Optimization of karst water monitoring network based on information entropy: A case study in typical groundwater source sites in Xuzhou
-
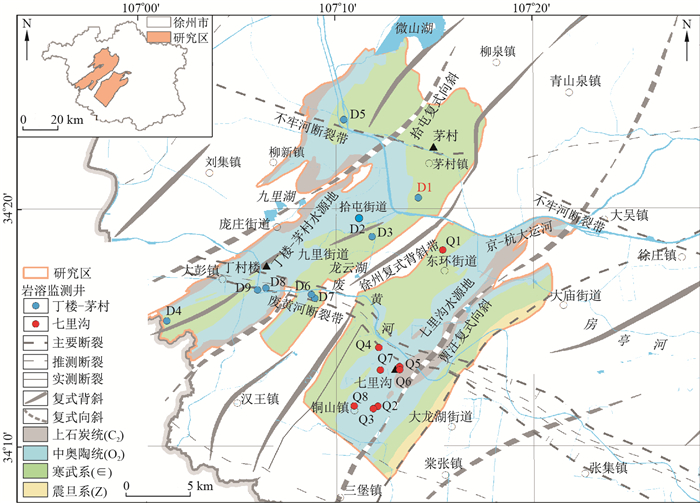
摘要: 在各级水利与自然资源部门地下水监测数据共享机制逐步完善背景下,针对日益凸显的原有监测系统中存在的监测井布局不合理问题以及岩溶含水系统具有的非均质性和各向异性特征,选取徐州市丁楼-茅村和七里沟2个典型水源地,分别采用互信息-距离(T-D)和最大信息最小冗余(MIMR)模型对研究区监测网信息冗余性和最优监测井组合进行了研究。结果显示:丁楼-茅村水源地水位监测数据离散程度、信息熵、信息传递量和信息衰减速率均大于七里沟水源地,2个水源地在ε取10-1时的水位信息有效传递距离分别为4.7,4.8 km,指示出两地相似的岩溶发育程度和水力传导性能。通过对比监测井控制范围的实际值和理论值发现2个水源地监测井之间均存在信息冗余。现有监测条件下,丁楼-茅村水源地最优监测井数为6眼,最优监测井组合为D1-D2-D4-D5-D7-D9;七里沟水源地最优监测井数量为5眼,最优组合为Q1-Q3-Q4-Q5-Q7。将优化结果与原监测网相比,2个水源地监测井数量均减少3眼,分别能提供原监测网信息总量的98.5%,94.9%,监测网控制范围分别下降0.4%,1.2%,信息冗余量分别减少49.0%,56.4%。表明优化后的监测网能够提供与原站网相当的信息量和控制范围,同时可以显著降低信息冗余度与监测成本。
-
关键词:
- 信息熵 /
- 岩溶水 /
- 监测网优化 /
- 互信息-距离模型 /
- 最大信息最小冗余模型
Abstract: In view of the unreasonable layout of monitoring wells and heterogeneity and anisotropy of the karst aquifer monitoring system, mutual information-distance (T-D) and maximum information minimum redundancy (MIMR) models can be used to study the information redundancy of the monitoring network and the optimal monitoring well combination.Dinglou-Maocun and Qiligou in Xuzhou City were selected to do the research.The results show that: the data dispersion degree, information entropy, information transfer amount and information attenuation rate in Dinglou-Maocun are all greater than those in Qiligou.When ε is set to be 10-1, the effective transmission distance of water level information is 4.7 km and 4.8 km respectively, indicating the similar karst development degree and hydraulic conductivity of the two sites.By comparing the actual value and the theoretical value of the control area of monitoring well, it can be found that information redundancy exists in both two water source sites.The optimized number of monitoring wells in Dinglou-Maocun is 6, and the corresponding combination of monitoring wells is D1-D2-D4-D5-D7-D9, while the optimized number of monitoring wells is 5 and the corresponding combination of monitoring wells is Q1-Q3-Q4-Q5-Q7 in Qiligou.Compared to the original monitoring network, three monitoring wells are reduced in both two water source sites with 98.5% and 94.9% of the total information retention, 0.4% and 1.2% of control range decrease, 49.0% and 56.4% of the information redundancy reduction, respectively.It shows that the optimized monitoring network can provide the same amount of information and control range as the original site network, and significantly reduce information redundancy and monitoring costs. -
表 1 研究区各监测井2014-2020年水位数据特征值
Table 1. Characteristic value of water level for each monitoring well in the study area from 2014-2020
研究区 原始编号 统一编号 最大值 最小值 平均值 中位数 方差 标准差 水位h/m 丁楼-茅村水源地 09133 D1 20.58 13.17 17.03 17.21 3.97 1.99 70002 D2 13.93 -0.56 4.49 3.15 10.73 3.28 70004 D3 29.33 14.79 23.86 24.68 12.35 3.51 09191 D4 20.69 -5.73 10.09 8.95 47.89 6.92 09171 D5 30.81 -2.37 14.22 14.66 98.22 9.91 09048 D6 28.04 -9.56 11.71 16.00 144.73 12.03 70003 D7 29.80 -7.70 13.71 17.35 145.80 12.07 70009 D8 32.31 -9.29 11.06 13.55 154.52 12.43 09175 D9 31.52 -9.47 11.28 14.03 157.18 12.54 七里沟水源地 70011 Q1 36.23 27.46 31.29 31.05 3.50 1.87 09206 Q2 26.73 15.22 21.88 21.79 5.71 2.39 75011 Q3 27.10 16.19 22.20 21.92 5.80 2.41 70010 Q4 28.58 16.50 23.89 23.69 5.93 2.44 70007 Q5 28.93 15.73 22.83 22.83 7.32 2.71 09068 Q6 28.07 14.94 22.29 22.33 7.52 2.74 09064 Q7 28.31 12.74 21.74 22.05 9.58 3.10 75017 Q8 21.67 5.63 13.51 13.80 9.64 3.10 注:原始编号始于7代表水利监测井,始于0代表自然资源监测井 表 2 不同ε取值对应的监测井控制范围
Table 2. Monitoring well control range corresponding to the ε with different value
研究区 T0/bits Tmin/bits K/km-1 ε/bits L/km 丁楼- 茅村水源地 3.545 1.636 0.623 10-4 15.82 10-3 12.13 10-2 8.43 10-1 4.73 七里沟水源地 1.368 0.397 0.471 10-4 19.48 10-3 14.60 10-2 9.71 10-1 4.83 表 3 优化前后监测网信息对照
Table 3. Comparison of monitoring network information before and after optimization
优化对照 监测井/眼 H/bits T/bits C/bits G/bits 丁楼-茅村 优化前 9 6.345 0 24.313 0.213 水源地 优化后 6 6.249 5.7 12.393 7.096 七里沟 优化前 8 6.273 0 12.573 2.504 水源地 优化后 5 5.952 5.3 5.477 7.903 -
[1] Yang Y, Burn D H. An entropy approach to data collection network design[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1994, 157(1/4): 307-324. [2] Husain T. Hydrologic uncertainty measure and network design[J]. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 1989, 25(3): 527-534. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.1989.tb03088.x [3] 陈植华. 地下水观测网的若干问题与基于信息熵的研究方法[J]. 地学前缘, 2001, 8(1): 135-142. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.01.017Chen Z H. Some confusions in groundwater monitoring network and the entropy method[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2001, 8(1): 135-142(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.01.017 [4] 杨建青, 章树安, 陈喜, 等. 国内外地下水监测技术与管理比较研究[J]. 水文, 2013, 33(3): 18-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2013.03.004Yang J Q, Zhang S A, Chen X, et al. Comparison between China and other countries on groundwater monitoring and management practices[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2013, 33(3): 18-24(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2013.03.004 [5] 严宇红, 周政辉. 国家地下水监测工程站网布设成果综述[J]. 水文, 2017, 37(5): 74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2017.05.014Yan Y H, Zhou Z H. Introduction to network layout of national groundwater monitoring project[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2017, 37(5): 74-78(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2017.05.014 [6] 孟祥帅. 区域地下水观测井网优化方法研究: 以沈阳市为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.Meng X S. Studies of optimal methods of the regional groundwater observation network: Taking Shenyang for example[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2012(in Chinese with English abstract). [7] 卢海军. 北京市潮白河冲洪积扇地下水监测站网优化研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.Lu H J. The study on optimization of groundwater monitoring station network of alluvial-proluvial fan in Chaobai River, Beijing[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [8] 田晓龙. 巩义市城区地下水评价及趋势分析[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2016.Tian X L. Groundwater evaluation and trend analysis in Gongyi City[D]. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [9] 张瑞钢, 钱家忠, 赵卫东, 等. 对应分析法在地下水化学特征分析中的应用[J]. 合肥工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 31(10): 1552-1555, 1560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2008.10.004Zhang R G, Qian J Z, Zhao W D, et al. Corresponding analysis of hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology, 2008, 31(10): 1552-1555, 1560(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2008.10.004 [10] Yang F G, Cao S Y, Liu X N, et al. Design of groundwater level monitoring network with ordinary Kriging[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2008, 20(3): 339-346. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(08)60066-9 [11] 陈植华, 陈刚. 基于信息熵技术对地下水观测网的层次分类: 以河北平原地下水观测网为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2002, 21(1): 41-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200201011.htmChen Z H, Chen G. Entropy-based grouping of groundwater monitoring networks[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2002, 21(1): 41-46(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200201011.htm [12] Masoumi F, Kerachian R. Optimal redesign of groundwater quality monitoring networks: A case study[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2010, 161(1/4): 247-257. [13] Li C, Singh V P, Mishra A K. Entropy theory-based criterion for hydrometric network evaluation and design: Maximum information minimum redundancy[J]. Water Resources Research, 2012, 48(5): 1-15. [14] Nazeri T M, Khashei S A, Ramezani Y. Redesigning and monitoring groundwater quality and quantity networks by using the entropy theory[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2019, 191(4): 1-17. [15] 邹胜章, 杨苗清, 陈宏峰, 等. 地下河系统水动态监测网络优化对比分析: 以桂林海洋-寨底地下河系统为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 326-335. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901032.htmZou S Z, Yang M Q, Chen H F, et al. Comparison and optimization of water dynamic monitoring network for underground river system: A case study of the Haiyang-Zhaidi underground river system, Guilin City[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 326-335(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901032.htm [16] 郭燕莎, 王劲峰, 殷秀兰. 地下水监测网优化方法研究综述[J]. 地理科学进展, 2011, 30(9): 1159-1166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKJ201109013.htmGuo Y S, Wang J F, Yin X L. Review of the optimization methods for groundwater monitoring network[J]. Progress in Geography, 2011, 30(9): 1159-1166(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKJ201109013.htm [17] 李大通, 罗雁. 中国碳酸盐岩分布面积测量[J]. 中国岩溶, 1983, 1(2): 147-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198302008.htmLi D T, Luo Y. Measurement of carbonate rocks distribution area in China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1983, 1(2): 147-150(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198302008.htm [18] 卢海平, 张发旺, 赵春红, 等. 我国南北方岩溶差异[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(增刊2): 317-319. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2018S2085.htmLu H P, Zhang F W, Zhao C H, et al. Differences between southern karst and northern karst besides scientific issues that need attention[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(S2): 317-319(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2018S2085.htm [19] 江川, 肖德安. 岩溶地区地下水环境监测难点及解决思路[J]. 中国环境监测, 2014, 30(5): 110-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2014.05.024Jiang C, Xiao D A. Difficulties and solutions of groundwater quality monitoring in karst area[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2014, 30(5): 110-113(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2014.05.024 [20] 缪世贤, 黄敬军, 武鑫, 等. 徐州岩溶地质调查及其发育特征分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2017, 44(2): 172-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201702026.htmMiao S X, Huang J J, Wu X, et al. Karst geological survey and analysis of its development characteristics in Xuzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(2): 172-177(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201702026.htm [21] 武鑫, 王艺霖, 黄敬军, 等. 徐州地区碳酸盐岩溶蚀特征及影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 120-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903011.htmWu X, Wang Y L, Huang J J, et al. Dissolution characteristics of carbonate and analysis of the key influence factors in Xuzhou region[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 120-126(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903011.htm [22] 周东来. 徐州市岩溶地下水运移规律的研究[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2006, 17(4): 65-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2006.04.014Zhou D L. Study on transport of karst groundwater of Xuzhou City[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2006, 17(4): 65-70(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2006.04.014 [23] Shannon C E. A mathematical theory of communication[J]. Bell System Technical Journal, 1948, 27(3): 379-423. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x [24] Alfonso L, Lobbrecht A, Price R. Information theory-based approach for location of monitoring water level gauges in polders[J]. Water Resources Research, 2010, 46(3): 1-14. [25] Alfonso L, Lobbrecht A, Price R. Optimization of water level monitoring network in polder systems using information theory[J]. Water Resources Research, 2010, 46(12): 1-13. [26] 朱常坤, 梁杏. 多参数层序地层的边缘最优智能划分算法及其应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(1): 466-470. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201501069.htmZhu C K, Liang X. An edge detection optimum intelligent division method and its application for multi-parameter log data[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(1): 466-470(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201501069.htm [27] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103Liang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103 [28] 朱常坤, 梁杏, 刘绍华, 等. 利用连续小波变换方法对潜水位进行气压和潮汐改正[J]. 地质科技情报, 2014, 33(3): 169-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201403024.htmZhu C K, Liang X, Liu S H, et al. Application of continuous wavelet transform to correct barometric and tidal response in the water table[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(3): 169-174(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201403024.htm -





 下载:
下载: