Distribution characteristics and genesis of nitrate in nested groundwater flow system in northern Ordos Basin
-
摘要: 水资源短缺的鄂尔多斯盆地内地下水遭受硝酸盐(NO3-)污染等问题日益突出,识别盆地不同地下水流系统的NO3-分布规律及其成因,对地下水资源的合理利用与保护具有重要意义。选取鄂尔多斯盆地北部湖泊集中区白垩系地下水系统为研究对象,基于水化学和聚类-主成分分析划分地下水流系统级次,在此基础上对比分析不同级次地下水流系统中NO3-分布特征,综合水化学和环境同位素分析识别多级次地下水流系统中NO3-来源及其潜在过程。研究表明:研究区ρ(NO3-)超出地下水质量标准(GB/T 14848-2017)Ⅲ类水标准的地下水样品集中在局部-中间地下水流系统,其超标率达到28%;区域地下水流系统中ρ(NO3-)均值约为1 mg/L。研究区不同级次地下水流系统中ρ(NO3-)分布特征主要与人类活动影响程度有关,而地下水蒸发富集和反硝化衰减作用对ρ(NO3-)的影响可以忽略。其中,局部-中间地下水流系统受到人类活动产生的污染影响显著,其NO3-污染主要来源于无机铵肥和粪便污水等;区域地下水流系统可能尚未受到人类活动污染,其NO3-来源于天然有机氮矿化。Abstract: Under the situation of water shortage and increasingly serious groundwater nitrate pollution in Ordos Basin, it is helpful for rational utilization and protection of groundwater resources to identify the distribution and causes of nitrate in different groundwater flow systems in Ordos Basin, so this research was carried out in the typical groundwater-fed lakes area within the basin.Hydrochemistry and multivariate statistical analysis (i.e., hierarchical cluster analysis and principal component analysis) were combined to identify the nested groundwater flow systems.Based on this, the distribution characteristics of nitrate in different groundwater flow systems were compared and analyzed.And both hydrochemistry and environmental isotopes were considered to further identify the sources and potential evolution processes of nitrate in nested groundwater flow systems.The results show that the groundwater samples with nitrate content exceeding the groundwater quality standard (GB/T 14848-2017) were taken from the local and intermediate groundwater flow system, with an over-standard rate reached 28%, and the mean nitrate content in the regional groundwater flow system is about 1 mg/L.The distribution of nitrate in different groundwater flow systems was dominated by the extent of human activities, while the influence of evaporation enrichment and denitrification attenuation processes can be ignored.And within the nested groundwater flow systems, the local and intermediate ones were significantly affected by pollution from human activities, with inorganic ammonium fertilizer and manure and sewage the main pollution sources of nitrate, but the regional one has not been polluted, with mineralization of natural organic nitrogen as its nitrate source.
-
Key words:
- groundwater flow system /
- nitrate /
- hydrochemistry /
- environmental isotopes /
- Ordos Basin
-
全球水资源硝酸盐(NO3-)污染形势严峻,水体中以人类活动输入为主的大量NO3-不仅引发了富营养化、水质恶化等生态环境问题,导致水质型缺水[1-2],还可能使人类罹患“蓝婴症”、结肠直肠癌等多种疾病[3]。故识别水体中NO3-来源及成因对于防控污染和保障用水安全至关重要[4]。
相对于地表水而言,储存于地下空间中的地下水具有一定的隐蔽性和较差的自净修复能力,地下水是否受到NO3-污染或污染程度并不直观可视。常规的水质监测仅反映了孤立的时空点上的水质情况,难以满足溯源和预测水质变化趋势的需求。随着同位素分析技术的发展,基于NO3-不同初始来源具有独特的同位素组成和稳定氮氧同位素在NO3-自然衰减过程中遵循一定的分馏规律[5],应用水化学结合稳定氮氧同位素识别水体中NO3-来源及转化过程取得了良好的效果[6-9]。但是随着人类活动的影响增强,地下水中NO3-来源的异质性增大,再叠加不同地区各异的环境背景条件,NO3-的生物地球转化过程也会复杂化,初始同位素组成特征也会被改变[10-11]。目前主要从统筹考虑环境同位素、水化学等物理化学指标和土地利用类型、人口密度等社会经济要素的角度分析地下水NO3-污染问题[10-14]。
值得注意的是以往的研究普遍将地下水单纯看作NO3-溶解、迁移的均质载体,忽视了地下水流的时空演化特性。受控于自然地理条件和人为因素的双重影响,流动的地下水会自组织地在地下空间中构成动态的地下水流系统,地下水流以不同级次的方式发生有序运移,耦合其中的水化学信息也由此具有了时空演化特性[15]。由于不同级次的地下水流可能具有不同的补给历史、相对独立的径流和排泄途径,其地下水循环条件存在差异,其中的NO3-主要来源和转化过程可能也因此不同[16]。同时,在同等强度外界条件作用下,地下水中NO3-污染程度也会因为地表NO3-输入位置处在地下水流系统的不同部位产生差异[17]。因此,识别地下水流系统的模式,对于构建地下水演化的时空四维图景,追溯并细化不同级次水流中NO3-来源和转化过程、明确当前人类活动的影响程度、推演未来水质发展趋势而言具有重要意义。
鄂尔多斯盆地地处我国西北干旱内陆,水资源匮乏,地下水是当地生活、生产、生态的主要供水水源。其中,鄂尔多斯盆地北部白垩系含水层内无连续的隔水层,整体构成一个巨厚型地下含水系统,对于当地生产生活供水具有重大意义[18]。由于其独特的波状起伏地形构成了多个潜在的势源和势汇,前人研究表明此白垩系地下含水系统内部发育了多级次地下水流系统[19-24]。随着农牧业等人类活动加剧,该区域地下水NO3-污染问题日益突出,使得水资源供需矛盾进一步加剧。然而,目前仅了解该区域地下水中NO3-的浓度分布特征和以农牧业活动等人为来源输入的特点[24-28],并不清楚当前人类活动对不同级次地下水流系统的影响程度。
基于此,笔者拟选取鄂尔多斯盆地北部典型的湖泊集中区作为研究区,在地下水流系统理论的指导下开展NO3-污染来源及成因研究。通过综合水文地质条件、水化学场和同位素数据,识别湖泊集中区白垩系地下水系统中发育的地下水流系统模式;分析不同级次地下水流中NO3-的含量特征和污染情况;确定不同级次地下水流中NO3-的主要来源。通过研究获知当地人类活动输入的NO3-对不同级次地下水流系统中水质的影响,并为地下水保护工作提供指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
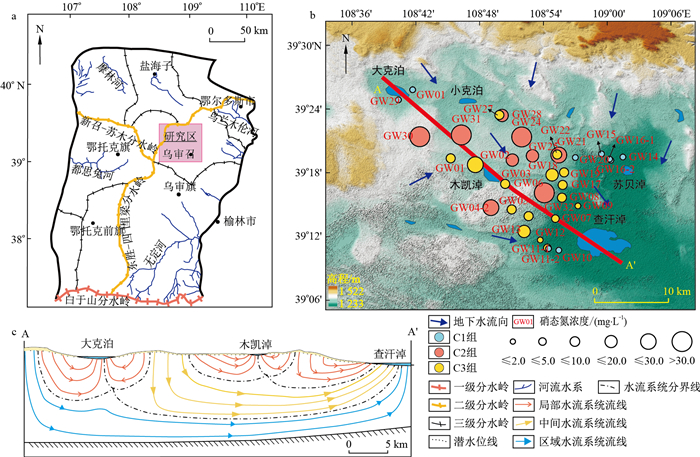
研究区位于鄂尔多斯盆地北部,总面积约200 km2。地形起伏较缓,高程为1 100~1 500 m,北西高,南东低。地貌类型主要为沙漠高原,在低洼处发育5个大型湖泊,即大克泊、小克泊、查汗淖、苏贝淖和木凯淖。降水主要集中在夏季,年平均降水量324 mm,年平均蒸发量2 349 mm,为典型的大陆性干旱半干旱气候。
研究区内地层由老至新依次为侏罗系碎屑岩系、白垩系保安群碎屑岩和第四系薄层松散沉积砂层。其中侏罗系主要岩性为泥岩、泥质灰岩,供水意义不大,是区域内的相对隔水层。本区的主要含水岩组为白垩系碎屑岩类孔隙-裂隙含水岩组和第四系松散岩类孔隙含水岩组。白垩系主要岩性为砂岩,夹少量泥岩和页岩,其间不存在连续稳定的隔水层。地下水主要接受降水补给,经过人为开采、汇流排泄至湖泊的方式排泄。受东胜-四十里梁分水岭的控制,地下水总体从北西流向南东[21]。其地下水循环系统在垂向上可划分为局部地下水流系统、中间地下水流系统和区域地下水流系统。其中局部地下水流系统主要发育在局部的地形高地和洼地之间,循环深度为100~150 m;中间地下水流系统主要发育在地表分水岭和较大型的湖泊之间,循环深度小于600 m;区域地下水流系统主要发育于地表分水岭和大型湖泊、河流之间,循环深度可达白垩系底界,为500~1 000 m[29]。第四系主要岩性为结构疏松的风积沙,渗透性强,储水意义不大,是包气带土壤的主要组成部分,其间水分蒸发强烈,蒸发极限深度在1 m以内[18, 30-31]。
1.2 样品采样与测试
2017年9月在研究区机民井内共采集了34个地下水样(图 1)。采用大流量抽水泵抽水,采样前通过哈希便携式多参数水质分析仪(HQ40d)现场分析地下水的pH、温度、溶解氧和电导率指标。待各项指标稳定后,采集地下水通过0.45 μm的针式滤器过滤后装满润洗过的聚乙烯样品瓶中,完成采集。其中,用于阳离子测试的样品现场加入优级纯浓硝酸(HNO3)酸化至pH值小于2,防止离子水解。碱度指标(HCO3-和CO32-浓度)在距采样时间24 h内利用酸碱中和滴定法进行测试。阴离子(Cl-、NO3-、SO42-)使用离子色谱仪(ICS-900)进行测试,阳离子(Ca2+、Mg2+、Na+、K+)采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(PE Optima 8300)进行测试,所有水样的阴阳离子电荷平衡相对误差均小于±10%。地下水氢氧同位素组成(δ2H和δ18O)在中国地质大学(武汉)盆地水文过程与湿地生态恢复学术创新基地用超高精度水同位素分析仪(L2130-I,Picarro)测定,水样δ2H和δ18O的测试精度分别为0.1‰和0.03‰,δ2H和δ18O值均是相对于维也纳标准平均海水(V-SMOW)表示。硝酸盐氮氧同位素组成(δ15N和δ18O)在自然资源部第三海洋研究所基于化学转化法采用GasBench II-IRMS在线连续分析系统进行分析,样品δ15N和δ18O的测试精度分别为0.2‰和0.3‰,δ15N和δ18O值分别是相对于大气氮(Air-N2)和维也纳标准平均海水(V-SMOW)表示。
1.3 多元统计分析
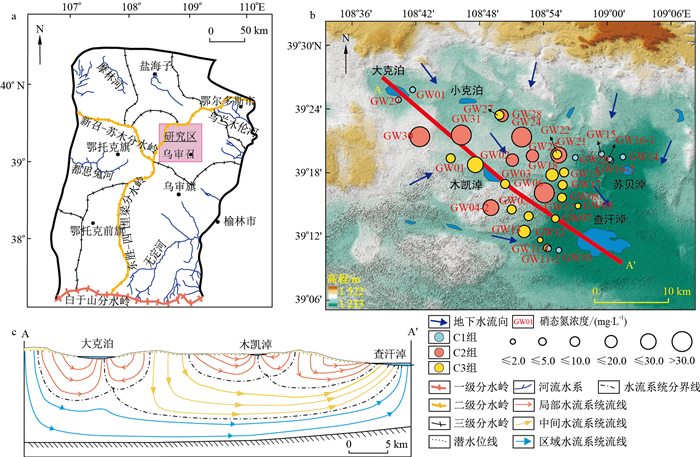
多元统计分析方法中聚类分析和主成分分析常被应用于分析地下水水化学演化问题。进行多元统计分析之前需要对变量进行选择,去除一些有着加和性质或是空间变异性小的变量[34]。本文通过排除皮尔逊系数>0.9(二者取其一)或变异系数< 5%的变量[35],确定选取Ca2+,Mg2+,Na+,K+,Cl-,SO42-,HCO3-共7个变量进行后续统计分析。利用Kolmogorov-Smirnov(K-S)正态性检验分析各变量是否为正态分布,其中Na+未通过正态性检验(p < 0.05),故对其进行了对数转换处理。所有数据还经过z得分标准化处理,保证各变量权重相等[34, 36]。经上述处理的数据应用于系统聚类分析和主成分分析。
系统聚类分析经常用于划分水化学数据,利用欧式距离和离差平方和法(Ward法)进行分析可以获得组间差异最大的分类结果[36]。但由于系统聚类分析产生的分类结果具有一定的主观性,故有必要对聚类结果的合理性进行检验。主成分分析是通过提取主成分实现数据降维且数据信息损失较少的统计分析方法。对提取的主成分的各变量的因子载荷和不同样品的因子得分绘制双变量图,可以展示出主成分、所分析变量和原始水化学数据之间的关系,分析出不同样品经历的主要水文地球化学过程。聚类分析形成的不同组别理论上有着独特的水化学演化过程,在双变量图中表现为不同组别的样品数据不发生重叠[35, 37]。
多元统计分析在SPSS 26.0软件中实现;变量关系分析图件在Origin 2021b软件中绘制;空间分布图在ArcGIS 10.3和CorelDRAW 2018软件中绘制。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 研究区地下水流系统级次划分
首先基于水化学和聚类-主成分分析方法,确定本研究采集的地下水样品所属的地下水流系统级次。图 2-a为基于所选变量对研究区地下水样品进行系统聚类分析的树状图。将链接距离等于10作为分类标准,可将研究区地下水样品划分为3组,分别命名为C1,C2,C3(图 2-a)。在主成分分析中,按照特征值大于1的原则提取了2个主成分(即PC1和PC2),它们的累计贡献率达到了76.97%(分别为48.23%,28.74%),说明前2个主成分PC1和PC2能够反映原始数据的基本信息。C1, C2和C3三组样品在主成分得分-载荷双变量图中得到很好的区分(图 2-b),表明上述聚类结果对于研究区地下水样品的分组是合理的。
C1、C2和C3三组地下水样品点的空间分布如图 1所示。C1组水样点(其中水样点GW29来源于自流井)靠近地势低洼的湖淖,部分点井深虽然在100 m以浅,但是其ρ(DO)很低(0.1~2.5 mg/L),并且主要水化学类型为HCO3-Na型和HCO3·SO4-Na型(表 1),表明该组地下水位于地下水排泄区,并可能具有很深的循环深度(或很长的循环路径)。
表 1 不同类别地下水样的水化学组成Table 1. Hydrochemical components in different clusters of groundwater samples地下水样品 ρ(DO)/(mg·L-1) ρ(TDS)/(mg·L-1) ρ(NO3-)/(mg·L-1) δ15NNO3/‰ δ18ONO3/‰ δ18OH2O/‰ δ2HH2O/‰ 主要水化学类型 C1 最小值~最大值 0.1~2.5 277.0~437.5 0.7~5.3 1.9~6.4 -2.0~11.6 -10.78~-9.10 -87.7~-75.0 HCO3-Na型和HCO3·SO4-Na型 均值 1.5 349.7 1.2 3.6 2.6 -10.18 -83.5 C2 最小值~最大值 8.0~10.6 366.4~681.3 64.8~191.8 -0.7~4.6 -2.8~4.1 -8.87~-7.58 -67.8~59.6 HCO3-Ca型和HCO3·NO3-Ca型 均值 9.6 496.1 123.3 2.3 -0.4 -8.21 -63.7 C3 最小值~最大值 1.6~9.6 201.8~409.0 0.8~97.8 2.3~6.9 -4.5~6.3 -11.44~-7.38 -88.1~58.9 HCO3-Ca型和HCO3-Na型 均值 5.7 286.3 32.1 4.4 0.6 -9.06 -70.6 C2组水样点位于局部地形高地,并且C2组水样采集深度相对最浅(100 m以浅),其ρ(DO)很高(8.0~10.6 mg/L),并且水化学类型以HCO3-Ca型为主(表 1),表明该组地下水循环深度较浅(或循环路径较短)。C3组水样点空间分布位于C1和C2之间,采样井深从几米到几百米不等,其ρ(DO)很高(1.6~9.6 mg/L),水化学类型以HCO3-Ca型和HCO3-Na型为主(表 1),表明该组地下水的循环深度(循环路径)介于C1和C2之间。
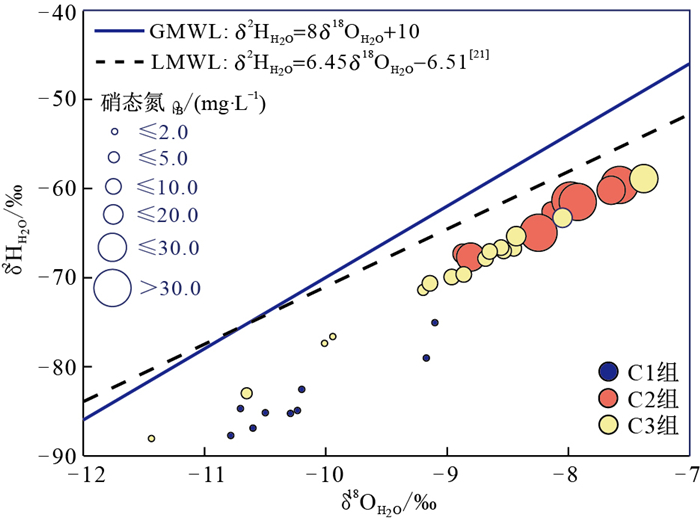
研究区各组地下水样品的氢氧同位素组成(δ2H和δ18O)均落在大气降水线附近(图 3),表明不同循环深度的地下水均来源于大气降水补给,并且未受到显著的蒸发作用影响。然而,C1组地下水样品的δ2H和δ18O值的变化范围分别为-87.7‰~-75.0‰和-10.78‰~-9.10‰,相比C2组的(δ2H和δ18O值分别为-67.8‰~-59.6‰和-8.87‰~-7.58‰)明显偏负(表 1)。C3组地下水样品的δ2H和δ18O值虽然处于C1和C2的范围之间,但大部分C3样品的δ2H和δ18O值更接近C2端(图 3)。类似地,Pan等[21]和Yin等[38]的研究表明鄂尔多斯地区深循环地下水的氢氧同位素组成相比现代大气降水明显偏负,认为其来源于晚更新世和早全新世时期较寒冷气候条件下的大气降水补给。因此,本次研究中各组地下水样品的δ2H和δ18O差异特征可以进一步证明C1来源于较寒冷时期的古大气降水补给,循环深度较深(或循环路径较长),更新速率较慢;而C2组地下水来源于现代大气降水补给,循环深度较浅(或循环路径较短),更新速率较快。
基于不同组别水样的水化学和环境同位素组成及其空间分布特征,有理由认为研究区内白垩系含水层中发育不同级次地下水流系统[39]。其中C1组地下水样取自区域地下水流系统,C2和C3组地下水样取自局部-中间地下水流系统。
2.2 不同级次地下水流系统中NO3-分布特征
本研究所采集的C1、C2、C3组地下水样中ρ(NO3-)分别为0.7~5.3,64.8~191.8,0.8~97.8 mg/L(表 1)。研究区地下水ρ(NO3-)在不同级次地下水流系统中存在显著差异(Kruskal-Walis H检验,p < 0.05),整体表现为随地下水循环深度增加而减小的特征(表 1)。其中,采自区域地下水流系统中的C1组水样的ρ(NO3-)很低,均值约为1 mg/L(表 1)。采自局部-中间地下水流系统中的C2和C3组水样ρ(NO3-)的均值分别达到123.3,32.1 mg/L,部分地下水样品中ρ(NO3-)浓度甚至高达191.8 mg/L(表 1),这表明研究区局部-中间地下水流系统明显受到人类活动产生的污染影响。研究区ρ(NO3-)超出地下水质量标准(GB/T 14848-2017)中的Ⅲ类水标准(NO3-N≤20.0 mg/L)的地下水样品集中在局部-中间地下水流系统,其超标率达到28%。
研究区属于农牧区,牧区分布连续且宽广,区内居民点和耕地在空间上呈现小的斑块状分布,人类活动较为分散[28]。研究区内潜在的硝酸盐污染来源包括农牧业活动(肥料施用、动物粪便裸露地表、牲畜排泄物堆肥等)和生活污水等,属于面源污染[25]。除取样编号GW29的水样取自远离人类活动的自流井之外,本次研究中其他地下水样都是采自居民点或耕地旁边的机民井,周围均存在人类活动。同时,取样位置相近的GW11-1水样(属于C3组)和GW11-2水样(属于C1组)的ρ(NO3-)分别为16.9,0.7 mg/L,分别表现为受人为活动污染和未受到人为活动污染。类似地,取样位置相近的C2组水样中(取样编号GW21和GW28)的ρ(NO3-)显著高于C3组水样(GW22和GW27)。因此,污染源空间分布及其强度并非控制研究区地下水系统中NO3-浓度差异的唯一因素,还可能与地下水流系统级次有关。研究区不同级次地下水流系统中NO3-浓度变异性的分布特征,一方面可能是由于农牧业活动对不同级次地下水流系统的直接污染的程度不同;另一方面可能是地表硝酸盐经淋滤作用渗入地下水中,在不同级次地下水流系统或深度中可能存在不同程度的反硝化作用,从而导致NO3-的自然衰减程度不一。
2.3 不同级次地下水流系统中NO3-分布成因
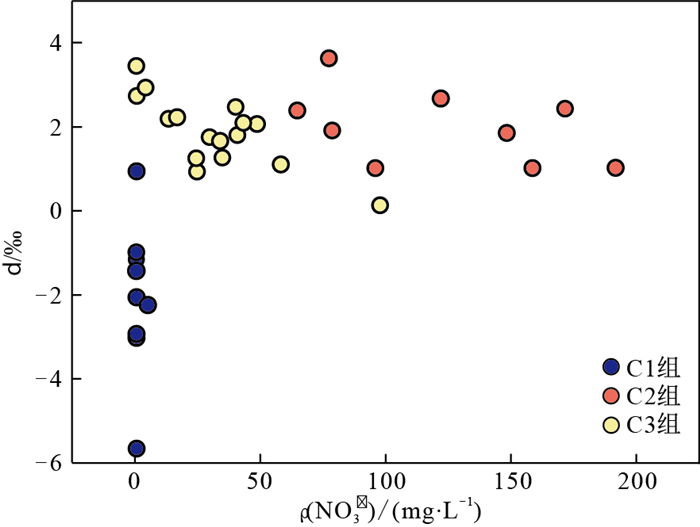
研究区地处干旱半干旱区,蒸发作用可能是水化学组分含量高低的潜在控制因素之一[26]。然而,δ2H和δ18O关系(图 3)表明研究区不同级次水流系统的地下水均未受到显著的蒸发作用影响。此外,随着地下水ρ(NO3-)增加,用于表征蒸发程度的氘过量参数(d=δ2H-8×δ18O)在C2和C3组地下水中基本保持稳定(图 4)。不同于新疆阿克苏地区承压含水层中隔水顶板对蒸发作用的阻碍[40],本研究区白垩系含水层属于潜水含水层,以上特征指示样品点的地下水埋深处在潜水蒸发极限深度之下,蒸发作用对地下水中ρ(NO3-)的影响可以忽略。
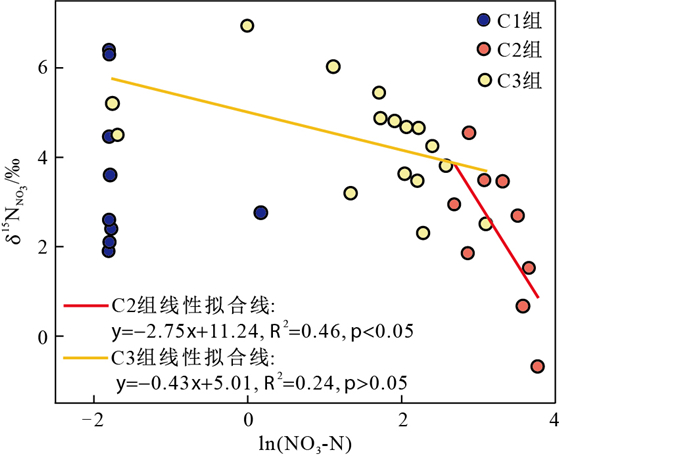
反硝化作用是厌氧或缺氧的地下水环境中NO3-的重要自然衰减途径,反硝化过程中NO3-的氮氧同位素组成变化遵循瑞利分馏,表现为随ρ(NO3-)降低而逐渐富集重同位素[41]。本研究区C1组地下水样品虽然同时呈现低ρ(DO)和低ρ(NO3-)特征,但是其δ15N值和ln(NO3-N)之间没有显著相关性(斯皮尔曼相关系数r=0.000,p>0.05)(图 5),即NO3-的氮同位素组成变化并未呈现出瑞利分馏特征。这表明研究区的区域地下水流系统中虽然处于缺氧环境但是并未发生反硝化作用,其ρ(NO3-)低(均值约为1 mg/L)是由于地表人类活动产生的硝酸盐尚未进入该区域地下水流系统中。因此,C1组地下水代表研究区的区域地下水流系统的天然环境,其ρ(NO3-)的天然背景值约为1 mg/L。
研究区C2和C3组样品采自局部-中间水流系统,其中C2组全部样品和C3组近70%样品的ρ(DO)大于5 mg/L,这表明局部-中间地下水流系统整体偏氧化环境,不利于反硝化作用的发生[42]。同时,C2和C3组水样中δ15N值和ln(NO3-N)拟合斜率分别为-2.75‰(p>0.05)和-0.43‰(p < 0.05)(图 5),远小于反硝化作用的氮同位素富集系数理论值(-5%~-40%),表明局部-中间地下水流系统中的反硝化程度很弱[43-44]。因此,同一局部-中间水流系统中NO3-浓度分布的空间异质性特征主要是由于污染源分布差异及其影响程度差异所致。相对于区域NO3-天然背景值而言,C2和C3组代表的局部-中间地下水流系统正在遭受严重的NO3-污染,其污染影响深度甚至达到200 m以上。由于氧化环境和微生物活动所需碳源的限制等,研究区地下水中反硝化作用微弱,局部-中间地下水流系统一旦受NO3-污染,则很难依靠自然衰减过程实现水质净化[25]。
2.4 NO3-来源识别
基于不同来源NO3-的氮氧同位素组成差异,可以利用δ15N和δ18O的关系分析NO3-来源[5]。研究区区域地下水流系统中NO3-属于天然来源,C1组地下水样中NO3-的δ15N和δ18O变化范围分别为1.9‰~6.4‰和-2.0‰~11.6‰(表 1),基本分布在土壤有机氮来源的区间范围(图 6)。这表明研究区的区域地下水流系统中NO3-主要来源于包气带、含水层沉积物中的有机氮矿化[12]。研究区C2和C3组地下水样中高ρ(NO3-)指示局部-中间地下水流系统明显受到人为活动产生的NO3-污染,其δ15N变化范围分别为-0.7‰~4.6‰和2.3‰~6.9‰,δ18O变化范围分别为-2.8‰~4.1‰和-4.5‰~6.3‰(表 1),均落在无机铵肥和粪便污水来源的区间范围(图 6)。
此外,C2和C3组地下水样的δ15N和δ18O值的拟合线斜率分别为1.09(p < 0.05)和0.83(p>0.05),不在反硝化作用的氮氧同位素富集系数比值的理论区间内(εN/εO=1.3~2.1)[45-46],再次证实局部-中间地下水流系统中没有发生强烈的反硝化作用。研究区属于干旱-半干旱的农牧区,并且包气带土壤为质地疏松的沙质土,具有很强的渗透性[27]。因此,大范围的农牧业活动(肥料施用、动物粪便裸露地表、牲畜排泄物堆肥等)和生活污水容易造成该地区局部-中间地下水流系统中硝酸盐污染。
3. 结语
为了识别鄂尔多斯盆地北部湖泊集中区白垩系地下水系统中硝酸盐的分布特征及其成因,利用水化学和聚类-主成分分析将采集的34份地下水样品划分为3个组别(C1~C3),不同组别的水化学、氢氧同位素组成和空间分布特征指示研究区白垩系含水层中发育三级地下水流系统。其中,ρ(NO3-)超出地下水质量标准(GB/T 14848-2017)Ⅲ类水标准的地下水样品集中在局部-中间地下水流系统,其超标率达到28%;区域地下水流系统中ρ(NO3-)均值约为1 mg/L。氘过量参数、稳定氮同位素与NO3-的关系指示研究区地下水中ρ(NO3-)受蒸发富集和反硝化衰减作用的影响可以忽略,不同级次地下水流系统中ρ(NO3-)分布特征主要与人类活动影响程度有关,其中局部-中间地下水流系统受到人类活动产生的污染影响显著,区域地下水流系统可能尚未受到人类活动污染。此外,δ15NNO3和δ18ONO3关系指示局部-中间地下水流系统中NO3-污染主要来源于无机铵肥和粪便污水等;区域地下水流系统中NO3-来源于天然有机氮矿化。由于包气带风积沙渗透性很强,农牧业活动和生活污水容易向地下水中输入NO3-,且氧化环境和微生物所需碳源等对反硝化作用的限制使地下水自我水质净化能力可能较弱。因此,研究区地下水污染防控应当着重采取措施调整农牧方式以减少NO3-的外源输入量,避免深层区域水流系统中地下水受到污染。
-
表 1 不同类别地下水样的水化学组成
Table 1. Hydrochemical components in different clusters of groundwater samples
地下水样品 ρ(DO)/(mg·L-1) ρ(TDS)/(mg·L-1) ρ(NO3-)/(mg·L-1) δ15NNO3/‰ δ18ONO3/‰ δ18OH2O/‰ δ2HH2O/‰ 主要水化学类型 C1 最小值~最大值 0.1~2.5 277.0~437.5 0.7~5.3 1.9~6.4 -2.0~11.6 -10.78~-9.10 -87.7~-75.0 HCO3-Na型和HCO3·SO4-Na型 均值 1.5 349.7 1.2 3.6 2.6 -10.18 -83.5 C2 最小值~最大值 8.0~10.6 366.4~681.3 64.8~191.8 -0.7~4.6 -2.8~4.1 -8.87~-7.58 -67.8~59.6 HCO3-Ca型和HCO3·NO3-Ca型 均值 9.6 496.1 123.3 2.3 -0.4 -8.21 -63.7 C3 最小值~最大值 1.6~9.6 201.8~409.0 0.8~97.8 2.3~6.9 -4.5~6.3 -11.44~-7.38 -88.1~58.9 HCO3-Ca型和HCO3-Na型 均值 5.7 286.3 32.1 4.4 0.6 -9.06 -70.6 -
[1] Chen Z X, Yu L, Liu W G, et al. Nitrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of water-soluble nitrate in Taihu Lake water system, China: Implication for nitrate sources and biogeochemical process[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 71(1): 217-223. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2425-9 [2] 黄艳雯, 杜尧, 徐宇, 等. 洞庭湖平原西部地区浅层承压水中铵氮的来源与富集机理[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 165-174. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0618Huang Y W, Du Y, Xu Y, et al. Source and enrichment mechanism of ammonium in shallow confined aquifer in the west of Dongting Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 165-174(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0618 [3] Ward M H, Jones R R, Brender J D, et al. Drinking water nitrate and human health: An updated review[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15(7): 1557. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15071557 [4] 陈新明, 马腾, 蔡鹤生, 等. 地下水氮污染的区域性调控策略[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(6): 130-143, 149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201306021.htmChen X M, Ma T, Cai H S, et al. Regional control of groundwater nitrogen contamination[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(6): 130-143, 149(in Chinese with English Abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201306021.htm [5] Nikolenko O, Jurado A, Borges A V, et al. Isotopic composition of nitrogen species in groundwater under agricultural areas: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 621: 1415-1432. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.086 [6] Xu S G, Kang P P, Sun Y. A Stable isotope approach and its application for identifying nitrate source and transformation process in water[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23: 1133-1148. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5309-6 [7] Kaushal S S, Groffman P M, Band L E, et al. Tracking nonpoint source nitrogen pollution in human-impacted watersheds[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2011, 45: 8225-8232. doi: 10.1021/es200779e [8] Zhang Y, Shi P, Li F, et al. Quantification of nitrate sources and fates in rivers in an irrigated agricultural area using environmental isotopes and a Bayesian isotope mixing model[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 208: 493-501. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.164 [9] Yue F J, Li S L, Liu C Q, et al. Tracing nitrate sources with dual isotopes and long term monitoring of nitrogen species in the Yellow River, China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 8537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08756-7 [10] Li C, Li S L, Yue F J, et al. Identification of sources and transformations of nitrate in the Xijiang River using nitrate isotopes and Bayesian model[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 646: 801-810. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.345 [11] Taufiq A, Effendi A J, Iskandar I, et al. Controlling factors and driving mechanisms of nitrate contamination in groundwater system of Bandung Basin, Indonesia, deduced by combined use of stable isotope ratios, CFC age dating, and socioeconomic parameters[J]. Water Research, 2019, 148: 292-305. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.049 [12] Blarasin M, Cabrera A, Matiatos I, et al. Comparative evaluation of urban versus agricultural nitrate sources and sinks in an unconfined aquifer by isotopic and multivariate analyses[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 741: 140374. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140374 [13] Yi Q, Chen Q, Hu L, et al. Tracking nitrogen sources, transformation, and transport at a basin scale with complex plain river networks[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2017, 51(10): 5396-5403. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b06278 [14] Minet E P, Goodhue R, Meier-Augenstein W, et al. Combining stable isotopes with contamination indicators: A method for improved investigation of nitrate sources and dynamics in aquifers with mixed nitrogen inputs[J]. Water Research, 2017, 124: 85-96. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.041 [15] Tóth J. Groundwater as a geologic agent: An overview of the causes, processes, and manifestations[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 1999, 7: 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s100400050176 [16] Villarreal P J, Ávila Olivera J A, Alcántara I I, et al. Nitrate as a parameter for differentiating groundwater flow systems in urban and agricultural areas: The case of Morelia-Capula area, Mexico[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2019, 27: 1767-1778. doi: 10.1007/s10040-019-01933-0 [17] Tóth J. Gravitational systems of groundwater flow: Theory, evaluation, utilization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009. [18] 侯光才. 鄂尔多斯白垩系盆地地下水系统及其水循环模式研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008.Hou G C. Groundwater system and water circulation pattern in Ordos Cretaceous groundwater Basin[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2008(in Chinese with English abstract). [19] Jiang X W, Wan L, Wang J Z, et al. Field identification of groundwater flow systems and hydraulic traps in drainage basins using a geophysical method[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41(8): 2812-2819. doi: 10.1002/2014GL059579 [20] Jiang X W, Wan L, Wang X S, et al. A Multi-method study of regional groundwater circulation in the Ordos Plateau, NW China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26: 1657-1668. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1731-4 [21] Pan G F, Li X Q, Zhang J, et al. Groundwater-flow-system characterization with hydrogeochemistry: A case in the lakes discharge area of the Ordos Plateau, China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2019, 27: 669-683. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1888-x [22] 王冬, 侯光才, 赵振宏. 鄂尔多斯盐海子地下水水流系统划分: 来自水化学方面的探讨[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(12): 122-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201412021.htmWang D, Hou G C, Zhao Z H. Division of groundwater flow system of Yanhaizi in Ordos: From the aspect of hydrochemistry[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2014, 28(12): 122-127(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201412021.htm [23] Lyu M, Pang Z, Yin L, et al. The control of groundwater flow systems and geochemical processes on groundwater chemistry: A case study in Wushenzhao Basin, NW China[J]. Water, 2019, 11(4): 790. doi: 10.3390/w11040790 [24] Lyu M, Pang Z, Huang T, et al. Hydrogeochemical evolution and groundwater quality assessment in the Dake Lake Basin, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2019, 320: 865-883. doi: 10.1007/s10967-019-06515-8 [25] 张晶, 刘运德, 周爱国, 等. 硝酸盐污染地下水中溶解性有机质光谱特征及其指示意义: 以鄂尔多斯盆地北部湖泊集中区为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 262-269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904028.htmZhang J, Liu Y D, Zhou A G, et al. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter and their implications in groundwater contaminated by nitrate of lake concentration area in northern Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(4): 262-269(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904028.htm [26] Yang Q C, Wang L C, Ma H Y, et al. Hydrochemical characterization and pollution sources identification of groundwater in Salawusu aquifer system of Ordos Basin, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 216: 340-349. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.076 [27] 王冬. 鄂尔多斯白垩系盆地北部潜水硝酸盐污染成因分析及防治对策[J]. 地下水, 2006(4): 56-57, 107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2006.04.021Wang D. Analysis on formation causes of nitrate contamination of shallow groundwater and control countermeasures in northern part of cretaceous Ordos Basin[J]. Groundwater, 2006(4): 56-57, 107(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2006.04.021 [28] Zhang Y, Liu Y, Zhou A, et al. Identification of groundwater pollution from livestock farming using fluorescence spectroscopy coupled with multivariate statistical methods[J]. Water Research, 2021, 206: 117754. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117754 [29] Yin L H, Hou G C, Dou Y, et al. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic study of groundwater in the Habor Lake Basin of the Ordos Plateau, NW China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 64: 1575-1584. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0383-z [30] 马稚桐. 鄂尔多斯盆地风沙滩区土壤-地下水蒸发研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019.Ma Z T. Research on soil-groundwater evaporation in the wind-blown sand area of Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [31] Chen J S, Liu X Y, Wang C Y, et al. Isotopic constraints on the origin of groundwater in the Ordos Basin of Northern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 66: 505-517. doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-1259-6 [32] 曹阳. 鄂尔多斯白垩系盆地北部典型湖淖地区地下水循环模式研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2009.Cao Y. Groundwater circulation patterns of typical lake area in northern Ordos Cretaceous Basin[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2009(in Chinese with English abstract). [33] Zhang J, Wang X S, Yin L H, et al. Inflection points on groundwater age and geochemical profiles along wellbores light up hierarchically nested flow systems[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(16): 1-10. [34] Cloutier V, Lefebvre R, Therrien R, et al. Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2008, 353(3/4): 294-313. [35] Castro R P, Ávila J P, Ye M, et al. Groundwater quality: Analysis of its temporal and spatial variability in a karst aquifer[J]. Groundwater, 2018, 56(1): 62-72. doi: 10.1111/gwat.12546 [36] Güler C, Thyne G D, McCray J E, et al. Evaluation of graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2002, 10: 455-474. doi: 10.1007/s10040-002-0196-6 [37] Woocay A, Walton J. Multivariate analyses of water chemistry: Surface and ground water interactions[J]. Groundwater, 2008, 46(3): 437-449. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2007.00404.x [38] Yin L, Hou G, Su X, et al. Isotopes (δD and δ18O) in precipitation, groundwater and surface water in the Ordos Plateau, China: Implications with respect to groundwater recharge and circulation[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2011, 19: 429-443. doi: 10.1007/s10040-010-0671-4 [39] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103Liang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Scienceand Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103 [40] 潘欢迎, 邹常健, 毕俊擘, 等. 新疆阿克苏典型山前洪积扇内高氟地下水的化学特征及氟富集机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 194-203. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0312Pan H Y, Zou C J, Bi J B, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and fluoride enrichment mechanisms of high-fluoride groundwater in a typical piedmont proluvial fan in Aksu area, Xinjiang, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 194-203(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0312 [41] Mariotti A, Germon J C, Hubert P, et al. Experimental determination of nitrogen kinetic isotope fractionation: Some principles; illustration for the denitrification and nitrification processes[J]. Plant and Soil, 1981, 62: 413-430. doi: 10.1007/BF02374138 [42] Rivett M O, Buss S R, Morgan P, et al. Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: A review of biogeochemical controlling processes[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(16): 4215-4232. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.07.020 [43] Xuan Y X, Tang C Y, Cao Y J. Mechanisms of nitrate accumulation in highly urbanized rivers: Evidence from multi-isotopes in the pearl River Delta, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 587: 124924. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124924 [44] Xue D M, Botte J, De Baets B, et al. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface- and groundwater[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(5): 1159-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.048 [45] Böttcher J, Strebel O, Voerkelius S, et al. Using isotope fractionation of nitrate nitrogen and nitrate oxygen for evaluation of microbial denitrification in a sandy aquifer[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1990, 114(3/4): 413-424. [46] Fukada T, Hiscock K M, Dennis P F, et al. A dual isotope approach to identify denitrification in groundwater at a river-bank infiltration site[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(13): 3070-3078. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00176-3 [47] Wang W, Song X, Ma Y. Identification of nitrate source using isotopic and geochemical data in the lower reaches of the Yellow River irrigation district(China)[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75: 936. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-5721-3 期刊类型引用(9)
1. 何景媛,张茹星,丁水波,李思维,李东阳,马志飞. 极端干旱气候下赣江下游及支流流域地下水硝酸盐污染特征及来源. 环境工程技术学报. 2025(01): 111-119 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 李丽君,李旭光. 西辽河平原浅层地下水中“三氮”分布特征及健康风险评价. 地质与资源. 2024(01): 90-97 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 翟虎威,张俊涛,张雪莲,高旭波,郭李奇. 山西长治辛安泉域岩溶水硫酸盐污染来源分析. 地质与勘探. 2024(03): 563-571 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 边超,蔡五田,陈涛,张怀胜,刘丹丹,张磊,史云. 基于现场检测的邢台百泉泉域岩溶水硝酸盐氮形成特征. 科学技术与工程. 2023(04): 1772-1780 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 李亚楠,胡春春,康莹,张新,刘冬跃,李心月. 北京市东北部地区地下水水质状况及变化特征. 广西水利水电. 2023(06): 38-44 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 郑小康,杨志兵. 岩溶含水层饱和-非饱和流动与污染物运移数值模拟. 地质科技通报. 2022(05): 357-366 .  本站查看
本站查看7. 李雅依,夏强,许模,曹聪. 隔档式构造区岩溶地下水流系统多级次嵌套结构的水化学识别. 地质科技通报. 2022(05): 405-413 .  本站查看
本站查看8. 王焰新. 星辰大海, 逐梦未来——中国地质大学校庆暨《地质科技通报》刊庆专辑序. 地质科技通报. 2022(05): 3 .  本站查看
本站查看9. 胡晓兵,方健聪,翟虎威,张凯,马永明,靳建红,高旭波. 硫氧同位素在识别辛安泉域岩溶水SO_4~(2-)来源中的应用. 地质科技通报. 2022(05): 333-340 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术