Stability prediction of landslide dams based on SSA-Adam-BP neural network model
-
摘要: 现有的堰塞坝稳定性预测模型多为线性模型, 无法充分考虑堰塞坝稳定性与其形态特征和水域条件之间的复杂非线性关系。鉴于此, 结合反向传播神经网络模型和樽海鞘优化算法, 提出了一种新型的堰塞坝稳定性预测模型SSA-Adam-BP。该模型通过网格搜索法选取确定模型结构的最佳超参数组合, 进而利用交叉验证和绘制ROC曲线的方式分别对采用不同优化算法的模型进行评估。使用开源数据库中的全球153例堰塞坝数据对模型的实际应用进行了说明及验证。与传统线性模型的对比表明神经网络模型预测准确率较高, 具有较低的误报率。将SSA与Adam优化算法结合提高了BP模型的全局搜索能力, 其平均交叉验证准确率达到了91.73%, 能够使用较少的参数实现对堰塞坝稳定性快速准确的预测。SSA-Adam-BP模型对近年来典型工程的稳定性能够准确预测, 具有一定的实用性和系统平台推广应用价值。Abstract: Most of the existing landslide dam stability prediction models are linear models, which cannot fully consider the complex nonlinear relationship between landslide dam stability and its morphological characteristics and hydrodynamic conditions.In view of this, a new SSA-Adam-BP model for predicting the stability of landslide dams is proposed by combining the back propagation neural network model and the salp optimization algorithm.The grid search method is used to select the best combination of hyperparameters that can determine the structure of the model.Then, the models with different optimization algorithms are evaluated by cross-validation and ROC curve drawing.The practical application of the model is explained and verified by using the global data of 153 landslide dams in the open source database.Compared with the traditional linear model, the combination of the SSA and Adam optimization algorithm improves the global search ability of the BP model, and its average cross-verification accuracy reaches 91.73%.It not only has a lower misjudgment rate but can also use fewer parameters to quickly and accurately predict the stability of landslide dams.The SSA-Adam-BP model can accurately predict the stability of typical projects in recent years, with certain practicality and system platform promotion application value.
-
受地震、降雨、人类活动的影响,河流两岸的大型斜坡往往在发生失稳破坏后堵塞河流,最终形成堰塞坝[1-2]。随着堰塞湖水位的增长,约85%的堰塞坝在一年内溃决,不仅直接对沿岸的人员和财产安全造成威胁,还对生态环境造成巨大破坏[3-5]。因此,为了尽可能避免或减轻灾害造成的损失,在堰塞坝形成初期对其稳定性进行快速准确的预测,从而为实施抢险救灾行动提供指导显得尤为重要。长期以来,使用较少的参数实现对堰塞坝稳定性的准确预测是该领域的重点研究课题。
目前,堰塞坝稳定性评估方法主要有物理实验、数值模拟和统计学方法3种。前2种方法大多对堰塞坝尺寸做了简化处理[1],且需要获取坝体物质组成的详细资料。而现实中堰塞坝往往位于偏远山区、几何形状与物质组成极其复杂,导致建立模型需要的坝体详细信息无法及时获取[6],从而限制了其在应急抢险中的应用。此类方法更适合用来研究单一因素对堰塞坝稳定性的影响[7]。
统计学方法因计算简单,堰塞坝地貌参数较容易获取等优点而得到了较广泛的应用。自1991年Costa等[8]首次建立了全球范围内463例堰塞坝数据库以来,国内外学者们基于整理的数据库,利用统计学方法建立了一系列可快速评价堰塞坝稳定性的判别公式。例如Casagli等[9]、Ermini等[10]使用坝体体积、集水区面积2个参数提出了使用堆积指数(blocked index, 简称BI)来初步预测堰塞坝的稳定性,后来在此基础上考虑了坝体高度的影响,提出了无量纲堆积体指标法(dimensionless blockage index, 简称DBI);Korup[11]基于新西兰232座堰塞坝数据提出了Is(backstow index)、Ia(basin index)、Ir(relief index)3种无量纲指数;Stefanelli等[12-13]在分析了300个意大利堰塞坝案例的基础上提出了水力形态学指标(HSDI);年廷凯等[1]基于60组堰塞坝案例,建立了坝长、坝宽和堰塞湖库容3参数的稳定性快速评估模型;Shan等[14]考虑了坝体组成材料的影响,基于逻辑回归原理建立了Ls(IVAS)和Ls(IVAM)模型。此类方法所需参数容易获取且不应考虑堰塞坝内部复杂的应力应变关系,能够在短时间内对堰塞坝稳定性进行预测[1]。然而,目前所提出的模型大多为线性预测模型,没有考虑到稳定性与诸多影响因素之间复杂的非线性关系,存在较多谎报、误报、无法确定的情况,精确程度仍然有较大的提升空间。
为弥补上述方法的缺陷,本次研究以153例堰塞坝为例,首先对每个案例的坝体高度H、坝体体积V和集水区面积A进行对数转化和归一化处理;然后建立用于堰塞坝稳定性预测的非线性BP神经网络模型,并将SSA算法与Adam算法进行结合,以提高模型的全局搜索能力,减弱权重初始值对模型训练结果的影响,实现堰塞坝稳定性的快速准确预测;最后采用该SSA-Adam-BP神经网络模型对近年来典型的堰塞坝案例的稳定性进行预测分析。
1. SSA-Adam-BP神经网络模型
1.1 反向传播神经网络模型
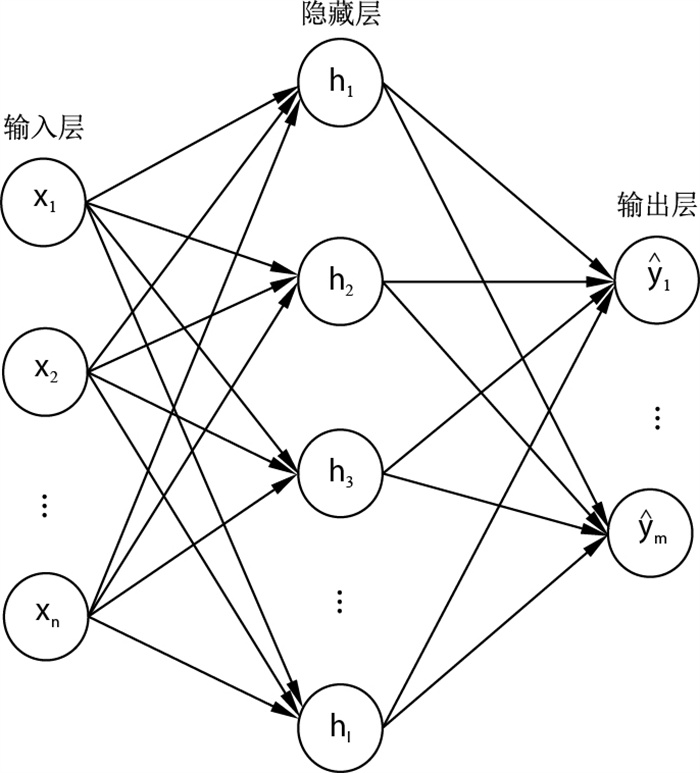
反向传播(back-propagation,简称BP)神经网络是目前最有代表意义和广泛用途的神经网络模型之一,能够适应求解高度非线性等复杂岩土工程问题[15]。其由输入层、隐藏层和输出层组成,不仅具有较强的非线性映射能力,而且因为网络的隐藏层层数、各层的神经元个数可根据具体情况设定,具有较好的普适性[16-18]。1989年,Hecht-Nielsen[19]证明了单隐藏层BP神经网络模型在理论上能够有效地逼近任何闭区间内的连续函数,结构如图 1所示。
BP神经网络模型的训练过程可以分为正向传播计算误差和反向传播优化权重参数2个部分,2个过程不断重复,当精度满足要求或达到迭代次数时停止训练[20]。设输入向量为x=(x1, x2, …, xn)T,输出向量为y=(y1, y2, …, ym)T,则其前向计算过程如下:
计算隐藏层的输出值hj,表达式为:
hj=f(n∑i=1wijxi−θh),j=1,2,3,⋯,l (1) 式中:f(x)为隐藏层激活函数;l为隐藏层神经元个数;wij为连接输入层和隐藏层的权重;θh为隐藏层偏置。
计算输出层的预测值ˆyk,表达式为:
ˆyk=g(l∑j=1wjkhj−θc),k=1,2,3,⋯,m (2) 式中:g(x)为输出层激活函数;m为输出层神经元个数;wjk为连接输出层和隐藏层的权重;θc为输出层偏置。
1.2 樽海鞘群优化算法
樽海鞘群算法(salp swarm algorithm, 简称SSA)是Mirjalili等[21]于2017年提出的新型群智能优化算法。相较于传统的群智能优化算法, SSA具有较好的鲁棒性和全局搜索能力[22]。通过模拟樽海鞘链在海洋中的觅食行为,以每个个体在空间中的位置代表优化问题的一组解,迭代过程中,领导者进行全局搜索,追随者则进行局部搜索,每个个体位置的更新过程如下:
领导者更新公式:
x1j={Fj+c1((ubj−lbj)c2+lbj),c3≥0Fj−c1((ubj−lbj)c2+lbj),c3<0 (3) c1=2e−(4l/L)2 (4) 式中:xj1为领导者在第j维中的位置;Fj为食物在第j维中的位置;ubj,lbj分别为j维的上界和下界;c2,c3为随机数;l为当前迭代次数;L为总迭代次数。
追随者更新公式:
xij=12(xij+xi−1j) (5) 式中:xji为第i个追随者在第j维度中的位置, i≥2。
1.3 模型评价指标
本次研究将堰塞坝稳定性预测作为一个二分类问题进行处理,模型的输出值为该样本属于稳定案例的概率,常用交叉熵损失函数和准确率作为评价模型性能的指标,二分类模型的交叉熵损失函数Loss以及准确率R的表达式分别为:
Loss =−[ylg(ˆy)+(1−y)lg(1−ˆy)] (6) R=TP+TNP+N (7) 式中:y和ˆy分别为真实值和预测值;TP、TN分别是正确分类的稳定案例数量和不稳定案例数量;P为稳定案例总数;N为不稳定案例总数。
1.4 SSA-Adam-BP模型及实现流程
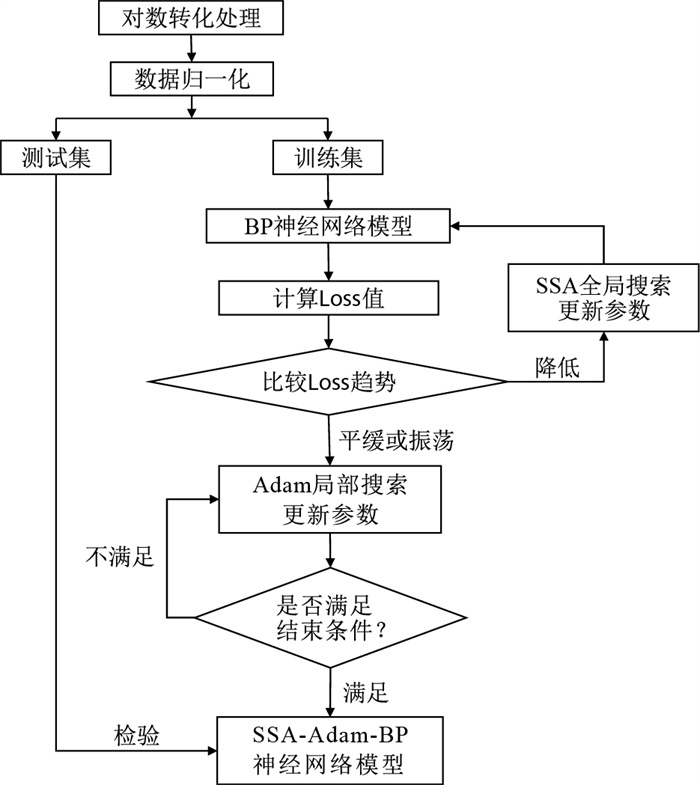
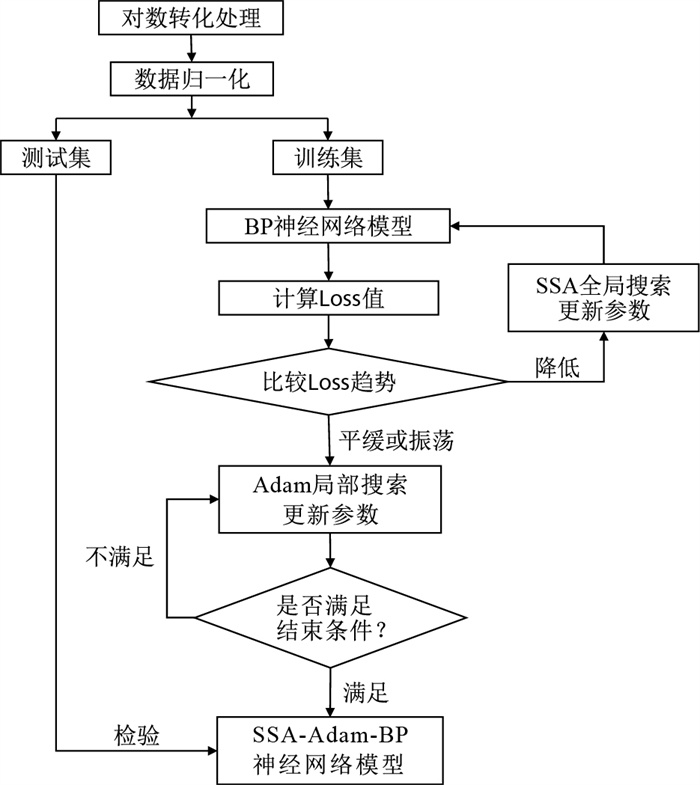
传统BP神经网络模型使用梯度下降算法更新参数导致模型的训练结果在很大程度上受随机生成参数初始值的影响,容易陷入局部最优,从而降低预测结果的准确性[23]。为了克服这一缺点,提高模型训练速度和泛化能力,本次研究采用结合SSA算法与梯度下降算法中自适应矩估计(adaptive moment estimation, 简称Adam) 算法[24-25]的方式对模型的参数进行更新,其过程如图 2所示。首先利用SSA算法进行全局搜索,随着迭代次数的增加,当损失函数Loss的值不再降低,或者出现振荡时停止迭代,然后在此基础上采用Adam算法进行局部搜索,直到精度满足要求或达到迭代次数时停止训练。在使用SSA算法更新参数的过程中,为了满足SSA算法输入要求,需将模型权重和偏置参数以输入层、隐藏层、输出层的顺序展开成一维向量,待参数更新完成后再按照神经网络模型的参数结构重新整合计算Loss值。
模型参数更新过程的伪代码如下所示:
按照超参数组合建立模型model
计算model的参数总数T
定义N, L, ub, lb, 初始化pop(N×T), bestloss=正无穷
Def SSA(pop):
For i=1, 2, 3, …, N do:
将pop中第i个个体,整合为数组weights
将weights喂入模型,按公式(6)计算Loss
End for
return minloss,id_minloss
//minloss为Loss最小值、id_minloss为minloss对应的个体
For l=1, 2, 3, …, L do:
minloss, id_minloss=SSA(pop)
If minloss < =bestloss do:
bestloss=minloss
//记录Loss的最小值,以便比较Loss趋势
F=id_minloss //更新食物位置
按公式(3)(4)(5)更新领导者、追随者,生成新种群pop
Else min_Loss值不再下降do:
将个体id_minloss,整合后喂入神经网络
For k=0, 1, 2, …, epoch do:
Adam算法更新权重参数
计算Loss值
If Loss值满足要求do:
break
End for
End for
2. 堰塞坝稳定性预测及结果
2.1 数据库的选取及数据预处理
考虑到堰塞坝的形成具有群发性,甚至同一条河流在其上下游形成多处堰塞坝,以及抢险时间短的特点,为实现堰塞坝稳定性的快速预测,从而为抢险救援赢得充足的时间,应尽量选取少量且容易获取的参数建立稳定性预测模型。基于此原则,本次研究选取Ermini堰塞坝数据库[10] (表 1)和Tabata堰塞坝数据库[26] (表 2)共计121例数据作为研究对象,其中共有50例稳定堰塞坝(SD, 计算时用1表示)和71例不稳定堰塞坝(UD,计算时用0表示),每个案例共包含3个特征变量,分别为:坝体高度H、坝体体积V和集水区面积A(完整版数据见网络版补充材料: https://github.com/ZH2580/data)。Ermini等[10]、Dong等[27-28]分别基于这3个特征变量提出了堰塞坝稳定性预测的线性预测模型,证明了这3个变量在堰塞坝稳定性预测中的重要性。Dong等[27-28]认为集水区面积是控制坝体稳定性的主要因素,坝高次之,但其并未对坝体体积的重要性进行评估。
表 3列出了这121例堰塞坝数据的基本统计信息,可以看出2数据库中堰塞坝各个参数的分布范围极广,例如集水区面积从0.19 km2到45 000 km2,而平均值仅为731.67 km2,最大值与平均值相差较大。
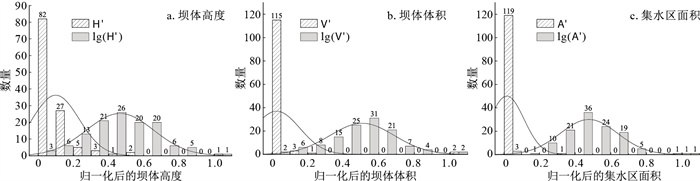
表 3 121例堰塞坝数据基本统计信息Table 3. Basic statistical information of 121 cases based on the landslide dam database特征变量 坝体高度H/m 坝体体积V/m3 集水区面积A/km2 最小值 3.00 8.70×107 0.19 最大值 500.00 2.20×109 4.50×104 平均值 52.88 5.70×107 731.61 标准差 65.87 2.86×108 4 321.71 为使神经网络模型更容易准确地收敛到最优解,通常在将数据输入到模型之前对其进行归一化处理,将其等比例缩放至[0, 1]之间,但由于此数据集少数案例与平均值相差多个数量级,若直接进行归一化,将会影响模型训练效果。为消除这种影响,本次研究在归一化处理前对输入参数进行对数变换处理,归一化的公式为:
X′=X−XminXmax−Xmin (8) 式中:X′为归一化后的值;X为实际值;Xmax,Xmin分别为输入参数的最大值和最小值。
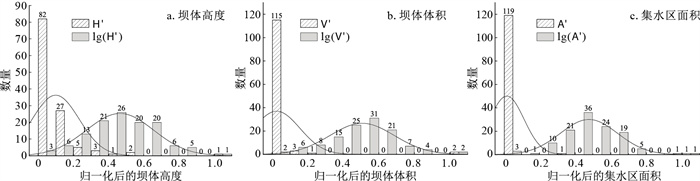
图 3分别为原始数据和对数变换处理后的数据在归一化后的统计分布直方图。使用Shapiro-Wilk检验分别对原始数据和对数转换后的数据进行正态分布检验,统计量W的值越高,表示样本数据与正态分布越匹配。Shapiro-Wilk检验的结果见表 4。从表 4和图 3中可以看出,经过对数转换处理后的数据均通过了检验(p值大于0.05),其在[0, 1]区间内的分布与未处理的原始数据相比更符合正态分布的特点。
表 4 Shapiro-Wilk检验结果Table 4. Testing results of Shapiro-Wilk变量 统计量W p值 在5%水平下的结论 H′ 0.68 0.00 排除正态性 V′ 0.19 0.00 排除正态性 A′ 0.14 0.00 排除正态性 lg(H′) 0.99 0.79 不能排除正态性 lg(V′) 0.999 0.70 不能排除正态性 lg(A′) 0.99 0.11 不能排除正态性 2.2 堰塞坝稳定性预测模型的搭建
本次研究使用keras-python库搭建神经网络模型,并引入使用单一优化算法的Adam-BP模型和SSA-BP模型作为对比模型。首先,选取对数转换后的坝体高度lg(H)、坝体体积lg(V)、集水区面积lg(A)3个参数作为神经网络模型的输入参数, 然后使用归一化方法对参数进行处理,最后使用网格搜索法确定最佳的神经网络结构并进行训练。此过程中采用五折交叉验证的方法对使用不同超参数组合及不同优化算法搭建的模型进行评价,具体方法为:每一次采用其中4/5案例作为训练集训练神经网络,使用剩下的1/5案例作为测试集进行验证,重复5次,将5次模型预测的准确率的平均值作为该模型的真实准确率,选取平均准确率最高的超参数组合搭建的模型作为预测模型。
由于堰塞坝稳定性预测属于二分类问题,采用Sigmoid函数作为输出层的激活函数,将模型输出值映射到0到1之间。当输出值小于0.5时认为堰塞坝不稳定,当输出值大于0.5时认为堰塞坝稳定。通过对比不同模型5次训练结果的平均准确率,确定最佳超参数组合为:隐藏层的层数为2层、神经元数量为32、激活函数为relu函数。Sigmoid函数和relu函数的表达式分别为:
g(x)=11+e−x (9) f(x)=max(0,x) (10) 2.3 模型训练结果及分析
表 5列出了3种分别采用不同优化算法的神经网络模型的预测结果,其中K为交叉验证组数。
表 5 不同BP神经网络模型的交叉验证准确率Table 5. Cross-verification accuracy of different BP neural network models模型 准确率/% 平均准确率/% K=1 K=2 K=3 K=4 K=5 Adam-BP 87.50 87.50 91.67 91.67 88.00 89.27 SSA-BP 87.50 83.33 91.67 91.67 88.00 88.43 SSA-Adam-BP 91.67 87.50 95.83 91.67 92.00 91.73 从表 5中可以看出采用不同子集作为测试集时,SSA-Adam-BP模型的准确率均大于等于其他2个只使用单一优化算法模型的准确率,尤其是采用第三子集(K=3)作为测试集时,SSA-Adam-BP模型的准确率最高,达到了95.83%。其平均准确率为91.73%,与其他2个模型相比,准确率分别提高了2.46%和3.30%。
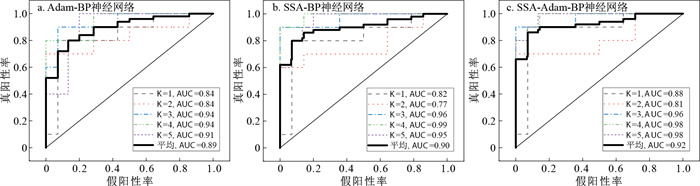
由于数据库中存在正样本与负样本比例不均衡的现象,为了更准确地评估模型的整体性能,本次研究在使用准确率评价的基础上分别根据3种不同神经网络模型得出的预测结果绘制接受者操作特征(receiver operating characteristic,简称ROC)曲线对所提出的模型进行综合分析。ROC曲线是由不同判断标准对应的假阳性率、真阳性率绘制而成的曲线。为了更方便进行量化比较,通常使用曲线下面积的大小(area under curve, 简称AUC)来表示该模型的整体性能,AUC的值越接近1,说明该模型的性能越好。
图 4为采用不同优化算法的BP神经网络模型的ROC曲线及AUC值,可以发现Adam-BP模型、SSA-BP模型和SSA-Adam-BP模型的平均AUC分别为0.89, 0.90, 0.92,3种模型的平均AUC值都超过了0.85,其中SSA-Adam-BP模型的平均AUC值最高,因而其性能最好。
结合图 4、表 5可以得出以下结论:虽然Adam-BP模型平均准确率(89.27%)高于SSA-BP模型(88.43%),但其AUC值略低,说明SSA-BP模型的整体性能高于Adam-BP模型,而将SSA优化算法与Adam优化算法相结合的SSA-Adam-BP模型,无论是准确率还是AUC值均高于其他2种模型,说明结合SSA优化算法与Adam优化算法对参数进行了更新,能够提高模型的全局搜索能力,从而收敛到最优解。结合2种算法对模型参数进行更新,虽然提高了模型的准确率,但同时也增加了模型的训练时间。
同时从表 5和图 4可以看出3种模型在K=1和K=2时的准确率以及AUC值与其他情况相比较低,特别是采用第2个子集(K=2)作为测试集时模型的预测效果最差。经分析发现第一子集和第二子集的案例大多来源于Tabata数据库,造成预测效果差的主要原因有以下两点:
(1) 两位作者建立数据库时数据采集标准、稳定性分类方法存在差异。
(2) Tabata数据库中的37例数据全部位于日本,地质环境的差异导致了测试结果较差。
由此可以看出,本次研究采用交叉验证方法训练神经网络模型,结合平均AUC值对模型进行筛选在一定程度上减小了数据集主观划分对模型性能的影响。为提高模型的鲁棒性,应尽量选取具有代表性的案例作为训练集对模型参数进行训练。
为验证本模型的预测能力,将本模型与3个使用相同数据库、相同变量建立的模型(表 6)进行对比,表 6中Ermini等[10]提出的DBI模型存在当DBI指数位于2.75和3.08之间时无法确定堰塞坝的稳定状态的问题,Dong等[27-28]提出的AHV_Dis模型和AHV_Log模型是分别基于判别分析和逻辑回归方法建立的。其中AHV_Log模型通过将Sigmoid函数作为逻辑函数引入了非线性因素,因而可以认为其属于非线性模型。但除去Sigmoid映射函数关系,其他的步骤、算法都是线性回归的,可以说,逻辑回归是以线性回归为理论支持的,所以其本质上仍是一个线性回归模型。
表 6 堰塞坝稳定性线性预测模型Table 6. Linear prediction model of landslide dam stability为保证对比结果的真实性与准确性,采用与三模型相同的数据集划分方式(Ermini数据库中的84例作为训练集,Tabata数据库37例数据作为测试集)对SSA-Adam-BP神经网络模型进行训练,并同时将误报率F作为评价模型性能的指标之一。误报率F系指实际不稳定案例被预测为稳定案例的数量占样本总数的比例。出于安全考虑,在准确率相差不多的情况下,应优先选择误报率低的模型。
表 7给出了各堰塞坝稳定性预测模型的预测结果(神经网络的权重及偏置参数见网络版补充材料: https://github.com/ZH2580/data)。从表 7可以看出,稳定性预测结果的准确率由大到小依次为:SSA-Adam-BP>AHV_Log>AHV_Dis> DBI, 误报率由小到大依次为:SSA-Adam-BP < AHV_Log < AHV_Dis < DBI,在使用相同参数、相同数据库的情况下,本文所提出的模型在新数据集上的准确率高于其他模型,且误报率仅为2.7%,其他线性模型的误报率达到13.51%~18.92%,说明本文提出的非线性模型更可靠,可以为抢险救灾提供技术支撑。
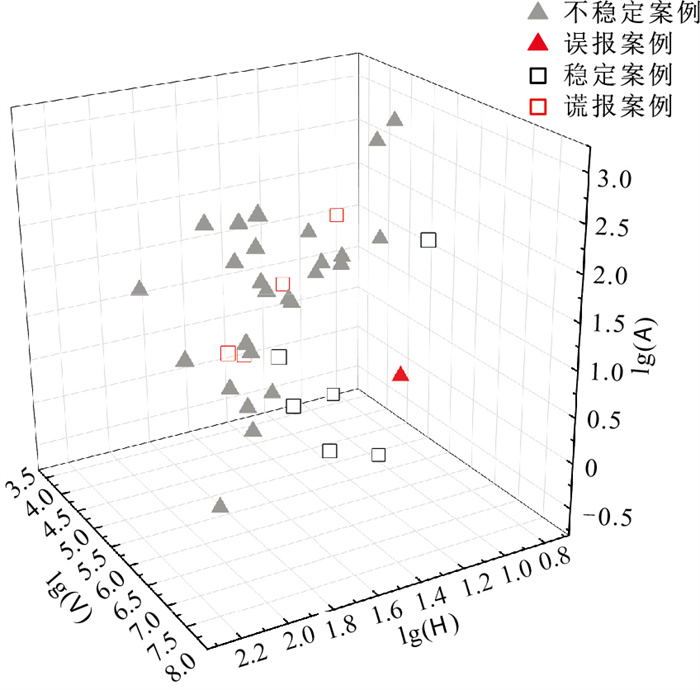
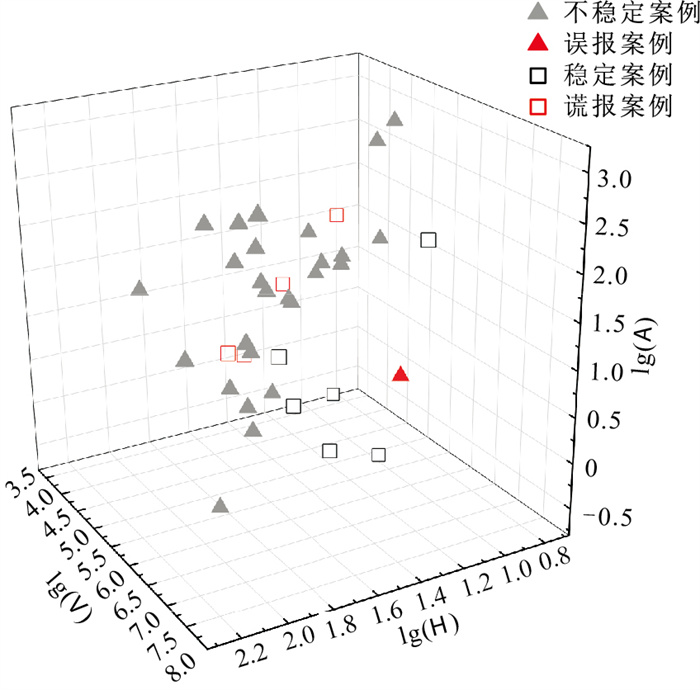
表 7 各堰塞坝稳定性预测模型的预测结果Table 7. Prediction results of the stability prediction models of landslide dams模型 准确数量 准确率/% 误报数量 误报率/% DBI 23 62.16 7 18.92 AHV_Dis 26 70.27 6 16.22 AHV_Log 27 72.97 5 13.51 SSA-Adam-BP 32 86.49 1 2.70 将不同模型预测结果进行对比后发现本文模型预测失误的5个案例使用其他模型同样未准确预测(除样本1使用DBI模型无法判断稳定性状态外,其他预测结果均和实际相反),图 5为用上述SSA-Adam-BP神经网络模型的预测结果绘制散点图。
从图 5中可以发现,预测失误案例(谎报案例及误报案例)的周围均为与其稳定性相反的案例,说明这些堰塞坝的稳定性可能仍然受其他影响因素的控制,例如坝体物质组成、突发降雨、地震等,因而需要发展考虑更多因素并更精确的模型对堰塞坝稳定性进行预测。
神经网络模型训练完成后,常采用平均影响值法衡量输入参数对预测结果的影响。具体方法为:将原训练样本在原基础上分别加减10%,形成2个新的数据集X1、X2;利用训练好的神经网络分别计算2个新数据集的输出值Y1、Y2;计算输出值差值Y1-Y2,其平均值即为平均影响值。其绝对值越大,说明对预测结果影响程度大,其正负代表相关的方向。表 8为各输入参数的平均影响值。
表 8 各输入参数的平均影响值Table 8. Mean influence value of each input parameter影响因素 Y1 Y2 平均影响值 坝体高度 32.04 46.31 -0.17 坝体体积 55.54 23.56 0.38 集水区面积 31.02 51.27 -0.24 从表 8中可以得出,对堰塞坝稳定性影响程度最大的因素是坝体体积,其次为集水区面积和坝体高度。其中坝体体积与堰塞坝稳定性呈正相关,集水区面积和坝体高度与堰塞坝稳定性均呈负相关,与基本物理规律相符合。
3. 工程案例分析
确定堰塞坝稳定性的预测模型之后,为验证SSA-Adam-BP模型在堰塞坝稳定性预测研究中的有效性和实用性,使用该模型对中国近年来形成的堰塞坝的稳定性进行预测。
近20年来,国内形成的堰塞坝案例超过100座,其大多位于我国西南区域,这是因为西南山区受青藏高原隆升的影响形成了边坡高陡、河谷深切的地形地貌,为堰塞坝的形成提供了有利的地形条件[29-30]。其中大部分堰塞坝案例因为交通不便、危害性较小等因素而缺少用于堰塞坝稳定性预测必要的参数。本次研究选取了32个具有详细参数的堰塞坝案例(表 9)作为测试案例,其中大部分堰塞坝案例都由地震触发,例如2008年汶川地震形成的唐家山、肖家桥等28例堰塞坝,2014年鲁甸“8·03”地震形成的红石岩堰塞坝以及2018年形成的白格堰塞坝;并且其中大多数堰塞坝受到了人类的干预,例如开挖泄洪道、清除、加固等,这些堰塞坝案例都被划分为不稳定案例[12-14]。因为即使没有人类干预,这些堰塞坝也会在短时间内溃决。
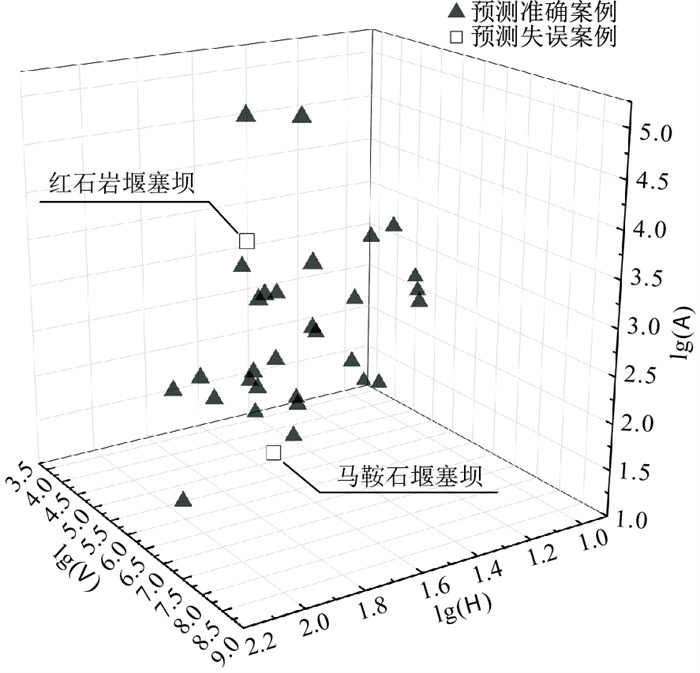
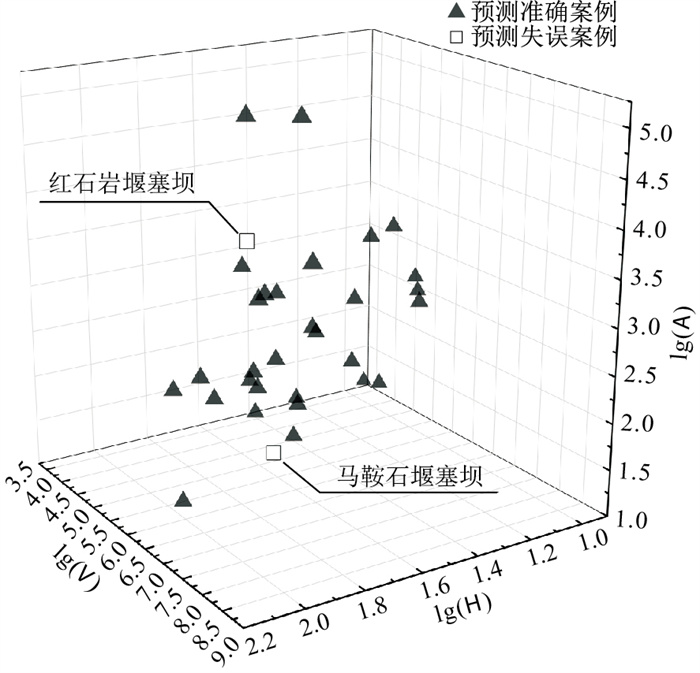
表 9 中国近年来典型堰塞坝事件[31]Table 9. Typical landslide dam cases in China in recent years序号 形成时间 名称 坝体高度H/m 坝体体积V/m3 集水区面积A/km2 稳定性分类 1 2000 易贡 80 300 000 000 13 533 不稳定 2 2008 白果村 15 400 000 3 564 不稳定 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 32 2018 白格(2) 81 10 000 000 173 484 不稳定 本次研究以网格搜索法确定的超参数组合建立神经网络模型,为了充分利用数据中的信息,使用Ermini数据库和Tabata数据库中的121例数据作为训练集对SSA-Adam-BP神经网络模型的参数重新进行训练,并利用训练好的模型对表 9中32例中国近些年来形成的堰塞坝的稳定性进行预测,其结果如图 6所示。
从图 6中可以看出除马鞍石堰塞坝被误报为稳定堰塞坝,红石岩堰塞坝被预测为不稳定堰塞坝外,其他30个案例的预测结果与实际稳定性情况一致。马鞍石堰塞坝是左侧山体在汶川地震的作用下发生滑坡堵塞河流形成的,位于石坎河上游,形成初期堰塞湖水位每天增长约1.1 m。造成模型预测结果与实际不一致的主要原因是该堰塞坝坝体主要由石块和泥松散堆积而成,大块岩体较少且结构上存在架空、松散等现象[32]。由这些物质组成的坝体抗剪强度和抗侵蚀能力低,易发生破坏[33],马鞍石堰塞坝稳定性受坝体材料组成控制。红石岩堰塞坝是世界首座“应急抢险—后续处置—整治利用”一体化水利枢纽工程,坝位于原红石岩水电站取水坝与厂房之间,由于其坝体材料以碎石为主,且坝体上游综合坡比约为1∶2.5,下游综合坡比约为1∶5.5,与常规堰塞坝相比较缓等原因增强了其稳定性,经过后期加固,至今未溃决[34-35]。
本次研究提出的SSA-Adam-BP模型成功地应用到中国近年来典型堰塞坝案例的稳定性预测中,预测的准确率达到93.75%,误报率仅为3.1%,从而证明了该模型具有较高的应用价值及应用前景,并且随着数据库的丰富、数据采集方法更加标准,准确率将会进一步提高。
4. 结论
(1) 基于全球153个具有完整数据的堰塞坝案例,通过结合SSA算法与Adam算法对BP模型的权重参数和偏置参数进行了更新,减小了随机生成参数初始值对模型训练结果的影响。SSA-Adam-BP模型的五折交叉验证平均准确率为91.73%,优于Adam-BP模型的89.27%和SSA-BP模型的88.43%,具有较高的全局搜索能力。通过平均影响法确定了对堰塞坝稳定性影响程度由大到小的因素依次为:坝体体积>集水区面积>坝体高度。
(2) 与传统的线性模型相比,BP神经网络模型能够更好地表征堰塞坝稳定性与影响因素之间存在的复杂的非线性关系,从而提高了堰塞坝稳定性预测的准确率,误报率仅为2.7%,与其他线性模型相比误报率降低了10.81%。
(3) 应用SSA-Adam-BP神经网络模型成功预测了32例中国近年来形成的堰塞坝的稳定性,预测值与实际值的一致性较好,达到了使用较少的参数实现对堰塞坝稳定性进行快速准确预测的效果,是一种有效的堰塞坝稳定性预测手段。
-
表 1 Ermini堰塞坝数据库
Table 1. Landslide dam database established by Ermini
表 2 Tabata堰塞坝数据库
Table 2. Landslide dam database established by Tabata
表 3 121例堰塞坝数据基本统计信息
Table 3. Basic statistical information of 121 cases based on the landslide dam database
特征变量 坝体高度H/m 坝体体积V/m3 集水区面积A/km2 最小值 3.00 8.70×107 0.19 最大值 500.00 2.20×109 4.50×104 平均值 52.88 5.70×107 731.61 标准差 65.87 2.86×108 4 321.71 表 4 Shapiro-Wilk检验结果
Table 4. Testing results of Shapiro-Wilk
变量 统计量W p值 在5%水平下的结论 H′ 0.68 0.00 排除正态性 V′ 0.19 0.00 排除正态性 A′ 0.14 0.00 排除正态性 lg(H′) 0.99 0.79 不能排除正态性 lg(V′) 0.999 0.70 不能排除正态性 lg(A′) 0.99 0.11 不能排除正态性 表 5 不同BP神经网络模型的交叉验证准确率
Table 5. Cross-verification accuracy of different BP neural network models
模型 准确率/% 平均准确率/% K=1 K=2 K=3 K=4 K=5 Adam-BP 87.50 87.50 91.67 91.67 88.00 89.27 SSA-BP 87.50 83.33 91.67 91.67 88.00 88.43 SSA-Adam-BP 91.67 87.50 95.83 91.67 92.00 91.73 表 6 堰塞坝稳定性线性预测模型
Table 6. Linear prediction model of landslide dam stability
表 7 各堰塞坝稳定性预测模型的预测结果
Table 7. Prediction results of the stability prediction models of landslide dams
模型 准确数量 准确率/% 误报数量 误报率/% DBI 23 62.16 7 18.92 AHV_Dis 26 70.27 6 16.22 AHV_Log 27 72.97 5 13.51 SSA-Adam-BP 32 86.49 1 2.70 表 8 各输入参数的平均影响值
Table 8. Mean influence value of each input parameter
影响因素 Y1 Y2 平均影响值 坝体高度 32.04 46.31 -0.17 坝体体积 55.54 23.56 0.38 集水区面积 31.02 51.27 -0.24 表 9 中国近年来典型堰塞坝事件[31]
Table 9. Typical landslide dam cases in China in recent years
序号 形成时间 名称 坝体高度H/m 坝体体积V/m3 集水区面积A/km2 稳定性分类 1 2000 易贡 80 300 000 000 13 533 不稳定 2 2008 白果村 15 400 000 3 564 不稳定 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 32 2018 白格(2) 81 10 000 000 173 484 不稳定 -
[1] 年廷凯, 吴昊, 陈光齐, 等. 堰塞坝稳定性评价方法及灾害链效应研究进展[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(8): 1796-1812. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201808003.htmNian T K, Wu H, Chen G Q, et al. Research progress on stability evaluation method and disaster chain effect of landslide dam[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(8): 1796-1812(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201808003.htm [2] Zhong Q M, Chen S S, Mei S A, et al. Numerical simulation of landslide dam breaching due to overtopping[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(6): 1183-1192. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0935-3 [3] Costa J E, Schuster R L. The formation and failure of natural dams[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1988, 100(7): 1054-1068. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1988)100<1054:TFAFON>2.3.CO;2 [4] 石振明, 马小龙, 彭铭, 等. 基于大型数据库的堰塞坝特征统计分析与溃决参数快速评估模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(9): 1780-1790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201409008.htmShi Z M, Ma X L, Peng M, et al. Statistical analysis of dam characteristics based on large-scale database and rapid evaluation model of collapse parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(9): 1780-1790(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201409008.htm [5] 叶华林. 基于堰塞坝几何形态的数理统计对其稳定性影响研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018.Ye H L. Research on the influence of mathematical statistics based on the geological characteristics of dam dams to its stability[D]. Chengdou: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [6] FanX M, Dufresne A, Subramanian S S, et al. The formation and impact of landslide dams: State of the art[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 203: 103116. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103116 [7] 彭铭, 王开放, 张公鼎, 等. 堰塞坝溃坝模型实验研究综述[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(5): 1007-1015. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202005010.htmPeng M, Wang K F, Zhang G D, et al. Review of model experimental studies on break of landslide dams[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(5): 1007-1015(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202005010.htm [8] Costa J E, Schuster R L. Documented historical landslide dams from around the world[R]. : US Geological Survey Open-file Report, 1991: 91-239. [9] Casagli N, Ermini L. Geomorphic analysis of landslide dams in the Northern Apennine[J]. Chikei, 1999, 20(3): 219-249. [10] Ermini L, Casagli N. Prediction of the behaviour of landslide dams using a geomorphological dimensionless index[J]. Earth Surface Processes & Landforms, 2003, 28(1): 31-47. [11] Korup O. Geomorphometric characteristics of New Zealand landslide dams[J]. Engineering Geology, 2004, 73(1/2): 13-35. [12] Stefanelli C T, Catani F, Casagli N. Geomorphological investigations on landslide dams[J]. Geoenvironmental Disasters, 2015, 2(1): 1-15. doi: 10.1186/s40677-014-0008-z [13] Stefanelli C T, Segoni S, Casagli N, et al. Geomorphic indexing of landslide dams evolution[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 208: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.04.024 [14] Shan Y B, Chen S S, Zhong Q M. Rapid prediction of landslide dam stability using the logistic regression method[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(12): 2931-2956. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01414-6 [15] 罗丹, 李昌彩, 吴长彬. 基于微粒群-BP神经网络算法的堆石坝坝体变形监控模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(增刊1): 2926-2931. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2012S1043.htmLuo D, Li C C, Wu C B. Study of monitoring model of faced rockfill dam's deformation based on particle swarm optimization-bp algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(S1): 2926-2931(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2012S1043.htm [16] 郭子正, 殷坤龙, 付圣, 等. 基于GIS与WOE-BP模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(12): 4299-4312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201912040.htmGuo Z Z, Yin K L, Fu S, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on GIS and WOE-BP model[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(12): 4299-4312(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201912040.htm [17] 马瑶, 赵江南. 机器学习方法在矿产资源定量预测应用研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 132-141. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0108Ma Y, Zhao J N. Advances in the application of machine learning methods in mineral prospectivity mapping[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 132-141(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0108 [18] 焦敬品, 李勇强, 吴斌, 等. 基于BP神经网络的管道泄漏声信号识别方法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2016, 37(11): 2588-2596. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2016.11.023Jiao J P, Li Y Q, Wu B, et al. Research on identi-fication method of pipeline leakage sound signal based on bpneural network[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2016, 37(11): 2588-2596(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2016.11.023 [19] Hecht-Nielsen R. Theory of the backpropagation neural network[J]. Neural Networks, 1988, 1: 593-605. [20] Guo Z Z, Chen L X, Gui L, et al. Landslide displacement prediction based on variational mode decomposition and WA-GWO-BP model[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17: 567-583. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01314-4 [21] Mirjalili S, Gandomi A H, Mirjalili S Z, et al. Salp swarm algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2017, 114: 163-191. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.07.002 [22] 刘小龙, 许岩, 徐维军. 基于统计引导和多项式差分学习的樽海鞘优化算法[J]. 运筹与管理, 2021, 30(1): 43-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YCGL202101008.htmLiu X L, Xu Y, Xu W J. Salp swarm algorithm based on statistical guidance and polynomial difference learning[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2021, 30(1): 43-49(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YCGL202101008.htm [23] 杨晓帆, 陈廷槐. 人工神经网络固有的优点和缺点[J]. 计算机科学, 1994, 21(2): 23-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJA199402004.htmYang X F, Chen T H. Inherent advantages and disadvantages of artificial neural networks[J]. Computer Science, 1994, 21(2): 23-26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJA199402004.htm [24] Kingma D, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]//International Conference Leaning Representation. :, 2015: 1-13. [25] 万里明, 吴均, 卢军凯, 等. 基于Adam-神经网络的致密砂岩脆性评价方法: 以南堡凹陷高北边坡为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 94-103. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0210Wan L M, Wu J, Lu J K, et al. Brittleness evaluation method of tight sandstone based on Adam-neural network: A case study of a block in Gaobei Slope, Nanpu Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 94-103(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0210 [26] Tabata S, Mizuyama T, Inoue K. Natural landslide dams hazards[J]. Engineering Geology, 2002, 110(3): 162-171. [27] Dong J J, Tung Y H, Chen C C, et al. Discriminant analysis of the geomorphic characteristics and stability of landslide dams[J]. Geomorphology, 2009, 110(3): 162-171. [28] Dong J J, Tung Y H, Chen C C, et al. Logistic regression model for predicting the failure probability of a landslide dam[J]. Engineering Geology, 2011, 117(1/2): 52-61. [29] 柴贺军, 刘汉超, 张倬元. 大型崩滑堵江事件及其环境效应研究综述[J]. 地质科技情报, 2000, 19(2): 87-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2000.02.021Chai H J, Liu H C, Zhang Z Y. The study on the environment and environmental effects of the collapse and closure of the Yangtze River[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2000, 19(2): 87-90(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2000.02.021 [30] 黄健, 贺子城, 黄祥, 等. 基于地貌特征的滑坡堰塞坝形成敏感性研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 253-262. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0040Huang J, He Z C, Huang X, et al. Formation sensitivity of landslide dam based on geomorphic characteristics[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 253-262(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0040 [31] 单熠博, 陈生水, 钟启明. 堰塞体稳定性快速评价方法研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(9): 1847-1859. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202009011.htmShan Y B, Chen S S, Zhong Q M. A rapid evaluation method of landslide dam stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(9): 1847-1859(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202009011.htm [32] 罗宗伟. 抛掷爆破技术在马鞍石堰塞湖应急排险处置中的应用[J]. 水利水电技术, 2008(8): 31-32, 35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0860.2008.08.010Luo Z W. Application of casting blast to emergency treatment of risk-elimination of Maanshi Landslide Dam[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2008(8): 31-32, 35(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0860.2008.08.010 [33] 柴贺军, 刘汉超, 张倬元, 等. 天然土石坝稳定性初步研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2001, 20(1): 77-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2001.01.017Chai H J, Liu H C, Zhang Z Y, et al. Preliminarily stability analysis of natural rock field dam resulting from damming landslide[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2001, 20(1): 77-81(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2001.01.017 [34] 张宗亮, 程凯, 杨再宏, 等. 红石岩堰塞坝应急处置与整治利用关键技术[J]. 水电与抽水蓄能, 2020, 6(2): 1-10, 25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBGC202002002.htmZhang Z L, Cheng K, Yang Z H, et al. Key technology of emergency remedy and treatment for hongshiyan barriers lake dam[J]. Hydropower and Pumped Storage, 2020, 6(2): 1-10, 25(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBGC202002002.htm [35] 刘建康, 程尊兰, 佘涛. 云南鲁甸红石岩堰塞湖溃坝风险及其影响[J]. 山地学报, 2016, 34(2): 208-215. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201602013.htmLiu J K, Cheng Z L, She T. Assessment of dam failure and secondary hazards for Hongshiyan dammed lake caused by Ludian earthquake in Niulanjiang River[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2016, 34(2): 208-215(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201602013.htm 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 周灵刚,胡奕挺,陈欣蔚,屠锋,吴朝峰,于洋,王彦兵,满银,李维朝. 基于神经网络的板墙组合式固化土地基承载力计算方法与优化设计. 地质科技通报. 2024(06): 102-113 .  本站查看
本站查看2. 瞿伟,刘祥斌,李久元,王宇豪,李达. 改进哈里斯鹰优化算法与BP神经网络组合的滑坡位移高精度预测模型. 地球科学与环境学报. 2023(03): 522-534 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 涂春梅,孙卫红,邵铁锋,梁曼. 基于透射图像的内印茧识别研究. 中国计量大学学报. 2023(02): 303-310 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(3)
-






 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术