Analyzing the characteristics and reason for the ground collapse hazard in Shenzhen
-
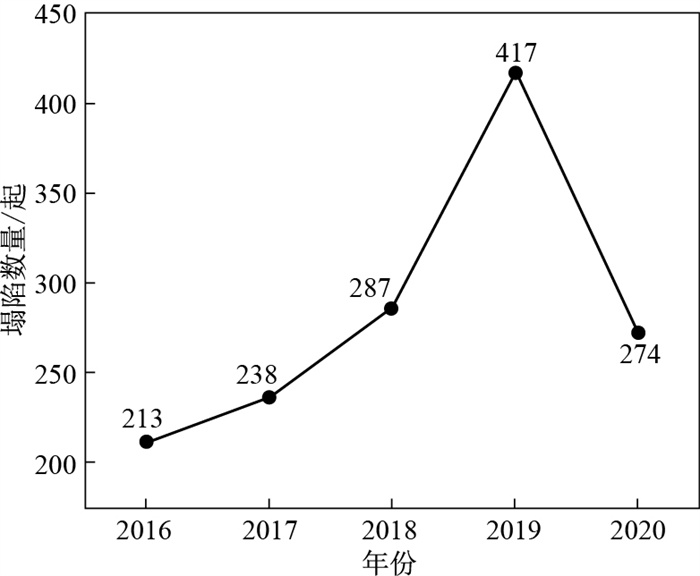
摘要: 为了查明深圳市地面塌陷成因并提出防治措施, 收集整理了深圳市2016-2020年地面塌陷灾害事故数据, 通过现场调查、数据统计分析以及GIS空间分析, 研究了深圳市地面塌陷灾害的时空分布、灾害危害程度以及塌陷成因等。结果表明: 深圳市地面塌陷灾害正处于持续增长阶段, 绝大多数属于小规模塌陷, 且绝大多数发生在雨季, 其中5-8月尤为严重; 地面塌陷发灾点主要集中分布在福田区、罗湖区以及光明区, 主要塌陷地点是市政道路和人行道; 塌陷成因主要包括管网破损、暗渠河道破损、施工不当、雨水冲刷、软土沉降、车辆荷载过大以及其他原因, 其中, 管网破损和施工不当是造成地面塌陷的最主要原因。本研究成果可为深圳市及其他类似城市地面塌陷的防治工作提供一定的参考与借鉴。Abstract: To ascertain the causes of ground collapse in Shenzhen and put forward prevention and control measures, this paper collects ground collapse accidents in Shenzhen between 2016 and 2020 and analyses the spatial and temporal distribution, hazard degree of ground collapse, and causes of ground collapse through field investigation, statistical data analysis and GIS spatial analysis. The results show that ground collapse disasters in Shenzhen are in a stage of continuous growth, most of which are small-scale ones, and most of which occur in the rainy season, especially from May to August. The disaster sites of ground collapse are mainly in Futian District, Luohu District and Guangming District, and the main sites of ground collapse are municipal roads and sidewalks. The main reason for ground collapse disasters is damage to water pipelines, damage to culverts, improper construction, rainwater erosion, settlement of soft soil, excessive vehicle loads and so on. Among them, water pipeline damage and improper construction are the main causes of ground collapse. The research results can provide some reference for the prevention and control of ground collapse in Shenzhen and other similar cities.
-
表 1 皮尔逊相关系数的关联程度
Table 1. Correlation of Pearson correlation coefficients
|r|的范围 相关程度 0.0≤|r| < 0.2 极弱相关或无关 0.2≤|r| < 0.4 弱相关 0.4≤|r| < 0.6 中等程度相关 0.6≤|r| < 0.8 强相关 0.8≤|r| < 1.0 极强相关 表 2 深圳市2016-2020年地面塌陷规模及财产损失统计
Table 2. Statistics of the ground collapse scale and property loss in Shenzhen from 2016 to 2020
塌陷深度/m 数量/起 占比/% 塌陷面积/m2 数量/起 占比/% 塌陷体积/m3 数量/起 占比/% 财产损失/万元 数量/起 占比/% >10 9 0.63 >100 29 2.03 >1 000 4 0.28 >100 30 2.11 (3, 10] 161 11.26 (30, 100) 59 4.13 (300, 1 000) 13 0.91 (30, 100] 89 6.22 [1,3] 623 43.57 [10,30] 175 12.25 [100, 300] 37 2.58 [10, 30] 227 15.87 < 1 636 44.54 < 10 1 166 81.59 < 100 1 375 96.23 < 10 1 083 75.80 合计 1 429 100.00 合计 1 429 100.00 合计 1 429 100.00 合计 1 429 100.00 -
[1] 张丽芬, 曾夏生, 姚运生, 等. 我国岩溶塌陷研究综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2007, 18(3): 126-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2007.03.027Zhang L F, Zeng X S, Yao Y S, et al. A review on karst collapse in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2007, 18(3): 126-130(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2007.03.027 [2] 胡亚波, 刘广润, 肖尚德, 等. 一种复合型岩溶地面塌陷的形成机理: 以武汉市烽火村塌陷为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2007, 26(1): 96-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200701017.htmHu Y B, Liu G R, Xiao S D, et al. Mechanism of a compound Karst surface collapse: A case study in Fenghuo Village of Wuhan City[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2007, 26(1): 96-100(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200701017.htm [3] 郑重, 张敬东, 杜建华. 基于分水岭算法的地质塌陷遥感识别方法研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(6): 226-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806028.htmZheng Z, Zhang J D, Du J H. Remote sensing identification method of geological subsidence using watershed algorithm[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(6): 226-231(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806028.htm [4] 郑晓明, 金小刚, 陈标典, 等. 湖北武汉岩溶塌陷成因机理与致塌模式[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2019, 30(5): 75-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201905010.htmZheng X M, Jing X G, Chen B D, et al. Genesis mechanism and collapse mode of karst collapse in Wuhan, Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(5): 75-82(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201905010.htm [5] 李喜, 殷坤龙, 陈标典, 等. 武汉白沙洲长江两岸岩溶塌陷易发性评价与地铁建设过程中的防治对策[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 121-130. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0612Li X, Yin K L, Chen B D, et al. Evaluation of susceptibility to karst collapse on both sides of the Yangtze River in Baishazhou, Wuhan and preventive measures in the process of metro construction[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 121-130(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0612 [6] 陈龙龙, 陈从新, 夏柏如, 等. 程潮铁矿东区地面塌陷机制及扩展机制初探[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(8): 2322-2334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201708024.htmChen L L, Chen C X, Xia B R, et al. Study on mechanism of formation and expansion of ground caving-in in the eastern Chengchao Iron Mine[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(8): 2322-2334(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201708024.htm [7] 谢晓深, 侯恩科, 高冠杰, 等. 宁夏羊场湾煤矿浅埋煤层开采地面塌陷发育规律及形成机理[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(12): 2233-2240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201812014.htmXie X S, Hou E K, Gao G J, et al. A study of the development regularity and formation mechanism of ground subsidence in shallow coal seam mining of Yangchangwan coal mine, Ningxia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2018, 37(12): 2233-2240(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201812014.htm [8] 陈昌彦, 肖敏, 贾辉, 等. 城市道路地下病害成因及基于综合探测的工程分类探讨[J]. 测绘通报, 2013(增刊2): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHTB2013S2003.htmChen C Y, Xiao M, Jia H, et al. Discussion on the causes of urban road underground diseases and engineering classification based on comprehensive detection[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2013(S2): 5-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHTB2013S2003.htm [9] 高明生. 城市道路塌陷原因分析及预防措施[J]. 市政技术, 2014, 32(增刊1): 39-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZJI2014S1014.htmGao M S. Cause analysis and preventive measures of urban road collapse[J]. Municipal Engineering Technology, 2014, 32(S1): 39-42(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZJI2014S1014.htm [10] 钟世英, 丛波日. 城市地面塌陷灾害成因机理分析及分类[J]. 工程地质学报, 2016, 24(增刊1): 341-346. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-GCDZ201610001052.htmZhong S Y, Cong B R. Analysis and classification of urban surface collapse hazard[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(S1): 341-346(in Chinese with English abstract). https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-GCDZ201610001052.htm [11] 王艳华, 谢汝强, 任岚, 等. 城市地面塌陷中渗流致灾机理及其控制分析[J]. 合肥学院学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 25(1): 59-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HFXZ201501016.htmWang Y H, Xie R Q, Ren L, et al. Seepage mechanism and control analysis of urban surface collapse[J]. Journal of Hefei University: Comprehensive Edtion, 2015, 25(1): 59-62(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HFXZ201501016.htm [12] 付栋, 蔡剑韬, 张海. 上海地区由管线渗漏引发地面塌陷数值模拟研究[J]. 岩土工程技术, 2018, 32(4): 189-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGJ201804006.htmFu D, Cai J T, Zhang H. Numerical simulation of ground collapse caused by pipeline leakage in Shanghai area[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2018, 32(4): 189-193(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGJ201804006.htm [13] 张成平, 张顶立, 王梦恕, 等. 城市隧道施工诱发的地面塌陷灾变机制及其控制[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(增刊1): 303-309. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2010S1050.htmZhang C P, Zhang D L, Wang M S, et al. The mechanism and control of ground collapse induced by urban tunnel construction[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(S1): 303-309(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2010S1050.htm [14] 白永学, 漆泰岳, 吴占瑞. 砂卵石地层盾构施工引发的滞后地面塌陷机理[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程, 2013, 35(1): 12-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JIAN201301004.htmBai Y X, Qi T Y, Wu Z R. Mechanism of lagging ground subsidence caused by shield tunneling in sandy gravel stratum[J]. Civil Construction and Environmental Engineering, 2013, 35(1): 12-19(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JIAN201301004.htm [15] 白永学, 漆泰岳, 李有道, 等. 基于LSSVM对盾构施工诱发地面塌陷变形预测[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(增刊2): 3666-3674. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2013S2085.htmBai Y X, Qi T Y, Li Y D, et al. Prediction of ground collapse and deformation induced by shield construction based on LSSVM[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(S2): 3666-3674(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2013S2085.htm -





 下载:
下载: