REE characteristics and geological significance of mudstones from Wenchang Formation in eastern Yangjiang Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要:
沉积岩中的稀土元素具有良好的化学稳定性, 能够较好保存原始沉积记录。为了揭示阳江东凹文昌组发育时期的物源区物质来源、构造背景和沉积环境, 选取凹陷内Y-1井文昌组泥岩样品进行元素测试, 系统分析研究区文昌组泥岩稀土元素地球化学特征。结果表明, 文昌组泥岩稀土元素含量高, 轻稀土元素相对富集, Eu为明显负异常, Ce为微弱正异常特征。文昌组物质来源以花岗岩为主, 含有少量沉积岩, 沉积源区为被动大陆边缘构造背景。Ceanom和
δ Ce参数指示文昌期水体处于还原环境, 为优质烃源岩发育提供良好的保存条件, 纵向上水体还原性演化规律为: 强→弱→强→弱, 与文昌组泥岩TOC变化趋势一致。Abstract:The REE in sedimentary rocks have strange chemical stability and can well record the original sedimentary message.In order to explore the material source, tectonic setting and sedimentary environment of the Wenchang Formation in Eastern Yangjiang Sag, the REE geochemical characteristics of Wenchang Formation mudstones from well Y-1 in the study area were systematically analyzed.The results show that the concentrations of REE in mudstones of Wenchang Formation is high, yielding relatively enrichedof LREE, obviouslyEu negative anomaly and weak Cepositive anomaly.The material of Wenchang Formation is mainly source fromgranite with a small amount of sedimentary rocks, and thus the sedimentary source area is likely to be the passive continental margin tectonic setting.TheCeanom and δCe indicate that the water was under reducing conditions, which could provide well preservation conditions for the development of high-quality source rocks. Furthermore, the temporal variations of redox conditions are consistent with the variation trend of TOC of mudstone in Wenchang Formation.
-
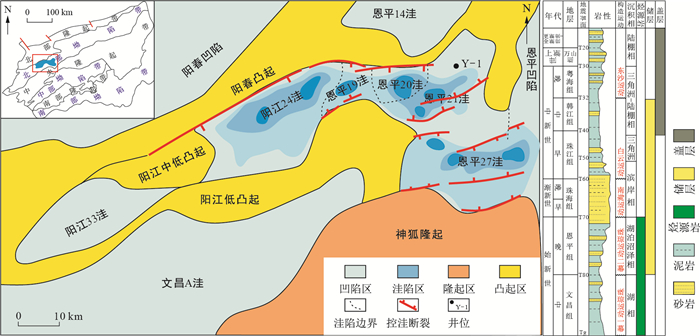
图 1 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷构造单元及地层划分(据参考文献[9]修编)
Figure 1. Tectonic units and stratigraphic column of Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin
图 5 阳江东凹文昌组泥岩La/Yb与w(∑REE)交会图(底图据文献[1])
Figure 5. La/Yb vs. ∑REE of mudstones from Wenchang Formation in eastern Yangjiang Sag
表 1 阳江东凹文昌组泥岩稀土元素质量分数
Table 1. REE contents of mudstones from Wenchang Formation in eastern Yangjiang Sag
wB/10-6 样号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 1 39.22 84.31 8.96 32.94 7.44 1.54 7.80 0.99 5.48 0.99 2.78 0.41 2.63 0.40 2 49.52 105.97 11.13 41.03 8.94 1.66 10.84 1.29 7.20 1.29 3.62 0.52 3.33 0.49 3 48.46 102.40 10.78 39.63 8.46 1.56 10.27 1.18 6.53 1.16 3.26 0.47 3.09 0.46 4 47.82 102.15 10.76 39.57 8.69 1.65 10.37 1.21 6.74 1.20 3.35 0.48 3.11 0.46 5 54.53 116.22 12.18 44.41 10.16 2.10 11.45 1.35 7.38 1.33 3.65 0.53 3.39 0.50 6 44.95 95.44 10.05 37.10 8.24 1.63 9.59 1.17 6.52 1.19 3.32 0.49 3.07 0.47 7 62.76 132.31 14.07 52.21 11.55 2.28 13.93 1.60 8.80 1.55 4.25 0.61 3.91 0.57 8 62.41 130.19 13.90 50.09 11.34 2.43 13.25 1.45 7.90 1.38 3.80 0.55 3.53 0.52 9 50.04 109.21 11.57 42.81 9.69 1.92 11.06 1.35 7.50 1.35 3.74 0.54 3.37 0.50 10 44.63 94.26 9.35 32.22 7.06 1.69 7.50 0.92 5.08 0.90 2.49 0.36 2.35 0.35 球粒陨石[16] 0.30 0.80 0.12 0.60 0.19 0.07 0.26 0.05 0.32 0.07 0.21 0.03 0.21 0.03 NASC[17] 32.00 73.00 7.90 33.00 5.70 1.24 5.20 0.85 5.80 1.04 3.40 0.50 3.10 0.48 PAAS[18] 38.00 80.00 8.90 32.00 5.60 1.10 4.70 0.77 4.40 1.00 2.90 0.40 2.80 0.43 注:NASC表示北美页岩中稀土元素的平均质量分数;PAAS表示澳大利亚后太古宙页岩中稀土元素的平均质量分数 表 2 阳江东凹文昌组泥岩元素分析结果
Table 2. REE analyses of mudstones from Wenchang Formation in eastern Yangjiang Sag
样号 w(TOC)/
%∑REE ∑LREE ∑HREE ∑LREE/
∑HREE(La/Sm)S (La/Yb)S (Gd/Yb)S (Dy/Sm)S δCe δEu Ceanom V/
(V+Ni)MgO/
Al2O3wB/10-6 1 2.43 195.90 174.41 21.49 8.12 3.34 10.43 2.39 0.44 1.03 0.64 0.001 9 0.84 5.35 2 2.82 246.83 218.25 28.58 7.64 3.51 10.41 2.63 0.48 1.03 0.53 0.001 6 0.85 3.99 3 2.45 237.70 211.29 26.41 8.00 3.63 10.98 2.69 0.46 1.02 0.53 -0.002 2 0.86 3.99 4 2.30 237.56 210.63 26.92 7.82 3.49 10.76 2.69 0.46 1.03 0.55 0.001 1 0.86 4.11 5 3.13 269.19 239.62 29.57 8.10 3.40 11.27 2.73 0.43 1.03 0.62 0.002 0 0.86 4.33 6 3.48 223.21 197.41 25.81 7.65 3.46 10.26 2.53 0.47 1.02 0.58 -0.001 3 0.85 4.35 7 2.66 310.40 275.18 35.22 7.81 3.44 11.24 2.88 0.45 1.01 0.57 -0.005 4 0.84 4.12 8 2.17 302.73 270.34 32.39 8.35 3.49 12.38 3.03 0.41 1.01 0.63 -0.005 5 0.80 4.29 9 3.49 254.64 225.23 29.41 7.66 3.27 10.39 2.65 0.46 1.04 0.59 0.006 2 0.82 3.05 10 6.00 209.16 189.20 19.95 9.48 4.01 13.31 2.58 0.43 1.04 0.73 0.012 3 0.90 1.74 注:稀土元素总量∑REE=La+Ce+Pr+Nd+Sm+Eu+Gd+Tb+Dy+Ho+Er+Tm+Yb+Lu;轻稀土元素质量分数∑LREE=La+Ce+Pr+Nd+Sm+Eu;重稀土元素质量分数∑HREE=Gd+Tb+Dy+Ho+Er+Tm+Yb+Lu;δCe=2CeS/(LaS+PrS),δEu=2EuS/(SmS+GdS);Ceanom=lg[3×CeN/(2×LaN+NdN)];下标S表示经过球粒陨石标准化,下标N表示经过北美页岩标准化 表 3 阳江东凹文昌组泥岩与不同构造背景杂砂岩稀土元素特征值比较
Table 3. Comparison of REE values between the mudstones of Wenchang Formation in eastern Yangjiang Sag and heterogeneous sandstones in different tectonic settings
构造背景 活动大陆边缘 被动大陆边缘 研究区校正后均值 w(La)/10-6 37.00 39.00 42.00 w(Ce)/10-6 78.00 85.00 89.00 w(∑REE)/10-6 186.00 210.00 207.00 ∑LREE/∑HREE 9.10 8.50 6.72 La/Yb 12.50 15.90 13.27 (La/Yb)N 8.50 10.80 9.29 δEu 0.60 0.56 0.50 注:数据值据参考文献[26] -
[1] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell, 1985. [2] 陈德潜, 陈刚. 实用稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1990.Chen D Q, Chen G. Practical REE geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1990(in Chinese). [3] Murray R W, Brink M R B T, Gerlach D C, et al. Rare earth, major, and trace elements in chert from the Franciscan Complex and Monterey Group, California: Assessing REE sources to fine-grained marine sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55(7): 1875-1895. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(91)90030-9 [4] 王欣欣, 郑荣才, 闫国强, 等. 基于稀土元素地球化学特征的泥岩沉积环境及物源分析: 以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长9油层组泥岩为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(9): 1387-1394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201409011.htmWang X X, Zheng R C, Yan G Q, et al. The mudstone sedimentary environment and provenance analysis based on the geochemical evidence of rare earth elements: Take Chang 9 oil-bearing layer in Longdong area of Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(9): 1387-1394(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201409011.htm [5] 曹婷婷, 徐思煌, 王约, 等. 川东北下寒武统筇竹寺组稀土元素特征及其地质意义: 以南江杨坝剖面为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(5): 716-723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201805016.htmCao T T, Xu S H, Wang Y. Characteristics of rare earth elements in Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in northeastern Sichuan Basin and its geological implications: A case study of Yangba section, Nanjiang[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(5): 716-723(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201805016.htm [6] 彭光荣, 张向涛, 许新明, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地阳江凹陷油气勘探重要发现与认识[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(3): 267-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.03.001Peng G R, Zhang X T, Xu X M, et al. Important discoveries and understandings of oil and gas exploration in Yangjiang Sag of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(3): 267-279(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.03.001 [7] 田立新, 张向涛, 彭光荣, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷石油地质特征及成藏主控因素[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(1): 13-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202001002.htmTian L X, Zhang X T, Peng G R, et al. Petroleum geological characteristics and main controlling factors of the Yangjiang Sag in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(1): 13-22(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202001002.htm [8] 刘军, 彭光荣, 朱定伟, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷东部地区断控成藏条件[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1): 123-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202101010.htmLiu J, Peng G R, Zhu D W, et al. Fault-controlled hydrocarbon accumulation in the eastern Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 123-130(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202101010.htm [9] 吴静, 张晓钊, 白海军, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷中新统潮控体系及其岩性圈闭勘探意义[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(10): 3673-3689. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202110021.htmWu J, Zhang X Z, Bai H J, et al. Miocene tidal control system and its exploration significance of lithologic trap in Yangjiang Sag, pearl river mouth basin[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(10): 3673-3689(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202110021.htm [10] 姜衍, 张向涛, 龙祖烈, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地烃源岩成因: 阳江凹陷的资源潜力[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1): 90-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202101008.htmJiang Y, Zhang X T, Long Z L, et al. Formation of source rocks in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea: Resource potential of the Yangjiang Sag[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 90-107(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202101008.htm [11] 易海, 张莉, 林珍. 南海北部中生代构造格局与盆地发育特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2012, 34(4): 388-394. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2012.04.008Yi H, Zhang L, Lin Z. Mesozoic tectonic framework and basin distribution characteristics of northern margin of South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2012, 34(4): 388-394(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2012.04.008 [12] 孙晓猛, 张旭庆, 张功成, 等. 南海北部新生代盆地基底结构及构造属性[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014, 44(6): 1312-1323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201406022.htmSun X M, Zhang X Q, Zhang G C, et al. Texture and tectonic attribute of Cenozoic basin basement in the northern South China Sea[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2014, 44(6): 1312-1323(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201406022.htm [13] 杜晓东, 彭光荣, 吴静, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江东凹断层特征及其对油气成藏的影响[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(4): 414-421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202004005.htmDu X D, Peng G R, Wu J, et al. Faults and its impacts on petroleum accumulation in eastern Yangjiang Sag, pearl river mouth basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2020, 41(4): 414-421 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202004005.htm [14] 陈斌, 李勇, 邓涛, 等. 晚三叠世龙门山前陆盆地须家河组泥页岩沉积环境及有机质富集模式[J]. 地质科学, 2019, 54(2): 434-451.Chen B, Li Y, Deng T, et al. The sedimentary environment and organic matter enrichment pattern of Xujiahe Formation shale in the Late Triassic Longmenshan foreland basin, SW China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2019, 54(2): 434-451(in Chinese with English abstract). [15] 石创, 龙祖烈, 朱俊章, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷恩平组泥岩元素地球化学特征及环境指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(5): 79-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202005008.htmShi C, Long Z L, Zhu J Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of elements of Enping Formation in Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(5): 79-86(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202005008.htm [16] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 [17] Boynton W V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P. Rare earth element geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984. [18] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The continental crust, its composition and evolution: An examination of the geochemical record preserved in sedimentary rocks[M]. London: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985. [19] 李杰, 黄宏业, 刘子杰, 等. 向阳坪铀矿床沥青铀矿微区原位LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及稀土元素特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 90-99. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0011Li J, Huang H Y, Liu Z J, et al. In-situ U-Pb dating of pitchblende and the REE characteristics using LA-ICP-MS in Xiangyangping uranium deposit[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 90-99(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0011 [20] 周红智, 魏俊浩, 石文杰, 等. 东昆仑鄂拉山岩浆带晚三叠世后碰撞伸展: 来自索拉沟高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的证据[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 150-164. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0430Zhou H Z, Wei J H, Shi W J, et al. Late Triassic post-collision extension at Elashan magmatic belt, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt: Insights from Suolagou highly fractionated I-type granite[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 150-164(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0430 [21] Shields G, Stille P. Diagenetic constrains on the use of cerium anomalies as paleoseawater redox proxies: An isotopic and REE study of Cambrian phosphorites[J]. Chemical Geology, 2001, 175: 29-48. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00362-4 [22] 王克兵, 孟庆涛, 刘招君, 等. 柴北缘鱼卡地区中侏罗统石门沟组页岩段稀土元素地球化学特征与地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2017, 36(3): 862-870. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2017.03.019Wang K B, Meng Q T, Liu Z J, et al. Rare earth element geochemical characteristics and geological significance of shale member in Middle Jurassic Shimengou Formation in Yuqia area of northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Global Geology, 2017, 36(3): 862-870(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2017.03.019 [23] Bhatia M R, Crook K A W. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1986, 92(2): 181-193. doi: 10.1007/BF00375292 [24] 柏道远, 蒋启生, 李彬, 等. 湘东北冷家溪群沉积岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 1-13. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0017Bo D Y, Jiang Q S, Li B, et al. Geochemistry and tectonic implication of the sedimentary rocks in Lengjiaxi Group in northeastern Hunan[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 1-13(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0017 [25] 李福来, 肖飞, 孟凡超, 等. 内蒙古索伦地区上二叠统林西组碎屑岩地球化学特征及其对物源的指示意义[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2016, 46(6): 1769-1780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201606016.htmLi F L, Xiao F, Meng F C, et al. Geochemical characteristics and implication for provenance of Upper Permian Linxi Formation clastic rocks in Solonker area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2016, 46(6): 1769-1780(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201606016.htm [26] Bhatia M R. Rare earth elements geochemistry of Australian Paleozoic graywacks and mudstones: Provenance and tectonic control[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1985, 45: 97-113. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(85)90025-9 [27] Murray R W, Buchholtz M R, Jones D L. Rare earth elements as indicators of different marine depositional environment in chert and shale[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(3): 268-271. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0268:REEAIO>2.3.CO;2 [28] Elderfield H, Greaves M J. The rare earth elements in seawater[J]. Nature, 1982, 296(5854): 214-219. doi: 10.1038/296214a0 -





 下载:
下载: