Evolution of groundwater fluoride in land subsidence areas after groundwater cessation: A case study at Cangzhou
-
摘要:
南水北调工程极大改善了我国北方的用水问题, 进一步减少了深层地下水的开采量, 缓解了华北平原地下水长期亏损的情况, 但其对区域地下水水化学演化的影响尚未可知。以地面沉降典型分布区沧州市为研究对象, 研究南水北调工程通水及地下水停采后对地下水水化学的影响。采集2017年及2021年区域第Ⅲ、Ⅳ层承压地下水样品, 探究水化学特征, 并通过SBAS-InSAR技术进一步评估区域年均地面形变量, 分析地下水停采后区域水质及氟时空变化的影响。研究发现: 压缩开采后深层地下水氟含量略微降低, 高值区面积减小, 高pH、TDS和
ρ (HCO3-), 低ρ (Ca2+)的地下水环境有利于氟的富集; 水化学类型没有改变, 地下水盐分含量升高, 岩盐、萤石溶解更充分; 同时, 全区地面沉降量及沉降速率较南水北调工程实施前明显放缓, 东南部存在小面积地面抬升区。地面沉降的减缓抑制了隔水层黏土压密释水, 减弱黏土孔隙高氟水的直接释放, 侧向径流补给占比上升, 含水层得到的有效补给变多, 使得区域地下水中氟浓度降低。但较长的水力停留时间及水岩相互作用, 可促使沉积物蒸发岩溶解迁移进入地下水中, 使得近海区域深层地下水中盐分含量升高。研究成果对沧州市饮用水安全和水资源管理提供了科学依据。Abstract:Objective The South-to-North Water Transfer Project (SNWTP) has improved water use in northern China and further reduced deep groundwater extraction in the North China Plain. However, its impact on the evolution of regional groundwater hydrochemistry is still unknown.
Methods In this paper, Cangzhou, which has experienced severe land subsidence due to groundwater overexploitation and has received water resources from the SNWTP since 2015, was selected as the study area to investigate the effects of the SNWTP on groundwater chemistry. In 2017 and 2021, groundwater samples from Ⅲ and Ⅳ confined aquifers were collected to determine the hydrochemical characteristics. Moreover, the average annual land subsidence of the regional layer was further evaluated by using SBAS-InSAR to identify the correlation between variations in land deformation and changes in groundwater chemistry.
Results The results showed that in comparison with those before the SNWTP, the groundwater fluoride concentration was slightly decreased, and the area of the high value zone was reduced after the SNWTP. The groundwater environment characterized by high pH, TDS and HCO3- concentrations and low Ca2+ concentrations favors fluoride enrichment in groundwater. The water chemistry type did not change, and the salinity concentrations in groundwater increased after the SNWTP. Groundwater receives more dissolution of halite and fluorite. Meanwhile, the amount and rate of land subsidence slowed after the SNWTP. A small degree of land uplift was even observed in the southeastern part of the region. The inhibition of land subsidence constrains clay compaction and the release of high fluoride porewater trapped in the clay layer. As a result, aquifers Ⅲ and Ⅳ received more effective lateral recharge, thereby causing a slight decrease in groundwater fluoride. However, it needs to be noted that the longer hydraulic residence time and stronger water-rock interaction after the SNWTP interaction promote the dissolution of sediment evaporites into groundwater, leading to an increase in groundwater salinity.
Conclusion The results of the study provide scientific support for drinking water safety and water resource management in Cangzhou.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- fluorine /
- South-to-North Water Transfer /
- groundwater cessation /
- land subsidence
-
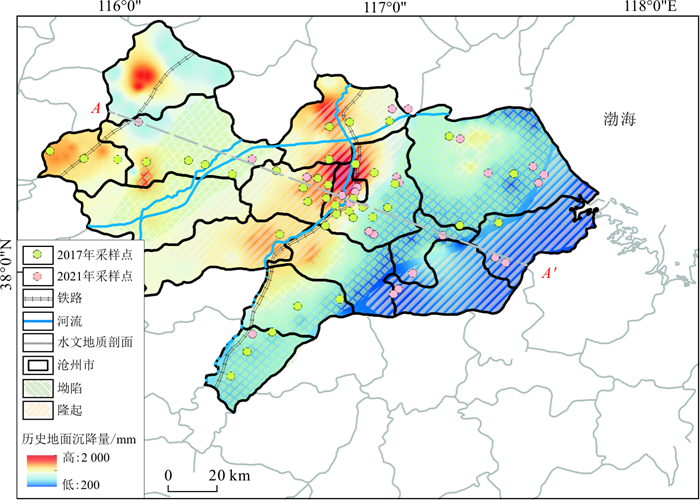
图 2 研究区水文地质剖面图[8]
Figure 2. Hydrogeological cross section of the study area
图 8 沧州市中部地区平均形变速率与2017-2021年ρ(F-)变化量(a), 区域1(b)和区域2(c)2017-2021年ρ(F-)变化量与形变速率的关系
Figure 8. Map of the mean deformation rate across central Cangzhou and the amount of change in F-concentration from 2017 to 2021(a), correlations between the amount of change in F-concentration and the deformation rate from 2017 to 2021 for region 1(b) and region 2(c)
表 1 沧州市第四系含水层地层、含水层组和岩性描述[26-28]
Table 1. Description of aquifer stratigraphy, aquifer group and lithology of the Quaternary aquifer in Cangzhou
含水层组 统 符号 底板埋深/m 总厚度/m 岩性描述 第1含水层组(Ⅰ) 全新统 Q4 15~30 20~30 含淤泥质粉土、粉质黏土夹细砂粉砂 第2含水层组(Ⅱ) 上更新统 Q3 120~220 50~150 粉土、粉质黏土、粉细砂、中细砂、卵石 第3含水层组(Ⅲ) 中更新统 Q2 250~350 80~180 粉质黏土夹砂、砾石 第4含水层组(Ⅳ) 下更新统 Q1 350~550 100~200 厚层黏土、粉质黏土夹砂 表 2 地下水样品常规水化学参数统计分析
Table 2. Statistical analysis of routine hydrochemical parameters of groundwater samples
指标 2017年 2021年 中位数 平均值 最大值 最小值 中位数 平均值 最大值 最小值 pH 8.25 8.27 9.03 7.82 9.01 8.94 10.06 6.95 ρ(TDS)/(mg·L-1) 858.3 960.6 2 203.0 288.8 1 292.0 1 477.0 3 596.0 320.0 ρ(F-)/(mg·L-1) 3.40 3.46 7.353 0.561 2.95 3.06 5.89 1.18 ρ(Cl-)/(mg·L-1) 137.6 199.1 657.2 34.01 386.9 537.2 1 760.0 30.47 ρ(SO42-)/(mg·L-1) 191.1 209.6 542.5 40.44 157.2 222.9 537.6 26.90 ρ(HCO3-+CO32-)/(mg·L-1) 365.9 338.4 491.7 130.6 350.2 308.4 547.8 102.8 ρ(K+)/(mg·L-1) 1.04 1.21 3.09 0.34 1.36 1.68 9.85 0.25 ρ(Na+)/(mg·L-1) 325.3 348.3 811.2 88.39 428.3 488.4 1 009 121.6 ρ(Ca2+)/(mg·L-1) 13.74 16.47 57.89 4.72 18.12 28.39 178.6 未检出 ρ(Mg2+)/(mg·L-1) 11.7 13.18 36.21 0.95 3.95 8.94 75.34 未检出 ρ(NO3-)/(mg·L-1) 0 0.09 3.32 未检出 0 0.04 1.02 未检出 Cl/Br摩尔比 1 468 1 355 2 501 530.4 1 020 1 090 1 929 468.8 -
[1] Wang Y X, Zheng C M, Ma R. Review: Safe and sustainable groundwater supply in China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26(8): 1301-1324. [2] Wang Y X, Shvartsev S L, Su C L. Genesis of arsenic/fluoride-enriched soda water: A case study at Datong, northern China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(4): 641-649. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.12.015 [3] Brahman K D, Kazi T G, Afridi H I, et al. Evaluation of high levels of fluoride, arsenic species and other physicochemical parameters in underground water of two sub districts of Tharparkar, Pakistan: A multivariate study[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(3): 1005-1020. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.10.042 [4] 潘欢迎, 邹常健, 毕俊擘, 等. 新疆阿克苏典型山前洪积扇内高氟地下水的化学特征及氟富集机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 194-203. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0312Pan H Y, Zou C J, Bi J B, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and fluoride enrichment mechanisms of high-fluoride groundwater in a typical piedmont proluvial fan in Aksu area, Xinjiang, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 194-203(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0312 [5] Rango T, Bianchini G, Beccaluva L, et al. Geochemistry and water quality assessment of central main ethiopian rift natural waters with emphasis on source and occurrence of fluoride and arsenic[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2010, 57(5): 479-491. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2009.12.005 [6] Wang Z, Guo H M, Xing S P, et al. Hydrogeochemical and geothermal controls on the formation of high fluoride groundwater[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 598(1/2): 126372. [7] Berger T, Mathurin F A, Drake H, et al. Fluoride abundance and controls in fresh groundwater in Quaternary deposits and bedrock fractures in an area with fluorine-rich granitoid rocks[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 569: 948-960. [8] Li J X, Wang Y T, Zhu C J, et al. Hydrogeochemical processes controlling the mobilization and enrichment of fluoride in groundwater of the North China Plain[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 730: 138877. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138877 [9] Li J X, Zhou H L, Qian K, et al. Fluoride and iodine enrichment in groundwater of North China Plain: Evidences from speciation analysis and geochemical modeling[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 598: 239-248. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.158 [10] Xing L N, Guo H, Zhan Y H. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and processes along flow paths in the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 70/71: 250-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.017 [11] Martinez-noguez I, Hinkelmann R. Land subsidence caused by a single water extraction well and rapid water infiltration[J]. Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences, 2015, 372: 33-38. doi: 10.5194/piahs-372-33-2015 [12] Avilés J, Pérez-Rocha L E. Regional subsidence of mexico city and its effects on seismic response[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2010, 30(10): 981-989. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2010.04.009 [13] Wang G, Turco M, Soler T, et al. Comparisons of OPUS and PPP solutions for subsidence monitoring in the greater Houston area[J]. Journal of Surveying Engineering, 2017, 143(4): 05017005. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000241 [14] 沈水龙, 许烨霜, 陶野郁雄. 海洋沉积环境中深层地下水溶性天然气开采引起的地面沉降[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(6): 1094-1098. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200606002.htmShen S L, Xu Y S, Tohno I. Land subsidence due to withdrawal of water soluble natural gas from deep marine sediments[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(6): 1094-1098(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200606002.htm [15] Tsutomu Y, Jun S, Maki T, et al. Tracing a confined groundwater flow system under the pressure of excessive groundwater use in the lower central plain, Thailand[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2011, 25(17): 2654-2664. doi: 10.1002/hyp.8007 [16] Sahu P, Sikdar P K. Threat of land subsidence in and around Kolkata City and East Kolkata Wetlands, West Bengal, India[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2011, 120(3): 435-446. doi: 10.1007/s12040-011-0077-2 [17] Esteller M V, Andreu J M. Anthropic effects on hydrochemical characteristics of the Valle De Toluca aquifer (central Mexico)[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2005, 13(2): 378-390. doi: 10.1007/s10040-004-0395-4 [18] Smith R, Knight R, Fendorf S. Overpumping leads to California groundwater arsenic threat[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 2089-2094. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04475-3 [19] 成建梅, 柳璨, 李敏敏, 等. 城市化进程下北京平原渗流场与地面沉降发展演化模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 43-52. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0105Cheng J M, Liu C, Li M M, et al. Numerical study on evolution of groundwater hydrodynamics and land subsidence under the process of metropolitan urbanization in Beijing Plain, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 43-52(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0105 [20] 薛禹群, 张云. 长江三角洲南部地面沉降与地裂缝[J]. 华东地质, 2016, 37(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ201601002.htmXue Y Q, Zhang Y. Ground subsidence and ground fractures in the southern Yangtze River Delta[J]. East China Geology, 2016, 37(1): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ201601002.htm [21] 刘勇. 黄河三角洲地区地面沉降时空演化特征及机理研究[D]. 山东青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2013.Liu Y. Spatiotemporal evolution of land subsidence and mechanism discussion in the Yellow River Delta, China[D]. Qingdao Shandong: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanography), 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] 李嘉, 唐河, 饶维龙, 等. 南水北调工程对华北平原水储量变化的影响[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2020, 37(6): 775-783. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB202006008.htmLi J, Tang H, Rao W L, et al. Influence of South-to-North Water Transfer Project on the changes of terrestrial water storage in North China Plain[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 37(6): 775-783(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB202006008.htm [23] 张婷婷, 杨刚, 张建国, 等. 南水北调东线一期工程输水干线水质变化趋势分析[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2022, 43(1): 8-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCAN202201002.htmZhang T T, Yang G, Zhang J G, et al. Trend analysis of water quality changes in the transmission trunk line of the first phase of the South-North Water Transfer Project[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2022, 43(1): 8-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCAN202201002.htm [24] 王英虎, 郭世娟. 河北省地下水超采综合治理河湖地下水回补试点做法及成效[J]. 中国水利, 2020, 895(13): 35-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLZG202013023.htmWang Y H, Guo S J. Pilot projects for controlling of groundwater overexploitation in Hebei Province by recharging water to aquifers near rivers and lakes[J]. China Water Resources, 2020, 895(13): 35-36(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLZG202013023.htm [25] 罗勇, 田芳, 秦欢欢, 等. 地下水人工回灌和停采对地面沉降控制的影响分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2020, 31(1): 52-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ202001008.htmLuo Y, Tian F, Qin H H, et al. Effects of groundwater artificial recharge and the termination of groundwater exploitation on land subsidence control[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2020, 31(1): 52-57(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ202001008.htm [26] 邢丽娜. 华北平原典型剖面上地下水化学特征和水文地球化学过程[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.Xing L N. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and hydrogeochemical processes approximately along the flow paths in the North China Plain[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2012(in Chinese with English abstract). [27] 陈建平, 毛宏涛, 王明玉, 等. 沧州深层地下水氟的分布及演化规律[J]. 地球与环境, 2015, 43(6): 607-618. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201506003.htmChen J P, Mao H T, Wang M Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and development mechanism of fluoride in deep groundwater in Cangzhou area, China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2015, 43(6): 607-618(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201506003.htm [28] 薛肖斌, 李俊霞, 钱坤, 等. 华北平原原生富碘地下水系统中碘的迁移富集规律: 以石家庄-衡水-沧州剖面为例[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(3): 910-921. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201803022.htmXue X B, Li J X, Qian K, et al. Spatial distribution and mobilization of iodine in groundwater systems of North China Plain: Taking hyrogeological section from Shijiazhuang, Hengshui to Cangzhou as an example[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(3): 910-921(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201803022.htm [29] Li X Q, Zhou A G, Gan Y Q, et al. Controls on the δ34S and δ18O of dissolved sulfate in the Quaternary aquifers of the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 400(3): 312-322. [30] Matsumoto T, Chen Z, Wei W, et al. Application of combined Kr-81 and He-4 chronometers to the dating of old groundwater in a tectonically active region of the North China Plain[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 493: 208-217. [31] 席北斗, 李娟, 汪洋, 等. 京津冀地区地下水污染防治现状、问题及科技发展对策[J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201901001.htmXi B D, Li J, Wang Y, et al. Strengthening the innovation capability of groundwater science and technology to support the coordinated development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region: Status Quo, Problems and Goals[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(1): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201901001.htm [32] 谢先军, 刘红杏, 高爽, 等. 典型纳污坑塘周边地下水污染来源识别及其健康风险评估[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 34-42. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0104Xie X J, Liu H X, Gao S, et al. Source identification and health risk assessment of groundwater pollution in typical sewage pits and ponds[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 34-42 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0104 [33] 朱菊艳. 沧州地区地面沉降成因机理及沉降量预测研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.Zhu J Y. Research on land subsidence mechanism and prediction of settlement in Cangzhou area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [34] 张玲, 葛大庆, 郭小方, 等. 近十年来沧州地区地面沉降演化状况[J]. 上海国土资源, 2014, 35(4): 72-75, 80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD201404019.htmZhang L, Ge D Q, Guo X F, et al. Land subsidence in Cangzhou over the last decade based on interferometric time series analysis[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 2014, 35(4): 72-75, 80(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD201404019.htm [35] Liu X X, Wang Y J, Yan S Y. Ground deformation associated with exploitation of deep groundwater in Cangzhou City measured by multi-sensor synthetic aperture radar images[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(1): 6. [36] 俞晓莹. 改进的SBAS地表形变监测及地下水应用研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.Yu X Y. Improved SBAS technology for land deformation detection and groundwater application[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012(in Chinese with English abstract). [37] 罗三明, 单新建, 朱文武, 等. 多轨PSInSAR监测华北平原地表垂直形变场[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(10): 3129-3139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201410004.htmLuo S M, Shan X J, Zhu W W, et al. Monitoring vertical ground deformation in the North China Plain using the multitrack PSInSAR technique[J]. Chinese J. Geophys, 2014, 57(10): 3129-3139(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201410004.htm [38] 田振君. 沧州市浅层地下水质量现状与变化趋势分析[J]. 地下水, 2020, 42(2): 38-40, 113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU202002012.htmTian Z J. Analysis of the current situation and change trend of shallow groundwater quality in Cangzhou City[J]. Ground water, 2020, 42(2): 38-40, 113(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU202002012.htm [39] 何锦, 范基姣, 刘元晴, 等. 沧州地区微咸水水化学特征及灌溉水质评价[J]. 人民黄河, 2016, 38(5): 134-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201605034.htmHe J, Fan J J, Liu Y Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics and irrigation water quality evaluation of Salinwater in Cangzhou region[J]. Yellow River, 2016, 38(5): 134-138(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201605034.htm [40] 毛宏涛. 沧州深层高氟地下水氟分布及演化规律研究[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2015.Mao H T. Distribution characteristics and development mechanism of fluorine in deep groundwater in Cangzhou[D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University of Engineering and Technology, 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [41] 雷德林, 付学功, 耿红凤, 等. 沧州市高氟水分布规律及环境影响分析[J]. 水资源保护, 2007, 98(2): 43-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZYB200702010.htmLei D L, Fu X G, Geng H F, et al. Distribution rules of high fluoride water and its environmental impacts in Cangzhou City[J]. Water resources protection, 2007, 98(2): 43-46(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZYB200702010.htm [42] 付晓娣. 沧州地下水流与地面沉降耦合模拟评价[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.Fu X D. The coupled modeling and evaluation of groundwater flow and land subsidence in Cangzhou[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [43] 黄建华, 鲍锋, 王蕴晨, 等. 并行差异断面顶管施工对地表变形的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 185-192. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0618Huang J H, Bao F, Wang Y C, et al. Influence of ground-surface deformation in pipe jacking construction with parallel differential section[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 185-192(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0618 [44] Li J X, Wang Y X, Xie X J, et al. Hierarchical cluster analysis of arsenic and fluoride enrichments in groundwaterfrom the Datong Basin, Northern China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 118: 77-89. [45] Kwong H T, Jiao J J, Liu K, et al. Geochemical signature of pore water from core samples and its implications on the origin of saline pore water in Cangzhou, North China Plain[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 157: 143-152. [46] Guo H M, Zhang Y, Xing L N, et al. Spatial variation in arsenic and fluoride concentrations of shallow groundwater from the town of Shahai in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2012, 27(11): 2187-2196. [47] Kumar M, Das N, Goswami R, et al. Coupling fractionation and batch desorption to understand arsenic and fluoride Co-contamination in the aquifer system[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 164: 657-667. [48] Pi K F, Wang Y X, Xie X J, et al. Hydrogeochemistry of co-occurring geogenic arsenic, fluoride and iodine in groundwater at datong basin, Northern China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 300: 652-661. [49] Liu H Y, Guo H M, Yang L J, et al. Occurrence and formation of high fluoride groundwater in the Hengshui area of the North China Plain[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74(3): 2329-2340. [50] Zhou Z M, Zhang G H, Yan M J, et al. Spatial variability of the shallow groundwater level and its chemistry characteristics in the low plain around the Bohai Sea, North China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2012, 184(6): 3697-3710. [51] Richard A, Banks D A, Mercadier J, et al. An evaporated seawater origin for the ore-forming brines in unconformity-related uranium deposits (Athabasca Basin, Canada): Cl/Br and δ37Cl analysis of fluid inclusions[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75(10): 2792-2810. [52] Cartwright I, Weaver T R, Fifield L K. Cl/Br ratios and environmental isotopes as indicators of recharge variability and groundwater flow: An example from the Southeast Murray Basin, Australia[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 231(1): 38-56. -





 下载:
下载: