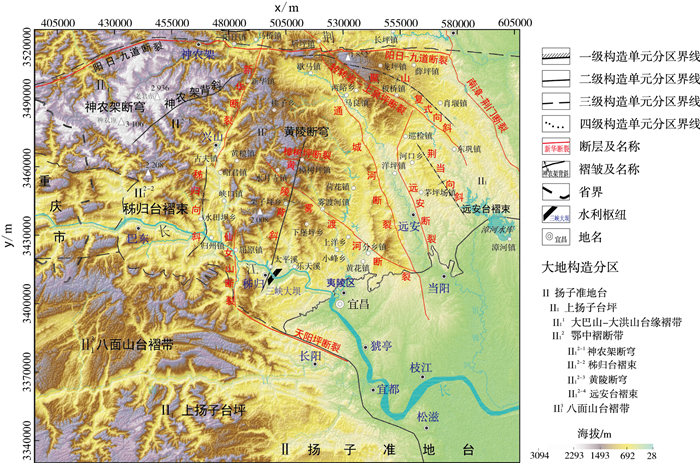
Characteristics and genesis of karst water flow system around Huangling anticline
-
摘要: 岩溶水流系统特征研究有助于地下水资源的合理评价和开发利用。借鉴水文学的研究方法,统计并量化了典型岩溶水流系统的空间特征以及其水文动态响应、温度场和电导率特征。划分了扇状、树枝状、平行状、梳状4种地下水系来综合反映岩溶水流系统的地表-地下岩溶特征,前两者主管道垂直于地层走向,构造裂隙起汇水作用,后两者主管道平行于地层走向,层面裂隙起汇水作用。黄陵穹隆西北翼、西翼和南翼以平行状和树枝状为主,东翼和北翼则以扇状水系和平行状水系为主。不同地下水系结构的形成及区域差异与含水系统和水系的空间关系和级次性密切相关,并表现出不同的动态特征。扇状和平行状岩溶水流系统对降雨响应最为敏感,而梳状水系岩溶水流系统响应和衰减过程最慢;基于岩溶地下水温度与出露高程和循环深度显著相关的关系建立了鄂西山区地下水温度线。这一基础性研究可为岩溶地下水流系统研究和当地工程实践提供一定的理论支持。Abstract: The study of the karst water flow system is helpful for the reasonable evaluation and utilization of groundwater resources.In this paper, the spatial characteristics, hydrological dynamic response, temperature field, and conductivity characteristics of the typical karst water flow system were calculated and quantified by referring to the methods of hydrology research.Four groundwater systems, i.e., fan-shaped, branch-shaped, flat-shaped, and comb-shaped, were divided to comprehensively reflect the surface-underground karst characteristics of the karst flow system.The main pipelines of the first two are perpendicular to the stratigraphic trend, and the structural fractures play a role in catching water.The main pipelines of the latter two are parallel to the stratigraphic trend, and the horizontal fractures play a role in collecting water.The northwest, west, and south wings of the Huangling anticline are branch-shaped and flat-shaped, while the east and north wings are fan-shaped and flat-shaped water systems.The formation and regional differences of different groundwater systems are closely related to the spatial relationship and hierarchy of aquifer systems and water systems which show different dynamic characteristics.The fan-shaped and flat-shaped karst flow system are the most sensitive to rainfall response, while the comb-shaped karst flow system has the slowest response and attenuation process.Based on the obvious correlation between karst groundwater temperature and exposed elevation and circulation depth, the groundwater temperature line in the mountainous area of western Hubei province is established.This study could provide certain theoretical support for karst groundwater flow system research and local engineering practice.
-
表 1 研究区含水系统划分结果
Table 1. Division result of aquifer system in the study area
一级 二级 三级 地层 厚度/m ZQ松散岩类孔隙含水系统Ⅰ Q < 10 岩溶含水系统Ⅱ 震旦系岩溶含水系统 Z 515 下寒武统岩溶含水系统 ∈1s2 180 中寒武统-奥陶系岩溶含水系统 寒武系天河板组-覃家庙组岩溶含水系统 ∈1t-∈2q 440 寒武系娄山关组-奥陶系红花园组岩溶含水系统 ∈2O1l、O1h 303~583 奥陶系牯牛谭组-宝塔组岩溶含水系统 O2g-O2-3b 72 二叠系-三叠系岩溶含水系统 二叠系岩溶含水系统 P 363 三叠系岩溶含水系统 T 1 242~1 297 基岩风化裂隙含水系统Ⅲ 碎屑岩孔隙裂隙水含水系统 J、K 岩浆岩变质岩风化裂隙含水系统 Pt2m、Pt2x、Pt2g 表 2 黄陵穹隆周缘典型岩溶水流系统特征统计
Table 2. Statistics of characteristics of typical karst water flow system around Huangling anticline
部位 岩溶水流
系统名类型 流量/
(L·s-1)水温/
℃电导率/
(μs·cm-1)面积/
km2地层
代号地层倾
角/(°)径流模数/
(L·s-1·km-2)平面形态 长宽比 补给区最
高点/m平均补给
高度/m出口高
度/m高差/
m水力
坡降地下水流
方向/(°)西北翼 黑龙泉 岩溶大泉 57 15.50 309 16.50 ∈ 19 3.45 平行状水系 3.36 1 402 850 550 852 0.11 158 白龙泉 岩溶大泉 60 15.30 343 9.30 ∈ 23 6.45 平行状水系 3.50 960 900 587 373 0.07 160 雾龙洞 岩溶大泉 51 13.70 319 8.70 ∈ 19 5.86 平行状水系 4.93 1 560 1 150 600 960 0.13 166 云龙洞 地下暗河 77 13.20 395 17.30 ∈ 19 4.45 平行状水系 2.56 1 560 1 200 615 945 0.14 187 响水洞 岩溶大泉 300 14.30 355 34.00 ∈ 16 8.82 梳状水系 4.31 1 693 1 060 304 1 389 0.08 235 水磨溪泉 岩溶大泉 150 16.10 378 13.00 O 18 11.54 树枝状水系 1.21 1 140 760 349 791 0.19 287 西翼 响龙洞 岩溶大泉 42 13.80 238 13.00 T 46 3.23 树枝状水系 1.21 1 650 1 300 356 1 294 0.28 255 南翼 鱼泉洞 地下暗河 36 14.50 249 9.80 ∈ 10 3.67 平行状水系 3.82 1 350 1 170 309 1 061 0.16 171 迷宫泉 岩溶大泉 27 14.30 187 6.20 ∈ 8 4.35 梳状水系 13.17 1 442 1 148 430 1 012 0.13 175 NZK04 钻孔 0 14.20 200 ∈ 8 1 442 1 250 305 1 153 潭 岩溶大泉 200 13.20 248 18.60 T 32 10.75 扇状水系 1.09 1 530 1 150 191 1 339 0.27 291 周坪龙洞 地下暗河 5 13.50 174 4.80 P 22 1.04 平行状水系 2.62 1 458 1 250 816 642 0.19 120 仙龙洞 岩溶大泉 12 11.60 163 3.30 E 25 3.64 树枝状水系 2.08 1 550 1 450 796 754 0.28 230 仙鱼泉 岩溶大泉 300 14.60 184 21.70 O 36 13.82 扇状水系 1.16 1 168 1 050 499 669 0.13 42 大鱼泉洞 岩溶大泉 100 14.70 223 9.50 P 24 10.53 树枝状水系 3.81 1 320 1 000 274 1 046 0.17 310 龙洞 地下暗河 15 16.50 394 2.90 ∈ 12 5.17 平行状水系 1.17 610 450 308 302 0.14 71 忘忧泉 地下暗河 20 16.10 272 3.90 ∈ 10 5.13 平行状水系 1.25 896 550 438 458 0.23 100 NZK06 钻孔 0 17.50 1 350 ∈ 25 227 潮水洞 岩溶大泉 20 15.80 394 4.80 ∈ 10 4.2 梳状水系 2.10 650 610 460 190 0.09 89 五爪泉 岩溶大泉 350 15.60 249 42.90 O 25 8.16 平行状水系 1.17 1 378 750 471 907 0.12 78 酒酙子泉 地下暗河 600 13.70 215 61.40 ∈ 30 9.77 梳状水系 5.51 1 670 1 300 420 1 250 0.05 97 东翼 白龙泉 岩溶大泉 400 15.30 225.5 46.00 ∈ 10 8.70 扇状水系 0.77 1 150 870 423 727 0.11 59 百家泉 地下暗河 15 16.50 174.5 2.10 O 10 7.14 平行状水系 2.40 700 610 480 220 0.11 53 老龙洞 岩溶大泉 30 14.90 204 7.50 ∈ 10 4.00 扇状水系 1.43 960 900 510 450 0.09 44 北翼 青龙口 岩溶大泉 60 11.00 200 17.00 ∈ 15 3.53 平行状水系 2.22 1 820 1 600 1 180 640 0.13 145 黄龙洞 地下暗河 80 13.00 240 13.20 ∈ 9 6.0 扇状水系 0.44 1 260 1 000 720 540 0.17 4 -
[1] 梁杏, 张人权, 靳孟贵. 地下水流系统: 理论、应用、调查[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015.Liang X, Zhang R Q, Jin M G, et al. Groundwater systems: Theory, application, investigation[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015(in Chinese). [2] 罗明明, 尹德超, 张亮, 等. 南方岩溶含水系统结构识别方法初探[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(6): 543-550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201506002.htmLuo M M, Yin D C, Zhang L, et al. Identifying methods of karst aquifer system structure in South China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(6): 543-550(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201506002.htm [3] 朱静静, 周宏. 水文地质剖面分析在岩溶水系统研究中的应用: 以鄂西响水洞岩溶水系统为例[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2017, 24(3): 1-7, 19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201703002.htmZhu J J, Zhou H. Application of hydrogeological profile analysis to karst water system: A case study on Xiangshuidong karst water system in western Hubei Province[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2017, 24(3): 1-7, 19(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201703002.htm [4] 李然, 谢凯, 周宏. 浅循环岩溶水系统分析: 以香溪河流域百城向斜为例[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2015, 22(6): 11-16, 22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201506003.htmLi R, Xie K, Zhou H. Analysis of shallow circulating karst water system: Based on Baicheng syncline in Xiangxi River basin[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2015, 22(6): 11-16, 22(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201506003.htm [5] 范威, 于瑶, 江越潇, 等. 湖北省地下水流系统划分研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2020, 34(4): 565-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK202004017.htmFan W, Yu Y, Jiang Y X, et al. Study on groundwater flow system division in Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2020, 34(4): 565-570(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK202004017.htm [6] 陈萍, 王明章. 基于地下水开发的岩溶地下水系统类型划分方案探讨[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(3): 234-237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201503005.htmChen P, Wang M Z. A classification scheme of karst groundwater systems based on groundwater exploitation[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(3): 234-237(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201503005.htm [7] 赵瑞. 四川盆地南缘地形梯度带区域岩溶水系统研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016.Zhao R. Research on the system of regional karst water in the topographic gradient zone of the south edge of Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [8] 吴慈华, 曹劲, 左丽敏. 鄂西南岩溶地下水系统划分和研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(增刊1): 55-62, 68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK2018S1011.htmWu C H, Cao J, Zuo L M. Division of karst groundwater system in Southwest Hubei[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018, 32(S1): 55-62, 68(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK2018S1011.htm [9] 潘晓东, 梁杏, 唐建生, 等. 黔东北高原斜坡地区4种岩溶地下水系统模式及特点: 基于地貌和蓄水构造特征[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(1): 85-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201501012.htmPan X D, Liang X, Tang J S, et al. The patterns and characteristics of four karst groundwater systems in Northeast Guizhou slope zone based on the landscape and reservoir structure[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2015, 36(1): 85-93(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201501012.htm [10] 张人权, 周宏, 陈植华, 等. 山西郭庄泉岩溶水系统分析[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 1991, 16(1): 1-17. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1991.01.002Zhang R Q, Zhou H, Chen Z H, et al. Karst water system analysis of Guozhuang Spring in Shanxi Province[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University Geosciences, 1991, 16(1): 1-17(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1991.01.002 [11] 祝安, 祝进, 张朝晖. 喀斯特流域水系分形、分维问题[J]. 贵州师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 18(4): 5-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NATR200004001.htmZhu A, Zhu J, Zhang C H. Fractal and fractals dirnersion of karst water system[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University: Natural Sciences Edition, 2000, 18(4): 5-8(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NATR200004001.htm [12] 罗明明, 肖天昀, 陈植华, 等. 香溪河岩溶流域几种岩溶水系统的地质结构特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(6): 13-19, 25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201406005.htmLuo M M, Xiao T J, Chen Z H, et al. Geological structure characteristics of several karst water systems in the Xiangxi River Karst basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(6): 13-19, 25(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201406005.htm [13] 张亮, 陈植华, 周宏, 等. 典型岩溶泉水文地质条件的调查与分析: 以香溪河流域白龙泉为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2015, 42(2): 31-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201502006.htmZhang L, Chen Z H, Zhou H, et al. Investigation and analysis of the hydrogeological characteristics of the typical karst spring in the Xiangxi River basin: Exemplified by the Bailong Spring in Xingshan County of Hubei[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(2): 31-37(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201502006.htm [14] 罗利川, 梁杏, 李扬, 等. 基于GMS的岩溶山区三维地下水流模式识别[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(5): 680-689. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201805005.htmLuo L C, Liang X, Li Y, et al. Identifying three-dimensional groundwater flow patterns in karst mountain areas based on GMS[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(5): 680-689(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201805005.htm [15] 蔡昊, 陈植华, 周宏. 裂隙对雾龙洞岩溶发育及地下径流的影响分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2015, 22(2): 1-6, 38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201502001.htmCai H, Chen Z H, Zhou H. Impact analysis of fracture on the karst development and groundwater flow of Wulong Cave[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2015, 22(2): 1-6, 38(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201502001.htm [16] 尹德超, 罗明明, 周宏, 等. 鄂西岩溶槽谷区地下河系统水资源构成及其结构特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2015, 42(3): 13-18, 26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201503005.htmYin D C, Luo M M, Zhou H, et al. Water resources composition and structure characteristics of the underground river system in the karst ridge-trough in the western Hubei Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(3): 13-18, 26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201503005.htm [17] 郭绪磊, 陈乾龙, 黄琨, 等. 宜昌潮水洞岩溶间歇泉动态特征及成因[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(12): 4524-4534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202012016.htmGuo X L, Chen Q L, Huang K, et al. The dynamic features and causes of the Chaoshuidong Siphonal Sping[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 45(12): 4524-4534(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202012016.htm [18] 罗明明, 周宏, 郭绪磊, 等. 峡口隧道间歇性岩溶涌突水过程及来源解析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 246-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202106027.htmLuo M M, Zhou H, Guo X L, et al. Processes and sources identification of intermittent karst water inrush in Xiakou tunnel[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 246-254(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202106027.htm [19] Luo M M, Chen Z H, Yin D C, et al. Surface flood and underground flood in Xiangxi River Karst Basin: Characteristics, models, and comparisons[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2016, 27(1): 15-21. [20] Luo M M, Chen Z H, Criss R E, et al. Dynamics and anthropogenic impacts of multiple karst flow systems in a mountainous area of South China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2016, 24(8): 1993-2002. [21] 张信宝, 刘彧, 王世杰, 等. 黄河、长江的形成演化及贯通时间[J]. 山地学报, 2018, 36(5): 661-668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201805001.htmZhang X B, Liu Y, Wang S J, et al. On the chronology of the Yellow River and the Yangtze Rivers[J]. Mountain Research, 2018, 36(5): 661-668(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201805001.htm [22] 赵诚. 长江三峡河流袭夺与河流起源[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1996(4): 69-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ604.012.htmZhao C. River capture and origin of the Yangtze Gorges[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Sciences, 1996(4): 69-74(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ604.012.htm [23] 郭绪磊. 基于SAC改进模型的岩溶流域降水-径流过程模拟研究: 以宜昌泗溪流域为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2019.Guo X L. A case study on the simulation of precipitation and runoff process in karst basin based on modified SAC model[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [24] 邓铭哲. 黄陵背斜及邻区构造建模[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.Deng M Z. Structural modeling of the Huangling anticline and its peripheral structural belt[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] 徐大良, 彭练红, 刘浩, 等. 黄陵背斜中新生代多期次隆升的构造-沉积响应[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2013, 29(2): 90-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC201302002.htmXu D L, Peng L H, Liu H, et al. Meso-Cenozoic tectono-sedimentary response of mutiphased uplifts of Huangling anticline, Central China[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2013, 29(2): 90-99(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC201302002.htm [26] 张婉婷. 鄂西黄陵断穹北部区域岩溶水系统特征及隧道工程适宜性探析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016.Zhang W T. Karst water system analysis and its suitability with the tunnel engineering in the north of Huangling faulted dome[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [27] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202001004.htmLiang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202001004.htm [28] 季怀松, 罗明明, 褚学伟, 等. 岩溶洼地内涝蓄水量与不同级次裂隙对溶质迁移影响的室内实验与模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 164-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202005020.htmJi H S, Luo M M, Chu X W, et al. Laboratory experiment and simulation of solute transport affected by different grades of fissures and water storage of waterlogging in karst depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 164-172 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202005020.htm [29] 朱彪, 陈喜, 张志才, 等. 西南喀斯特流域枯季地下水电导率特征及水-岩作用分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47(4): 459-463. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201904007.htmZhu B, Chen X, Zhang Z C, et al. Characteristics of groundwater conductivity in dry season and water rock interaction implications in a Southwest karst basin[J]. Earth and Environment, 2019, 47(4): 459-463(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201904007.htm -





 下载:
下载: