A review of sedimentary forward modeling methods for different sedimentary systems of clastic rock series
-
摘要:
随着沉积学研究向定量化、过程化、体系化发展,沉积正演日益受到重视。首先阐述了目前沉积正演的主要输入和输出数据,梳理了输入参数的确立方法。随后综述了沉积正演分类的方法,分类原则包括模拟原理、模拟过程数量、模拟结果类型、模拟维度、模拟尺度、忠实数据程度、是否包含源-汇系统的源区等。然后介绍了不同碎屑岩系沉积体系的沉积正演方法,包括山坡地形、河流和深水水道、三角洲、朵体和滑坡。通过介绍各个体系的某一典型模拟程序,说明这一体系需要重点模拟的沉积特征及其对应的模拟原理,并尽量涵盖多种模拟方法,扩宽对于沉积正演的认识。最后对沉积正演的发展进行了展望,认为其将向三维可视化、多过程融合、多学科融合方向发展,并建议加强计算机、数学、力学、地学的复合人才培养;加强沉积正演假想实验研究来研究沉积理论;尝试多种模拟方法;以及由应用为主转向以研发为主。
Abstract:More and more attention has been paid to the sedimentary forward modeling (SFM) since the study on the sedimentology is targeted toward quantification, process orientation and systematization. This review first stated the main input and output data of the current sedimentary forward modeling and sorted out the determination methods of the input parameters. Then it reviewed the classification methods of the sedimentary forward modeling, and the classification principles included principle of simulation, number of simulation processes, types of simulation results, simulation dimension, simulation scale, data fidelity and source region covering source-sink system. Subsequently, it introduced the sedimentary forward modeling methods for the different sedimentary systems of clastic series, including hillside landform, river and deep-draft waterway, delta, lobe and landslide. It also described some classic simulation programs for the individual series, indicated the sedimentary characteristics of this series to be essentially simulated and their corresponding principles of simulation and covered multiple simulation methods as much as possible to expand the understanding of the sedimentary forward modeling. Finally, it looked into the development of the sedimentary forward modeling believed it would be targeted toward the three-dimension visualization, multi-process integration and multi-discipline integration, proposed to strengthen the training of compound talents in computer, mathematics, mechanics and geosciences; strengthened the experimental study on the sedimentary forward modeling hypothesis to study the sedimentation theory; tried multiple simulation methods and shifted the application foremost to the research and development foremost.
-
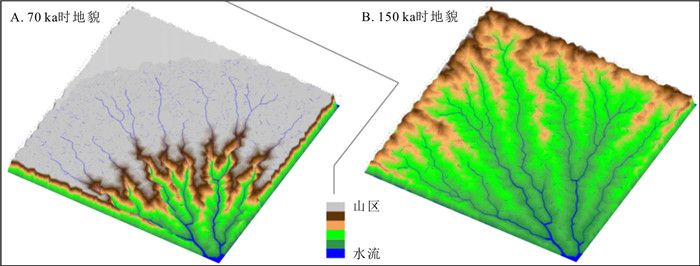
图 1 SIGNUM模拟山川地形演化(改自文献[22])
Figure 1. Evolvement of landscape simulated with SIGNUM
图 2 深水河道迁移模拟(改自文献[21])
A.10时间步长时的地表形态;B.90时间步长时的基底地表形态;C.10时间步长时的基底形态;D.90时间步长时的基底形态;E.水道-天然堤复合体剖面。蓝色为低地势;绿色为高地势
Figure 2. Migration simulation of deep water channel
图 3 Delta-RCM模拟高含砂率与低含砂率三角洲演化(改自文献[26])
A.含砂率25% 200 d时的三角洲沉积;B.含砂率75% 200 d时的三角洲沉积;C.含砂率25% 1 000 d时的三角洲沉积;D.含砂率25% 1 000 d时的三角洲沉积。蓝色为高水流量区域;白色为低水流量区域
Figure 3. Evolvement of delta with high and low percent sand simulated with Delta-RCM
图 4 朵体迁移演化(改自文献[28])
A.多个形态相似的朵体叠加在一起;B.横切物源剖面图;C.基本的扇体形态;D.加入随机扰动后的扇体形态
Figure 4. Migration simulation of lobe migration
图 5 FLOW-R预测的滑坡区域(改自文献[30])
A.底形;B.人工定义的易滑坡区域;C.Flow-R自动识别的易滑坡区域。红线标记的为沉积区;蓝线标记的为侵蚀区
Figure 5. Prediction of landslide regions for debris flow by FLOW-R
表 1 沉积正演方法分类
Table 1. Classification of sedimentary forward modeling
分类原则 类型 基本特征 范例 模拟原理 水动力型 基于水力学和泥沙动力学 Sedsim 扩散型 基于扩散规律 Dionisos 几何规律型 基于沉积体几何规律 SEDPAK 模拟过程数量 单模块 单一沉积过程 Delta-RCM 多模块 多个沉积过程 Dionisos 模拟结果类型 分析类 模拟单一特征 Hall等[15] 建模类 重建沉积体系 Dionisos 忠实数据程度 基于栅格类 地质统计学建模 Petrel 基于对象类 地质统计学与沉积规律共同控制 Petrel 基于规则类 沉积规律控制 Pyrcz等[16] 基于过程类 沉积过程物理规律控制 Sedsim 模拟维度 二维正演 剖面或平面随时间演化 SEDPAK 三维正演 三维沉积体随时间演化 Dionisos 模拟尺度 事件级别 0.1~10 a Flow-3D 储层级别 1~10 ka Pyrcz等[16] 盆地级别 >100 ka Badland 源-汇研究思路 完整源-汇区系统型 模拟源区侵蚀,恢复沉积物通量 Badland 只模拟汇区型 只模拟沉积区,沉积物通量需要人工设定 Delta-RCM 表 2 各个沉积体系沉积正演方法
Table 2. Sedimentary forward modeling for different sedimentary systems
模拟方法 模拟对象 关键特征 模拟程序 模拟结果 是否开源 研究单位 相关文献 河网提取与水流能量公式 山坡地形 树杈状河网和溯源侵蚀 SIGNUM 地貌高程随时间演化 开源 意大利国家研究委员会 文献[22-23] 中线迁移公式和剖面形态模拟 曲流河与深水水道 中线摆动迁移和截弯取直 文献[21] 河道水道随时间从直线型变为高弯度型 非开源 壳牌石油公司 文献[21, 24-25] 加权统计和简化流体泥沙动力学 三角洲 分支河道与鸟足状、朵状形态 Delta-RCM 水流量、岩性与高程随时间的演化 开源 美国明尼苏达大学 文献[26-27] 随机建模和朵体几何形态模拟 朵体 朵体迁移叠加 文献[16] 朵体叠加后形成的复合体 非开源 雪弗龙石油公司 文献[16, 28] 失稳概率评估和半经验公式 滑坡 条带状侵蚀区与朵状沉积区 Flow-R 滑坡体分布预测 开源 瑞士洛桑大学 文献[29-31] -
[1] Burgess P M, Roberts D, Bally A. A brief review of developments in stratigraphic forward modelling, 2000-2009[J]. Regional Geology and Tectonics: Principles of Geologic Analysis, 2012, 1: 379-404. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444530424000145 [2] Paola C. Quantitative models of sedimentary basin filling[J]. Sedimentology, 2000, 47: 121-178. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.2000.00006.x [3] Potter P E, Pettijohn F J. Paleocurrents and basin analysis (1963-1976)[M]. New York: Springer, 1977. [4] Pettijohn F J. Sedimentary rocks[M]. New York: Harper & Row, 1975. [5] Schlee J. Upland gravels of southern Maryland[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1957, 68(10): 1371-410. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1957)68[1371:UGOSM]2.0.CO;2 [6] Sloss L. Stratigraphic models in exploration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1962, 46(7): 1050. http://archives.datapages.com/data/meta/sepm/journals/v01-32/data/032/032003/pdfs/0415_firstpage.pdf [7] Harbaugh J W, Bonham-Carter G. Computer simulation in geology[M]. [S. l. ]: Stanford Univ. Calif., 1970. [8] Allen J R. Physical processes of sedimentation[M]. New York: American Elsevier Pub. Co., 1970. [9] Pitman Iii W C. Relationship between eustacy and stratigraphic sequences of passive margins[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1978, 89(9): 1389-1403. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1978)89<1389:RBEASS>2.0.CO;2 [10] Jordan T E. Thrust loads and foreland basin evolution, Cretaceous, Western United States[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1981, 65(12): 2506-2520. http://terra.rice.edu/department/faculty/morganj/ESCI536/Readings/sevier/Jordan-AAPGBull1981.pdf [11] Tetzlaff D M, Harbaugh J W. Simulating clastic sedimentation[M]. New York: Springer, 1989. [12] Strobel J, Cannon R, Christopher G S, et al. Interactive (Sedpak) simulation of clastic and carbonate sediments in shelf to basin settings[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 1989, 15(8): 1279-1290. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034998432410_b42b.html [13] Granjeon D, Joseph P. Concepts and applications of a 3-D multiple lithology, diffusive model in stratigraphic modeling[C]//Harbaugh J W, Watney W L, Rankey E C, et al. Numerical experiments in stratigraphy: Recent advances in stratigraphic and sedimentologic computer simulations. [S. l. ]: [s. n. ], 1999: 197-210. [14] Syvitski J P, Milliman J D. Geology, geography, and humans battle for dominance over the delivery of fluvial sediment to the coastal ocean[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2007, 115(1): 1-19. doi: 10.1086/509246 [15] Hall B, Meiburg E, Kneller B. Channel formation by turbidity currents: Navier-stokes-based linear stability analysis[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2008, 615: 185-210. doi: 10.1017/S0022112008003467 [16] Pyrcz M J, Catuneanu O, Deutsch C V. Stochastic surface-based modeling of turbidite lobes[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2005, 89(2): 177-191. doi: 10.1306/09220403112 [17] Salles T, Duclaux G. Combined hillslope diffusion and sediment transport simulation applied to landscape dynamics modelling[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2015, 40(6): 823-839. doi: 10.1002/esp.3674 [18] Pyrcz M J, Sech R P, Covault J A, et al. Stratigraphic rule-based reservoir modeling[J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 2015, 63(4): 287-303. doi: 10.2113/gscpgbull.63.4.287 [19] 杜威, 纪友亮, 李其海, 等. 不同沉积过程尺度下正演数值模拟研究进展及油气地质意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(2): 62-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202002009.htmDu W, Ji Y L, Li Q H, et al. Sedimentary forward numerical modeling at different sedimentary scales: Progress and hydrocarbon significance[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(2): 62-71(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202002009.htm [20] Li J, Liu P, Sun S, et al. Sedapp V2021: A nonlinear diffusion-based forward stratigraphic model for shallow marine environments[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2021, 14(8): 4925-4937. doi: 10.5194/gmd-14-4925-2021 [21] Sylvester Z, Pirmez C, Cantelli A. A model of submarine channel-levee evolution based on channel trajectories: Implications for stratigraphic architecture[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(3): 716-727. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.05.012 [22] Refice A, Giachetta E, Capolongo D. Signum: A Matlab, TIN-based landscape evolution model[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2012, 45: 293-303. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Domenico_Capolongo/publication/220027603_SIGNUM_A_Matlab_TIN-based_landscape_evolution_model/links/00b4951a098c5d0a2f000000.pdf?ev=pub_ext_doc_dl_meta [23] 杨蓉. 几种地形演化的数值模拟模型简述[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(6): 1173-1184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.06.006Yang R. A brief review of several models of topographic evolution[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2017, 39(6): 1173-1184(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.06.006 [24] Yi A. Modeling of flow and migration of subaerial and submarine meandering channels[D]. [S. l. ]: University of South Carolina, 2006. [25] 舒晓, 金宝强, 缪飞飞, 等. 基于曲流河演化模拟的海上大井距油田点坝内部构型建模方法[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2019, 12(1): 38-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ201901008.htmShu X, Jin B Q, Miao F F, et al. Internal architecture modeling of point bar in offshore oilfields with large well-spacing based on evolution simulation of meandering river[J]. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 2019, 12(1): 38-43(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ201901008.htm [26] Liang M, Voller V, Paola C. A reduced-complexity model for river delta formation: Part 1. Modeling deltas with channel dynamics[J]. Earth Surface Dynamics, 2015, 3(1): 67-86. doi: 10.5194/esurf-3-67-2015 [27] Liang M, Geleynse N, Edmonds D, et al. A reduced-complexity model for river delta formation: Part 2. Assessment of the flow routing scheme[J]. Earth Surface Dynamics, 2015, 3(1): 87-104. doi: 10.5194/esurf-3-87-2015 [28] Bertoncello A, Sun T, Li H, et al. Conditioning surface-based geological models to well and thickness data[J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 2013, 45(7): 873-893. doi: 10.1007/s11004-013-9455-4 [29] Horton P, Jaboyedoff M, Rudaz B E, et al. Flow-R, a model for susceptibility mapping of debris flows and other gravitational hazards at a regional scale[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2013, 13(4): 869-885. doi: 10.5194/nhess-13-869-2013 [30] Miura H. Fusion analysis of optical satellite images and digital elevation model for quantifying volume in debris flow disaster[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(9): 1096. doi: 10.3390/rs11091096 [31] Rickenmann D. Empirical relationships for debris flows[J]. Natural Hazards, 1999, 19(1): 47-77. doi: 10.1023/A:1008064220727 [32] 刘泽, 李三忠, Bukhari S W H, 等. 动态古地貌再造: Badlands软件在盆地分析中的应用[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(1): 29-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202001002.htmLiu Z, Li S Z, Bukhari S W H, et al. Reconstruction of dynamic palaeogeomorphy: Application of Badlands software in basin analysis[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography: Chinese Edition, 2020, 22(1): 29-38(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202001002.htm [33] 李少华, 刘显太, 王军, 等. 基于沉积过程建模算法Alluvsim的改进[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(1): 140-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301016.htmLi S H, Liu X T, Wang J, et al. Improvement of the alluvsim algorithm modeling based on depositional processes[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(1): 140-144(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301016.htm [34] 黄秀, 刘可禹, 邹才能, 等. 鄱阳湖浅水三角洲沉积体系三维定量正演模拟[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(5): 1005-1013. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201305012.htmHuang X, Liu K Y, Zou C N, et al. Forward stratigraphic modelling of the depositional process and evolution of shallow water deltas in the Poyang Lake, southern China[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2013, 38(5): 1005-1013(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201305012.htm [35] Ikeda S, Parker G, Sawai K. Bend theory of river meanders: Part 1. Linear development[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1981, 112: 363-377. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035831603110_01e4.html [36] 冯文杰, 吴胜和, 张可, 等. 曲流河浅水三角洲沉积过程与沉积模式探讨: 沉积过程数值模拟与现代沉积分析的启示[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(9): 2047-2064. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201709009.htmFeng W J, Wu S H, Zhang K, et al. Depositional process and sedimentary model of meandering-river shallow delta: Insights from numerical simulation and modern deposition[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(9): 2047-2064 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201709009.htm [37] 贺婷婷, 谈心, 段太忠, 等. 综合沉积正演与多点地质统计模拟辫状河三角洲: 以塔河T区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 54-66. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0301He T T, Tan X, Duan T Z, et al. Integrated sedimentary forward modeling and multipoint geostatistics in braided river delta simulation: A case from Block T of Tahe Oilfield[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 54-66(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0301 [38] 张文彪, 段太忠, 刘彦锋, 等. 定量地质建模技术应用现状与发展趋势[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 264-275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903029.htmZhang W B, Duang T Z, Liu Y F, et al. Application status and development trend of quantitative geological modeling[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 264-275(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903029.htm [39] 谷宇峰, 张道勇, 鲍志东, 等. 利用GS-LightGBM机器学习模型识别致密砂岩地层岩性[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 224-234. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0416Gu Y F, Zhang D Y, Bao Z D, et al. Lithology prediction of tight sandstone formation using GS-LightGBM hybrid machine learning model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 224-234(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0416 [40] Harris A D, Baumgardner S E, Sun T, et al. A poor relationship between sea level and deep-water sand delivery[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2018, 370: 42-51. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S0037073818300939&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1523590335&md5=6aa41c84fc003cd7198367dbe56d0254 [41] Zhang J, Kim W, Olariu C, et al. Accommodation-versus supply-dominated systems for sediment partitioning to deep water[J]. Geology, 2019, 47(5): 419-422. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/331657015_Accommodation-_versus_supply-dominated_systems_for_sediment_partitioning_to_deep_water [42] 高抒. 海洋沉积地质过程模拟: 性质与问题及前景[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201105003.htmGao S. Numerical modeling of marine sedimentary processes: The nature, scientific problems, and prospect[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(5): 1-7(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201105003.htm -





 下载:
下载: