Drivers of ecological environment changes in the Baozhainao lake-basin system, Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
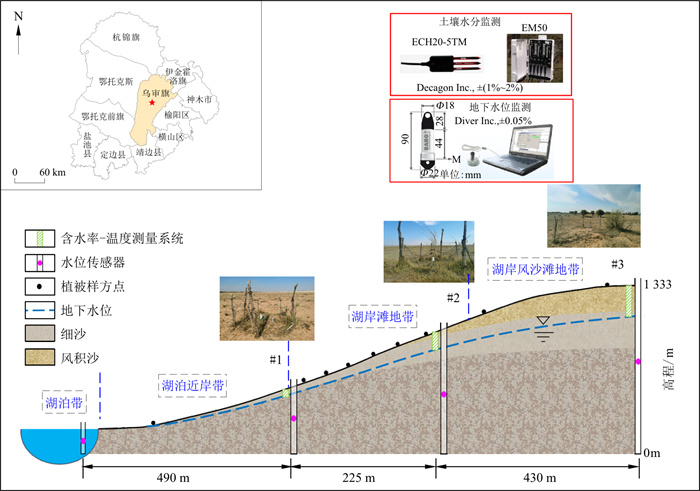
在干旱半干旱地区,湖盆生态系统是流域安全屏障的重要组成部分,在维持生态格局稳定性方面具有重要作用。然而,近年来湖盆生态环境逐渐退化,其变化过程伴随着复杂的动力学机制。为探究湖盆生态环境空间变异及其驱动力,以鄂尔多斯盆地毛乌素沙地堡寨淖为研究区,采用原位动态监测、样方调查、统计分析与数值模拟相结合的方法,分析了堡寨淖湖盆地区典型植被的分布特征,揭示了地下水文过程与湖岸生态系统的互馈机制。结果表明,堡寨淖湖盆生态系统由4种分带类型组成,分别是湖泊带、湖泊近岸波动带、湖岸滩地带和湖岸风沙滩地带,地下水位埋深从湖泊带至湖岸风沙滩地带呈逐渐增大的趋势,植被类型由喜水耐盐植物过渡到耐旱植被,证实湖岸植被的存在显著地影响地下水流系统的循环模式,湖泊与地下水转化主要发生在局部水流系统,造成地下水对湖泊补给量明显减小。研究结果可以为旱区湖泊波动带-风沙滩地带植被物种多样性以及植被生态系统的修复与保护提供科学依据。
Abstract:In arid and semiarid regions, lake-basin ecosystems are an important part of watershed security barriers, playing an important role in maintaining the stability of ecological patterns. However, the ecological environment of the lake-basin system has been gradually degraded in recent years, and its change process is accompanied by a complex dynamic mechanism. In the present study, we explored the spatial variability of the ecological environment of the lake-basin system and its drivers by taking Baozhainao Lake in the Mu Us Sandy Land of the Ordos Basin as the study area.In-situ dynamic monitoring, sample survey, statistical analysis and numerical simulation were employed. The distribution patterns of typical vegetation in the basin were determined and the mechanisms underlying the mutual feedbacks between subsurface hydrological process and lakeshore ecosystem was explored. The results show that the Baozhainao lake-basin ecosystem consists of four zoning types, namely, the lake zone, the lake nearshore fluctuation zone, the lakeshore beach zone, and the lakeshore wind beach zone. From the lake to the beach zone, the depth of water table increased gradually and the vegetation type transitions from water-loving and salt-tolerant to drought-tolerant. It was further found that the presence of vegetation on the lake shore significantly affects the circulation mode of the groundwater flow system. The conversion between lake and groundwater occurs mainly in the local groundwater flow system, resulting in a significant reduction in groundwater recharge to the lake.The results of this study can provide a scientific basis for the restoration and conservation of plant species diversity and vegetated ecosystems in the lake nearshore fluctuation zoneand lakeshore wind beach zone in arid regions.
-
表 1 CCA排序前两轴的特征值、物种-环境相关性及方差累计百分比
Table 1. Eigenvalues, species-environment correlations and cumulative percentage variance for the first two axes of CCA ranking
排序轴1 排序轴2 排序轴3 排序轴4 特征值 0.712 0.442 0.194 0.018 物种与环境的相关性 0.972 0.821 0.653 0.394 物种与环境关系的变化累计比例/% 52.2 84.5 98.7 100 -
[1] 黄金廷, 王文科, 何渊, 等. 鄂尔多斯沙漠高原湖淖群的形成演化及生态功能探讨[J]. 资源科学, 2006, 28(2): 140-146. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2006.02.021Huang J T, Wang W K, He Y, et al. The formation and evolution and ecological functions of lakes in Ordos Desert Plateau[J]. Resources Science, 2006, 28(2): 140-146 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2006.02.021 [2] Tian L, Zhang J Y, Claus H, et al. Vegetation pattern in northern Tibet in relation to environmental and geo-spatial factors[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2018, 9(5): 526-537. doi: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2018.05.010 [3] Fu A H, Chen Y N, Li W H. Water use strategies of the desert riparian forest plant community in the lower reaches of Heihe River Basin, China[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(6): 1293-1305. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4680-8 [4] He B, Cai Y L, Ran W R, et al. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of soil salinity after the establishment of vegetation on a coastal saline field[J]. Catena, 2015, 127(4): 129-134. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0341816214003804 [5] Chen Y N, Pang Z H, Chen Y, et al. Response of riparian vegetation to water-table changes in the lower reaches of Tarim River, Xinjiang Uygur, China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2008, 16(7): 1371-1379. doi: 10.1007/s10040-008-0306-1 [6] 杨剑洲, 龚晶晶, 马生明, 等. 海南岛北部种植园土壤中多环芳烃的质量分数、来源及生态风险[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 268-275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202106029.htmYang J Z, Gong J J, Ma S M, et al. Contents, sources and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in agricultural soils of plantations in northern Hainan Island[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 268-275 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202106029.htm [7] 张敏, 胡学玉, 胡晓晓, 等. 硫对地球表层生态系统中镉迁移转化影响的研究进展: 以土壤-植物系统为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 236-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202203026.htmZhang M, Hu X Y, Hu X X, et al. Research progress on the effects of sulfur on the migration and transformation of cadmium in the earth surface ecosystem: A case study of soil-plant system[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 236-245(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202203026.htm [8] 张晓雅, 赵锐锋, 张丽华, 等. 不同生态保护地植物特征和土壤性质的对比研究: 以黑河中游湿地为例[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(9): 3027-3039. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB202009020.htmZhang X Y, Zhao R F, Zhang L H, et al. Comparative study of plant characteristics and soil properties in different ecological protected arcas: A case study of middle reaches of the Heihe River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(9): 3027-3029(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB202009020.htm [9] 程东会, 王文科, 侯光才, 等. 毛乌素沙地植被与地下水关系[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2012, 42(1): 184-189. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201201025.htmCheng D H, Wang W K, Hou G C, et al. Relationship between vegetation and groundwater in Muus Desert[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(1): 184-189 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201201025.htm [10] Klijn F, Witte J P M. Eco-hydrology: Groundwater flow and site factors in plant ecology[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 1999, 7(1): 65-77. doi: 10.1007/s100400050180 [11] Antonellinl M, Mollema P N. Impact of groundwater salinity on vegetation species richness in the coastal pine forests and wetlands of Ravenna, Italy[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2010, 36(9): 1201-1211. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.12.007 [12] 孙自永, 王俊友, 葛孟琰, 等. 基于水稳定同位素的地下水型陆地植被识别: 研究进展、面临挑战及未来研究展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 11-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202001003.htmSun Z Y, Wang J Y, Ge M Y, et al. Isotopic approaches to identify groundwater dependent terrestrial vegetation: Progress, challenges, and prospects for future research[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 11-20 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202001003.htm [13] Zhao M, Wang W K, Wang Z F, et al. Water use of salix in the variably unsaturated zone of a semiarid desert region based on in-situ observation[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 591(3): 125579. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169420310398 [14] 钟娇娇, 陈杰, 陈倩, 等. 秦岭山地天然次生林群落MRT数量分类、CCA排序及多样性垂直格局[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(1): 277-285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201901027.htmZhong J J, Chen J, Chen Q, et al. Quantitative classification of MRT, CCA ordination, and species diversity along elevation gradients of a natural secondary forest in the Qinling Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(1): 277-285 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201901027.htm [15] 李志新, 许迪, 李益农, 等. 畦灌施肥地表水流与非饱和土壤水流-溶质运移集成模拟: Ⅰ. 模型[J]. 水利学报, 2009, 40(6): 673-678, 687. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB200906005.htmLi Z X, Xu D, Li Y N, et al. Integrated simulation of surface-subsurface flow and solute transport for border strip fertigation: l. Model[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2009, 40(6): 673-678, 687 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB200906005.htm [16] 徐建霞, 王建柱. 三峡库区香溪河消落带植被群落特征与土壤环境相关性[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(12): 3661-3669. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201812022.htmXu J X, Wang J Z. Correlation between vegetation community and soil physical-chemical factors in water-level fluctuation zone of Xiangxi River of the Three Goraes Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(12): 3661-3669 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201812022.htm [17] 王文科, 宫程程, 张在勇, 等. 旱区地下水文与生态效应研究现状与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(7): 702-718. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201807004.htmWang W K, Gong C C, Zhang Z Y, et al. Research status and prospect of the subsurface hydrology and ecological effect in arid regions[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(7): 702-718 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201807004.htm [18] Odindi J O, Kakembo V. The hydrological response of Pteronia incana-invaded areas in the eastern Cape Province, South Africa[J]. Ecohydrology, 2011, 4(6): 832-840. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/John_Odindi/publication/264725692_The_hydrological_response_of_Pteronia_incana-_invaded_areas_in_the_Eastern_Cape_Province_South_Africa/links/55ba1e1c08ae9289a0926231.pdf [19] 黄金廷, 侯光才, 陶正平, 等. 鄂尔多斯高原植被生态分区及其水文地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(8): 1330-1334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200808036.htmHuang J T, Hou G C, Tao Z P, et al. Vegetation ecological areas of the Ordos Plateau, China and their hydrogeological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(8): 1330-1334 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200808036.htm [20] Chimner R A, Copper D J. Using stable oxygen isotopes to quantify the water source used for transpiration by native shrubs in the San Luis Valley, Colorado USA[J]. Plant and Soil, 2004, 260(1/2): 225-236. doi: 10.1023%2FB%3APLSO.0000030190.70085.e9.pdf [21] Sardans J, Penuelas J. Hydraulic redistribution by plants and nutrient stoichiometry: Shifts under global change[J]. Eco-hydrology & Hydrobiology, 2014, 7(1): 1-20. http://www.creaf.uab.cat/Global-Ecology/Pdfs_UEG/2014%20Ecohydrology.pdf [22] 赵明, 王文科, 王周锋, 等. 半干旱区沙地沙蒿生物量及根系分布特征研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2018, 41(4): 786-792. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL201804015.htmZhao M, Wang W K, Wang Z F, et al. Biomass of Artemisia ordosica in sand land and its root system distribution characteristics in the semiarid regions[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2018, 41(4): 786-792 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL201804015.htm [23] Shannon S, Lunt D J. A new dust cycle model with dynamic vegetation: LPJ-dust version 1.0[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2011, 4(7): 85-105. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2112775313 [24] Li J, Yu B, Zhao C, et al. Physiological and morphological re-sponses of Tamarix ramosissima and Populus euphratica to altered groundwater availability[J]. Tree Physiology, 2013, 33(l): 57-68. http://treephys.oxfordjournals.org/content/33/1/57.full.pdf [25] 王思宇, 龙翔, 孙自永, 等. 干旱区河岸柽柳水分利用效率(WUE)对地下水位年内波动的响应[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(4): 215-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201704028.htmWang S Y, Long X, Sun Z Y, et al. Response of water use efficiency (WUE) of Tamarix ramosissima to annual fluctuation of groundwater level in arid region[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(4): 215-221 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201704028.htm [26] Salem Z E, Temamy A A, Salah M K, et al. Origin and characteristics of brackish groundwater in Abu Madi coastal area, Northern Nile Delta, Egypt[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 178(5): 21-35. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S0272771416301585&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1471597977&md5=98ddd32168e83fd391fc0b18d58896ed [27] Qadir M, Ghafoor A, Murtaza G. Use of saline-sodic waters through phytoremediation of calcareous saline-sodic soils: Science direct[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2001, 50(3): 197-210. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035507311710_eea4.html [28] 宋怀龙. 全球气候变化中被忽略的重大问题: 盐碱(混合)尘暴[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(1): 45-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201301009.htmSong H L. Saline-ackaline mixed dust storms: An ignored issue for global climate change[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(1): 45-55 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201301009.htm -





 下载:
下载: