在万年时间尺度上的安全性。基于区域遥感构造解译、地质构造演化分析、地球物理勘探以及水文地质钻探,获取了典型剖面的水文地质结构与渗透特征;综合区域水文地质调查、水文地球化学与同位素特征数据,构建了甘肃北山-河西走廊-祁连山山区的水文循环概念模型;并通过构建区域地下水流动数值模型与多情景模拟,分析了甘肃北山-河西走廊-祁连山山区的地下水流动模式。结果表明,地形对于该地区的地下水流动模式具有主控作用,祁连山山区地下水难以越过海拔最低的河西走廊至北山山区排泄,河西走廊是祁连山山区地下水系统与北山山区地下水系统的边界;北山山区地下水在地形与岩性的控制下,仅发育局部流动系统且渗流速度缓慢。同时由于该地区地质构造的阻滞作用,北山新场地下水无法径直向南穿越构造向花海盆地排泄,渗流路径长度明显增加;仅有F95断裂构造以南山前地带地下水可向花海盆地排泄,但由于集水流域有限、渗流速度缓慢、循环交替能力差,排泄量较小。本研究探究了山区-盆地地下水循环模式,为高放废物地质处置库候选场址的适宜性评价提供了科学依据。Abstract: Groundwater flow in mountainous areas is controlled by climate conditions, topography, geological structure, and other factors.Due to the restrictions such as data acquisition, the groundwater flow pattern and control mechanism in mountainous areas are still not clearly understood.Taking Beishan area as an example, which locates the pre-selected area of the Geological Repository for High-Level radioactive Waste in China, groundwater flow pattern is of great significance for the safety of the repository on the ten-thousand-year time scale.In this study, characteristics of the hydrogeological structure and permeability in Beishan area, Hexi Corridor, and Qilian Mountains were obtained based on regional remote sensing interpretation, geological structure evolution analysis, geophysical exploration, and hydrogeological drilling.A conceptual model was proposed through comprehensive hydrogeological survey, hydrogeochemical and isotope analysis.In addition, regional groundwater flow numerical models and multi-scenario simulations were used to understand the groundwater flow patterns in the Beishan-Hexi Corridor-Qilian Mountains in Gansu.Results show that topography plays a dominant role in the groundwater flow pattern in the area.Groundwater from Qilian Mountains is difficult to pass through the Hexi Corridor to discharge in the Beishan Mountains.With the lowest altitude in the region, the Hexi Corridor can be regarded as the boundary of the groundwater system between the Qilian Mountains and the Beishan Mountain.Under the control of topography and lithology, the groundwater in Beishan mountain area only develops local flow systems and the flow velocity is small.At the same time, due to the blocking effect of the faults in this area, the groundwater from Xinchang, the key pre-selected high level radioactive waste disposal site in Beishan, cannot flow directly to the south into the Huahai Basin.In addition, its length of the flow path is greatly increased.Only the groundwater on the south side of the F95 fault can discharge to the Huahai Basin, but due to the limited catchment basin, slow flow velocity and poor circulation condition, the discharge is weak.This study investigates the mountain-basin groundwater circulation pattern, and provides a scientific basis for the site evaluation of the geological repository for high-level radioactive waste in Beishan, Gansu.
-
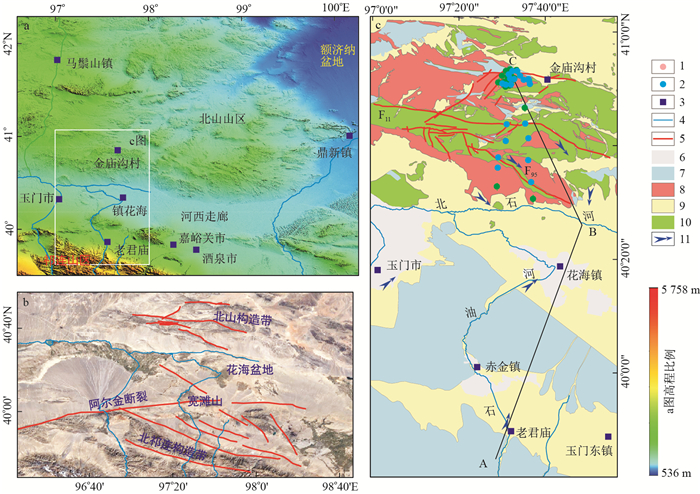
图 2 研究区地质与地球物理剖面结构(剖面线位置见图 1c中A-B-C)
a.祁连山-宽滩山-花海盆地-北山地质剖面(据玉门幅水文地质图修改);b.EH4电阻率剖面
Figure 2. Geological and geophysical sectin structure of the study aera
图 3 北区地质结构(剖面B-C位置见图 1-c)
Figure 3. Geological structure in north part of the study area
-
[1] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103Liang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103 [2] 江欣悦, 李静, 郭林, 等. 豫北平原浅层地下水化学特征与成因机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 290-300. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0511Jiang X Y, Li J, Guo L, et al. Chemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in the northern Henan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 290-300(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0511 [3] Wang L, Dong Y, Xu Z. A synthesis of hydrochemistry with an integrated conceptual model for groundwater in the Hexi Corridor, northwestern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 146: 20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.04.023 [4] 邢文乐, 马瑞, 孙自永, 等. 敦煌盆地地下水水化学特征及水质评价[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(5): 196-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605027.htmXing W L, Ma R, Sun Z Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of groundwater in Dunhuang Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(5): 196-202(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605027.htm [5] 王驹. 中国高放废物地质处置21世纪进展[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2019, 53(10): 2072-2082. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZJS201910036.htmWang J. Progress of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China in the 21st century[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2019, 53(10): 2072-2082(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZJS201910036.htm [6] 郭永海, 刘淑芬, 王驹, 等. 高放废物处置库选址中的水文地质特性评价[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2007, 24(4): 233-237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2007.04.009Guo Y H, Liu S F, Wang J, et al. Hydrological performance assessment on siting the high level radioactive waste repository[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2007, 24(4): 233-237(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2007.04.009 [7] Markovich K H, Manning A H, Condon L E, et al. Mountain-block recharge: A review of current understanding[J]. Water Resources Research, 2019, 55(11): 8278-8304. doi: 10.1029/2019WR025676 [8] Bresciani E, Cranswick R H, Banks E W, et al. Using hydraulic head, chloride and electrical conductivity data to distinguish between mountain-front and mountain-block recharge to basin aquifers[J]. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 2018, 22(2): 1629-1648. doi: 10.5194/hess-22-1629-2018 [9] Ajami H, Troch P A, Maddock T, et al. Quantifying mountain block recharge by means of catchment-scale storage-discharge relationships[J]. Water Resources Research, 2011, 47(4): W04504. [10] 丁宏伟, 张举, 吕智, 等. 河西走廊水资源特征及其循环转化规律[J]. 干旱区研究, 2006, 23(2): 241-248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ200602008.htmDing H W, Zhang J, Lv Z, et al. Characteristics and cycle conversion of water resources in the Hexi Corridor[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2006, 23(2): 241-248(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ200602008.htm [11] 王礼恒. 甘肃北山区域-盆地-岩体多尺度地下水数值模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 2015.Wang L H. Multi-scale groundwater numerical simulation study of regional-basin-site in Beishan area of Gansu[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [12] 陈建生, 赵霞. 塔里木盆地与北山地区高放废物处置地质环境安全性对比分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 89(增刊1): 3297-3303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2007S1105.htmChen J S, Zhao X. Contrastive analysis of geological condition security for disposal location of high-level nuclear waste between Tarim Basin and Beishan area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 89(S1): 3297-3303(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2007S1105.htm [13] 郭永海, 刘淑芬, 吕川河. 高放废物处置系统地下水同位素特征[J]. 地球学报, 2003, 24(6): 525-528. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2003.06.008Guo Y H, Liu S F, Lü C H. Isotope characteristics of groundwater in the potential site of a high-level waste repository in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2003, 24(6): 525-528(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2003.06.008 [14] 庞忠和, 郭永海, 苏锐, 等. 北山花岗岩裂隙地下水循环属性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(增刊2): 3954-3958. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2007S2052.htmPang Z H, Guo Y H, Su R, et al. Experimental study on cycle property of groundwater in fractured granite in Beishan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(S2): 3954-3958(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2007S2052.htm [15] 李杰彪, 苏锐, 周志超, 等. 基于环境示踪剂氯的北山地区浅部地下水补给研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(1): 135-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL202001016.htmLi J B, Su R, Zhou Z C, et al. Estimation of shallow groundwater recharge using the environmental tracer chloride method in Beishan area[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2020, 43(1): 135-143(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL202001016.htm [16] 周志超. 高放废物处置库北山预选区深部地下水成因机制研究[D]. 北京: 核工业北京地质研究院, 2014.Zhou Z C. The mechanism of genesis of groundwater in the potential site of a high-level waste repository in Beishan[D]. Beijing: Nuclear Industry Geological Research Institute in Beijing, 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] Liu Y, Song C, Meng Q, et al. Paleoclimate change since the Miocene inferred from clay-mineral records of the Jiuquan Basin, NW China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 550: 109730. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109730 [18] 高雄雄. 酒泉盆地花海凹陷下白垩统致密油成藏条件与富集机理[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2013.Gao X X. Research on the hydrocarbon accumulation condition and enrichment mechanism of tight oil of Lower Cretaceous in the Huahai Depression of Jiuquan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [19] 熊章强. 根据地球物理场特征评价核废物处置场址: 对疏勒河断裂带稳定性评价[J]. 华东地质学院学报, 2001, 24(3): 209-213. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2001.03.007Zhang X Q. Characters of geology and geophysics field in the middle region of Shulei River fault zone and stability evaluations on the nuclear waste disposal repository[J]. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 2001, 24(3): 209-213(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2001.03.007 [20] Saar M O, Manga M. Depth dependence of permeability in the Oregon Cascades inferred from hydrogeologic, thermal, seismic, and magmatic modeling constraints[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2004, 109(B4): B04204. [21] Worthington S R H, Davies G J, Alexander E C. Enhancement of bedrock permeability by weathering[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 160: 188-202. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.07.002 [22] Welch L A, Allen D M. Hydraulic conductivity characteristics in mountains and implications for conceptualizing bedrock groundwater flow[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2014, 22(5): 1003-1026. doi: 10.1007/s10040-014-1121-5 [23] 赵良菊, 尹力, 肖洪浪, 等. 黑河源区水汽来源及地表径流组成的稳定同位素证据[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(1): 58-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201101009.htmZhao L J, Yin L, Xiao H L, et al. Isotopic evidence for the moisture origin and composition of surface runoff in the headwaters of the Heihe River basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(1): 58-70(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201101009.htm [24] Qin D, Qian Y, Han L, et al. Assessing impact of irrigation water on groundwater recharge and quality in arid environment using CFCs, tritium and stable isotopes, in the Zhangye Basin, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 405(1/2): 194-208. [25] 李杰彪, 苏锐, 周志超, 等. 北山地区大气降水中水化学及稳定同位素特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(12): 5152-5161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.12.006Li J B, Su R, Zhou Z C, et al. Hydrochemical and stable isotope characteristics of precipitation in Beishan area[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(12): 5152-5161(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.12.006 [26] Wang L, Li G, Dong Y, et al. Using hydrochemical and isotopic data to determine sources of recharge and groundwater evolution in an arid region: A case study in the upper-middle reaches of the Shule River basin, northwestern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(4): 1901-1915. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3719-2 [27] 王礼恒, 董艳辉, 宋凡, 等. 甘肃石油河流域地下水补给来源与演化特征分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(1): 54-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL201701009.htmWang L H, Dong Y H, Song F, et al. Recharge sources and hydrogeochemical properties of groundwater in the Shiyou River, Gansu Province[J]. Arid Land Zone, 2017, 40(1): 54-61(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL201701009.htm [28] Wang L, Dong Y, Xie Y, et al. Distinct groundwater recharge sources and geochemical evolution of two adjacent sub-basins in the lower Shule River Basin, northwest China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2016, 24(8): 1967-1979. doi: 10.1007/s10040-016-1456-1 [29] Tóth Á, Havril T, Simon S, et al. Groundwater flow pattern and related environmental phenomena in complex geologic setting based on integrated model construction[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 539: 330-344. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.05.038 [30] 曹潇元, 侯德义, 胡立堂. 甘肃北山区域地下水流数值模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(2): 9-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202002003.htmCao X Y, Hou D Y, Hu L T. Numerical simulation of regional groundwater flow in the Beishan area of Gansu[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geolgogy, 2020, 47(2): 9-16(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202002003.htm [31] 武毅, 郭建强, 朱庆俊, 等. 基岩水与平原水转换关系的地球物理勘查技术探讨[J]. 地球学报, 2004, 25(3): 369-372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2004.03.016Wu Y, Guo J Q, Zhu Q J, et al. Geophysical prospecting techniques for the interchange between bedrock water and plain water[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2004, 25(3): 369-372(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2004.03.016 -





 下载:
下载: