Three-dimensional discrete element simulation of the amplification effect of the slope surface under the action of strong earthquakes
-
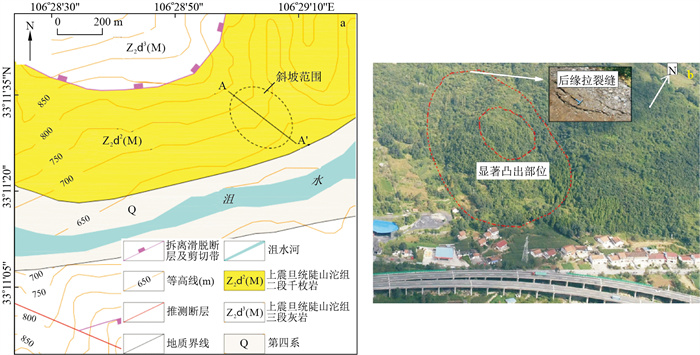
摘要: 为研究强震作用下斜坡表面的动力放大效应, 以陕西勉县某岩质斜坡为例, 建立了三维模型。运用离散元软件3DEC, 模拟了动力条件下斜坡的变形失稳过程, 分析了斜坡表面的动力响应特征, 研究了不同地震波输入工况条件下坡体表面动力响应差异。研究结果表明: 考虑地震纵波的影响时, 竖向加速度得到显著增强, 坡面的PGA放大系数增强了约1.62倍; 坡面形态强烈影响着斜坡表面的动力响应特征, 强震作用下, 斜坡坡肩及坡形转折处的放大效应均十分强烈, 凸出部位次之, 坡表两侧的放大效应最弱; 不同输入工况下, 斜坡坡形转折处的水平向PGA放大系数均维持较高值, 特别是在仅输入水平向加速度的条件下, 该部位在地震滑坡灾害预防中应特别注意; 强震作用下滑坡的运动过程可概括为滑坡孕育启动阶段—挤压碰撞高速运动阶段—堆积阶段。研究成果可为该地区防灾减灾工作提供一定理论支持。Abstract: To study the dynamic amplification effect of slope surfaces under the action of strong earthquakes, a three-dimensional model was established using a rocky slope in Mian County, Shaanxi Province, as an example. The discrete element software 3DEC is used to simulate the deformation and instability process of the slope under dynamic conditions, analyse the dynamic response characteristics of the slope surface, and study the difference in the dynamic response of the slope surface under different seismic wave input conditions. The main conclusions are that when considering the influence of seismic longitudinal waves, the vertical acceleration is significantly enhanced, and the PGA amplification factor of the slope is increased by approximately 1.62 times. The slope shape strongly affects the dynamic response characteristics of the slope surface. Under the action of strong earthquakes, the amplification of the slope shoulder and the slope turning point is very strong, followed by the protruding parts, and the amplification on both sides of the slope surface is the weakest. Under different input conditions, the horizontal PGA amplification factor at the slope turning point maintains a high value, especially when only the horizontal acceleration is input, and this part should be given special attention in the prevention of earthquake landslide disasters. The movement process of a landslide caused by strong earthquakes can be summarized as the initiation stage of the landslide-the high-speed movement stage of the squeeze collision-the accumulation stage. The research results can provide certain theoretical support for disaster prevention and mitigation in this region.
-
Key words:
- strong earthquakes /
- 3DEC /
- rock slope /
- dynamic response /
- amplification of surface
-
图 8 近场工况下坡表放大效应(图中数字对应图 4中的监测点号)
Figure 8. Acceleration coefficient curve of the slope surface
表 1 岩体材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of rock mass
岩体及结构面 抗拉强度/MPa 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 法向刚度/GPa 切向刚度/GPa 基岩 0.7 2 685 0.26 1.65 30 滑体 0.2 2 570 0.24 0.85 15 J1、J2 0.65 15 1.8 1.3 J3、J4 0.88 16 2.0 1.6 -
[1] 张倬元. 工程地质分析原理[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016.Zhang Z Y. Principles of engineering geological analysis[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016(in Chinese). [2] 杨国香, 伍法权, 董金玉, 等. 地震作用下岩质边坡动力响应特性及变形破坏机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(4): 696-702. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.04.008Yang G X, Wu F Q, Dong J Y, et al. Study on the dynamic response characteristics and deformation failure mechanism of rock slopes under earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(4): 696-702(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.04.008 [3] 黄润秋, 李果, 巨能攀. 层状岩体斜坡强震动力响应的振动台试验[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(5): 865-875. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2013.05.003Huang R Q, Li G, Ju N P. Shaking table test of strong vibration response of layered rock mass slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(5): 865-875(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2013.05.003 [4] 巨能攀, 邓天鑫, 李龙起, 等. 强震作用下陡倾顺层斜坡倾倒变形机制离心振动台试验[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(1): 99-108, 117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201901007.htmJu N P, Deng T X, Li L Q, et al. Centrifugal shaking table test on the dumping deformation mechanism of steeply inclined bedding slopes under strong earthquakes[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(1): 99-108, 117(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201901007.htm [5] 黄少平, 晏鄂川, 尹晓萌, 等. 不同临空条件的层状反倾岩质边坡倾倒变形几何特征参数影响规律[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 159-165. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0111Huang S P, Yan E C, Yin X M, et al. Influence law of geometric characteristic parameters of toppling deformation of layered anti-dip rock slope with different air-side conditions[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 159-165(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0111 [6] 杨背背, 殷坤龙, 梁鑫, 等. 三峡库区麻柳林滑坡变形特征及演化模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 122-129. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0213Yang B B, Yin K L, Liang X, et al. Deformation characteristics and evolution simulation of the Malulin landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 122-129(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0213 [7] 吴益平, 卢里尔, 薛阳. 基于临界状态的边坡渐进破坏力学模型分析及应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 1-7. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0501Wu Y P, Lu L E, Xue Y. Application of landslide progressive failure mechanical model based on the critical stress state[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 1-7(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0501 [8] 郑颖人, 叶海林, 黄润秋. 地震边坡破坏机制及其破裂面的分析探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(8): 1714-1723. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.08.024Zheng Y R, Ye H L, Huang R Q. Analysis and discussion on the failure mechanism and fracture surface of seismic slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(8): 1714-1723(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.08.024 [9] 曹琰波, 戴福初, 许冲, 等. 唐家山滑坡变形运动机制的离散元模拟[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(增刊1): 2878-2887. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2011S1039.htmCao Y B, Dai F C, Xu C, et al. Discrete element simulation of deformation mechanism of Tangjiashan landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(S1): 2878-2887(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2011S1039.htm [10] 崔芳鹏, 胡瑞林, 殷跃平, 等. 纵横波时差耦合作用的斜坡崩滑效应离散元分析: 以北川唐家山滑坡为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(2): 319-327. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201002015.htmCui F P, Hu R L, Yin Y P, et al. Discrete element analysis of slope avalanche-slip effect coupled with time difference of vertical and horizontal waves: Taking Beichuan Tangjiashan landslide as an example[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(2): 319-327(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201002015.htm [11] 赵伟华, 黄润秋, 赵建军, 等. 强震条件下碎裂岩体崩塌机理及崩塌后壁对堆积体稳定性影响研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2011, 19(2): 205-212. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.02.010Zhao W H, Huang R Q, Zhao J J, et al. Study on the collapse mechanism of the cataclastic rock mass and the influence of the collapsed wall on the stability of the deposit under strong earthquake conditions[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(2): 205-212(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.02.010 [12] 李龙起, 张帅, 何川, 等. 基于离散元技术的软硬互层斜坡动力响应及失稳机理研究[J]. 水利水电技术, 2020, 51(4): 203-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJWJ202004024.htmLi L Q, Zhang S, He C, et al. Research on the dynamic response and instability mechanism of soft and hard interbedded slopes based on discrete element technology[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Technology, 2020, 51(4): 203-211(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJWJ202004024.htm [13] 言志信, 史盛, 党冰, 等. 地震作用下坡面形态对岩质边坡稳定性的影响[J]. 山东科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 32(2): 43-48, 78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3767.2013.02.006Yan Z X, Shi S, Dang B, et al. The influence of slope shape on the stability of rock slope under earthquake action[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2013, 32(2): 43-48, 78(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3767.2013.02.006 [14] 王多军, 裴向军, 宋金龙. 地震作用下顺层岩质边坡变形破坏坡面效应[J]. 公路, 2012(8): 12-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2012.08.003Wang D J, Pei X J, Song J L. Slope effect of deformation and failure of bedding rock slope under earthquake[J]. Highway, 2012(8): 12-16(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2012.08.003 [15] Xu X W, Wen X Z, Yu G H, et al. Coseismic reverse- and oblique-slip surface fault-ing generated by the 2008 MW7.9 Wenchuan Earthquake, China[J]. Geology, 2009, 37(6): 515-518. doi: 10.1130/G25462A.1 [16] Zhang P Z, Wen X Z, Shen Z K, et al. Oblique, high-angle, listric-reverse faulting and associated development of strain: The Wenchuan Earthquake of May 12, 2008, Sichuan, China[J]. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., 2010, 38: 353-382. [17] 王明明. 汉中盆地发育机制及构造演化研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 2013: 4-8.Wang M M. Research on the development mechanism and tectonic evolution of the Hanzhong Basin[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, 2013: 4-8(in Chinese with English abstract). [18] Itasca Consulting Group, Inc. USA. 3DEC 3 dimensional distinct element code, version3.0, user's manual[M]. : Itasca Consulting Group, Inc. USA., 2005. [19] 蔡国军, 陈锡锐, 尹保国, 等. 岩体力学参数对反倾边坡稳定性影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 人民珠江, 2020, 41(9): 25-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2020.09.004Cai G J, Chen X R, Yin B G, et al. Numerical simulation study on the influence of rock mass mechanical parameters on the stability of anti-dipping slopes[J]. People's Pearl River, 2020, 41(9): 25-31(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2020.09.004 [20] Bertero V, Mahin S, Herrera R. Aseismic design implications of near-fault San Fernando Earthquake records[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 1978, 6(1): 31-42. doi: 10.1002/eqe.4290060105 [21] Kuhlemeyer R L, Lysmer J. Finite element method accuracy for wave propagation problems[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, ASCE, 1973, 99(5): 421-417. doi: 10.1061/JSFEAQ.0001885 [22] 庄建琦, 崔鹏, 葛永刚, 等. 5·12汶川地震崩塌滑坡分布特征及影响因子评价: 以都江堰至汶川公路沿线为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2009, 28(2): 16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2009.02.004Zhuang J Q, Cui P, Ge Y G, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors evaluation of collapse and landslides during the 5·12 Wenchuan Earthquake: Taking the Dujiangyan-Wenchuan highway as an example[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2009, 28(2): 16-22(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2009.02.004 [23] 顾金, 王运生, 曹文正, 等. 1786年磨西地震烂田湾滑坡形成机制及过程[J]. 山地学报, 2016, 34(5): 520-529. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201605003.htmGu J, Wang Y S, Cao W Z, et al. The formation mechanism and process of Lantianwan landslide in Moxi Earthquake in 1786[J]. Journal of Mountain Research, 2016, 34(5): 520-529(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201605003.htm [24] 罗永红, 王运生. 汶川地震诱发山地斜坡震动的地形放大效应[J]. 山地学报, 2013, 31(2): 200-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2013.02.009Luo Y H, Wang Y S. The topographic amplification effect of the mountain slope shaking induced by the Wenchuan Earthquake[J]. Journal of Mountain Research, 2013, 31(2): 200-210(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2013.02.009 [25] 刘铮, 李滨, 贺凯, 等. 地震作用下西藏易贡滑坡动力响应特征分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(4): 471-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202004004.htmLiu Z, Li B, He K, et al. Analysis of dynamic response characteristics of the Yigong landslide in Tibet under earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(4): 471-480(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202004004.htm -





 下载:
下载: