Application of groundwater stratified exploration technology in groundwater flow system research
-
摘要: 地下水流是一种运动流体,空间上分布连续且能传递压力,在能量(势)差驱使下发生从水头高处向低处的运动。通常在补给(势源)区,地下水垂向上由上向下运动,而在排泄(势汇)区地下水由下向上运动,即地下水整个生命过程中总是由源到汇、向着能量减小的方向做径流运动,无论是在单个或多个透水岩层中都是如此。地下水分层勘查技术使在垂向上分层监测水头、水温和水质等成为可能,从而实现对不同及同一含水岩层的上下不同点间地下水流要素的比较,并判断全井或单井不同垂向区段的势源汇条件,为地下水流空间运动方向判定和地下水流系统划定奠定基础。本文以地下水流系统理论与试验观测研究为基础,论述了地下水分层勘查技术的原理、系统结构和功能,结合张掖盆地实例阐述了分层勘查技术在地下水补给与排泄区判识的应用方法。Abstract: The groundwater stored in the aquifer is a kind of moving fluid, which is continuously distributed in space and can transmit pressure.It is driven by the potential energy difference to move from high to low head.Usually in the recharge area (high head), the groundwater moves vertically from top to bottom, while in the drainage area (low head), the groundwater moves from bottom to top.The movement of groundwater in aquifers is like the same life process, in which it always moves from the source to the sink in the direction of energy reduction, whether it is in a single or multiple permeable rock formations.Hydrogeological stratified exploration technology (HSET) makes it possible to monitor different depths of groundwater elements such as head, temperature and quality in the vertical direction, so as to realize the comparison of groundwater elements between the vertical points of multi-layer aquifer rock formations.At the same time, HSET can judge the potential source and sink conditions of different vertical sections of a full well or a single well, laying a foundation for finely describing the spatial movement of groundwater flow and delimiting the groundwater system.This paper discusses the principle, system structure and function of groundwater layered exploration based on the theory and experimental observation of groundwater flow system and expounds the application method of layered exploration technology in the identification of groundwater recharge or discharge area in Zhangye Basin.
-
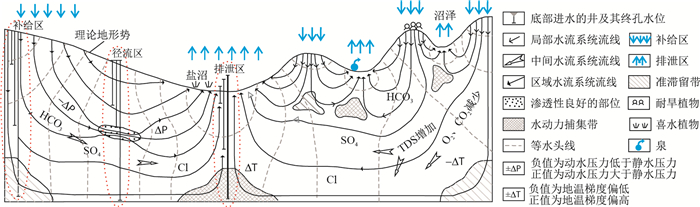
图 1 流域盆地地下水流系统及其伴生现象(据文献[10]修改)
Figure 1. Groundwater flow system and its associated phenomena in basin-type watershed
图 2 地下水流系统物理模拟结果(据文献[12]修改)
Figure 2. Physical simulation results of groundwater flow system
图 3 定水头条件下不同排泄点及流场内地下水流演示图(据文献[14]修改)
a.3个排泄点形成的多级水流系统; b.复杂流场内“死角”水重力下移引起的沿着隔水顶板的快速依赖水流
Figure 3. Demonstration diagram of groundwater flow in different discharge points and flow fields under constant head conditions
-
[1] Gao Z J, Liu Y G. Groundwater flow driven by heat[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 2013(3): 22-27. [2] 高宗军, 刘永贵. 地下水运动的热驱动机理[J]. 地下水, 2014, 36(2): 7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2014.02.003Gao Z J, Liu Y G. Research on application of thermally driven in groundwater movement[J]. Groundwater, 2014, 36(2): 7-9(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2014.02.003 [3] Kochina P I A, De Wiest R J M. Theory of groundwater movement[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1962. [4] King F H. Principles and conditions of the movements of ground water[M]. Washington: US Government Printing Office, 1899. [5] Hubbert K M. The theory of groundwater motion[J]. Transactions American Geophysical Union, 1940, 21(2): 648. [6] Tóth J. A theoretical analysis of groundwater flow in small drainage basins[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1963, 68(16): 4795-4812. doi: 10.1029/JZ068i016p04795 [7] Engelen G B, Jones G P. Developments in the analysis of groundwater flow systems[M]. Wallingford: Internation Association of Hydrologocal Sciences, 1986. [8] Engelen G B, Kloosterman F H. Hydrological systems analysis: Methods and applications[M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Acdemic Publisher, 1996. [9] Mádl-Szónyi J. The contribution of József Tóth to modernization of Hungarian hydrogeology[J]. Central European Geology, 2009, 51(3): 189-201. [10] 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵, 等. 水文地质学基础[M]. 第7版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018.Zhang R, Liang X, Jin M, et al. Fundamentals of hydrogeology[M]. 7th Edition. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2018(in Chinese). [11] Tóth J. Gravitational systems of groundwater flow: Theory, evaluation, utilization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009. [12] Liang X, Liu Y, Jin M G, et al. Direct observation of complex Tóthian groundwater flow systems in the laboratory[J]. Hydrological Process, 2010, 24: 3568-3573. doi: 10.1002/hyp.7758 [13] 刘彦, 梁杏, 权董杰, 等. 改变入渗强度的地下水流模式实验[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(6): 111-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201006015.htmLiu Y, Liang X, Quan D J, et al. Experiments of groundwater flow patterns under changes of infiltration intensity[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(6): 111-116(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201006015.htm [14] 高宗军. 地下水流系统分异的试验演示及其意义[J]. 山东科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 32(2): 17-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3767.2013.02.003Gao Z J. Experimental demonstration and significance of groundwater flow system differentiation[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2013, 32(2): 17-24(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3767.2013.02.003 [15] Gao Z J. The experimental investigations on motion features of groundwater flow near the pumping well[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 2014, 2(1): 1-11. http://doc.paperpass.com/journal/20140001dxskxygcywb.html [16] 高宗军. 抽水井附近地下水流运动特征[J]. 山东科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 33(3): 11-19, 37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY201403002.htmGao Z J. Themotion features of groundwater flow near pumping well[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology: Natrunal Science Edition, 2014, 33(3): 11-19, 37(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY201403002.htm [17] 郭清海, 王焰新. 水文地球化学信息对岩溶地下水流动系统特征的指示意义: 以山西神头泉域为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2006, 25(3): 85-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2006.03.015Guo Q H, Wang Y X. Hydrogeochemistry as an indicator for karst groundwater flow: A case study in the Shentou karst water system, Shanxi, China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2006, 25(3): 85-88(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2006.03.015 [18] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103Liang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103 [19] 王喆. 岩溶地下水系统演化的数值模拟[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(4): 201-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201304032.htmWang Z. Numerical simulation of the karst groundwater system evolution[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(4): 201-206(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201304032.htm [20] 侯光才. 鄂尔多斯白垩系盆地地下水系统及其水循环模式研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008.Hou G C. Groundwater system and water circulation pattern in Ordos Cretaceous groundwater basin[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2008(in Chinese with English abstract). [21] 赵振宏, 王冬, 陶正平, 等. 鄂尔多斯高原地下水流系统的多层结构循环模式: 来自深孔中PACKER系统分层水头测定的证据[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(8): 1131-1137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.08.005Zhao Z H, Wang D, Tao Z P, et al. Multi- layer circulation model of groundwater flow systems on the Ordos Plateau, China: Evidence from water head measurements at different depths of a deep borehole by the Packer system[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(8): 1131-1137(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.08.005 [22] 杨郧城, 侯光才, 张茂省, 等. 双Packer系统在鄂尔多斯盆地地下水勘查中的应用[J]. 西北地质, 2005, 38(1): 113-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2005.01.016Yang Y C, Hou G C, Zhang M S, et al. Applications of double packer system to exploration of the groundwater in Ordos Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2005, 38(1): 113-115(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2005.01.016 [23] 许毅, 马思锦, 刘惠宁. 分层取样系统在地下水勘查研究中的应用[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 2004.Xu Y, Ma S J, Liu H N. Application of stratified sampling system in groundwater exploration and research[M]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press, 2004(in Chinese). [24] 郭建强, 张福存, 武毅, 等. 西部严重缺水地区地下水勘查新技术应用与综合研究成果报告[R]. 河北保定: 中国地质调查局水文地质工程地质技术方法研究所, 2006.Guo J Q, Zhang F C, Wu Y, et al. Application and comprehensive research achievement report of new techniques of groundwater exploration in the severe water shortage areas of western China[R]. Baoding Hebei: Institute of Hydrogeology and Engineering Geotechnical Methods, China Geological Survey, 2006(in Chinese). [25] 解伟, 王明明. 地下水分层勘查技术研究与应用专题成果报告[R]. 河北保定: 中国地质调查局水文地质环境地质调查中心, 2019.Jie W, Wang M M. Report on the research and application of groundwater layer exploration technology[R]. Baoding Hebei: Center for Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology Survey, CGS, 2019(in Chinese). [26] 李文鹏, 安永会. 黑河流域重点地区1: 5万水文地质调查[R]. 河北保定: 中国地质调查局水文地质环境地质调查中心, 2018.Li W P, An Y H. 1: 50000 hydrogeological survey in key areas of the Heihe River basin[R]. Baoding Hebei: Center for Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology Survey, CGS, 2018(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: