LA-ICP-MS cassiterite U-Pb ages and the geological significance of the Maogaitu Sn ore spot in Hexigten Banner, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
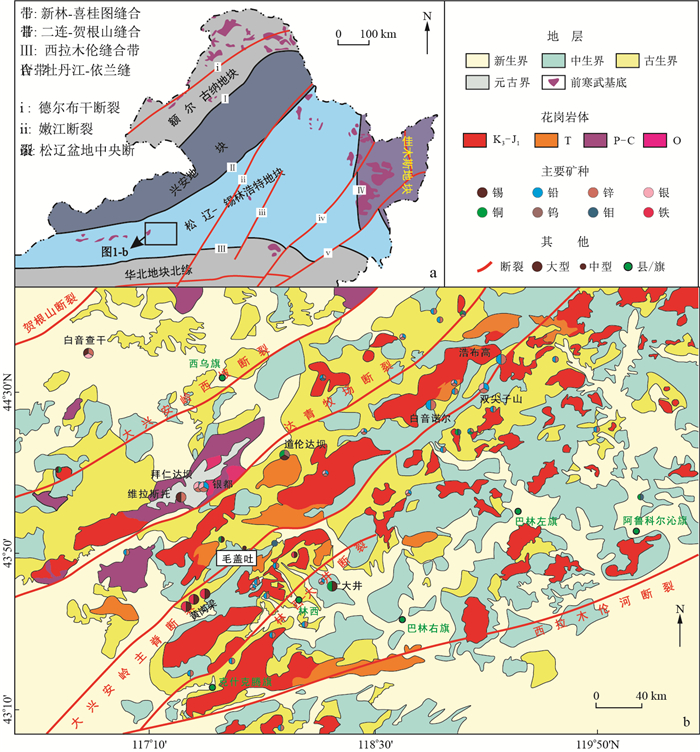
毛盖吐锡矿点为北京矿产地质研究院在大兴安岭南段新发现的矿点, 位于内蒙古克什克腾旗境内。矿点地处大兴安岭中南段多金属成矿带, 矿化类型为锡石石英脉型。矿石矿物主要为锡石和少量闪锌矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿以及银的矿物, 脉石矿物主要为石英以及少量的萤石。该矿由于首次发现, 研究程度较低, 关于其矿床成因、成矿时代等规律尚不明确。大兴安岭中南段多金属成矿带上发育多个锡多金属矿床, 目前的研究表明这些锡多金属矿床的成矿年龄多集中在早白垩世, 成因与早白垩世花岗岩相关。为了研究毛盖吐锡矿与区域锡多金属成矿作用的联系, 开展了对毛盖吐锡矿点成矿时代的研究, 本研究选取1件石英脉型锡矿石样品进行LA-ICP-MS锡石U-Pb定年, 获得锡石的207Pb/206Pb-238U/206Pb谐和年龄为130.2±3.4 Ma(
MSWD =2.9), 表明毛盖吐锡矿点形成于早白垩世, 这与区域上主要的锡多金属矿床成矿时代一致, 说明在大兴安岭中南段寻找锡多金属矿床拥有很好的前景。Abstract:The Maogaitu Sn ore spot in Hexigten Banner, Inner Mongolia is a newly discovered ore spot in the south section of Greater Khingan Range by Beijing Institute of Geology for Mineral Resources. It is tectonically located in the polymetallic metallogenic belt in the south centralsection of Greater Khingan Range, and the mineralization is characterized by cassiterite-quartz veins. Ore minerals of the ores are dominated by cassiterite with trace amounts of sphalerite, galena, chalcopyrite and silver minerals, while gangue minerals are mainly quartz and fluorite. As discovered recently without detailed studies, the genesis and age of the Maogaitu Sn ore spot are not clearly addressed. A number of tin polymetallic deposits are documented to develop in the polymetallic metallogenic belt in the south central section of Greater Khingan Range. The ages of these tin polymetallic deposits are constrained to be mostly around the Early Cretaceous, and to be genetically related to the Early Cretaceous granite. In order to address the relationship of the Maogaitu Sn ore spot with regional metallogeny, we obtained the age of the Maogaitu Sn ore spot by using LA-ICPMS U-Pb isotopic dating of cassiterite from a quartz vein-type tin ore sample. The results show that the sample yields a 207Pb/206Pb-238U/206Pb concordant age of (130.2±3.4) Ma (
MSWD =2.9), similar to the timing of the major tin mineralization event in the region. The new findings imply that the middle and south sections of Greater Khingan Range could be good targets for Sn polymetallic exploration. -
表 1 毛盖吐锡矿点LA-ICP-MS锡石U-Pb定年数据
Table 1. Results of LA-ICP-MS cassiterite U-Pb dating of the Maogaitu Sn ore spot
分析点号 同位素比值 207Pb/235U 2σ 206Pb/238U 2σ 238U/206Pb 2σ 207Pb/206Pb 2σ SHY-46-2 0.418 5 0.025 9 0.022 9 0.000 3 43.657 7 1.397 8 0.132 5 0.000 8 SHY-46-3 0.140 5 0.004 5 0.020 5 0.000 2 48.805 1 1.519 5 0.049 7 0.000 4 SHY-46-4 0.141 2 0.004 1 0.020 1 0.000 2 49.753 1 1.547 5 0.050 9 0.000 1 SHY-46-5 0.147 7 0.009 6 0.020 1 0.000 3 49.721 7 1.702 3 0.053 3 0.000 1 SHY-46-6 0.141 2 0.005 8 0.020 1 0.000 2 49.818 9 1.574 4 0.051 0 0.000 6 SHY-46-7 0.148 7 0.008 4 0.019 9 0.000 3 50.356 4 1.723 0 0.054 3 0.000 4 SHY-46-8 0.138 4 0.004 2 0.020 7 0.000 1 48.260 6 1.489 1 0.048 5 0.002 1 SHY-46-9 0.150 4 0.005 1 0.020 6 0.000 2 48.446 2 1.504 9 0.052 9 0.000 1 SHY-46-12 1.277 6 0.164 8 0.034 7 0.003 4 28.794 3 2.970 1 0.266 8 0.000 9 SHY-46-13 2.883 2 0.255 0 0.046 7 0.003 3 21.394 6 1.630 3 0.447 4 0.003 4 SHY-46-14 0.143 9 0.004 1 0.020 8 0.000 2 48.056 5 1.485 8 0.050 2 0.000 3 SHY-46-15 0.104 0 0.032 7 0.020 9 0.000 2 47.890 0 1.532 4 0.036 1 0.000 4 注:测试单位为中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室;测试方法为激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱法(LA-ICP-MS) 表 2 维拉斯托锡多金属矿和毛盖吐锡矿点地质特征对比
Table 2. Comparison of geological characteristics between Weilasituo tin polymetallic deposit and the Maogaitu Sn ore spot
维拉斯托锡多金属矿床 毛盖吐锡矿点 区域地质背景 黄岗梁-甘珠尔庙多金属成矿带 黄岗梁-甘珠尔庙多金属成矿带 赋矿围岩 锡林郭勒杂岩 二叠系砂岩 矿体形态 主要为脉状 脉状 矿化组合 Sn-Cu-Pb-Zn-Ag Sn-Cu-Pb-Zn-Ag 矿物组合 锡石、黝锡矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿、黄铁矿、黄玉、石英、萤石等 锡石、闪锌矿、方铅矿、石英、萤石等 蚀变 云英岩化 云英岩化 成矿岩体 碱长花岗岩 花岗岩 成矿时代 早白垩世 早白垩世 -
[1] 祝新友, 张志辉, 付旭, 等. 内蒙古赤峰维拉斯托大型锡多金属矿的地质地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(1): 188-208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.014Zhu X Y, Zhang Z H, Fu X, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Weilasito Sn-Zn deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(1): 188-208(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.014 [2] 刘新, 王京彬, 祝新友, 等. 内蒙古白音查干锡多金属矿床成矿作用研究Ⅰ: 金属矿物组合及其成因机制[J]. 矿产勘查, 2017, 8(6): 967-980. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2017.06.007Liu X, Wang J B, Zhu X Y, et al. Mineralization process of the Baiyinchagan tin polymetallic deposit in Inner Mongolia I: Metallic mineral assemblage and metallogenic mechanism[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2017, 8(6): 967-980(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2017.06.007 [3] 祝新友, 黄行凯, 邹滔, 等. 内蒙古有色金属基地综合地质调查2017年度报告[R]. 北京: 北京矿产地质研究院, 2017.Zhu X Y, Huang X K, Zou T, et al. The 2017 report of comprehensive geological survey of Chifeng Nonferrous Metals Bases, Inner Mongolia[R]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Geology for Mineral Resources, 2017(in Chinese). [4] 刘瑞麟, 武广, 李铁刚, 等. 大兴安岭南段维拉斯托锡多金属矿床LA-ICP-MS锡石和锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(5): 183-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201805014.htmLiu R L, Wu G, Li T G, et al. LA-ICP-MS cassiterite and zircon U-Pb age of the Weilasituo tin-polymetallic deposit in the southern Great Xing'an Range and their geological significance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(5): 183-201(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201805014.htm [5] 姚磊, 吕志成, 叶天竺, 等. 大兴安岭南段内蒙古白音查干Sn多金属矿床石英斑岩的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学和Nd-Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(10): 3183-3199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201710014.htmYao L, Lü Z C, Ye T Z, et al. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemical and Nd-Hf isotopic characteristics of quartz porphyry in the Baiyinchagan Sn polymetallic deposit, Inner Mongolia, southern Great Xing'an Range, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(10): 3183-3199(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201710014.htm [6] 陈公正, 武广, 李铁刚, 等. 内蒙古道伦达坝铜钨锡矿床LA-ICP-MS锆石和锡石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2018, 37(2): 225-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201802002.htmChen G Z, Wu G, Li T G, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon and cassiterite U-Pb ages of Daolundaba copper - tungstentin deposit in Inner Mongolia and their geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2018, 37(2): 226-245(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201802002.htm [7] 要梅娟, 曹烨, 刘家军, 等. 内蒙古黄岗梁铁锡矿床辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其成因意义[J]. 矿产勘查, 2016, 7(3): 399-403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2016.03.003Yao M J, Cao Y, Liu J J, et al. Isotope age of Re-Os in molybdenite and genetic implication of Huanggangliang Fe-Sn deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2016, 7(3): 399-403(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2016.03.003 [8] 杨星, 管育春, 蒋斌斌, 等. 土壤地球化学测量在内蒙古毛盖吐地区锡多金属找矿中的应用[J]. 矿产勘查, 2021, 12(3): 677-684. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2021.03.021Yang X, Guan Y C, Jiang B B, et al. Application of soil geochemical survey in prospecting for tin polymetals deposit in Maogaitu area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2021, 12(3): 677-684(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2021.03.021 [9] Plimer I R, Lu J, Kleeman J D. Trace and rare earth elements in cassiterite sources of components for the tin deposits of the Mole granite, Australia[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1991, 26: 267-274. [10] Jiang S Y, Yu J M, Lu J J. Trace and rare-earth element geochemistry in tourmaline and cassiterite from the Yunlong tin deposit, Yunan, China: Implication for migmatitic hydrothe- rmal fluid evolution and ore genesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 209: 193-213. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.04.021 [11] Yuan S D, Peng J T, Hu R Z, et al. A precise U-Pb age on cassiterite from the Xianghualing tin-polymetallic deposit, Hunan, South China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2008, 43: 375-382. doi: 10.1007/s00126-007-0166-y [12] 王志强, 陈斌, 马星华. 南岭芙蓉锡矿田锡石原位LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年代学及地球化学研究: 对成矿流体来源和演化的意义[J]. 科学通报, 2014, 59(25): 2505-2519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201425009.htmWang Z Q, Chen B, Ma X H. In situ LA-ICP-MS U-Pb age and geochemical data of cassiterite of the Furong tin deposit, the Nanling Range: Implications for the origin and evolution of the ore-forming fluid[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(25): 2505-2519(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201425009.htm [13] Li C Y, Zhang R Q, Ding X, et al. Dating cassiterite using laser ablation ICP-MS[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 313-322. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.016 [14] 闫庆贺, 王核, 丘增旺, 等. 粤东塌山斑岩型锡多金属矿床锆石及锡石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(4): 718-731. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201804011.htmYan Q H, Wang H, Qiu Z W, et al. Zircon and cassiterite U-Pb ages and Lu-Hf isotopic compositions of Tashan tin-bearing porphyry in Guangdong Province, SE China, and its geological significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2018, 42(4): 718-731(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201804011.htm [15] 徐备, 赵盼, 鲍庆中, 等. 兴蒙造山带前中生代构造单元划分初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(7): 1841-1857. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201407001.htmXu B, Zhao P, Bao Q Z, et al. Preliminary study on the pre-Mesozoic tectonic unit division of the Xing-Meng Orogenic Belt(XMOB)[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(7): 1841-1857(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201407001.htm [16] Liu Y J, Li W M, Feng Z Q, et al. A review of the Paleozoic tectonics in the eastern part of Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.01. [17] 蒋孝君, 苗爱生, 李华明, 等. 内蒙古多伦山间盆地砂岩型铀矿新发现及找矿前景[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 88-96, 105. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0609Jiang X J, Miao A S, Li H M, et al. New discovery and prospecting prospect of sandstone type uranium deposits in Duolun Intermountain Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 88-96, 105 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0609 [18] 薛伟, 宋卡迪, 刘鑫扬, 等. 内蒙古多伦县三道沟地区中生代火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学研究及其铀成矿意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 69-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906010.htmXue W, Song K D, Liu X Y, et al. Zircon U-Pb chronology of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Sandaogou area, Duolun County, Inner Mongolia and its ore-prospecting significance[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 69-80(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906010.htm [19] 王艺龙, 敖光, 王海鹏, 等. 大兴安岭中段索伦地区早白垩世花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及构造意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1): 45-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901006.htmWang Y L, Ao G, Wang H P, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic significance of Early Cretaceous ganites in Suolun area of central Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(1): 45-57(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901006.htm [20] 张德全. 大兴安岭南段不同构造环境中的两类花岗岩[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1993, 12(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW199301000.htmZhang D Q. Two granitoid series in different tectonic environment of southern Dahinggan Mountains, China[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 1993, 12(1): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW199301000.htm [21] 周振华, 吕林素, 杨永军, 等. 内蒙古黄岗锡铁矿区早白垩世A型花岗岩成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(12): 3521-3537.Zhou Z H, Lü L S, Yang Y J, et al. Petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous A-type granite in the Huanggang Sn-Fe deposit, Inner Mongolia: Constraints from zircon U-Pb dating and geochemis try[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(12): 3521 -3537(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] 王喜龙, 刘家军, 翟德高, 等. 内蒙古边家大院矿区石英斑岩U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(5): 654-665. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.05.012Wang X L, Liu J J, Zhai D G, et al. U-Pb dating, geochemistry and tectonic implications of Bianjiadayuan quartz porphyry, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2014, 33(5): 654-665(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.05.012 [23] 陈守余, 赵鹏大, 童祥, 等. 个旧东区蚀变花岗岩型锡铜多金属矿床成矿特征及找矿意义[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(2): 277-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201102013.htmChen S Y, Zhao P D, Tong X, et al. Metallogenic characteristics of western low altered tin-copper polymetallic deposit and its prospecting significance in east part of Gejiu, Yunnan[J]. Earth Science: Journal of Chinese University of Geosciences, 2011, 36(2): 277-281(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201102013.htm [24] Yuan S D, Peng J T, Hao S, et al. In-situ LA-MC-ICP-MS and ID-TIMS U-Pb geochronology of cassiterite in the giant Furong tin deposit, Hunan Province, South China: New constraints on the timing of tin-polymetallic mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 43(1): 235-242. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.08.002 [25] Ludwig K R. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.0: A geochronological toolkit for microsoft excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003. [26] 郝爽, 李惠民, 李国占, 等. LA-ICP-MS测定锡石U-Pb同位素年龄时两种普通铅扣除方法的原理及适用性比较[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(4): 622-632. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.04.019Hao S, Li H M, Li G Z, et al. The comparison of the principle and applicability between two methods of deducting the initial common lead for in situ LA-ICP-MS U-Pb isotope dating of cassiterite[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(4): 622-632(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.04.019 [27] Gulson B L, Jones M T. Cassiterite: Potential for direct dating of mineral deposits and a precise age for the Bushveld complex granites[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(4): 355-358. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0355:CPFDDO>2.3.CO;2 [28] Mcnaughton N J, Pollard P J. Cassiterite: potential for direct dating of mineral deposits and a precise age for the Bushveld complex granites: Comment and reply[J]. Geology, 1993, 21(3): 286-286. [29] 廖震, 王玉往, 王京彬, 等. 内蒙古大井锡多金属矿床锡石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb测年及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2014, 33(增刊1): 421-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2014S1213.htmLiao Z, Wang Y W, Wang J B, et al. LA-ICP-MS cassiterite U-Pb age of Dajing tin- polymetallic deposit in Inner Mongolia and its significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2014, 33(S1): 421-422(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2014S1213.htm [30] 王国政. 内蒙古安乐锡铜矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 矿床地质, 1997, 16(3): 260-271. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ703.007.htmWang G Z. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Anle tin-copper deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1997, 16(3): 260-271(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ703.007.htm [31] 刘玉强. 内蒙古毛登锡铜矿床地质及成因[J]. 矿床地质, 1996, 15(2): 133-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199602003.htmLiu Y Q. Geology and origin of the Maodeng tin-copper deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1996, 15(2): 133-143(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199602003.htm [32] 王承洋. 内蒙古黄岗梁-甘珠尔庙成矿带铅锌多金属成矿系列与找矿方向[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015.Wang C Y. Lead-zinc polymetallogenic series and prospecting direction of Huanggangliang-Ganzhuermiao metallogenic belt, Inner Mongolia[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [33] 蒋斌斌, 祝新友, 黄行凯, 等. 大兴安岭南段白音诺尔铅锌矿床成矿时代确定及其找矿意义[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(10): 2844-2855. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.005Jiang B B, Zhu X Y, Huang X K, et al. Determination of metallogenic age and prospecting significance of the Baiyinnuoer lead zinc deposit in the southern Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(10): 2844-2855(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.005 [34] 阮班晓, 吕新彪, 刘申态, 等. 内蒙古边家大院铅锌银矿床成因: 来自锆石U-Pb年龄和多元同位素的制约[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(3): 501-514. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.03.004Ruan B X, Lü X B, Liu S T, et al. Genesis of Bianjiadayuan Pb-Zn-Ag deposit in Inner Mongolia: Constraints from U-Pb dating of zircon and multi-isotope geochemistry[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(3): 501-514(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.03.004 [35] Pei Q, Zhang S, Santosh M, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry, fluid inclusion and C, O and Hf isotope compositions of the Shuitou fluorite deposit, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 83: 174-190. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.12.022 [36] 陈言飞, 王玉往, 王京彬, 等. 与A型花岗岩有关锡矿的云英岩化蚀变矿化地球化学: 以新疆卡姆斯特和干梁子矿床为例[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(9): 248-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201809017.htmChen Y F, Wang Y W, Wang J B, et al. Greisenized alteration-mineralization geochemistry of the tin deposit related to A-type granite: Case study on the Kamusite and Ganliangzi deposits, Xinjiang[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(9): 248-262(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201809017.htm [37] 李胜虎, 李建康, 张德会, 等. 广西栗木钽铌锡多金属矿床的成矿流体演化及其对成矿过程的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(4): 954-966. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201504005.htmLi S H, Li J K, Zhang D H, et al. The evolution of ore-forming fluid and its constrain to the ore-forming process in Limu Ta-Nb-Sn polymetallic ore deposit, Guangxi, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(4): 954-966(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201504005.htm [38] 张家菁, 陈郑辉, 王登红, 等. 福建行洛坑大型钨矿的地质特征、成矿时代及其找矿意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2008, 32(1): 92-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2008.01.012Zhang J J, Chen Z H, Wang D H, et al. Geological characteristics and metallogenic epoch of the Xingluokeng tungsten deposit, Fujian Province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2008, 32(1): 92-97(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2008.01.012 [39] 曾昭法. 内蒙古林西地区萤石矿床地球化学特征与成因探讨[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.Zeng Z F. Geochemistry characteristics and genesis of fluorite deposits in Linxi region, Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [40] 曹华文, 张寿庭, 邹灏, 等. 内蒙古林西萤石矿床石英ESR年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 888-894. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.04.015Cao H W, Zhang S T, Zou H, et al. ESR dating of quartz from Linxi fluorite deposits, Inner Mongolia and its geological implications[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(4): 888-894(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.04.015 [41] 聂凤军, 许东青, 江思宏, 等. 内蒙古苏莫查干敖包特大型萤石矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 矿床地质, 2008, 27(1): 1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2008.01.001Nie F J, Xu D Q, Jiang S H, et al. Geological features and origin of Sumoqagan Obo supergiant fluorite-only deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2008, 27(1): 1-13(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2008.01.001 -





 下载:
下载: