Determinations of the critical sliding surface of planar sliding rock slopes and their stability analysis
-
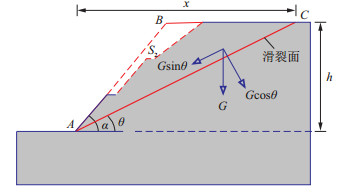
摘要: 由于传统搜索方法对岩质边坡滑裂面的确定无法兼顾效率与精度, 如何迅速准确确定潜在滑裂面仍然是个难题。极限平衡法在岩质边坡稳定性分析中备受认可, 采用岩质边坡平面剪切滑动模型, 以滑裂面的倾角来表征潜在滑裂面的位置; 基于极值法, 推导了极限平衡条件下平面剪切破坏型岩质边坡潜在滑裂面的解析解, 并结合香港秀茂坪路边坡对其准确性进行了验证, 进一步对四川宜宾打营盘山公路多级边坡进行了整体稳定性分析。结果表明: 香港秀茂坪边坡采用本文方法确定的边坡潜在滑裂面倾角与实际滑坡倾角基本一致。实际工程应用中, 采用Slide软件中布谷鸟搜索法和模拟退火法两种搜索方法得到的滑裂面倾角分别为38.0°和37.0°, 本解析法所得倾角为34.8°; 选用Janbu法、Morgenstern-Price法和Sarma法分别计算对应的稳定系数, 结果均为1.04左右, 本文所得稳定系数为1.15, 可见本文方法所得结果基本准确。通过参数敏感性分析发现, 随着黏聚力的增加, 边坡滑裂面倾角越来越小, 稳定系数也随之增加; 而当内摩擦角增大时, 边坡滑裂面倾角和稳定系数也随之增大。Abstract: It is still a difficult problem to determine the sliding surface of a rock slope quickly and accurately because the efficiency and accuracy cannot be met at the same time in traditional searching methods. The limit equilibrium method is widely accepted in the stability analysis of rock slopes. The planar shear sliding model of a rock slope is adopted to characterize the position of the potential sliding surface by the inclination of the sliding surface; the analytical solution of the potential sliding surface of a multistage rock slope under the condition of limit equilibrium is derived based on the extreme value method, and its accuracy is verified combined with the Sau Mau Ping slope in Hong Kong. Furthermore, the system stability of the Dayingpanshan slope in Yibi, Sichuan Province with multiple steps in a highway is analysed. The results show that the slope potential sliding surface inclination determined by this method is in agreement with the practical sliding inclination of the Sau Mau Ping slope. In practical engineering applications, the dip angles of the sliding surface obtained by using the Cuckoo search method and simulated annealing method in Slide software are 38.0° and 37.0°, respectively, and the dip angle obtained by the analytical method in this paper is 34.8°.The Janbu method, Morgenstern-Price method and Sarma method are selected to calculate the corresponding stability coefficients, the results are approximately 1.04. The stability coefficient obtained in this paper is 1.15. The results obtained by this method are basically accurate. Through parameter sensitivity analysis, it is found that with the increase in cohesion, the inclination angle of the slope slip surface decreases, and the stability coefficient also increases. When the internal friction angle increases, the slope slip surface inclination and stability coefficient also increase.
-
Key words:
- rock slope /
- sliding surface /
- stability analysis /
- limit equilibrium method
-
表 1 秀茂坪路岩质边坡参数
Table 1. Parameters of the rock slope at Sau Mau Ping Road
参数 注释 大小 h 边坡高度 60 m hw 破坏面上水位高度 h/2=30 m γw 水的重度 9.8 kN/m3 γr 岩石的重度 27 kN/m3 c 岩石的黏聚力 100 kPa φ 岩石的内摩擦角 35° α 岩石的坡脚 50° θ 破坏面倾角 35° 表 2 岩土物理力学性质指标建议值
Table 2. Recommended values of the physical mechanics parameters of rock and soil
岩土名称 状态 天然重度
γ/(kN·m-3)直接快剪 饱和极限抗压强度
frk/MPa地基承载力基本容许值
fa0/kPa挖方边坡永久坡率 岩质边坡类别 凝聚力标准值
ck/kPa内摩擦角标准
值φk/(°)泥岩 W3 22 / 35 / 250 1∶1.25 Ⅳ 泥岩 W2 24 / 45 5 450 1∶1 Ⅳ 砂岩 W3 22 / 35 / 350 1∶1.25 Ⅳ 砂岩 W2 25 / 55 12 800 1∶0.75 Ⅳ 表 3 岩石各级物理力学参数
Table 3. Physical and mechanical parameters of graded rocks
级别 重度γ/(kN·m-3) 内摩擦角
φ/(°)黏聚力
c/MPa变形模量
E/MPa泊松比 Ⅰ >26.5 >60 >2.1 >33 0.2 Ⅱ >26.5 [60, 50) [2.1, 1.5) [33, 20) [0.2, 0.25) Ⅲ [26.5, 24.5) [50, 39) [1.5, 0.7) [20, 6) [0.25, 0.3) Ⅳ [24.5, 22.5] [39, 27] [0.7, 0.2] [6, 1.3] [0.3, 0.35] Ⅴ < 22.5 < 27 < 0.2 < 1.3 < 0.35 表 4 打营盘山岩土参数
Table 4. The parameters of rock and soil of Mount Dayingpan
岩土名称 重度γ/(kN·m-3) 内摩擦角φ/(°) 黏聚力c/kPa 中风化砂岩 25 28 50 强风化砂岩 22 25 40 中风化泥岩 24 23 10 表 5 不同方法计算所得稳定系数
Table 5. Factor of safety of slopes using different methods
稳定系数 布谷鸟搜索 模拟退火法 Janbu法 1.050 1.050 Morgenstern-Price法 1.041 1.040 Sarma法 1.038 1.039 -
[1] 朱冬雪, 许强, 李松林. 三峡库区大型-特大型层状岩质滑坡成因模式及地质特征分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 158-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202002019.htmZhu D X, Xu Q, Li S L. Genetic types and geological features of large scale and extra-large scale layered landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 158-167(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202002019.htm [2] 丁戈媛, 胡新丽. 大奔流顺层岩质滑坡溃屈型破坏力学机制研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 186-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202002022.htmDing G Y, Hu X L. Mechanical mechanism of buckling failure ofDabenliu consequent bedding rockslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 186-190(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202002022.htm [3] 王成华, 夏绪勇. 边坡稳定分析中的临界滑动面搜索方法述评[J]. 四川建筑科学研究, 2002, 28(3): 34-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ACZJ200203013.htmWang C H, Xia X Y. A review of critical slip surface search methods in slope stability analysis[J]. Sichuan Building Science, 2002, 28(3): 34-39(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ACZJ200203013.htm [4] Huang Y H. Stability analysis of earth slopes[M]. [S. l. ]: Springer US, 1983. [5] 江见鲸. 土建工程常用微机程序汇编[M]. 北京: 水利电力出版社, 1987.Jiang J J. Microcomputer program assembly commonly used in civil engineering[M]. Beijing: Water Resources and Electric Power Press, 1987(in Chinese). [6] Garber M D. Variational method for investigating the stability of slopes[J]. Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering, 1973, 10(1): 77-79. [7] 孙君实. 条分法的提法及数值计算的最优化方法[J]. 水力发电学报, 1983, 2(1): 52-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SFXB198301005.htmSun J S. The formulation of the method of slices and the optimization method of numerical calculation[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 1983, 2(1): 52-64(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SFXB198301005.htm [8] 陈祖煜, 邵长明. 最优化方法在确定边坡最小安全系数方面的应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1988, 10(4): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC198804000.htmCheng Z Y, Shao C M. Timization for minimizing safety factors in slope stability analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1988, 10(4): 1-13(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC198804000.htm [9] Fellenius W. Calculation of the stability of earth dams[C]//Proc. of the Second Congress on Large Dams. [S. l. ]: [s. n. ], 1936: 445-462. [10] Siegel R A. Computer analysis of general slope stability problems[D]. Indians: Durdue University, 1975: 210. [11] Husein-Malkawi A I, Hassan W F, Sarma S K. Global search method for locating general slip surface using Monte Carlo techniques[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2001, 127(8): 688-698. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2001)127:8(688) [12] 张子映, 柴军瑞, 张书滨, 等. 基于混合变异策略差分进化算法的边坡滑裂面搜索研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2018, 29(4): 218-223. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201804037.htmZhang Z Y, Chai J R, Zhang S B, et al. Research on slope sliding surface search based on differential evolution algorithm with mixed mutation strategy[J]. Journal of Water Resources& Water Engineering, 2018, 29(4): 218-223(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201804037.htm [13] 王华俊, 卿翠贵, 姚文杰. 一种改进的遗传算法在边坡工程中的应用[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报, 2015, 13(3): 195-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSJS201503040.htmWang H J, Qing C G, Yao W J. Application of an improved genetic algorithmin slope engineering[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2015, 13(3): 195-199(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSJS201503040.htm [14] 马俊, 资强, 吕录娜, 等. 基于改进蚁群算法的边坡稳定分析方法研究[J]. 水利规划与设计, 2019, 31(7): 64-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLGH201907019.htmMa J, Zi Q, Lü L N, et al. Study on slope stability analysis method based on improved ant colony algorithm[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design, 2019, 31(7): 64-68(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLGH201907019.htm [15] 路畅, 白桃. 采用模拟退火法进行土体参数空间变异边坡的安全系数求解[J]. 公路工程, 2017, 42(3): 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGL201703005.htmLu C, Bai T. Solution of safety factor of the spatially variable soil slope using simulated annealing algorithm[J]. Highway Engineering, 2017, 42(3): 26-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGL201703005.htm [16] Zheng H, Liu D F, Li C G. Slope stability analysis based on elasto-plastic finite element method[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2005, 64(14): 1871-1888. [17] Zheng H, Liu D F, Li C G. On the assessment of failure in slope stability analysis by the finite element method[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2008, 41(4): 629-639. [18] Zheng H, Tham L G. Improved Bell's method for the stability analysis of slopes[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2009, 33(14): 1673-1689. [19] Zheng H, Sun G H, Liu D F. A practical procedure for searching critical slip surfaces of slopes based on the strength reduction technique[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2009, 36(1): 1-5. [20] 章瑞环, 叶帅华, 陶晖. 基于改进极限平衡法的多级均质黄土边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(3): 813-825. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202103024.htmZhang R H, Ye S H, Tao H. Stability analysis of multistage homogeneous loess slopes by improved limit equilibrium method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(3): 813-825(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202103024.htm [21] 蔡美峰, 何满朝, 刘东燕. 岩石力学与工程[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002.Cai M F, He M C, Liu D Y. Rock mechanics and engineering[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002(in Chinese). [22] 钱家欢, 殷宗泽. 土工原理与计算[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 1996: 302-307.Qian J H, Yin Z Z. Geotechnical principles and calculations[M]. Beijing: China Water&Power Press, 1996: 302-307(in Chinese). [23] 重庆市城乡建设委员会. 建筑边坡工程技术规范: GB 50330-2013[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2013.Chongqing Urban and Rural Development. Technical code forbuilding slope engineering: GB50330-2013[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2013(in Chines). [24] 中华人民共和国水利部. 工程岩体分级标准: GB/T 50218-2014[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2014.Ministry of Water Resources of the People's Republic of China. Standard for engineering classification of rock mass: GB/T 50218-2014[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2014. [25] Hoek E. Practical rock engineering[M]. Toronto: Rocscience, 2000: 92-104. -





 下载:
下载: