Shrinkage mechanism of red clay based on changes in the thickness of bound water film
-
摘要:
结合水的含量及存在形式对红黏土的物理力学性质具有重要影响, 而红黏土宏观收缩会引起土粒、孔隙、结合水微观结构变化, 进而可能产生土体浅表层开裂引发渗透、失稳等工程地质问题。采用热重分析试验、BET测试试验、电镜扫描和Zeta电位试验对原状红黏土收缩过程中结合水的变化特征进行了研究, 建立了基于结合水膜均匀分布下的球状和薄片状黏土颗粒结构模型, 并推导出结合水膜厚度的计算公式。研究结果表明, 原状红黏土中的水分大部分以结合水的形式存在, 红黏土的收缩过程一直贯穿着弱结合水的损失, Zeta电位和比表面积不断减小, 结合水膜厚度也不断减小。研究结果揭示了红黏土失水收缩的内在机理, 可为解决环境工程地质问题提供理论支持。
Abstract:Objective The content and existence form of bound water have an important influence on the physical and mechanical properties of red clay, and macroscopic shrinkage of red clay leads to microstructure changes of soil particles, pores and bound water, which in turn may cause soil surface cracking, triggering infiltration, destabilization, and other engineering geological problems.
Methods Thermogravimetric analysis tests, BET tests, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and zeta potential tests were conducted to study the variation characteristics of bound water during the shrinkage of undisturbed red clay. The structural model of spherical and lamellar clay particles based on the uniform distribution of bound water film was established, and the formula for the calculation of bound water film thickness was derived.
Results The results showed that most of the water in undisturbed red clay exists in the form of bound water and the loss of weakly-bounded water continues throughout the shrinkage process of red clay. During the process, the zeta potential, specific surface area and the thickness of the bound water film decreased continuously.
Conclusion The results reveal the intrinsic mechanism of water loss and shrinkage of red clay, which can provide theoretical support for solving environmental engineering geological problems.
-
Key words:
- bound water /
- red clay /
- shrinkage test /
- thermogravimetric analysis /
- microscopic test
-
表 1 基本物理指标
Table 1. Basic physical indicators
天然含水率/
%相对密度 液限/
%塑限/
%干密度/
(g·cm-3)孔隙比 68.9 2.39 80.7 50.9 1.14 1.11 表 2 红黏土矿物成分
Table 2. Mineral composition of red clay
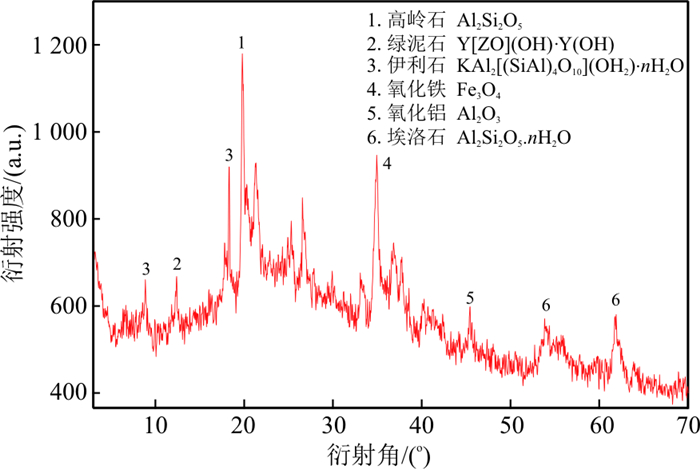
矿物成分 埃洛石 高岭石 绿泥石 伊利石 氧化铁 氧化铝 其他 wB/% 60.4 3.9 6.0 7.0 11.9 6.8 3.0 注:其他主要包括结晶比较弱或者非晶矿物等物质 表 3 各收缩阶段蒸发水类型
Table 3. Type of evaporated water at each stage of shrinkage
试样 质量含水率
wB/%质量绝对含水率
wB/%收缩阶段 自由水质量分数wB/% 弱结合水质量分数wB/% 强结合水质量分数wB/% S1 64.9 64.0 初始阶段 1.17 — — 正常收缩阶段 — 21.90 — 残余收缩阶段 — 9.88 — 零收缩阶段 — 15.53 5.92 S2 69.5 69.1 初始阶段 1.07 — — 正常收缩阶段 — 27.35 — 残余收缩阶段 — 8.67 — 零收缩阶段 — 19.75 — 表 4 不同收缩阶段红黏土结合水膜厚度
Table 4. Thickness of the bonded water film of red clay at different stages of shrinkage
收缩阶段 吸附水含水量wB/% 比表面积
Sg/
(m2·g-1)结合水密度
ρw/
(g·cm-3)结合水膜的厚度
h/nm初始阶段 64.9 20.202 1.783 18.018 正常收缩阶段 46.6 19.524 1.787 13.356 残余收缩阶段 35.7 18.128 1.791 10.996 零收缩阶段 24.0 16.885 1.793 7.927 -
[1] 廖义玲, 朱立军. 贵州碳酸盐岩红土[M]. 贵阳: 贵州人民出版社, 2004.Liao Y L, Zhu L J. Carbonate laterites of Guizhou[M]. Guiyang: Guizhou People's Publishing House, 2004(in Chinese). [2] 朱建群, 易亮, 龚琰, 等. 贵州红黏土的胀缩性与水敏性研究[J]. 湖南科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 31(4): 35-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTKY201604007.htmZhu J Q, Yi L, Gong Y, et al. Study on the swelling and shrinking properties and water sensitivity of red clay in Guizhou[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 31(4): 35-39(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTKY201604007.htm [3] 赵成刚, 白一冰, 王运霞. 土力学原理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004.Zhao C G, Bai Y B, Wang Y X. Principles of soil mechanics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004(in Chinese). [4] 余敦猛, 杨果林, 方薇. 武广客专红黏土变形特性及形成机理研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报2010, 34(6): 1255-1259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JTKJ201006045.htmYu D M, Yang G L, Fang W. Study on the deformation characteristics and formation mechanism of red clay for the Wuhan-Guangzhou Passenger Highway[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology 2010, 34(6): 1255-1259(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JTKJ201006045.htm [5] 穆锐, 黄质宏, 姚未来, 等. 分级循环荷载下原状红黏土动力特性试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2022, 49(3): 94-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202203010.htmMu R, Huang Z H, Yao W L, et al. An experimental study of the dynamic characteristics of the undisturbed laterite under graded cyclic loading[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(3): 94-102(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202203010.htm [6] Krzywoblocsi M Z. On the fundamentals of the boundary layer theory[J]. Pergamon, 1953, 255(4): 289-299. [7] 李广信. 高等土力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004.Li G X. Advanced geomechanics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004(in Chinese). [8] 陈宗淇, 王光信, 徐桂英. 胶体与界面化学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2001.Chen Z Q, Wang G X, Xu G Y. Colloid and interface chemistry[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2001(in Chinese). [9] Pyper J W. 应用微波方法测量有机材料中的结合水分和游离水分[J]. 国外科技资料, 1992(10): 87-95.Pyper J W. Application of microwave methods to the measurement of bound and free moisture in organic materials[J]. Foreign Science and Technology Information, 1992(10): 87-95(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] Prost R, Koutit T, Benchara A. State and location of water absorbed on clay minerals: Consequences of the hydration and swelling-shrinkage phenomena[J]. Clays and Clayminerals, 1998, 146(5): 297-302. [11] Bridgeman C H, Skipper N T. A Monte Carlo study of water at an uncharged clay surface[J]. Journal of Physics, 1997, 9(20): 4081-4087. [12] Tone K, Kamori M, Shibasaki Y. Adsorbed cations and water film thickness on the kaolinitic clay surface[J]. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 1993, 101(12): 1395-1399. [13] 吴凤彩. 黏性土吸附结合水容重测量[J]. 水利水运科学研究, 1987(4): 69-74.Wu F C. Measurement of adsorbed combined water capacity of clayey soils[J]. Water Resources and Water Transport Scientific Research, 1987(4): 69-74(in Chinese with English abstract). [14] 王平全. 黏土表面结合水定量分析及水合机制研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油学院, 2001.Wang P Q. Quantitative analysis of water binding on clay surface and study of hydration mechanism[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum Institute, 2001(in Chinese with English abstract). [15] 王铁行, 李彦龙, 苏立君. 黄土表面吸附结合水的类型和界限划分[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(5): 942-948. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201405026.htmWang T X, Li Y L, Su L J. Classification of types and boundaries of adsorbed bound water on loess surfaces[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(5): 942-948(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201405026.htm [16] 何攀, 许强, 刘佳良, 等. 基于核磁共振技术的结合水含量对重塑黄土抗剪强度影响试验研究[J]. 山地学报, 2020, 38(4): 571-580. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA202004009.htmHe P, Xu Q, Liu J L, et al. Experimental study on the effect of combined water content on the shear strength of remodeled loess based on nuclear magnetic resonance technique[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2020, 38(4): 571-580(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA202004009.htm [17] 苏俊霖, 董汶鑫, 冯杰, 等. 黏土表面结合水的低场核磁共振定量研究[J]. 钻井液与完井液, 2018, 35(1): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYW201801002.htmSu J L, Dong W X, Feng J, et al. Quantitative study of low-field NMR of clay surface bound water[J]. Drilling and Completion Fluids, 2018, 35(1): 8-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYW201801002.htm [18] Dao M H. 膨润土缓冲回填材料干裂特性及缩裂机制研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2019.Dao M H. Study on dry cracking characteristics and shrinkage cracking mechanism of bentonite buffer backfill materials[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [19] Kucerik J, Siewert C. Practical application of thermogravimetry in soil science[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2014, 116(2): 563-570. [20] Wan K, Ji P, Miao Z Y, et al. Analysis of water forms in lignite and pore size distribution measurement utilizing bound water as a molecular probe[J]. Energy Weekly News, 2017, 31(11): 884-891. [21] Chauhan R, Kumar R, Diwan P K, et al. Thermogravimetric analysis and chemometric based methods for soil examination: Application to soil forensics[J]. Forensic Chemistry, 2020, 17: 100191. [22] Zhang R, Xiao Y P, Wu M L, et al. Measurement and engineering application of adsorbed water content in fine-grained soils[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(5): 1555-1569. [23] 韩博, 鲁光银, 曹函, 等. 基于图像处理技术的聚合物水基钻井液微观结构分形研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2): 221-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802030.htmHan B, Lu G Y, Cao H, et al. Study on microstructure fractalization of polymeric water-based drilling fluid based on image processing technology[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(2): 221-228(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802030.htm [24] 彭双麒, 柯灵, 郑体, 等. 基于图像识别的碎屑流颗粒分布特征及碎屑流与房屋相互作用探究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 226-235. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0622Peng S Q, Ke L, Zheng T, et al. Exploration of debris flow particle distribution characteristics and debris flow-housing interaction based on image recognition[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 226-235(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0622 [25] 井旭, 谢婉丽, 单帅. 原状及重塑黄土双轴试验微观力学特征离散元模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 184-193. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0311Jing X, Xie W L, Shan S. Discrete element simulation of micromechanical characteristics of in-situ and remodeled loess biaxial tests[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 184-193(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0311 -





 下载:
下载: