Coexistence and controlling factors of ammonium and phosphorus in groundwater along the middle reaches of the Yangtze River
-
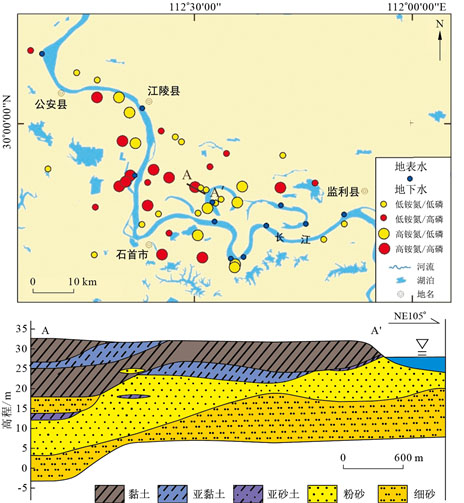
摘要: 长江中游平原区面临着一系列严重的地质环境问题,其中地下水铵氮和磷的问题十分突出,但目前对于二者共存规律的认识还十分薄弱。以长江中游沿岸故道区为典型研究区,对采集的地下水样品进行了水文地球化学分析,并综合运用因子分析和随机森林模型探讨了铵氮和磷的赋存规律。结果表明:地下水整体处于还原环境中,NH4-N的质量浓度为0.03~71.0 mg/L(均值9.92 mg/L),P的质量浓度为0.02~3.38 mg/L(均值0.51 mg/L)。地下水中高浓度的铵氮与磷均主要为天然成因,但铵氮与磷的迁移富集过程存在差异:铵氮的迁移富集与含氮有机质矿化过程密切相关;磷的迁移富集与铁氧化物或氢氧化物的还原性溶解密切相关,而含磷有机质矿化是磷富集的次要过程。Eh很低的地下水环境易产生高浓度铵氮的地下水,相对中等的还原环境会产生高浓度的磷但通常不会伴生高浓度的铵氮;当地下水中S2-,DOC,I均处于相对较高的浓度水平时会伴生大量的铵氮,而磷的浓度在很大程度上受控于Fe2+浓度;当DOC,I和Fe2+浓度都高时,通常会出现铵氮和磷浓度都较高的现象。Abstract: The plain area of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River is faced with a series of serious geological environment problems, among which the groundwater ammonium and phosphorus are the most abnormal, but the understanding of their coexistence is still very weak.In this paper, the hydrogeochemical analysis was carried out on the groundwater samples collected from the oxbows along the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, and the occurrence rules of ammonium and phosphorus were discussed by means of factor analysis and random forest model.The results showed that: Groundwater is in reductive environment as a whole, the mass concentration of NH4-N is 0.03-71.0 mg/L(the mean is 9.92 mg/L), and the mass concentration of P is 0.02-3.38 mg/L(the mean is 0.51 mg/L).High concentration of ammonium and phosphorus in groundwater are mainly from natural causes.However, the migration and enrichment processes of ammonium and phosphorus are different.The migration and enrichment of ammonium is closely related to the mineralization process of organic matter.The migration and enrichment of phosphorus is closely related to the reductive dissolution of iron oxide/hydroxide, and the mineralization of organic matter containing phosphorus is the secondary process of phosphorus enrichment.A low Eh groundwater environment is prone to produce high ammonium groundwater, while a relatively medium reduction environment will produce high phosphorus but usually not associated with high ammonium nitrogen.When S2-, DOC and I are in relatively high concentrations, a large amount of ammonium is associated, while the concentration of phosphorus is largely controlled by the concentration of Fe2+.When DOC, I, and Fe2+ are all high, high concentrations of ammonium and phosphorus are usually present.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- ammonium /
- phosphorus /
- organic matter /
- iron oxide
-
表 1 研究区水样水化学指标统计
Table 1. Statistics of chemical parameters of water samples in the study area
水化学指标 地表水(n=14) 地下水(n=59) 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 pH 7.57 9.26 8.14 6.08 8.08 7.15 Eh/mV 39.6 217 125 -207.8 122.5 -95.4 ρB/(mg·L-1) NH4-N 0.02 0.64 0.21 0.03 71.0 9.92 P 0.01 4.94 0.41 0.02 3.38 0.51 Fe2+ — — — < 0.001 38.5 6.32 HCO3- 102.24 210.0 150.88 104 1 753 681 DOC < 0.001 7.83 3.89 1.39 22.51 8.35 TDS 90 213 179 49 1 058 501 Fe < 0.001 0.22 0.03 0.01 24.6 8.84 Mn < 0.001 0.06 0.01 < 0.001 2.97 0.66 K 0.88 6.61 3.0 0.32 13.1 3.67 Ca 23.03 49.19 39.84 15.5 334.03 154.4 Na 4.66 16.7 11.77 9.02 167.27 21.66 Mg 6.74 15.36 10.52 4.23 166.4 44.03 Cl- 11.3 24.05 16.02 0.72 58.26 9.15 NO3- 0.34 8.86 3.8 < 0.001 8.14 — SO42- 4.05 36.54 25.94 < 0.001 89.58 — ρB/(μg·L-1) S2- — — — < 0.1 192 12 As 1.44 9.06 4.02 0.37 625.0 122.4 I 1.3 10.53 4.64 2.1 594.36 87.36 注:—表示大部分水样质量浓度低于检出限 表 2 因子分析结果
Table 2. The results of factor analysis
因子 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 P 0.261 0.556 -0.179 0.003 -0.389 Eh -0.255 -0.680 -0.218 -0.048 -0.161 NH4-N 0.901 0.193 0.130 0.058 -0.131 Mg2+ 0.743 0.000 0.564 -0.065 -0.081 Fe2+ -0.130 0.819 0.200 -0.200 -0.124 Na+ 0.074 -0.107 -0.010 0.936 -0.065 Ca2+ 0.060 0.085 0.857 -0.289 -0.167 K+ 0.583 0.063 0.039 0.087 0.610 Fe 0.179 0.810 -0.039 -0.112 -0.246 S2- 0.055 -0.074 -0.191 0.829 0.377 DOC 0.539 0.370 0.217 0.151 0.187 pH -0.559 -0.084 0.271 0.472 -0.109 Cl- -0.003 -0.285 -0.051 0.092 0.738 TDS 0.127 0.054 0.812 0.101 0.279 As -0.019 0.785 -0.014 -0.031 -0.057 HCO3- 0.596 0.145 0.682 0.112 -0.271 I 0.687 -0.027 0.057 0.018 0.099 特征值 4.735 2.983 1.988 1.596 1.126 贡献率/% 19.7 17.8 14.6 11.7 9.3 累积贡献率/% 19.7 37.5 52.1 63.8 73.1 注:字体加粗表示该因子中具有较高载荷的特征值;TDS.总溶解固体 -
[1] Mitsch W J, Day J W, Zhang L, et al. Nitrate nitrogen retention in wetlands in the Mississippi River Basin[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2005, 24(4): 267-278. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2005.02.005 [2] 陈新明, 马腾, 蔡鹤生, 等. 地下水氮污染的区域性调控策略[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(6): 130-143, 149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201306021.htmChen X M, Ma T, Cai H S, et al. Regional regulatory strategies for nitrogen contamination in groundwater[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32 (6): 130-143, 149(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201306021.htm [3] 高伟, 高波, 严长安, 等. 鄱阳湖流域人为氮磷输入演变及湖泊水环境响应[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(9): 3137-3145.Gao W, Gao B, Yan C A, et al. Evolution of anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus input and lake water environment response in Poyang Lake Basin[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 36(9): 3137-3145(in Chinese with English abstract). [4] 黄艳雯, 杜尧, 徐宇, 等. 洞庭湖平原西部地区浅层承压水中铵氮的来源与富集机理[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 165-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202006018.htmHuang Y W, Du Y, Xu Y, et al. Source and enrichment mechanism of ammoniumin shallow confined aquifer in the west of Dongting Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Scienceand Technology, 2020, 39(6): 165-174(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202006018.htm [5] Du Y, Ma T, Deng Y M, et al. Sources and fate of high levels of ammonium in surface water and shallow groundwater of the Jianghan Plain, Central China[J]. Environmental Science Processes and Impacts, 2017, 19(2): 161-172. doi: 10.1039/C6EM00531D [6] Buss S R, Herbert A W, Morgan P, et al. A review of ammonium attenuation in soil and groundwater[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 2004, 37(4): 347-359. doi: 10.1144/1470-9236/04-005 [7] Grimm M, Muller A, Hein G, et al. High phosphorus intake only slightly affects serum minerals, urinary pyridinium crosslinks and renal function in young women[J]. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2001, 55: 153-161. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601131 [8] Yoo K D, Kang S, Choi Y, et al. Sex, age, and the association of serum phosphorus with all-cause mortality in adults with normal kidney function[J]. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 2016, 67: 79-88. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.06.027 [9] Dhingra R, Sullivan L M, Fox C S, et al. Relations of serum phosphorus and calcium levels to the incidence of cardiovascular disease in the community[J]. Archives of Internal Medicine, 2007, 167(9): 879-885. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.9.879 [10] 孟伟, 于涛, 郑丙辉, 等. 黄河流域氮磷营养盐动态特征及主要影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 2007, 27(12): 2046-2051. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2007.12.019Meng W, Yu T, Zheng B H, et al. Dynamic characteristics and main influencing factors of the salt in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2007, 27(12): 2046-2051(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2007.12.019 [11] 王志齐, 李宝, 梁仁君, 等. 南四湖内源氮磷释放的对比研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(2): 487-493. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201302027.htmWang Z Q, Li B, Liang R J, et al. Comparative study of endogenous nitrogen and phosphorus release in Nansi Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 33(2): 487-493(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201302027.htm [12] 宋玉芝, 丰叶, 王锦旗, 等. 水体及沉积物氮磷水平对附植藻类的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(12): 4721-4727. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201812020.htmSong Y Z, Feng Y, Wang J Q, et al. Effect of water and sediment nitrogen and phosphorus levels on attached algae[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 38(12): 4721-4727(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201812020.htm [13] Meinikmann K, Hupfer M, Lewandowski J, et al. Phosphorus in groundwater discharge a potential source for lake eutrophication[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 524: 214-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.02.031 [14] Kazmierczak J, Müller S, Nilsson B, et al. Groundwater flow and heterogeneous discharge into a seepage lake: Combined use of physical methods and hydrochemical tracers[J]. Water Resources Research, 2016, 52: 9109-9130. http://dialog.proquest.com/professional/docview/1905773678?accountid=131175 [15] Hannappel S, Kopp C, Reijman R E. Groundwater as a source of phosphorus pollution in the lake Arend reply[J]. Hydrol Und Wasserbewirtsch, 2018, 62: 293-294. [16] Driscoll C T, Whitall D, Aber J, et al. Nitrogen pollution in the Northeastern United States: Sources, effects, and management options[J]. BioScience, 2003, 53(4): 357-374. doi: 10.1641/0006-3568(2003)053[0357:NPITNU]2.0.CO;2 [17] Wells N S, Hakoun V, Brouyère S, et al. Multi-species measurements of nitrogen isotopic composition reveal the spatial constraints and biological drivers of ammonium attenuation across a highly contaminated groundwater system[J]. Water Research, 2016, 98: 363-375. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.04.025 [18] Sanchez V G, Gutierrez C A, Gomez D S, et al. Pesticide residues monitoring in underground drinking water, Neuquen Province, Northern Patagonia, Argentina[J]. Revista Internacional de Contaminacion Ambiental, 2019, 35(3): 641-649. doi: 10.20937/RICA.2019.35.03.10 [19] Jiao J J, Wang Y, Cherry J A, et al. Abnormally high ammonium of natural origin in a coastal aquifer-aquitard system in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2010, 44(19): 7470-7475. doi: 10.1021/es1021697 [20] Kazmierczak J, Postma D, Müller S, et al. Groundwater-controlled phosphorus release and transport from sandy aquifer into lake[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2020, 65: 2188-2204. doi: 10.1002/lno.11447 [21] Norrman J, Sparrenbom C J, Berg M, et al. Tracing sources of ammonium in reducing groundwater in a well field in Hanoi (Vietnam) by means of stable nitrogen isotope (δ15N)values[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2015, 61: 248-258. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.06.009 [22] Dubrovsky N M, Burow K R, Clark G M, et al. The quality of our nation's waters: Nutrients in the nation's streams and groundwater, 1992-2004[J]. U.S. Geological Survey Circular, 2010, 1350: 174. http://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201300153654 [23] Jason W, Stephanie G L. A database of georeferenced nutrient chemistry data for mountain lakes of the Western United States[J]. Scientific Data, 2017, 4: 170069. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2017.69 [24] Zhang D, Wang X X, Zhou Z G. Impacts of small-scale industrialized swine farming on local soil, water and crop qualities in a hilly red soil region of subtropical China[J]. International Joural of Environmental Reaserch and Public Health, 2017, 14(12): 1524. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14121524 [25] 鲁宗杰, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等. 江汉平原高砷地下水中DOM三维荧光特征及其指示意义[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5): 771-782. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201705012.htmLu Z J, Deng Y M, Du Y, et al. Three-dimensional fluorescence characteristics of DOM in high-arsenic groundwater in Jianghan Plain[J]. Earth Sciences, 2017, 42 (5): 771-782(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201705012.htm [26] 熊峰, 甘义群, 段艳华. 江汉平原地下水中氮素与砷迁移富集的相关性研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2015, 22(2): 39-43, 48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201502008.htmXiong F, Gan Y Q, Duan Y H. Correlation of nitrogen and enrichment of arsenic migration in groundwater in Jianghan Plain[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2015, 22 (2): 39-43, 48(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201502008.htm [27] Du Y, Deng Y M, Ma T, et al. Enrichment of geogenic ammonium in quaternary alluvial lacustrine aquifer systems: Evidence from carbon isotopes and DOM characteristics[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2020, 54(10): 6104-6114. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c00131 [28] Tao Y Q, Deng Y M, Du Y, et al. Sources and enrichment of phosphorus in groundwater of the Central Yangtze River Basin[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 737: 139837. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139837 [29] Fang J Y, Rao S, Zhao S Q. Human-induced long-term changes in the lakes of the Jianghan Plain, central Yangtze[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2005, 3(4): 186-192. doi: 10.1890/1540-9295(2005)003[0186:HLCITL]2.0.CO;2 [30] Niu B B, Wang H H, Loaiciga H A, et al. Temporal variations of groundwater quality in the Western Jianghan Plain, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 578: 542-550. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.225 [31] Deng Y M, Li H J, Wang Y X, et al. Temporal variability of groundwater chemistry and relationship with water-table fluctuation in the Jianghan Plain, central China[J]. Procedia Earth Planet Science, 2014, 10: 100-103. doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2014.08.018 [32] Singh K P, Malik A, Sinha S. Water quality assessement and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti River (India)using multivariate statistical technique: A case study[J]. Analytica Chemica Acta, 2005, 538: 355-374. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2005.02.006 [33] 卜红梅, 刘文治, 张全发. 多元统计方法在金水河水质时空变化分析中的应用[J]. 资源科学, 2009, 31(3): 429-434. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2009.03.012Bu H M, Liu W Z, Zhang Q F. Application of multivariate statistical method in analysis of spatial temporal variation in Jinshui River[J]. Resource Science, 2009, 31 (3): 429-434(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2009.03.012 [34] Du Y, Deng Y M, Ma T, et al. Hydrogeochemical evidences for targeting sources of safe groundwater supply in arsenic-affected multi-level aquifer systems[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 645: 1159-1171. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.173 [35] 戴九兰. 碘在土壤-植物系统中的生物有效性[D]. 山东青岛: 山东农业大学, 2004.Dai J L. Bioeffectiveness of iodine in soil-plant systems[D]. Qingdao Shandong: Shandong Agricultural University, 2004(in Chinese with English abstract). [36] Burgess W G, Hoque M A, Michael H A, et al. Vulnerability of deep groundwater in the Bengal aquifer system to contamination by arsenic[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2010, 3: 83-87. doi: 10.1038/ngeo750 [37] Li J X, Wang Y X, Xie X J, et al. Hydrogeochemistry of high iodine groundwater: A case study at the Datong Basin, northern China[J]. Environmental Science Processes and Impacts, 2013, 15(4): 848-859. doi: 10.1039/c3em30841c [38] Liu R, Ma T, Zhang D T, et al. Spatial distribution and factors influencing the different forms of ammonium in sediments and pore water of the aquitard along the Tongshun River, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 266: 115212. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115212 [39] Li Z, Zhang T, Chen B, et al. Dynamics of soluble organic carbon and its relation to mineralization of soil organic carbon[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2004, 41: 544-552. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB200404007.htm [40] Reszat T N, Hendry M J. Complexation of aqueous elements by doc in a clay aquitard[J]. Groundwater, 2007, 45(5): 542-553. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2007.00338.x [41] Zou J Y, Varenyam A. Sources and dynamics of inorganic carbon within the upper reaches of the Xi River basin, southwest China[J]. Plos One, 2016, 11(8): e0160964. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160964 [42] Dhiraj P, Sufia K K, Ashok K G, et al. Diversity, metabolic properties and arsenic mobilization potential of indigenous bacteria in arsenic contaminated groundwater of West Bengal, India[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(3): e0118735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118735 [43] Golterman H L. The calcium-and iron bound phosphate phase diagram[J]. Hydrobiologia, 1988, 159: 149-151. doi: 10.1007/BF00014722 [44] Heiberg L, Pedersen T V, Jensen H S, et al. A comparative study of phosphate sorption in lowland soils under oxic and anoxic conditions[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2010, 39(2): 734-743. doi: 10.2134/jeq2009.0222 [45] Prem M, Hansen H C B, Wenzel W, et al. High spatial and fast changes of iron redox state and phosphorus solubility in a seasonally flooded temperate wetland soil[J]. Wetlands, 2015, 35(2): 237-246. doi: 10.1007/s13157-014-0608-0 [46] 罗义鹏, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等. 长江中游故道区高碘地下水分布与形成机理[J]. 地球科学, 2021. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.031Luo Y P, Deng Y M, Du Y, et al. Distribution and formation mechanism of high iodine groundwater in the middle of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Earth Sciences, 2021. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.031 (in Chinese with English abstract). [47] 薛江凯, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等. 长江中游沿岸地下水中有机质分子组成特征及其对碘富集的指示[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(11): 1-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202111026.htmXue J K, Deng Y M, Du Y, et al. Characteristics of organic matter molecular composition in groundwater along the middle Yangtze River and its indication of iodine enrichment[J]. Earth Sciences, 2021, 46(11): 1-20(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202111026.htm [48] Huang Y W, Du Y, Ma T, et al. Dissolved organic matter characterization in high and low ammonium groundwater of Dongting Plain, central China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 208: 111779. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111779 [49] Neidhardt H, Schoeckle D, Schleinitz A, et al. Biogeochemical phosphorus cycling in groundwater ecosystems: Insights from South and Southeast Asian floodplain and delta aquifers[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 644: 1357-1370. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.056 [50] Nisbeth C S, Jessen S, Bennike O. Role of groundwater-borne geogenic phosphorus for the internal P release in shallow lakes[J]. Water, 2019, 11: 1783. doi: 10.3390/w11091783 [51] Nisbeth C S, Kidmose J, Weckstrom K B. Dissolved inorganicgeogenic phosphorus load to a groundwater-fed lake: Implications of terrestrial phosphorus cycling by groundwater[J]. Water, 2019, 11: 2213. doi: 10.3390/w11112213 [52] Liu R, Ma T, Qiu W K, et al. Effects of Fe oxides on organic carbon variation in the evolution of clayey aquitard and environmental significance[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 701: 134776. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969719347679 [53] Jones R I, Shaw P J, De H H. Effects of dissolved humic substances on the speciation of iron and phosphate at different pH and ionic strength[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 1993, 27(6): 1052-1059. http://eurekamag.com/pdf.php?pdf=002363877 [54] Gerke J, Hermann R. Adsorption of orthophosphate to humic-Fe-complexes and to amorphous Fe-oxide[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 1992, 155(3): 233-236. doi: 10.1002/jpln.19921550313/abstract -





 下载:
下载: