Geochemical characteristics of light hydrocarbons in condensate oil from the southwestern Huizhou of the Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要:
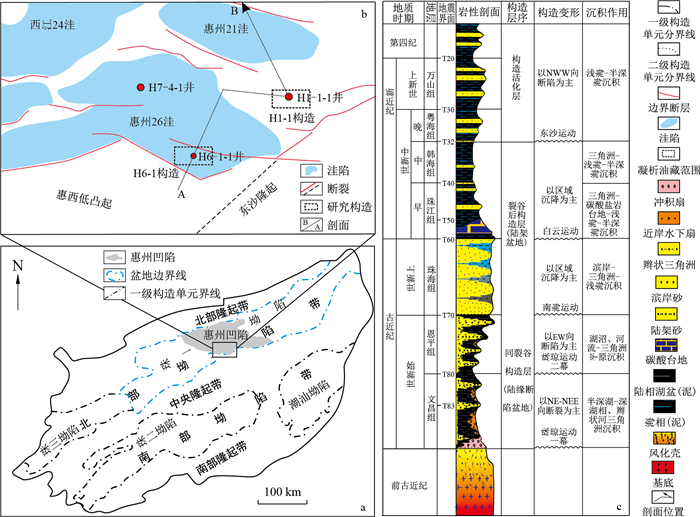
惠西南地区是珠江口盆地珠一坳陷重要的原油富集区, 但近年来在新近系珠江组上段和古近系恩平组、文昌组以及基岩潜山储层中陆续发现了凝析油气。利用全油气相色谱和饱和烃色谱-质谱分析技术对凝析油样开展了轻烃和生物标志化合物地球化学特征分析, 探讨了惠西南地区凝析油的成因。研究表明: 轻烃组分特征、C7异构烷烃、环烷烃及正构烷烃和生物标志化合物特征均指示H6-1构造凝析油来源于半深湖-深湖相文昌组烃源岩, 为腐泥型烃源岩在相对高成熟阶段(
R o处于1.2%~1.3%)生成的凝析油; H1-1构造凝析油来源于浅湖沼泽相恩平组烃源岩, 为偏腐殖型烃源岩在相对低成熟阶段(R o处于0.9%~1.1%)生成的富低碳数烷烃油气; 揭示了惠西南凝析油的形成受到烃源母质类型和热演化阶段的双重控制。研究结果为富油生烃凹陷凝析油气勘探潜力评价分析提供了地球化学依据和支撑。Abstract:The southwestern Huizhou is an important crude oil enrichment area in the Zhu Ⅰ Depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin. However, condensate oil and gas have been discovered in the upper memberof Neogene Zhujiang Formation, Paleogene Enping and Wenchang formations, and basement buried hill reservoirs in recent years. In this study, the origin of condensate oil was revealed based on the integration of light hydrocarbons and biomarkers characteristics, which were obtained from GC of whole-oil and GC-MS of saturated fractions.The results, including light hydrocarbon composition, C7 is o-alkanes, naphthene, n-alkanes and other biomarkers indicate that the condensate oil in the H6-1 structure came from the semi-deep to deep lacustrine source rock in Wenchang Formation, which was generated by sapropelic kerogen with relatively high maturity (1.2%-1.3%
R o). In contrast, the condensate oil in the H1-1 structure originated from the shallow lake to peat facies source rock in Enping Formation, the oil was rich in alkanes with low-carbon number which was generated by humic kerogen with relatively low maturity (0.9%-1.1%R o).The results suggest that the formation of condensate oil in the southwestern Huizhou is both controlled by organic matter type and thermal evolution stage of source rock. This study provides a geochemical basis and support for the evaluation and analysis of condensate oil and gas exploration potential in hydrocarbon-rich depressions.-
Key words:
- condensate oil /
- light hydrocarbons /
- biomarkers /
- Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
图 4 C7轻烃稳态催化动力学演化模式示意图[12]
P1.正庚烷;P2.2-甲基已烷+3-甲基已烷;N2.1, 1-二甲基环戊烷+1, 3-二甲基环戊烷(顺、反);P3.3-乙基戊烷+3, 3-二甲基戊烷+2, 3-二甲基戊烷+2, 4-二甲基戊烷+2, 2-二甲基戊烷+2, 2, 3-三甲基丁烷;N15.乙基环戊烷+1, 2-二甲基环戊烷(顺、反);N16.甲苯+甲基环已烷
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of steady-state catalytic kinetics evolution mode for C7 light hydrocarbons
图 5 惠西南地区凝析油轻烃N16/N15-(N16+N15)/(P2+P3+N2)分布图
P2.2-甲基已烷+3-甲基已烷;N2.1, 1-二甲基环戊烷+1, 3-二甲基环戊烷(顺、反);P3.3-乙基戊烷+3, 3-二甲基戊烷+2, 3-二甲基戊烷+2, 4-二甲基戊烷+2, 2-二甲基戊烷+2, 2, 3-三甲基丁烷;N15.乙基环戊烷+1, 2-二甲基环戊烷(顺、反);N16.甲苯+甲基环已烷
Figure 5. Distribution of light hydrocarbons N16/N15-(N16+N15)/(P2+P3+N2) of condensate oil in the southwestern Huizhou
图 11 惠西南地区凝析油成藏模式图(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 11. Accumulation model of condensate oil in the southwestern Huizhou
表 1 惠西南地区凝析油物性特征
Table 1. Physical properties of condensate oil in the southwestern Huizhou
凝析油藏 密度20℃/(t·m-3) 黏度50℃/(mPa·s) 含蜡量/% 凝固点/℃ H6-1 0.767 0.815 5.7 11 H1-1 0.740 0.023 — 6 注:—低于检测下限 表 2 用于轻烃C7星状图的化合物沸点和水溶解度[15]
Table 2. Parameters for the star chart of C7 light hydrocarbons
化合物名称 沸点/℃ 水溶解度/10-6 2, 2-二甲基戊烷 79.2 4.4 2, 3-二甲基戊烷 89.8 5.3 2, 4-二甲基戊烷 80.5 4.4 3, 3-二甲基戊烷 86.1 5.9 3-乙基戊烷/ 93.5 3.0 P3 85.0 5.0 -
[1] Walters C C, Isaksen G H, Peters K E. Applications of light hydrocarbon molecular and isotopic compositions in oil and gas exploration: Analytical Advances for Hydrocarbon Research[M]. New York: Springer, 2003. [2] 段毅, 赵阳, 姚泾利, 等. 轻烃地球化学研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(12): 1875-1887. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.12.1875Duan Y, Zhao Y, Yao J L, et al. Research advance and tendency of light hydrocarbon geochemistry[J]. Natureal Gas Geoscinece, 2014, 25(12): 1875-1887 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.12.1875 [3] 张学预, 田世澄. 轻烃的分析方法及其在石油地质研究中的意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 1983, 2(4): 91-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ198304026.htmZhang X Y, Tian S C. Analysis methods of light hydrocarbon and significance in research on oil geology[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1983, 2(4): 91-97 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ198304026.htm [4] 田立新, 刘杰, 张向涛, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州26-6大中型泛潜山油气田勘探发现及成藏模式[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202004001.htmTian L X, Liu J, Zhang X T, et al. Discovery and accumulation pattern of HZ26-6 large-medium sized pan-buried hill oil and gas field in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(1): 1-11 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202004001.htm [5] 施和生, 代一丁, 刘丽华, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷油气藏地质特征与分布发育基本模式[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(增刊2): 120-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2015S2011.htmShi H S, Dai Y D, Liu L H, et al. Geological characteristics and distribution model of oiland gasreservoirs in Zhu I depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(S2): 120-133 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2015S2011.htm [6] 朱明, 张向涛, 杨兴业, 等. 珠江口盆地惠南半地堑恩平组烃类充注特征与砂岩致密化成因分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(6): 14-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201806002.htmZhu M, Zhang X T, Yang X Y, et al. Hydrocarbon charging characteristics and sandstone densification genesis of Enping Formation in Huinan half-graben, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(6): 14-24 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201806002.htm [7] 陈维涛, 杜家元, 施和生, 等. 珠江口盆地惠西南地区复式油气成藏特征及富集规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(2): 194-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201502009.htmChen W T, Du J Y, Shi H S, et al. Compound hydrocarbon accumulation and enrichment in southwestern Huizhou area, Pearl River Mouth Basin, southern China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(2): 194-199 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201502009.htm [8] 戴金星. 各类烷烃气的鉴别[J]. 中国科学: B辑, 1992, 22(2): 185-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199202010.htmDai J X. Identification of various alkane gases[J]. Science China: Series B, 1992, 22(2): 185-193 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199202010.htm [9] 戴金星. 利用轻烃鉴别煤成气和油型气[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1993, 20(5): 26-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199305003.htmDai J X. Identification of coal formed gas and oil type gas by light hydrocarbons[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1993, 20(5): 26-32 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199305003.htm [10] 胡国艺, 李剑, 李谨, 等. 判识天然气成因的轻烃指标探讨[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 2007, 37(2): 111-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2007S2013.htmHu G Y, Li J, Li J, et al. Preliminary study on the origin identification of natural gas by the parameters of light hydrocarbon[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2007, 37(2): 111-117 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2007S2013.htm [11] Mango F D. An invariance in the isoheptanes of petroleum[J]. Science, 1987, 237: 514-517. [12] Mango F D. The origin of light hydrocarbons in petroleum: A kinetic test of the steady-state catalytic hypothesis[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1990, 54(5): 1315-1323. [13] Mango F D. The origin of light hydrocarbons in petroleum: Ring preference in the closure of carbocyclic rings[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(2): 895-901. [14] 张敏, 张俊. Mango轻烃参数的开发与应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1998, 25(6): 26-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK806.007.htmZhang M, Zhang J. Development and application of Mango's light hydrocarbon parameters[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1998, 25(6): 26-28 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK806.007.htm [15] Halpern H I. Development and applications of light-hydrocarbon-based star diagrams[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1995, 79(6): 801-815. [16] 张敏, 张俊, 徐中一. 轻烃星图在石油勘探中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1998, 25(4): 30-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK802.008.htmZhang M, Zhang J, Xu Z Y. Application of light hydrocarbon star diagrams in petroleum exploration[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1998, 25(4): 30-33 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK802.008.htm [17] Atwah I, Sweet S, Pantano J, et al. Light hydrocarbon geochemistry: Insight into Mississippian crude oil sources from the Anadarko Basin, Oklahoma, USA[J]. Geofluids, 2019, 2019(5): 1-15. [18] Thompson K. Light hydrocarbons in subsurface sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(5): 657-672. [19] 蒋启贵, 李志明, 张彩明, 等. 东营凹陷烃源岩轻烃特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2008, 27(5): 87-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200805016.htmJiang Q G, Li Z M, Zhang C M, et al. Characteristics of light hydrocarbons of source rocks in Dongying Depression[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2008, 27(5): 87-91(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200805016.htm [20] Thompson K. Classification and thermal history of petroleum based on light hydrocarbons[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1983, 47(2): 303-316. [21] 孙林婷. 莺—琼盆地原油地球化学特征及来源[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017.Sun L T. Geochemical characteristics and origins of oils inYinggehai and Qiongdongnan Basins[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017 (in Chinese with English abstract). [22] Hunt J M. Genesis of petroleum hydrocarbons in marine sediments[J]. Science, 1980, 209: 403-404. [23] 曾立飞. 准噶尔盆地侏罗系煤系烃源岩生烃动力学研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2020.Zeng L F. Petroleum generation kinetics of Jurassic coaly source rocks in Junggar Basin[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020 (in Chinese with English abstract). [24] 朱俊章, 施和生, 庞雄, 等. 珠江口盆地番禺低隆起凝析油地球化学特征及油源分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2006, 18(2): 103-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200602006.htmZhu J Z, Shi H S, Pang X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and oil sources of condensates in Panyu Low Uplift, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2006, 18(2): 103-106 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200602006.htm [25] 朱明, 施洋, 朱俊章, 等. 惠州凹陷HZ21-1构造油气成因来源及有利滚动勘探区预测[J]. 中国海上油气, 2017, 29(6): 12-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201706002.htmZhu M, Shi Y, Zhu J Z, et al. Hydrocarbon origin and favorable progressive exploration area of H1 structure in Huizhou Sag[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2017, 29(6): 12-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201706002.htm [26] 姜玉涵, 侯读杰, 刁慧, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷不同构造带原油陆源生物标志化合物特征及其指示意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 89-98. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0310Jiang Y H, Hou D J, Diao H, et al. Characteristics and indication of terrestrial biomarkers of crude oil in different local structures of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 89-98 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0310 [27] 刁慧, 邹玮, 李宁, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷武云亭构造油气来源与成藏模式[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 110-119. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0312Diao H, Zou W, Li N, et al. Hydrocarbon origin and reservoir forming model of Wuyunting structure in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 110-119(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0312 [28] 邓棚. 南海北部陆缘古近纪多幕裂陷作用属性及转换: 以珠江口盆地珠一坳陷为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.Deng P. The nature and tectonic transition of the multiphase rifting in the northern margin of the South China Sea: Based on the study of the ZhuⅠdepression in Pearl River Mouth basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: