Numerical simulation of diagenetic evolution and porosity prediction in eastern area of Wushi Sag
-
摘要:
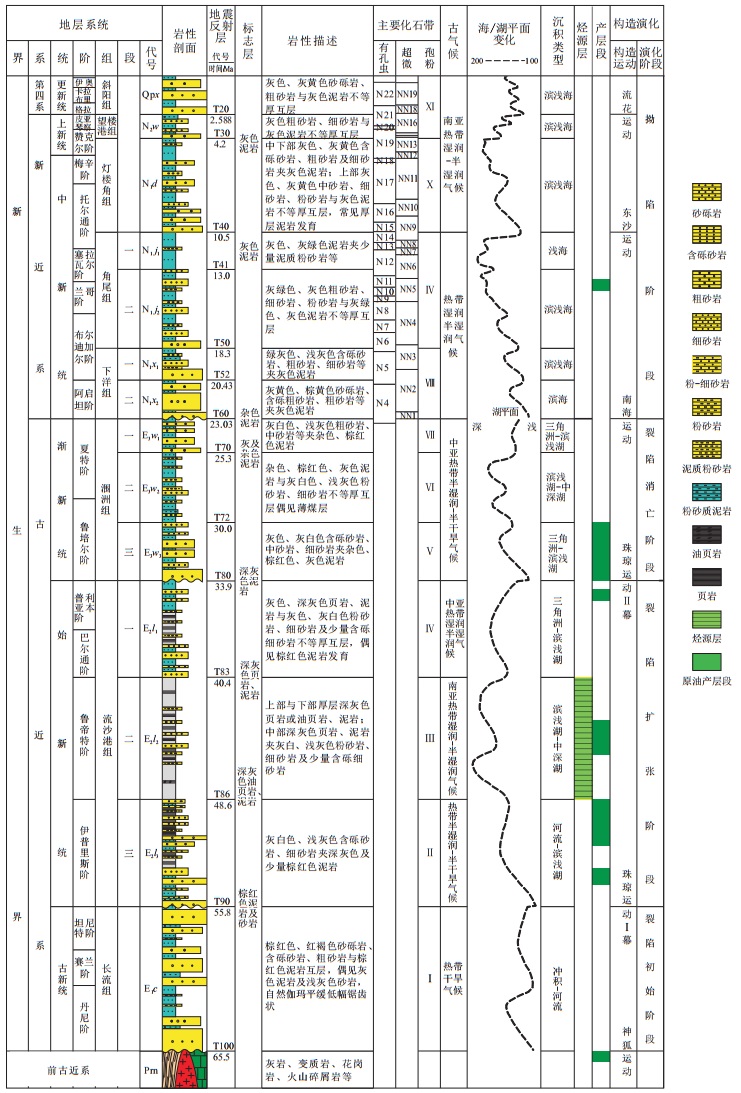
乌石东区已发现的商业性油田主要形成于复杂陆相沉积环境, 受构造、沉积和成岩作用综合影响, 储层非均质性强, 油藏渗流特征复杂, 直接影响着油田的开发方案制定。因此, 有必要开展储层物性主控因素分析, 从理论上和技术上实现甜点区预测。研究采用成岩数值模拟的方法, 基于成岩环境参数, 应用化学动力学模型, 通过对镜质组反射率、古地温、伊/蒙混层中蒙皂石层含量和石英自生加大的模拟, 加权平均得到成岩指数。根据成岩指数的变化对储层成岩阶段及孔隙度横向展布规律进行预测。模拟结果表明, 乌石东区成岩阶段主要为中成岩A1-A2期, 凹陷中心成岩作用较强, 向北逐渐减弱。综合沉积、成岩等认识, 建立孔隙度预测模型, 对孔隙度进行平面预测, 预测结果表明: 顺物源方向, 随埋深增大, 储层物性变差, 同成岩作用变化趋势一致。
Abstract:The commercial oil fields discovered in the eastern area of Wushi Sag in recent years are mainly formed in a complex continental sedimentary environment, which was influenced by the tectonic movement, sedimentation and diagenesis.The reservoir in the oilfields of the study is characterized by a strong heterogeneity, complex reservoir seepage mechanism, which affects the development program Therefore, the analysis of the main controlling factors of the reservoir physical properties is extremely necessary, which can help the decision-makers to predict the sweet spot area theoretically and technically.In this paper, the method of numerical simulation of diagenetic evolution was adopted, in which the diagenesis index was obtained by the simulation of vitrinite reflectance, paleotemperature, smectite content in illite/smectite mixed layer, and quartz autogenesis increase based on the diagenetic environment parameter and chemical kinetic model.Moreover, the diagenetic stage and the lateral distribution of porosity were predicted based on the change of the diagenetic index.The results show that the diagenesis stage in the eastern area of Wushi Sag is the middle diagenesis stage A1-A2, and the diagenesis in the central sag is strong and gradually weaken.Combining the understanding of sedimentary and diagenesis, establishing the porosity prediction model and predicting it in horizon, the results indicate that: Following the source of sedimentary, the reservoir physical properties worsen with increasing burial depth, which is consistent with the change trend of diagenesis.
-
Key words:
- Wushi Sag /
- diagenesis /
- diagenetic stage /
- numerical diagenetic simulation /
- porosity prediction
-
表 1 平面模拟实测数据与模拟数据对比表
Table 1. Comparison between measured data and simulated data in plane simulation
层位 井名 模拟Ro/% 实测Ro/% 误差/% 流一段 A1 0.57 0.51 11.76 A4 0.53 0.58 -8.62 A5 0.54 0.54 0 C1 0.57 0.55 3.64 C2d 0.52 0.55 -5.45 AW4d 0.58 0.54 7.41 流二段 A1 0.73 0.70 4.29 A2 0.81 0.80 1.25 A4 0.68 0.71 -4.23 A5 0.62 0.59 5.98 B1 0.58 0.59 -1.69 B9 0.64 0.59 9.40 D1 0.68 0.74 -8.11 AW4d 0.73 0.73 0 流三段 A2 0.99 1.03 -3.88 A4 0.83 0.88 -5.68 A5 0.71 0.69 3.35 AW4d 0.79 0.90 -11.73 B1 0.63 0.68 -7.35 B9 0.69 0.66 4.55 注:实测数据据中海油实验中心湛江实验中心 表 2 乌石东区孔隙度预测与实测数据对比表
Table 2. Comparison of porosity prediction and measured data in eastern Wushi area
井名 层位 实测孔隙度/% 预测孔隙度/% 误差/% W1 流一段 18.50 17.12 -7.46 A1 流一段 18.72 19.55 4.42 A2 流一段 19.13 18.46 -3.50 A7d 流一段 17.33 18.03 4.05 E1 流一段 16.36 17.69 8.16 D1 流一段 19.25 17.97 -6.63 A5 流二段 17.29 16.63 -3.80 AW1 流二段 15.11 14.32 -5.23 AW7 流二段 14.12 14.44 2.25 C3 流二段 20.89 19.96 -4.45 B14 流二段 16.49 17.01 3.13 F3 流二段 17.84 16.22 -9.09 A4 流三段 7.73 7.95 2.79 C2 流三段 19.32 18.29 -5.34 C4 流三段 18.03 20.01 10.95 B14 流三段 17.96 17.81 -0.81 B7 流三段 18.17 18.72 3.00 注:实测数据据中海油实验中心湛江实验中心 -
[1] 康昱, 陈刚, 张卫岗, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地姬源油区铁边城区块长8储层成岩致密化及其与油气成藏关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(2): 64-75. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0207Kang Y, Chen G, Zhang W G, et al. Diagenetic densification of Chang 8 sandstone reservoirs and its relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation in Tiebiancheng area, Jiyuan Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletion of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 64-75(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0207 [2] 林承焰, 王文广, 董春梅, 等. 储层成岩数值模拟研究现状及进展[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(5): 1084-1143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201705016.htmLin C Y, Wang W G, Dong C M, et al. State quo of reservoir diagenetic numerical simulation and its advancement[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2017, 46(5): 1084-1143(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201705016.htm [3] 肖力华, 孟元林, 王建国, 等. 碎屑岩成岩温度的数值模拟和成岩阶段的预测[J]. 中国海上油气: 地质, 1995, 9(6): 389-394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199506006.htmXiao L H, Meng Y L, Wang J G, et al. Modelling of diagenetic temperature and lateral prediction of diagenetic stages for clastic rocks[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas(Geology), 1995, 9(6): 389-394(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199506006.htm [4] Lander R H, Laubach S E. Insights into rates of fracture growth and sealing from a model for quartz cementation in fractured sandstones[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2015, 123(3/4): 516-538. [5] Ehrenberg S N, Nadeau P H. Sandstone vs carbonate petroleum reservoirs: A global perspective on porosity depth and porosity permeability relation-ships[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2005, 89(4): 435-445. doi: 10.1306/11230404071 [6] 甘军, 杨希冰, 胡林, 等. 乌石凹陷烃源岩生烃特征及差异成藏模式[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 174-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903018.htmGan J, Yang X B, Hu L, et al. Hydrocarbon generation characteristics and hydrocarbon differential accumulation model in Wushi Sag[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 174-179(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903018.htm [7] 汪新光, 张冲, 张辉, 等. 基于微观孔隙结构的低渗透砂岩储层分类评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 93-103. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0429Wang X G, Zhang C, Zhang H, et al. Classification and evaluation of low permeability sand reservoir based on micro pore-structure[J]. Bulletion of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 93-103(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0429 [8] 孟元林, 张磊, 陶士振, 等. 碎屑岩成岩阶段细分与应用[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2020, 49(5): 920-930. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202005012.htmMeng Y L, Zhang L, Tao S Z, et al. The subsection of diagenetic stages in clastic rocks and applications[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2020, 49(5): 920-930(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202005012.htm [9] Mackenzie A S, McKenzie D. Isomerization and aromatization of hy-drocarbon in sedimentary basin formed by extension[J]. Geology Magzine, 1983, 20: 417-470. [10] Meng Y L, Yang J S, Xiao L H, et al. Diagenetic evolution modeling system and its application[C]//Hao Dongheng. Treatises of ⅩⅢ Kerulien International Conference of Geology. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang University of Economics, 2001. [11] Meng Y L, Xiao L H, Zhang J. Basin modeling by gravity, magnetics and electrical information and its application[C]//Liu B J, Li S T. Basin Analysis, Global Sedimentary Geology and Sedimentology. Amsterdam: VSP, 1997. [12] 孟元林, 肖丽华, 王建国, 等. 黏土矿物转化的化学动力学模型及其应用[J]. 沉积学报, 1996, 14(2): 110-116.Meng Y L, Xiao L H, Wang J G, et al. Kinetic model of clay mineral transformation and its application[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1996, 14(2): 110-116(in Chinese with English abstract). [13] 孟元林, 牛嘉玉, 肖丽华, 等. 歧北凹陷沙二段超压背景下的成岩场分析与储层孔隙度预测[J]. 沉积学报, 2005, 23(3): 389-396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.03.003Men Y L, Niu J Y, Xiao L H, et al. Diagenetic field analysis and porosity prediction of the Sha'er Member(Es2) in over pressure setting in the Qibei Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2005, 23(3): 389-396(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.03.003 [14] 肖丽华, 孟元林, 牛嘉玉, 等. 歧口凹陷沙河街组成岩史分析和成岩阶段预测[J]. 地质科学, 2005, 40(3): 346-362. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2005.03.005Xiao L H, Meng Y L, Niu J Y, et al. Diagenetic history and diagenetic stages prediction of Shahejie Formation in the Qibkou Sag[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 2005, 40(3): 346-362(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2005.03.005 -





 下载:
下载: