Influence of anchor uncertainty on the failure probability of reinforced slope
-
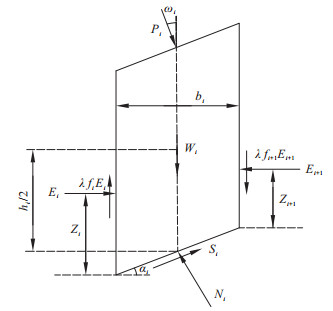
摘要: 为了探究锚杆不确定性对加固边坡失稳概率的影响, 建立了施加锚杆后的边坡模型, 通过以下两种途径来考虑锚杆的不确定性: 其一是假定锚杆与锚固体之间接触面上的单位表面摩擦力为对数正态分布变量, 其二是引入锚杆与锚固体之间接触面上的单位表面摩擦力衰减系数来考虑运营过程中锚杆的不确定性。采用极限平衡分析法并结合蒙特卡罗抽样法, 计算并对比分析了两种途径下锚固边坡失稳概率变化曲线, 最后以深圳假日酒店基坑边坡支护工程为例, 证明所提方法的有效性。结果表明: 对于途径一, 在相同土体统计参数下, 随着锚杆与锚固体之间接触面上单位表面摩擦力变异系数的增加, 加固边坡的失稳概率缓慢增加, 增幅介于18.03%~41.90%之间。对于途径二, 随着锚杆衰减系数自1.0逐步减小至0, 加固边坡失稳概率迅速增加, 增幅介于55.64%~124.90%之间; 在同一衰减系数下, 加固边坡失稳概率随着锚杆衰减根数的增加而增大。研究结果可以为锚杆施工与运营期间的管理提供决策支持。Abstract: To explore the influence of anchor uncertainty on the failure probability of reinforced slopes, the uncertainty of anchors is considered through the following two approaches: one assumes that the friction force on the unit surface of the contact surface between the anchor and the anchor solid is a log-normal distribution variable, and the other introduces the attenuation coefficient of the friction force on the unit surfaceof the contact surface between the anchor and the anchor solid to consider the uncertainty of the anchor during construction and maintenance. The limit equilibrium method and Monte Carlo sampling method are used to calculate and compare the variation curve of the failure probability of the reinforced slope through two approaches.Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method is validated against an example of the slope retaining project of the Shenzhen Holiday Inn foundation pit.The results show that the failure probability of the reinforced slope increases gradually with the increase range in the coefficient of variation of unit surface friction on the contact surface between the anchor and the anchor solid under the same soil statistical parameters, and the increase range is between 18.03% and 41.90% for the first approach. For the second approach, the failure probability of the reinforced slope increases rapidly with the decrease in the attenuation coefficient of the anchor ranging from 1.0 to 0.0, and the increase range is between 55.64% and 124.90%. Under the same attenuation coefficient, the failure probability of the reinforced slope increases with the increase in the number of attenuation anchors. The research results provide decision support for the management of anchors during construction and operation.
-
表 1 锚杆与锚固体之间接触面上的单位表面摩擦力Ff对数正态分布模型下边坡失稳概率
Table 1. Slope failure probability under the log-normal distribution model of unit surface friction Ff on the contact surface between the anchor and the anchor solid
黏聚力c 内摩擦角φ 锚杆与锚固体之间接触面上的单位表面摩擦力Ff 均值/kPa 分布类型 COV 均值/(°) 分布
类型COV 均值/kPa 分布类型 COV 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 不同COV下的失稳概率pf/% 5.0 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 50 LN 38.55 38.90 41.30 41.70 45.50 7.5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 50 LN 26.00 26.20 29.50 30.10 33.20 10.0 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 50 LN 17.90 18.20 19.40 25.30 25.40 注:COV为变异系数(coefficient of variation),LN为对数正态分布 表 2 随机1根锚杆局部失效下的边坡失稳概率
Table 2. Slope failure probability under partial failure of on eanchor at random
黏聚力c 内摩擦角φ 衰减系数
Ki其中1根锚杆
Ffi/kPa另外2根锚杆
Ffi/kPa失稳概率/% 均值/kPa 分布类型 COV 均值/(°) 分布类型 COV 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0 0 50 60.00 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0.1 5 50 58.75 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0.3 15 50 53.60 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0.5 25 50 49.30 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0.7 35 50 45.75 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0.9 45 50 39.00 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 1.0 50 50 38.55 表 3 随机2根锚杆局部失效下的边坡失稳概率
Table 3. Slope failure probability under partial failure of two anchors at random
黏聚力c 内摩擦角φ 衰减系数
Ki其中两根锚杆
Ffi/kPa另外一根锚杆
Ffi/kPa失稳概率/% 均值/kPa 分布类型 COV 均值/(°) 分布类型 COV 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0 0 50 86.70 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0.1 5 50 82.60 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0.3 15 50 71.30 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0.5 25 50 62.55 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0.7 35 50 52.20 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 0.9 45 50 41.15 5 LN 0.3 25 LN 0.3 1.0 50 50 38.55 表 4 各岩土层参数
Table 4. Parameters of each rock layer
岩土层名称 层厚/m 重度γ/(kN·m-3) 泊松比 黏聚力c/kPa 分布类型 COV 内摩擦角φ/(°) 分布类型 COV 素填土 1.75 18.0 0.45 10.0 LN 0.3 8 LN 0.3 粉质黏土 16.25 18.9 0.38 24.9 LN 0.3 20 LN 0.3 花岗岩 6.40 26.0 0.30 160.0 LN 0.3 35 LN 0.3 表 5 锚杆物理力学参数
Table 5. Physical and mechanical parameters of anchors
锚杆编号 起点坐标/m 终点坐标/m 锚杆长度/m 黏结直径d/m 锚杆水平间距/m 层面夹角δ/(°) 单位表面摩擦力均值Ff/kPa 抗剪强度σs/MPa 抗拉强度σtb/MPa 锚杆1 (19.18, 21.35) (32.34, 16.56) 14 0.3 2 20 70 300 168 锚杆2 (18.37, 18.35) (29.64, 14.25) 12 0.3 2 20 70 300 168 锚杆3 (17.55, 15.35) (26.95, 11.93) 10 0.3 2 20 70 300 168 锚杆4 (16.74, 12.35) (24.25, 9.61) 8 0.3 2 20 70 300 168 表 6 4根锚杆中随机1根、2根和3根锚杆局部失效模型下的失稳概率
Table 6. Failure probability of one, two and three anchors of four anchors under partial failure
衰减系数
Ki随机1根锚杆局部失效 随机2根锚杆局部失效 随机3根锚杆局部失效 Ffi/kPa 失稳概率/% Ffi/kPa 失稳概率/% Ffi/kPa 失稳概率/% 0 0 21.40 0 34.20 0 56.70 0.1 7 21.10 7 31.10 7 50.80 0.3 21 17.90 21 25.00 21 41.20 0.5 35 17.80 35 23.20 35 31.80 0.7 49 13.40 49 17.20 49 24.60 0.9 63 13.00 63 12.40 63 12.80 1.0 70 12.10 70 12.10 70 12.10 -
[1] Huang R Q. Mechanisms of large-scale landslides in China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2011, 71(1): 161-170. [2] 黄少平, 晏鄂川, 尹晓萌, 等. 不同临空条件的层状反倾岩质边坡倾倒变形几何特征参数影响规律[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 159-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101017.htmHuang S P, Yan E C, Yin X M, et al. The action law of geometrical characteristic parameters in the anti-dip rock slopes under different free face condition[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 159-165(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101017.htm [3] Li L, Zhai M, Ling X, et al. On the location of multiple failure slip surfaces in slope stability problems using the meshless SPH algorithm[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020(3): 1-8. [4] 陈祖煜, 詹成明, 姚海林, 等. 重力式挡土墙抗滑稳定分析安全判据和标准研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(8): 2129-2137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201608001.htmChen Z Y, Zhan C M, Yao H L, et al. Safety criterion and standards for stability analysis of gravity retaining walls[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(8): 2129-2137(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201608001.htm [5] 咸玉建, 陈学军, 汪志刚, 等. 基于有限元强度折减系数法岩土边坡稳定性分析与抗滑桩设计[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(4): 176-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2015.04.017Xian Y J, Chen X J, Wang Z G, et al. Geotechnical slope stability analysis and the design of anti-slide pile based on strength reduction FEM[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(4): 176-182(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2015.04.017 [6] Chen F, Zhang R, Wang Y, et al. Probabilistic stability analyses of slope reinforced with piles in spatially variable soils[J]. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2020, 122: 66-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2020.04.006 [7] 安彩龙, 梁烨, 王亮清, 等. 岩质边坡平面滑动锚固方向角的三维优化方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 23-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202005004.htmAn C L, Liang Y, Wang L Q, et al. Three-dimensional optimization method for the anchorage direction angle of plane sliding in rock slope[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 23-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202005004.htm [8] Zhang J, Wang H, Huang H W, et al. System reliability analysis of soil slopes stabilized with piles[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 229: 45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.09.009 [9] 李典庆, 蒋水华, 张利民, 等. 考虑锚杆腐蚀作用的岩质边坡系统可靠度分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(6): 1137-1144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2013.06.007Li D Q, Jiang S H, Zhang L M, et al. System reliability analysis of rock slopes considering rock bolt corrosion[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(6): 1137-1144(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2013.06.007 [10] 陈祖煜, 宗露丹, 孙平, 等. 加筋土坡的可能滑移模式和基于库仑理论的稳定分析方法[J]. 土木工程学报, 2016, 49(6): 113-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC201606013.htmChen Z Y, Zong L D, Sun P, et al. Investigation on possible failure modes of geotextile reinforced slopes and stability analysis methods based on Coulomb theory[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2016, 49(6): 113-122(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC201606013.htm [11] Blatz J A, Bathurst R J. Limit equilibrium analysis of large-scale reinforced and unreinforced embankments loaded by a strip footing[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2003, 40(6): 1084-1092. doi: 10.1139/t03-053 [12] 徐前卫, 丁文其, 朱合华, 等. 不同锚固方式下软弱破碎岩质边坡渐进破坏特性的模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(6): 1069-1079. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201206017.htmXu Q W, Ding W Q, Zhu H H, et al. Experimental study on progressive failure properties of weak and fractured rock slopes with different anchoring modes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(6): 1069-1079(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201206017.htm [13] 林杭, 陈宝成, 范祥, 等. 锚杆长短相间布置形式对边坡稳定性的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 46(2): 625-630. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201502034.htmLin H, Chen B C, Fan X, et al. Effect of bolt with long-short layout on slope stability[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2015, 46(2): 625-630(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201502034.htm [14] 韩冬冬, 门玉明, 胡兆江. 土质滑坡格构锚杆抗滑机制及受力试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 41(4): 1189-1194, 1202.Han D D, Men Y M, Hu Z J. Experimental study of anti-sliding mechanism and force of lattice anchor in soil landslide[J] Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(4): 1189-1194, 1202(in Chinese with English abstract). [15] 李国维, 赫新荣, 吴建涛, 等. 泥质砂软岩边坡加固锚杆黏结疲劳特征原位试验[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(9): 1729-1738. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202009001.htmLi G W, He X R, Wu J T, et al. Insitu test on bond fatigue characteristics of bolts for reinforcing soft shaly sandstone slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(9): 1729-1738(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202009001.htm [16] 张季如, 唐保付. 锚杆荷载传递机理分析的双曲函数模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2002, 24(2): 188-192. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2002.02.013Zhang J R, Tang B F. Hyperbolic function model to analyze load transfer mechanism on bolts[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2002, 24(2): 188-192(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2002.02.013 [17] Ren F, Yang Z, Chen J F, et al. An analytical analysis of the full-range behaviour of grouted rockbolts based on a tri-linear bond-slip model[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2010, 24(3): 361-370. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2009.08.021 [18] Chakravorty M, Frangopol D M, Mosher R L, et al. Time-dependent reliability of rock-anchored structures[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 1995, 47(3): 231-236. [19] 陈昌富, 成晓炜. 双滑块边坡锚固系统时变可靠性分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(1): 197-203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.01.031Chen C F, Cheng X W. Time-varying reliability analysis of anchor system of rock slopes with double slide blocks[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(1): 197-203(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.01.031 [20] 陈昌富. 仿生算法及其在边坡和基坑工程中的应用[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2001.Chen C F. Bionic algorithm and its application to slope and excavation engineering[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2001(in Chinese with English abstract). [21] 王辉, 程建华. 锚杆自由段对潜在滑移面的影响机制分析[J]. 广西大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 44(1): 165-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXKZ201901019.htmWang H, Cheng J H. Influence mechanism of unbounded part of anchor on potential sliding surface[J]. Journal of Guangxi University: Natural Science Edition, 2019, 44(1): 165-169(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXKZ201901019.htm -





 下载:
下载: