Fine-grained sublacustrine fan deposits and their significance in shale oil reservoirs in the Lucaogou Formation in the Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin
-
摘要:
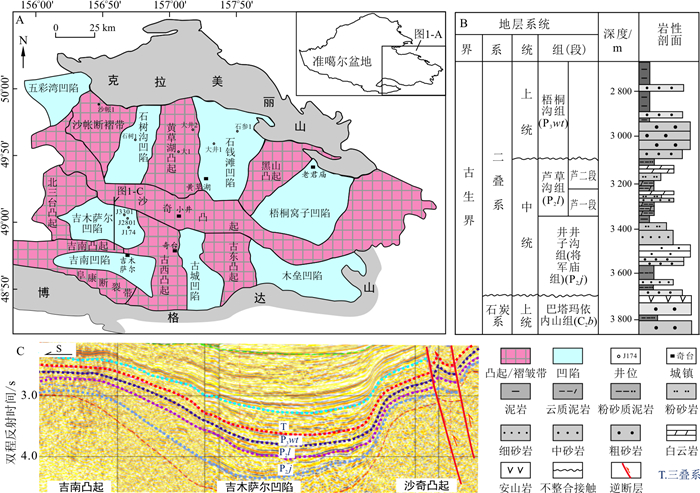
准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷是我国页岩油成功勘探的代表性地区之一,但至今对页岩油富集层段二叠系芦草沟组的沉积相认识还存在分歧,存在浅湖与半深湖-深湖2种不同观点,并将其中的砂岩夹层识别为三角洲前缘远砂坝、浅湖滩坝沉积。通过岩心观察和砂岩粒度、测井相、储层物性分析等方法对二叠系芦草沟组沉积相特征进行了研究。研究结果表明,研究区湖盆内部以半深湖-深湖背景下湖底扇发育为特征,以细粒浊流为搬运-沉积机制;以透镜状-波状层理泥质粉砂岩-粉砂岩为主要岩相类型,其次是平行层理粉砂岩、递变层理粉砂岩和块状-递变层理细砂岩;其粒度累计概率曲线呈以悬浮总体为主的平滑上拱式,在
C-M 图上样品点分布于递变悬浮段。湖底扇包括席状朵叶、重力流水道-天然堤微相,分别表现为反、正沉积旋回。发育于湖底扇(尤其是广泛分布的席状朵叶微相)内部较多的粉-细砂岩夹层,以及作为细粒沉积中外源碎屑颗粒来源的浊流活动,造就了“甜点”储层“低黏土、高斜长石”矿物含量特点和溶蚀孔隙的大量发育,从而提高了细粒储层的储集性。本研究总结了细粒湖底扇的沉积物粒度细、砂层薄和频繁发育等特点,指明了“甜点”储层分布于细粒湖底扇发育的层段和地区,对研究区页岩油勘探具有指导意义。Abstract:Objective The Jimsar Sag of the Junggar Basin is representative of successful shale oil exploration in China. However, the sedimentary facies in the Permian Lucaogou Formation hosting shale oil has long been disputed. Previous studies proposed two contradictory environments of shallow lakes and semideep to deep lakes in the interior lacustrine basin and identified sandstone interlays as deltaic distal sandbar deposition and beach and bar deposition.
Methods The study combined core observations with analyses of sandstone granularity, logging facies, and reservoir properties to identify the development of sublacustrine fans in a semi-deep to deep lake background.
Results Fine-grained turbidity currents played a significant role in the transportation and deposition of sediment in these fans. The lithofacies observed included lenticular-wave bedded muddy siltstone to siltstone (dominant type), parallel bedded siltstone, graded siltstone, and massive-graded bedded siltstone to fine-grained sandstone. The cumulative probability granularity curves exhibited smooth upper arches with a high suspension population, and the cross-spots on the
C-M diagram were located in the grade suspension zone. The sublacustrine fans consisted of sedimentary microfacies of sheet-like lobes and gravity flow channel levees, showing fining- and coarsening-upwards successions, respectively. These fans contained numerous interlayers of siltstone and fine-grained sandstone, as well as terrigenous detrital particles that influenced the mineral content and enhanced shale oil reservoir properties by promoting the growth of solution pores.Conclusion The study concluded that sublacustrine fan deposits are thin-bedded and fine-grained, and they occur frequently. It also determined that desert reservoirs formed in the areas where sublacustrine fans were deposited, which has significant implications for shale oil exploration in the study area.
-
图 2 细粒与中粒浊积岩沉积序列对比[22]
Figure 2. Comparative sedimentary successions between fine- and medium-grained turbidities
图 3 细粒湖底扇沉积的岩相组成及特征(井位见图 1-A)
A.J3301井, 3 397.92 m(顶深),灰白色荧光正递变泥质粉砂岩-粉砂岩;B.J3301井, 3 433.9 m,灰色块状粉砂岩,底部较多深灰色棱角状泥砾;C.J3301井, 3 548.08 m,深灰色荧光波状层理粉砂质泥岩,夹粉砂岩纹层,下部含灰白色方沸石斑块;D.J3301井, 3 534.65 m,深灰色泥岩,夹波状层理泥质粉砂岩,略具反旋回;E.J2801井, 3 052.72 m,灰黑色油迹泥岩,夹透镜状白云岩和波状层理粉砂岩,下部见负载构造;F.J3301井, 3 533.07 m,深灰色荧光泥岩,夹块状-波状层理粉砂岩;G.J3301井, 3 554.5 m,深灰色荧光泥岩,夹波状-透镜状层理粉砂岩;H.J3301井, 3 554.5 m,深灰色荧光泥岩,夹泥质粉砂岩纹层,局部见包卷层理;I.J2801井, 3 053.59 m,灰黑色块状泥岩,夹液化变形构造粉砂岩;J.J2801井, 3 049.8 m,灰黑色块状泥岩,夹肠状构造粉砂岩;K.J174井, 3 375 m,深灰色泥岩,夹较多递变、透镜状层理粉-细砂岩纹层。黄色三角形示意单个浊流事件沉积
Figure 3. Lithofacies composition and characteristics in fine-grained sublacustrine fan deposits
图 6 J174井芦草沟组岩心沉积相分析(井位见图 1-A)
Figure 6. Sedimentary facies based on core description in the Lucaogou Formation of Well J174
图 7 J2801井芦草沟组岩心沉积微相分析(井位见图 1-A)
Figure 7. Sedimentary facies based on core description in the Lucaogou Formation of Well J2801
图 10 J174井芦草沟组下“甜点”段不同岩性的砂质颗粒分布特征及溶蚀孔隙
A.3 274.14 m, (-),凝灰质细砂岩,颗粒以斜长石为主,较多粒间溶孔(蓝色铸体);B.3 308.18 m, (-),云泥质粉砂岩,较多粒间和斜长石颗粒粒内溶孔;C.3 297.45 m, (-),泥质粉砂岩,夹有机质纹层,粉砂质颗粒以斜长石为主,顺层分布,少量粒间溶孔;D.3 277.5 m, (+),粉砂质泥岩,粉砂质颗粒顺层排列显示纹层;E.3 292.01 m, (+),云质粉砂质泥岩,粉砂质颗粒主要为斜长石,纹层状分布,较多溶孔, 白云石呈细小菱形;F.3 305.33 m, (-),含粉砂微晶云岩,粉砂颗粒以斜长石为主,漂浮状分布,少量溶孔, 白云石呈细小菱形
Figure 10. Sandy particle distribution and solution pores in various kinds of lithology, the lower dessert interval, Lucaogou Formation of Well J174
表 1 J174井芦草沟组砂岩粒度参数统计
Table 1. Statistical parameters of sandstone grain-size in the Lucaogou Formation of Well J174
样品深度/m 平均粒径/ϕ 岩性 标准偏差 分选性级别 偏度 偏度级别 峰度 峰度等级 3 114.86 4.50 粉砂岩 2.67 差 0.44 很正偏态 1.01 中等 3 115.56 3.70 细砂岩 2.68 差 0.46 很正偏态 1.06 中等 3 127.53 3.42 细砂岩 2.53 差 0.44 很正偏态 1.09 中等 3 142.13 5.15 粉砂岩 2.64 差 0.39 很正偏态 1.00 中等 3 145.19 4.14 粉砂岩 2.91 差 0.47 很正偏态 0.88 平坦 3 147.35 3.22 细砂岩 2.50 差 0.40 很正偏态 0.90 平坦 3 147.64 3.49 细砂岩 2.41 差 0.44 很正偏态 1.05 中等 3 152.46 3.67 细砂岩 2.77 差 0.49 很正偏态 1.03 中等 3 158.49 3.59 细砂岩 2.87 差 0.28 正偏态 0.82 平坦 3 159.75 3.51 细砂岩 2.57 差 0.52 很正偏态 1.25 尖锐 3 160.41 4.07 粉砂岩 2.92 差 0.38 很正偏态 0.89 平坦 3 173.56 3.57 细砂岩 2.62 差 0.54 很正偏态 1.16 尖锐 表 2 J174井芦草沟组”甜点”段与“非甜点”段主要矿物的平均质量分数
Table 2. Average contents of the main mineral ingredients in the dessert and nondessert intervals in the Lucaogou Formation of Well J174
wB/% 层段 矿物成分 黏土矿物 长英质类 碳酸盐类 黄铁矿 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 白云石 铁白云石 上“甜点”段 7.94 21.32 3.88 28.82 3.93 25.19 7.87 0.06 下“甜点”段 8.50 19.50 5.39 30.31 4.71 27.92 2.66 1.01 非“甜点”段 15.15 21.44 3.33 20.26 12.53 22.76 3.25 0.93 -
[1] 邹才能, 陶士振, 袁选俊, 等. 连续型油气藏形成条件与分布特征[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(3): 324-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200903003.htmZou C N, Tao S Z, Yuan X J, et al. The formation conditions and distribution characteristics of continuous petroleum accumulations[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(3): 324-331 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200903003.htm [2] 贾承造, 郑民, 张永峰. 中国非常规油气资源与勘探开发前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(2): 129-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201202002.htmJia C Z, Zheng M, Zhang Y F. Unconventional hydrocarbon resources in China and the prospect of exploration and development[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(2): 129-136(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201202002.htm [3] 贾承造, 邹才能, 李建忠, 等. 中国致密油评价标准、主要类型、基本特征及资源前景[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(3): 344-350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201203000.htmJia C Z, Zou C N, Li J Z, et al. Assessment criteria, main types, basic features and resource prospects of the tight oil in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(3): 344-350(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201203000.htm [4] 朱如凯, 邹才能, 吴松涛, 等. 中国陆相致密油形成机理与富集规律[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(6): 1168-1183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201906002.htmZhu R K, Zou C N, Wu S T, et al. Formation mechanism and enrichment law of continental tight oil in China[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2019, 40(6): 1168-1183(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201906002.htm [5] 赵贤正, 蒲秀刚, 周立宏, 等. 深盆湖相区页岩油富集理论、勘探技术及前景: 以渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷古近系为例[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(2): 143-162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202102001.htmZhao X Z, Pu X G, Zhou L H, et al. Enrichment theory, exploration technology and prospects of shale oil in lacustrine facies zone of deep basin: A case study of the Paleogene in Huanghua Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(2): 143-162(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202102001.htm [6] 邓远, 陈世悦, 蒲秀刚, 等. 渤海湾盆地沧东凹陷孔店组二段细粒沉积岩形成机理与环境演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(4): 811-890. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004015.htmDeng Y, Chen S Y, Pu X G, et al. Formation mechanism and environmental evolution of fine-grained sedimentary rocks from the Second Member of Kongdian Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 811-890(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004015.htm [7] 宋明水, 向奎, 张宇, 等. 泥质重力流沉积研究进展及其页岩油气地质意义: 以东营凹陷古近系沙河街组三段为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(4): 740-751. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201704008.htmSong M S, Xiang K, Zhang Y, et al. Research progresses on muddy gravity flow deposits and their significances on shale oil and gas: A case study from the 3rd oil-member of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation in the Dongying Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(4): 740-751(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201704008.htm [8] 杨仁超, 尹伟, 樊爱萍, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部三叠系延长组湖相重力流沉积细粒岩及其油气地质意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(5): 791-806. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201705005.htmYang R C, Yin W, Fan A P, et al. Fine-grained, lacustrine gravity-flow deposits and their hydrocarbon significance in the Triassic Yanchang Formation in southern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography: Chinese Edition, 2017, 19(5): 791-806(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201705005.htm [9] Zhang S M, Cao Y C, Liu K Y, et al. Characterization of lacustrine mixed fine-grained sedimentary rocks using coupled chemostratigraphic-petrographic analysis: A case study from a tight oil reservoir in the Jimusar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 99: 453-472. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.10.039 [10] 匡立春, 唐勇, 雷德文, 等. 准噶尔盆地二叠系咸化湖相云质岩致密油形成条件与勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(6): 657-667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201206004.htmKuang L C, Tang Y, Lei D W, et al. Formation conditions and exploration potential of tight oil in the Permian saline lacustrine dolomitic rock, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(6): 657-667(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201206004.htm [11] 斯春松, 陈能贵, 余朝丰, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组致密油储层沉积特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(5): 528-533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201305011.htmSi C S, Chen N G, Yu C F, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of tight oil reservoir in Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2013, 35(5): 528-533(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201305011.htm [12] 邵雨, 杨勇强, 万敏, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组沉积特征及沉积相演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2015, 36(6): 635-641. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201506003.htmShao Y, Yang Y Q, Wan M, et al. Sedimentary characteristic and facies evolution of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xingjiang Petroleum Geology, 2015, 36(6): 635-641(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201506003.htm [13] 张亚奇, 马世忠, 高阳, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组致密油储层沉积相分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(2): 358-370. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201702013.htmZhang Y Q, Ma S Z, Gao Y, et al. Depositional facies analysis on tight reservoir of Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(2): 358-370(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201702013.htm [14] 马克, 侯加根, 刘钰铭, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组咸化湖混合沉积模式[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(6): 636-648. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201706003.htmMa K, Hou J G, Liu Y M, et al. The sedimentary model of saline lacustrine mixed sedimentation in Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(6): 636-648(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201706003.htm [15] 李书琴, 印森林, 高阳, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组混合细粒岩沉积微相[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(2): 235-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202002009.htmLi S Q, Yin S L, Gao Y, et al. Study on sedimentary microfacies of mixed fine-grained rocks in Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(2): 235-249(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202002009.htm [16] 张治恒, 田继军, 韩长城, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组储层特征及主控因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(2): 116-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202102012.htmZhang Z H, Tian J J, Han C C, et al. Reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors of Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Jungger Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(2): 116-126(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202102012.htm [17] 陈发景, 汪新文, 汪新伟. 准噶尔盆地的原型和构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(3): 77-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200503012.htmChen F J, Wang X W, Wang X W. Prototype and tectonic evolution of the Junggar Basin, northwestern China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(3): 77-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200503012.htm [18] 吴孔友, 查明, 王绪龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化与动力学背景再认识[J]. 地球学报, 2005, 26(3): 217-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200503004.htmWu K Y, Zha M, Wang X L, et al. Further researches on the tectonic evolution and dynamic setting of the Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2005, 26(3): 217-222 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200503004.htm [19] 何登发, 张磊, 吴松涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化阶段及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 845-861. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805002.htmHe D F, Zhang L, Wu S T, et al. Tectonic evolution stages and features of the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 845-861 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805002.htm [20] 支东明, 唐勇, 杨智峰, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷陆相页岩油地质特征与聚集机理[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(3): 524-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201903009.htmZhi D M, Tang Y, Yang Z F, et al. Geological characteristics and accumulation mechanism of continental shale oil in Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3): 524-534 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201903009.htm [21] 蔺连第, 朗艳, 金蕙, 等. 二连盆地乌里雅斯太凹陷早白垩世湖底扇[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(3): 27-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200503007.htmLin L D, Lang Y, Jin H, et al. Early Cretaceous sublacustrine fan in Wulivasitai Sag, Erlian Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(3): 27-32 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200503007.htm [22] 陈广坡, 王天奇, 李林波, 等. 箕状断陷湖盆湖底扇特征及油气勘探: 以二连盆地赛汉塔拉凹陷腾格尔组二段为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(1): 63-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201001011.htmChen G P, Wang T Q, Li L B, et al. Characteristics of sublacustrine fan in half-graben rift lake basin and its petroleum prospecting: Case study on the Second Member of Tenggeer Formation, Saihantala Sag, Erlian Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(1): 63-69 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201001011.htm [23] 王华, 陈思, 巩天浩, 等. 牵引流化重力流沉积过程与堆积机制: 以渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 95-104. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0111Wang H, Chen S, Gong T H, et al. Sedimentary process and accumulation mechanism of traction fluidization gravity flow: An example from Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 95-104(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0111 [24] Chen P, Xian B Z, Li M J, et al. A giant lacustrine flood-related turbidite system in the Triassic Ordos Basin, China: Sedimentary processes and depositional architecture[J]. Sedimentology, 2021, 68: 3279-3306. doi: 10.1111/sed.12891/abstract [25] Xian B Z, Wang J H, Liu J P, et al. Classification and sedimentary characteristics of lacustrine hyperpycnal channels: Triassic outcrops in the south Ordos Basin, central China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2018, 368: 68-82. [26] Stow D A V, Shanmugam G. Sequence of structures in fine-grained turbidites: Comparison of recent deep-sea and ancient flysch sediments[J]. Sedimentary geology, 1980, 25: 23-42. [27] Feng Z Q, Zhang S, Cross T A, et al. Lacustrine turbidite channels and fans in the Mesozoic Songliao Basin, China[J]. Basin Research, 2009, 22(1): 96-107. [28] Bouma A H. Coarse-grained and fine-grained turbidite systems as end member models: Applicability and dangers[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(2): 137-143. [29] Bouma A H. Fine-grained, mud-rich turbidite systems: Model and comparison with coarse-grained, sand rich systems[C]//Bouma A H, Stone C G. Fine-grained turbidite systems. AAPG Memoir 72. [S. l. ]: SEPM Special Publication, 2000, 68: 9-20. [30] 龚峤林, 李飞, 苏成鹏, 等. 细粒浊积岩特征、分布及发育机制: 以川北唐家河剖面寒武系郭家坝组为例[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(3): 349-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201803001.htmGong Q L, Li F, Su C P, et al. Characteristics, distribution and mechanisms of fine-grained turbidite: A case study from the Cambrian Guojiaba Formation in Tangjiahe Section, Northern Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography: Chinese Edition, 2018, 20(3): 349-364 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201803001.htm [31] 易承龙. 河南省泌阳凹陷安棚地区古近系核桃园组含碱地层层序特征及其意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2016, 18(1): 93-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201601008.htmYi C L. Sequence stratigraphy characteristics and its significance of alkaliferous strata of the Paleogene Hetaoyuan Formation in Anpeng area, Biyang Sag, Henan Province[J]. Journal of Paleogeography: Chinese Edition, 2016, 18(1): 93-100(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201601008.htm [32] 钟大康, 朱筱敏, 王贵文, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷溶孔溶洞型白云岩储层特征与分布规律[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(2): 162-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200402006.htmZhong D K, Zhu X M, Wang G W, et al. Characteristics and distribution of dissolved porous and caved dolomitic reservoirs in the Biyang Sag of the Nanxiang Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2004, 50(2): 162-169(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200402006.htm [33] 郭强, 钟大康, 张放东, 等. 内蒙古二连盆地白音查干凹陷下白垩统湖相白云岩成因[J]. 古地理学报, 2012, 14(1): 59-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201201010.htmGuo Q, Zhong D K, Zhang F D, et al. Origin of the Lower Cretaceous lacustrine dolostones in Baiyinchagan Sag of Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography: Chinese Edition, 2012, 14(1): 59-68(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201201010.htm [34] 焦鑫, 柳益群, 靳梦琪, 等. 新疆三塘湖薄层状岩浆-热液白云质喷流沉积岩[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(6): 1087-1096. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201706001.htmJiao X, Liu Y Q, Jin M Q, et al. Thin bed magmatic-hydrothermal dolomitic exhalative sedimentary rocks in Santanghu Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(6): 1087-1096(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201706001.htm [35] 李红, 柳益群, 张丽霞, 等. 准噶尔盆地东部中二叠统平地泉组具"斑状"结构热水喷流沉积岩的成因及地质意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(2): 211-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201702003.htmLi H, Liu Y Q, Zhang L X, et al. Origin and geological significance of sedimentary exhalative rocks with "porphyritic" structures in the Middle Permian Pingdiquan Formation, eastern Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography: Chinese Edition, 2017, 19(2): 211-226(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201702003.htm [36] 陈志鹏, 任战利, 于春勇, 等. 银额盆地哈日凹陷下白垩统热水沉积岩特征及成因[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(6): 1941-1956. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201806012.htmChen Z P, Ren Z L, Yu C Y, et al. Characteristics and genetic analysis of hydrothermal sediment of Lower Cretaceous in Hari Depression, Yin'e Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(6): 1941-1956(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201806012.htm [37] 张帅, 柳益群, 焦鑫, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷中二叠统芦草沟组云质岩沉积环境及白云石成因探讨[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(1): 33-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201801003.htmZhang S, Liu Y Q, Jiao X, et al. Sedimentary environment and formation mechanisim of dolomitic rocks in the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimusar Depression, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Paleogeography: Chinese Edition, 2018, 20(1): 33-48 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201801003.htm [38] 李哲萱, 柳益群, 焦鑫, 等. 湖相细粒沉积岩中的"斑状"深源碎屑: 以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(2): 220-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202002008.htmLi Z X, Liu Y Q, Jiao X, et al. Deep-derived clastics with porphyroclastic structure in lacustrine fine-grained sediments: Case study of the Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(2): 220-234 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202002008.htm [39] 曾宏斌, 王芙蓉, 罗京, 等. 基于低温氮气吸附和高压压汞表征潜江凹陷盐间页岩油储层孔隙结构特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 242-252. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0022Zeng H B, Wang F R, Luo J, et al. Characteristics of pore structure of intersalt shale oil reservoir by low temperature nitrogen adsorption and high pressure mercury pressure methods in Qianjiang Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 242-252(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0022 [40] 孙中良, 王芙蓉, 韩元佳, 等. 潜江凹陷盐间页岩油储层孔隙结构分形表征与评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 125-137. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0063Sun Z L, Wang F R, Han Y J, et al. Evaluation of fractal characteristics of intersalt shale oil reservoirs in Qianjiang Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 125-137(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0063 [41] 葸克来, 操应长, 朱如凯, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组致密油储层岩石类型及特征[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(12): 1495-1507. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201512005.htmXi K L, Cao Y C, Zhu R K, et al. Rock types and characteristics of tight oil reservoir in Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(12): 1495-1507(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201512005.htm -





 下载:
下载: