Abnormal event detection of city slope monitoring data based on multi-sensor information fusion
-
摘要: 为预防和管控城市突发地质灾害造成的人民生命和财产损失, 国家针对城市地质灾害易发地区部署了大量的各类传感器, 用来感知和监测城市边坡等地质体的变化情况, 以支持对地质灾害的预警。从边坡监测数据特点和时序数据分析技术出发, 针对监测数据噪声混杂、模式分析困难、预警阈值的不确定性等问题, 给出了一种基于多传感器信息融合的边坡监测数据异常事件检测方法。主要工作包括: ①边坡监测数据变化模式可以归结为周期项、趋势项以及噪声项的叠加, 实践中在预处理基础上对边坡监测数据进行周期为24 h的重采样, 同时趋势项可以近似看作是经典的牛顿运动, 以此构建形变运动模型, 为卡尔曼滤波的状态转移提供理论支持; ②采用集中式衰减记忆卡尔曼滤波, 引入衰减记忆因子, 对多传感器边坡监测数据进行特征级融合, 降低了噪声的影响, 提高了边坡监测数据的可靠性; ③引入惩罚系数, 应用改进的动态时间弯曲算法对于周期序列数据进行相似性度量。在此基础上基于K-means聚类和局部异常因子分析对边坡监测数据进行异常检测, 并基于3σ准则确定预警阈值。该方法能将正常模式和异常模式的时序数据进行区分, 有效检测出边坡监测数据的异常, 为灾害预防提供支持。最后以深圳市典型边坡监测数据为例验证了此方法的可行性。
-
关键词:
- 时序数据 /
- 多传感器信息融合 /
- 卡尔曼滤波 /
- 动态时间弯曲 /
- 边坡监测数据异常事件检测
Abstract: To prevent and control the loss of people's lives and property caused by sudden urban geological disasters, China has deployed a large number of sensors for urban geological disaster-prone areas to perceive changes in urban underground space. In this article, based on the characteristics of slope monitoring data and the analysis technology of time series data, aiming at problems such as noise mixtures in monitoring data, the difficulty of mode analysis and the uncertainty of early warning thresholds, a method of abnormal event detection in slope monitoring data based on multisensor information fusion is proposed. The results show that: ① Aiming at the disadvantage that the optimal estimation of the Kalman filter requires known noise information, the attenuation memory factor is introduced, and the centralized attenuation memory Kalman filter is used to fuse the multisensor slope monitoring data, which reduces the influence of noise and improves the reliability of slope monitoring data. ② The change mode of slope monitoring data can be summed up as the superposition of periodic term, trend term and noise term. The period is 24 hours, and the trend term can be approximately regarded as the classic Newtonian motion. Based on this, the deformation motion model can be constructed to provide theoretical support for the state transfer of the Kalman filter. ③ The penalty coefficient is introduced to make the improved DTW have a better measurement effect for the periodic sequence. On this basis, anomaly detection is carried out on the slope monitoring data based on K-means clustering, and local anomaly factors are used to analyse the abnormal conditions of the monitoring data. This method can distinguish the time series data of thenormal mode and abnormal mode better, detect abnormal slope monitoring data effectively, and provide guarantees for disaster prevention. Therefore, in view of the insufficiency of slope monitoring data processing and analysis processes, different information fusion technologies are adopted to improve the reliability and robustness of slope monitoring data. The feasibility of the proposed method is verified by slope monitoring data in Shenzhen. -
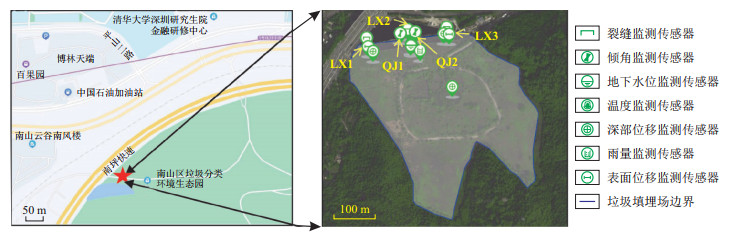
表 1 边坡监测实验数据
Table 1. Monitoring experimental data of the slope
期数 位移量/mm 期数 位移量/mm 期数 位移量/mm 期数 位移量/mm 1 186.251 5 186.251 9 186.150 13 186.091 2 186.253 6 186.256 10 186.096 14 186.066 3 186.256 7 186.257 11 186.033 4 186.256 8 186.260 12 186.098 290 188.378 表 2 实验区水平位移监测点LX1及倾角监测点QJ2监测数据
Table 2. Monitoring data of horizontal displacement and dip angle in monitoring area
时间 LX1位移/mm 时间 QJ2倾角/(°) 00∶04∶31 186.258 00∶04∶43 -0.945 00∶14∶02 186.258 00∶15∶24 -0.947 00∶24∶44 186.257 00∶24∶57 -0.948 00∶35∶23 186.257 00∶35∶36 -0.947 00∶45∶00 186.258 00∶46∶20 -0.948 00∶56∶13 186.258 00∶54∶58 -0.947 23∶26∶28 186.257 23∶48∶30 -0.949 23∶36∶30 186.256 23∶59∶07 -0.949 23∶47∶06 186.257 23∶56∶44 186.255 Algorithm 1: Improved centralized Kalman filter algorithm Inputs: A过程误差矩阵W B观测误差矩阵V C状态转移矩阵A D测量矩阵H E误差协方差矩阵P F初始状态向量X Algorithm steps 1 While Get(Lk) do 2 $ \hat{\boldsymbol{X}}_{k}^{-}=\boldsymbol{A} \hat{\boldsymbol{X}}_{k-1}+\boldsymbol{B} \boldsymbol{u}_{k-1} $//预测 先验估计X 3 $\boldsymbol{P}_{k}^{-}=\boldsymbol{A}\left(\lambda \boldsymbol{P}_{k-1}\right) \boldsymbol{A}^{\mathrm{T}}+\boldsymbol{Q} $//预测 先验估计误差协方差 4 $\boldsymbol{K}_{k}=\boldsymbol{P}_{k}^{-} \boldsymbol{H}_{k}^{\mathrm{T}}\left(\boldsymbol{H}_{k} \boldsymbol{P}_{k}^{-} \boldsymbol{H}_{k}{}^{\mathrm{T}}+\boldsymbol{R}\right)-1 $//校正 后验估计卡尔曼增益 5 $\hat{\boldsymbol{X}}_{k}=\hat{\boldsymbol{X}}{}_{k}^{-}+\boldsymbol{K}_{k}\left[\boldsymbol{Z}_{k}-\boldsymbol{H}_{k} \hat{\boldsymbol{X}}{}_{k}^{-}\right] $//校正 后验估计状态向量X 6 $\boldsymbol{P}_{k}=\left[I-\boldsymbol{K}_{k} \boldsymbol{H}_{k}\right] \boldsymbol{P}_{k}^{-} $//校正 后验估计误差协方差 7 End While Outputs: A最优估计状态向量$\hat{X} $ 表 3 仿真实验模拟数据
Table 3. Simulation experiment data
序号 真实值 传感器1测量值 传感器2测量值 融合值 1 25.003 24.519 24.527 24.570 2 25.038 24.829 26.115 25.254 3 25.055 26.308 25.166 25.712 4 25.127 24.303 25.867 25.457 5 24.977 24.414 24.335 24.894 6 24.818 24.314 24.808 24.677 48 32.456 258 67 31.489 33.981 32.569 49 32.911 428 72 32.389 34.334 33.258 50 33.593 419 76 33.824 33.252 33.723 表 4 不同方法的RMSE
Table 4. RMSE of different methods
方法 RMSE 传感器1 0.710 2 传感器2 0.758 9 平均(传感器) 0.734 5 改进的自适应集中式卡尔曼滤波 0.335 8 表 5 实验区3个边坡表面水平位移监测点的原始数据
Table 5. Original data from three monitoring points in the experimental area
位移/mm 监测日期 LX1 LX2 LX3 2020-03-18 188.294 187.763 187.543 2020-03-25 188.256 187.716 187.732 2020-04-01 188.224 187.674 186.910 2020-04-08 188.756 188.402 187.762 2020-04-15 188.792 188.239 187.790 2020-04-22 188.346 187.663 187.443 2020-04-29 188.745 187.861 187.542 2020-05-06 188.156 187.263 187.145 2021-03-03 186.147 185.333 184.981 2021-03-10 186.182 185.744 185.061 2021-03-17 186.214 185.912 185.355 Algorithm 2:K-nearest neighbor local anomaly detection algorithm Inputs: A Timeseries TS B Number of nearest neighbors K Algorithm steps 1 L= len(TS); 2 for i in range(1, L) 3 for j in range(1, L) 4 if i!=j: 5 Data(i).add(point, dist(i, j)) 6 Sorted(Data(i)) 7 k-dist(p)= Data(i)[k][1] 8 for i in Data(i): 9 if Data(i)[1] < k-dist(p) 10 Nk(p).add(Data(i)[k][0]) 11 for i in range(1, L) 12 Data(i).lrd=getLrd 13 for i in range(1, L) 14 Data(i).lof=getLof Outputs: A Local Outlier Factor LOF 表 6 混淆矩阵
Table 6. Confusion matrix
类别 正常 异常预警 正常(100) 98 2 异常(50) 12 38 -
[1] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 王力哲, 等. 基于大数据的城市地质环境智能监管思路与方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 157-163. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0117Wu C L, Liu G, Wang L Z, et al. Thinking and methods of intelligent supervision of urban geological environment based on big data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 157-163(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0117 [2] 刘军旗, 刘强, 刘千慧, 等. 大数据时代地质灾害数据管理及应用模式探讨[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 276-282, 292. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0627Liu J Q, Liu Q, Liu Q H, et al. Discussion of geological hazard data management and application model in big data era[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 276-282, 292(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0627 [3] 许强. 对滑坡监测预警相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(2): 360-374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202002017.htmXu Q. Understanding the landslide monitoring and early warning: Consideration to practical issues[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(2): 360-374(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202002017.htm [4] 仝德富, 谭飞, 苏爱军, 等. 基于多源数据的谭家湾滑坡变形机制及稳定性评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 162-170. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0432Tong D F, Tan F, Su A J, et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Tanjiawan landslide based on multi-source data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 162-170(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0432 [5] 熊寄然. GNSS技术在城市边坡监测中的应用[J]. 重庆建筑, 2019, 18(8): 47-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJZ201908021.htmXiong J R. Application of GNSS technology in urban slope monitoring[J]. Chongqing Architecture, 2019, 18(8): 47-49(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJZ201908021.htm [6] 王腾军, 赖百炼, 叶俊华, 等. 基于GM(1, 1)数据融合算法的滑坡预测研究[J]. 测绘通报, 2012(5): 63-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHTB201205021.htmWang T J, Lai B L, Ye J H, et al. Research on landslide prediction based on GM(1, 1) data fusion algorithm[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2012(5): 63-65(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHTB201205021.htm [7] 侯圣山, 李昂, 陈亮, 等. 基于普适型仪器的滑坡监测预警初探: 以甘肃兰州岷县三处滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2020, 31(6): 47-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202006006.htmHou S S, Li A, Chen L, et. al. Application of universal geo-hazard monitoring instruments in landslides and early warning of three landslides in Gansu Province: A case study in Minxian County and Lanzhou City of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 47-53(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202006006.htm [8] 王智伟, 王利, 黄观文, 等. 基于BP神经网络的滑坡监测多源异构数据融合算法研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(4): 575-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202004014.htmWang Z W, Wang L, Huang G W, et al. Research on multi-source heterogeneous data fusion algorithm of landslide monitoring based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(4): 575-582(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202004014.htm [9] 刘超云, 尹小波, 张彬. 基于Kalman滤波数据融合技术的滑坡变形分析与预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2015, 26(4): 30-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201504007.htmLiu C Y, Yin X B, Zhang B. Analysis and prediction of landslide deformations based on data fusion technology of Kalman-filter[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2015, 26(4): 30-35(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201504007.htm [10] 张福荣. 自适应卡尔曼滤波在变形监测数据处理中的应用研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2009.Zhang F R. Application of adaptive kalman filter in deformation monitoring data processing[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2009(in Chinese with English abstract). [11] 朱自强, 吴顺川, 刘洋, 等. 基于自适应Kalman滤波融合技术的边坡变形分析[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2020, 40(1): 16-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYK202001004.htmZhu Z Q, Wu S C, Liu Y, et al. Slope deformation analysis based on adaptive Kalman-filter fusion technology[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2020, 40(1): 16-21(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYK202001004.htm [12] 吴艳. 多传感器数据融合算法研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2003.Wu Y. Study of multisensor data fusion algorithms[D]. Xi'an: Xidian University, 2003(in Chinese with English abstract). [13] Novikov I Y. Asymptotics of the roots of bernstein polynomials used in the construction of modified daubechies wavelets[J]. Mathematical Notes, 2002, 71(1): 217-229. [14] 李秀珍. 滑坡变形突变异常的小波识别方法[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2015, 24(6): 50-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201506006.htmLi X Z. Wavelet identification method for deformation abnormality of landslides[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2015, 24(6): 50-56(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201506006.htm [15] 李新源, 贺可强, 贾玉跃, 等. 堆积层滑坡位移矢量角异常变化分析: 以新滩滑坡为例[J]. 价值工程, 2010, 29(17): 88-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZGC201017060.htmLi X Y, He K Q, Jia Y Y, et al. Analysis on the displacement vector angle abnormal of colluvial landslide: Xintan landslide as an example[J]. Value Engineering, 2010, 29(17): 88-89(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZGC201017060.htm [16] 袁勇, 许强, 陈聆. 基于人工免疫算法的数据压缩技术在滑坡异常提取中的应用研究[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 34(6): 621-625. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200706008.htmYuan Y, Xu Q, Chen L. Application of data compression based on AIS to the extraction of landslide anomaly[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2007, 34(6): 621-625(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200706008.htm [17] Li D, Liu S, Zhang H. A boundary-fixed negative selection algorithm with online adaptive learning under small samples for anomaly detection[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2016, 50: 93-105. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2015.12.014 [18] Safa M, Sari P A, Shariati M, et al. Development of neuro-fuzzy and neuro-bee predictive models for prediction of the safety factor of eco-protection slopes[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2020, 550: 124046. [19] 陈小惠, 万德钧, 王庆. 模糊逻辑在分布式多目标跟踪融合中的应用研究[J]. 东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 33(6): 754-757. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNDX200306017.htmChen X H, Wan D Y, Wang Q. Study for distributed multitarget tracking fusion using fuzzy logic[J]. Journal of Southeast University: Natural Science Edition, 2003, 33(6): 754-757(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNDX200306017.htm [20] 卢鋆, 吴忠望, 王宇, 等. 基于KNN算法的异常行为检测方法研究[J]. 计算机工程, 2007, 33(7): 133-134, 138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJC200707048.htmLu Y, Wu Z W, Wang Y, et al. Research on abnormal behavior detection based on KNN algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering, 2007, 33(7): 133-134, 138(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJC200707048.htm [21] Breunig M M, Kriegel H P, Raymond T N, et al. LOF: Identifying density-based local outliers[C]//Proc. ACM SIGMOD Int. Conf. on Management of Data. Dalles, TX, USA: [s. n. ], 2000: 1-12. [22] 武小年, 彭小金, 杨宇洋, 等. 入侵检测中基于SVM的两级特征选择方法[J]. 通信学报, 2015, 36(4): 23-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TXXB201504003.htmWu X N, Peng X J, Yang Y Y, et al. Two-level feature selection method based on SVM for intrusion detection[J]. Journal on Communications, 2015, 36(4): 23-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TXXB201504003.htm [23] 王思敬, 杨志法, 刘竹华. 地下工程岩体稳定分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984.Wang S J, Yang Z F, Liu Z H. Stability analysis of underground engineering rock mass[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984(in Chinese). [24] Thuy H, Anh D T, Chau V. Efficient segmentation-based methods for anomaly detection in static and streaming time series under dynamic time warping[J]. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 2021, 56(3): 121-146. -





 下载:
下载: