Characteristics of karst groundwater flow systems of typical faulted basins in Yimeng Mountain area: A case study of Laiwu Basin
-
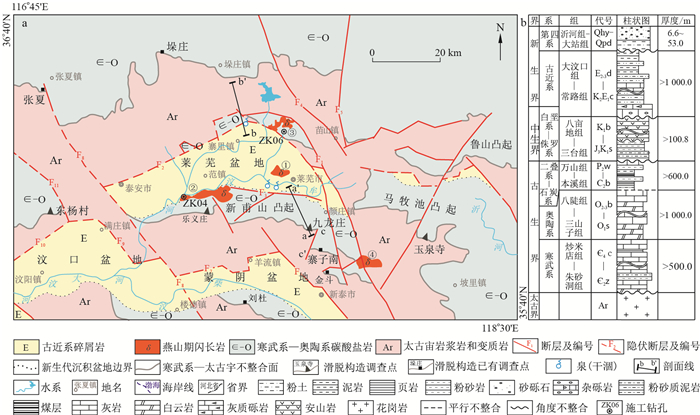
摘要: 2011年以来,中国地质调查局在沂蒙山区组织实施了1:5万标准图幅水文地质调查4万余km2,并在严重缺水村镇开展了大量的找水打井示范工作,获得了较为丰富的地质数据,对断陷盆地地下水流系统取得了新认识。受中新生代构造影响,沂蒙山区发生断裂褶皱、伸展滑脱及岩浆侵入活动,形成一系列"南超覆北断陷"的地堑-半地堑盆地,并最终形成现今典型的"盆-山"岩溶水文地质结构,及以盆地为单元的相对独立的岩溶地下水流系统。为研究沂蒙山区地下水流系统发育特征,选择莱芜盆地为典型研究区,基于野外地质调查,通过综合分析盆地南北两侧地貌单元、含水岩组立体空间分布及地下水水位、水化学及同位素结果等,探讨了沂蒙山区典型"盆-山"结构塑造的多级岩溶地下水流系统特征。结果表明,莱芜盆地岩溶地下水由盆地外围向盆地中心呈"向心式"径流;受人类活动影响、地质构造控制和含水层分布制约,盆地南北两侧地下水流系统特征存在差异:盆地南部发育中间和局部两级地下水流系统;盆地北部则仅发育单一的局部地下水流系统,但占有已勘查论证的近1/2的地下水水源地。此外,研究发现在大汶河最低侵蚀基准面,区域滑脱构造及热液混合作用拆离的空隙,与岩层面、层间裂隙、顺层溶蚀空隙等共同构成立体的岩溶地下水网络,影响着岩溶水循环途径及深度。以此认识为指导,实施的探采结合井成井率达到86%,强化了地下水流系统理论在北方基岩山区水文地质工作中理论与实践的结合。Abstract: China Geological Survey has organized and implemented 1:50 000 standard map hydrogeological survey with an area of more than 40000 square kilometers in Yimeng Mountain area. And it carried out a large amount of water prospecting and well drilling demonstration work in villages and towns with serious water shortage, obtained rich geological data and gained a new understanding of groundwater flow systems. Under the influence of Mesozoic and Cenozoic structures, the faults and folds, extensional detachment and magmatic intrusion occurred in Yimeng Mountain area, formed a series of graben-semi graben basins characterized by overlapping in the south and faulting in the north, and finally formed today's typical "basin-mountain" karst hydrogeological structure and the relatively independent karst groundwater system, which taking basin as unit. In order to study the development characteristics of groundwater flow system in Yimeng Mountain area, Laiwu Basin was selected as a typical study area. On the basis of the field geological survey, through comprehensively analyze the geomorphic units, the three-dimensional spatial distribution of water bearing rock groups, groundwater level, hydrochemistry, and water isotope results on the north and south sides of the basin, this paper comprehensively discusses the characteristics of multistage karst groundwater flow systems with typical "basin-mountain" structure in Yimeng Mountain area. The results show that, the karst groundwater in Laiwu Basin presents a "centripetal" runoff from the outer periphery to the center of the basin. Affected by human activities, controlled by geological structure and aquifer distribution, the characteristics of groundwater flow systems between the north and south sides of the basin are different. There are mainly intermediate and local groundwater flow systems in the south of the basin, while a single local groundwater flow system is developed in the north of the basin, however, it occupies nearly 1/2 of the groundwater sources that have been explored and demonstrated. In addition, it is found that at the lowest erosion base level of Dawen River, the voids separated by regional detachment structure and hydrothermal mixing, together with rock layer, interlayer fissures and bedding dissolution voids, form a three-dimensional karst groundwater network, which influence the circulation path and depth of karst water. Guided by this understanding, the completion rate of exploration production combined wells has reached 86%, which strengthens the combination of theory and practice of groundwater flow system theory in hydrogeological work in bedrock mountainous areas in North China.
-
图 7 谷家台矿区大理岩溶洞分布与矿体距离关系图(据文献[35])
Figure 7. Relation diagram of distance between marble karst caves and Oredeposits in Gujiatai Orefield
表 1 研究区各含水岩组碳酸盐岩化学组分测试数据
Table 1. Chemical component content test data of each water bearing rock formation in the study area
含水岩组 岩性 CaO MgO 折算CaCO3 折算MgCO3 可溶组分平均值 样品个数 φB/% 马家沟群(O2-3M) 厚层-块状灰岩 46.76 4.29 83.50 9.00 90.74 17 三山子组(O1s) 厚层白云岩 32.83 16.47 58.62 34.59 93.21 16 炒米店组(∈4O1c) 竹叶状灰岩 43.57 6.08 77.80 12.76 90.56 11 崮山组(∈3-4g) 瘤状灰岩 39.29 2.34 70.15 4.70 74.85 7 张夏组(∈3z) 鲕粒灰岩 46.21 3.26 82.52 6.85 81.72 15 馒头组(∈2-3m) 薄板状灰岩 32.08 5.75 57.29 12.08 69.37 12 朱砂洞组(∈2zd) 燧石条带白云岩 40.57 7.91 72.45 16.61 89.06 7 -
[1] Darnault C J G. Karst aquifers: Hydrogeology and exploitation[M]. [S.l.]: Nato Security Through Science, 2011. [2] 袁道先. 新形势下我国岩溶研究面临的机遇和挑战[J]. 中国岩溶, 2009, 28(4): 329-331. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2009.04.001Yuan D X. Challenges and opportunities for karst research of our country under the new situation[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2009, 28(4): 329-331(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2009.04.001 [3] 袁道先. 我国北方岩溶研究的形势和任务[J]. 中国岩溶, 2010, 29(3): 219-221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2010.03.001Yuan D X. The situation and tasks for northern karst research of our country[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2010, 29(3): 219-221(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2010.03.001 [4] 梁杏, 张人权, 靳孟贵. 地下水流系统: 理论、应用、调查[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015.Liang X, Zhang R Q, Jin M G. Groundwater flow system: Theory, application and investigation[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015(in Chinese). [5] 约瑟夫·托特. 重力驱动地下水流系统理论及其应用[M]. 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵, 等译. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014. Tóth J. Gravitional systems of groundwater flow: Theory, evaluation, utilization[M]. Zhang R Q, Liang X, Jin M G, et al(Trans). Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2014(in Chinese). [6] 张人权. 关于水文地质学的一些思考[J]. 地质科技情报, 2002, 21(1): 3-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2002.01.002Zhang R Q. Some thinking on development of hydrogeology[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2002, 21(1): 3-6(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2002.01.002 [7] 侯光才, 梁永平, 尹立河, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地地下水系统及水资源潜力[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2009, 36(1): 18-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.01.004Hou G C, Liang Y P, Yin L H, et al. Groundwater systems and water resources potential in the Ordos Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2009, 36(1): 18-23(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.01.004 [8] Han D M, Xu H L, Liang X. GIS-based regionalization of a karst water system in Xishan Mountain area of Taiyuan Basin, North China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2006, 331(3/4): 459-470. [9] 罗利川, 梁杏, 李扬, 等. 基于GMS的岩溶山区三维地下水流模式识别[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(5): 680-689. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201805005.htmLuo L C, Liang X, Li Y, et al. Identifying three-dimensional groundwater flow patterns in karst mountain areas based on GMS[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(5): 680-689(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201805005.htm [10] 黄金瓯, 鲜阳, 黎伟, 等. 典型滨海平原区地下水流系统水化学场演化及成因: 以杭嘉湖平原为例[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(7): 2565-2582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202107023.htmHuang J O, Xian Y, Li W, et al. Hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater flow system in the typical coastal plain: A case study of Hangjiahu Plain[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(7): 2565-2582(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202107023.htm [11] 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵. 末次盛冰期以来河北平原第四系地下水流系统的演变[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(3): 217-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201303026.htmZhang R Q, Liang X, Jin M G. The evolution of groundwater flow systems in the Quaternary of Hebei Plain since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(3): 217-226(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201303026.htm [12] 尹立河, 张俊, 王哲, 等. 西北内陆河流域地下水循环特征与地下水资源评价[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(4): 1094-1111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202104010.htmYin L H, Zhang J, Wang Z, et al. Groundwater circulation patterns and its resources assessment of inland river catchments in northwestern China[J]. Geology China, 2021, 48(4): 1094-1111(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202104010.htm [13] 魏兴, 周金龙, 梁杏, 等. 新疆喀什三角洲地下水流系统的水化学和同位素标记[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(5): 1807-1817. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202005023.htmWei X, Zhou J L, Liang X, et al. Hydrochemical and isotopic markers of groundwater flow systems in the Kashgar delta area in Xinjiang[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(5): 1807-1817(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202005023.htm [14] 文冬光. 用环境同位素论区域地下水资源属性[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2002, 27(2): 141-147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2002.02.003Weng D G. Groundwater resources attribute based on environmental isotopes[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2002, 27(2): 141-147(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2002.02.003 [15] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103Liang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103 [16] 梁杏, 张人权, 牛宏, 等. 地下水流系统理论与研究方法的发展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(5): 143-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201205020.htmLiang X, Zhang R Q, Niu H, et al. Development of the theory and research method of groundwater flow system[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(5): 143-151(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201205020.htm [17] 梁杏, 牛宏, 张人权, 等. 盆地地下水流模式及其转化与控制因素[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(2): 269-275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201202011.htmLiang X, Niu H, Zhang R Q, et al. Basinal groundwater flow systems patterns and their transformation and dominant factors[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University Geosciences, 2012, 37(2): 269-275(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201202011.htm [18] 张俊, 侯荣哲, 尹立河, 等. 盆地地下水流系统形成与影响因素分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2017, 44(4): 8-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201704002.htmZhang J, Hou R Z, Yin L H, et al. Formation and influencing factors of regional groundwater flow systems[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(4): 8-14(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201704002.htm [19] 徐军祥, 康凤新, 张中祥, 等. 山东省重大水文地质问题: 理论技术创新与应用[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 2014.Xu J X, Kang F X, Zhang Z X, et al. Major hydrogeological problems in Shandong Province: Theoretical and technological innovation and application[M]. Jinan: Shandong Science and Technology Press, 2014(in Chinese). [20] 刘元晴, 周乐, 李伟, 等. 鲁中山区下寒武统朱砂洞组似层状含水层成因分析[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(3): 653-663. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201903012.htmLiu Y Q, Zhou L, Li W, et al. Genetic analysis of Lower Cambrian Zhushadong Formation layered aquifer in the Central Mountain area of Shandong Province[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(3): 653-663(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201903012.htm [21] 周乐, 刘元晴, 李伟, 等. 山东大汶河流域中上游古近系含水岩组水文地质特征[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(2): 316-327. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201902009.htmZhou L, Liu Y Q, Li W, et al. Characteristics of the Paleogene waterbearing formation in the middle and upper reaches of the Dawenhe River basin, Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(2): 316- 327(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201902009.htm [22] 贺可强, 刘炜金, 邵长飞. 鲁中南岩溶水资源综合类型及合理调蓄研究[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(4): 369-374. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.04.015He K Q, Liu W J, Shao C F. The comprehensive type classification and proper adjustment of karst water resource in the Central-South region of Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2002, 23(4): 369-374(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.04.015 [23] 李守军, 郑德顺, 蔡进功, 等. 鲁北和鲁西南地区古近纪盆地沉积特征与控制因素探讨[J]. 地质论评, 2003, 49(3): 225-232. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.03.001Li S J, Zheng D S, Cai J G, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of basins in the North Shandong and Southwest Shandong in Palaeogene[J]. Geological Review, 2003, 49(3): 225-232(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.03.001 [24] 刘元晴, 周乐, 李伟, 等. 山东莱芜盆地西北缘古近系半固结含水岩组的特征及其成因[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(6): 737-748.Liu Y Q, Zhou L, Li W, et al. The characteristics and genetic analysis of the Paleogene semi- consolidated water-bearing formation on the northwestern margin of Laiwu Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(6): 737-748(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] 李三忠, 王金铎, 刘建忠, 等. 鲁西地块中生代构造格局及其形成背景[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(4): 487-497. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.04.006Li S Z, Wang J D, Liu J Z, et al. Mesozoic structure and its tectonic setting in the western Shandong Block[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(4): 487-497(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.04.006 [26] 张宏仁, 张永康, 蔡向民, 等. 燕山运动的"绪动": 燕山事件[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(12): 1779-1790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201312001.htmZhang H R, Zhang Y K, Cai X M, et al. The triggering of Yanshan movement: Yanshan event[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(12): 1779-1790(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201312001.htm [27] 王瑜, 孙立新, 周丽云, 等. 燕山运动与华北克拉通破坏关系的讨论[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(5): 521-535. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201805002.htmWang Y, Sun L X, Zhou L Y, et al. Discussion on the relationship between the Yanshanian movement and Cratonic destruction in North China[J]. Science China: Earth Science, 2018, 48(5): 521-535(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201805002.htm [28] 康凤新, 徐军祥, 张中祥. 山东省地下水资源及其潜力评价[J]. 山东国土资源, 2010, 26(8): 4-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2010.08.002Kang F X, Xu J X, Zhang Z X. Groundwater resources and its potential in Shandong Province[J]. Land and Resources in Shandong Province, 2010, 26(8): 4-12(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2010.08.002 [29] Liang Y P, Gao X B, Zhao C H, et al. Review: Characterization, evolution, and environmental issues of karst water systems in northern China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26(1): 1-15. doi: 10.1007/s10040-017-1706-x [30] 梁永平, 王维泰. 中国北方岩溶水系统划分与系统特征[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(6): 860-868. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201006017.htmLiang Y P, Wang W T. The division and characteristics of karst water systems in Northern China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(6): 860-868(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201006017.htm [31] Zhang X B, Li X, Gao X B. Hydrochemistry and coal mining activity induced karst water quality degradation in the Niangziguan karst water system, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(7): 6286-6299. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5838-z [32] 申豪勇, 梁永平, 赵春红, 等. 古堆泉岩溶地下水系统特征及系统圈划[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2020, 50(1): 217-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202001018.htmShen H Y, Liang Y P, Zhao C H, et al. Hydro-geological characteristics and demarcation of Gudui spring karst groundwater system[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2020, 50(1): 217-225(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202001018.htm [33] 胡海涛, 许贵森. 论构造体系与地下水网络[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1980(3): 5-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG198003000.htmHu H T, Xu G S. Discussion ontectonic system and groundwater network[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1980(3): 5-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG198003000.htm [34] 刘元晴, 周乐, 马雪梅, 等. 莱芜盆地地下水开发利用中的环境地质问题及成因[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(11): 118-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202011018.htmLiu Y Q, Zhou L, Ma X M, et al. Environmental geological problems and causes during development and utilization of groundwater in Laiwu Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34(11): 118-124(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202011018.htm [35] 梁永平, 申豪勇, 赵春红, 等. 对中国北方岩溶水研究方向的思考与实践[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(3): 363-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202103001.htmLiang Y P, Shen H Y, Zhao C H, et al. Thinking and practice on the research direction of karst water in northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(3): 363-380(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202103001.htm [36] 刘元晴, 周乐, 李伟, 等. 山东莱芜盆地碳酸盐岩热液溶蚀特征及水文地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(1): 199-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202001019.htmLiu Y Q, Zhou L, Li W, et al. Characteristics and hydrogeological siginificance of hydrothermal dissolution in carbonate rocks from Laiwu Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(1): 199-206(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202001019.htm [37] Clark I D, Fritz P. Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology[M]. New York: Lewis Publishers, 1997. -





 下载:
下载: