Occurrence state and migration mechanism of arsenic in metal mines
-
摘要:
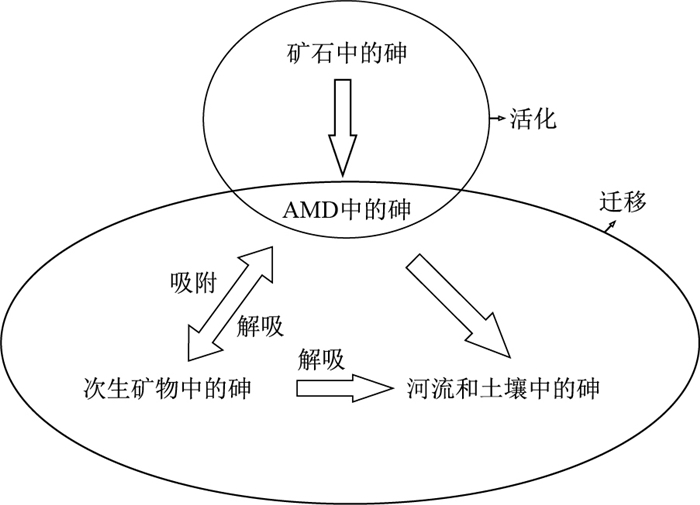
金属矿山在采矿、选矿、冶炼的过程中经常会产生环境污染的问题, 其中矿山酸性废水(acid mine drainage, 简称AMD)所带来的砷污染是最为严重的重金属污染问题之一。总结了砷在金属矿山中的赋存形态及其在不同矿物中活化、迁移的化学过程和形态转化规律, 认为: ①黄铁矿和毒砂是金属矿山中最普遍的含砷矿物; ②砷随着原生矿物的氧化溶解活化出来, 在AMD中主要以砷酸盐和亚砷酸盐的形态存在, 其中亚砷酸盐的迁移性更强; ③AMD中次生矿物(如黄钾铁钒、针铁矿、臭葱石等)吸附沉淀可以减缓砷的迁移速率、减少砷的迁移量但不能阻止砷的迁移。含砷矿物的次生氧化过程和次生矿物中砷的稳定能力研究可以对砷在矿山环境中迁移机制的深入理解和砷污染治理方案的制定提供新的思路和研究方向。
Abstract:Environmental pollution often occurs in the process of mining, beneficiation and smelting of metal mines.Arsenic pollution caused by acid mine drainage (AMD) is one of the most serious pollution problems of heavy metals. At present, the understanding of the evolution process of secondary minerals is insufficient. This paper summarizes the occurrence form of arsenic in metal sulfide.The specific chemical process of activation and migration in different minerals are discussed.Three rules of form transformation are concluded. ①Pyrite and arsenopyrite are the most common arsenic-bearing minerals in metal sulfide mines; ②Arsenic is activated by the oxidation and dissolution of primary minerals, existing mainly in the form of arsenate and arsenite in AMD of which arsenite is more migratory. ③Adsorptive precipitation of secondary minerals in AMD (such as ferro-vanadium, goethite, scallion, etc.) can slow the migration rate and reduce the migration amount of arsenic but cannot prevent the migration process. The migration mechanism of arsenic in the mine environment is reviewed, and new treatment schemes and research directions are proposed.
-
Key words:
- arsenic /
- occurrence state /
- activation and migration mechanism /
- secondary mineral /
- metal mine
-
表 1 常见的含砷矿物及化学式
Table 1. Common arsenic-bearing minerals and chemical formula
中文名称 英文名称 分子式 中文名称 英文名称 分子式 自然砷 arsenic As 雄黄 realgar As2S2 黄铁矿(含砷黄铁矿) pyrite(arsenian pyrite) FeS2-As 雌黄 orpiment As2S3 磁铁矿 pyrrhotite Fe1-xS 毒砂 arsenopyrite FeAsS 硫砷铜矿 enargite Cu3AsS4 砷黝铜矿 tennantite (Cu.Fe)12As4S13 砷铜矿 domeykite Cu3As 红砷镍矿 nickeline NiAs 砷锑矿 stibarsen SbAs 铂砷矿 sperrylite PtAs2 方钴矿 skutterudite Co4(As4)3 复砷镍矿 chloanthite (Ni.Co)As2-3 斜方砷铁矿 loellinglite FeAs2 砷镍矿 maucherite NiAs3 硫砷矿 dimorphite As4S3 淡红银矿 proustite Ag3AsS3 砷华 asenolite As2O3 辉砷钴矿 cobaltite CoAsS 白砷石 claudetite As2O3 臭葱石 scorodite FeAsO4·2H2O -
[1] 宋波, 刘畅, 陈同斌. 广西土壤和沉积物砷含量及污染分布特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 2017, 32(4): 654-668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZX201704011.htmSong B, Liu C, Chen T B. Contents and pollution distribution characteristics of arsenic in soils and sediments in Guangxi Zhang Autonomous Region[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2017, 32(4): 654-668(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZX201704011.htm [2] 杨娟. 矿山砷废石污染及其治理[J]. 工业安全与防尘, 1992, 18(5): 2-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYAF199205001.htmYang J. Pollution of arsenic waste rock in mine and its treatment[J]. Industrial Safety and Dustproof, 1992, 18(5): 2-3(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYAF199205001.htm [3] 魏忠义. 有色金属尾矿库土地复垦与环境治理的生态封闭模式[Z]. 中国江苏盐城, 2014.Wei Z Y. Ecological closure mode of land reclamation and environmental management of non-ferrous metal tailings Pond[Z]. Yancheng, Jiangsu, China, 2014(in Chinese). [4] Zhi Yuan, Li Z M T J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014(468/469): 843-853. [5] 郑刘根, 刘桂建, 高连芬, 等. 中国煤中砷的含量分布、赋存状态、富集及环境意义[J]. 地球学报, 2006, 27(4): 355-366. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.04.011Zheng L G, Liu G J, Gao L F, et al. Arsenic in chinese coals: Its abundance, distribution, modes of occurrence, enrichment processes, and environmental significance[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2006, 27(4): 355-366(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.04.011 [6] 王敬华. 地方性砷中毒研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 1997, 16(4): 80-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ704.016.htmWang J H. Research progress of endemicarsenism[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1997, 16(4): 80-84(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ704.016.htm [7] 陈志澄, 毋福海, 黄丽玫, 等. 砷矿尾砂污染及其治理研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2006, 28(3): 180-182.Chen Z C, Wu F H, Huang L M, et al. Study on pollution and remediation of arsenic minerals tailings, 2006, 28(3): 180-182(in Chinese with English abstract). [8] 刘崴, 胡俊栋, 路国慧. 石门雄黄矿区砷污染水平及风险评价[J]. 湖南科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 35(4): 96-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTKY202004014.htmLiu W, Hu J D, Lu G H. Assessment of arsenic contamination and risk in Shimen realgar mine[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Technology: Natural Science, 2020, 35(4): 96-102(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTKY202004014.htm [9] 温其谦, 阎秀兰, 申俊峰, 等. 半壁山金矿矿业活动区砷赋存的矿物特征及其对农田土壤砷累积的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(11): 5090-5097. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201911040.htmWen Q Q, Yan X L, Shen J F, et al. Mineral characteristics of arsenic in the active area of the Banbishan gold mine and its effect on arsenic accumulatic in farmland soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 40(11): 5090-5097(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201911040.htm [10] 王京. 云南个旧锡多金属矿区砷污染地球化学研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2011.Wang J. Geochemical study on arsenic pollution in Gejiu tin polymetallic mining area, Yunnan Province[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2011(in Chinese with English abstract). [11] 莫昌琍, 吴丰昌, 符志友, 等. 湖南锡矿山锑矿区农用土壤锑、砷及汞的污染状况初探[J]. 矿物学报, 2013, 33(3): 344-350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201303011.htmMo C L, Wu F C, Fu Z Y, et al. Antimony, arsenic and mercury polluton in agricultural soil of antimony mine area in Xikuangshan, Hunan[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2013, 33(3): 344-350(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201303011.htm [12] 雷鸣, 曾敏, 郑袁明, 等. 湖南采矿区和冶炼区水稻土重金属污染及其潜在风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2008, 28(6): 1212-1220. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.06.029Lei M, Zeng M, Zheng Y M, et al. Heavy metals pollution and potential ecological risk in paddy soils around mine areas and smelting areas in Hunan Province[J]. Acta Scientiae Environmentologica Sinica, 2008, 28(6): 1212-1220(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.06.029 [13] 吕达. 铜陵市冬瓜山铜矿区土壤重金属污染现状与评价[J]. 湖北理工学院学报, 2019, 35(1): 18-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSGD201901004.htmLu D. Situation and evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution in Dongguashan copper mine, Tongling[J]. Journal of Hubei University of Technology, 2019, 35(1): 18-22(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSGD201901004.htm [14] 朱翔宇, 王汝成, 陆现彩, 等. 湖南石门碳酸盐岩型雄黄矿含雄黄、雌黄尾矿中次生含砷矿物的研究[C]//中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第14届学术年会论文摘要专辑. 南京: 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会, 2013.Zhu X Y, Wang R C, Lu X C, et al. Study on secondary Arsenic-bearing minerals in tailings of Realgar and oecious yellow from Shimen Carbonate Realgar Deposit in Hunan Province[C]//Abstracts of Papers of the 14th Annual Conference of the Chinese Society of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry. Nanjing: 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [15] 肖细元, 陈同斌, 廖晓勇, 等. 中国主要含砷矿产资源的区域分布与砷污染问题[J]. 地理研究, 2008, 27(1): 201-212. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2008.01.022Xiao X Y, Chen T B, Liao X Y, et al. Regional distribution and arsenic pollution of arsenic-bearing mineral resources in China[J]. Geographical Research, 2008, 27(1): 201-212(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2008.01.022 [16] Sánchez España J, López Pamo E, Santofimia E, et al. Acid mine drainage in the Iberian Pyrite Belt (Odiel River watershed, Huelva, SW Spain): Geochemistry, mineralogy and environmental implications[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20(7): 1320-1356. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.01.011 [17] 史振环, 莫佳, 莫斌吉, 等. 有色金属矿山尾矿砷污染及其研究意义[J]. 有色金属: 矿山部分, 2015, 67(2): 58-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKU201502014.htmShi Z H, Mo J, Mo B J, et al. Arsenic pollution from tailings of non-ferrous metal mine and its research significance[J]. Nonferrous Metals: Mine Part, 2015, 67(2): 58-62(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKU201502014.htm [18] Cheng H, Hu Y, Luo J, et al. Geochemical processes controlling fate and transport of arsenic in acid mine drainage (AMD) and natural systems[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165(1/3): 13-26. [19] Asta M P, Cama J, Martínez M, et al. Arsenic removal by goethite and jarosite in acidic conditions and its environmental implications[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 171(1/3): 965-972. [20] Antelo J, Fiol S, Carabante I, et al. Stability of naturally occurring AMD-schwertmannite in the presence of arsenic and reducing agents[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 220: 106677. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106677 [21] 张皓月, 刘文波, 张绪教, 等. 河套平原地下水中砷的空间变异特征及影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 192-199. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0014Zhang H Y, Liu W B, Zhang X J, et al. Analysis of spatial variability and influencing factors of arsenic in groundwater of Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 192-199(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0014 [22] Coudert L, Bondu R, Rakotonimaro T V, et al. Treatment of As-rich mine effluents and produced residues stability: Current knowledge and research priorities for gold mining[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 386: 121920. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121920 [23] Tabelin C B, Corpuz R D, Igarashi T, et al. Acid mine drainage formation and arsenic mobility under strongly acidic conditions: Importance of soluble phases, iron oxyhydroxides/oxides and nature of oxidation layer on pyrite[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 399: 122844. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122844 [24] 曹烨, 孙小虹, 唐尧, 等. 中国砷矿成矿规律概要[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(增刊1): 806-807. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2015S1382.htmCao Y, Sun X H, Tang Y, et al. Synopsis of metallogenic regularity of arsenic deposits in China[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(S1): 806-807(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2015S1382.htm [25] Hu Z, Gao S. Upper crustal abundances of trace elements: A revision and update[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 253(3/4): 205-221. [26] Wu Y, Zhou X, Lei M, et al. Migration and transformation of arsenic: Contamination control and remediation in realgar mining areas[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2017, 77: 44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.05.012 [27] 胡毅鸿, 周蕾, 李欣荣, 等. 石门雄黄矿区As污染研究: As空间分布、化学形态与酸雨溶出特性[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(8): 1515-1521. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201508012.htmHu Y H, Zhou L, Li X R, et al. Arsenic contamination in Shimen realgar mine I: As spatial distribution, chemical fractionations and leaching[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(8): 1515-1521(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201508012.htm [28] 丁爱中, 杨双喜, 张宏达. 地下水砷污染分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2007, 37(2): 319-325. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200702019.htmDing A Z, Yang S X, Zhang H D. Analysis on arsenic contamination in groundwater[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2007, 37(2): 319-325(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200702019.htm [29] Liu A, Jiang M, Ulrich T, et al. Ore genesis of the Bake gold deposit, southeastern Guizhou Province, China: Constraints from mineralogy, in-situ trace element and sulfur isotope analysis of pyrite[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 102: 740-756. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.09.018 [30] Simon G, Huang H, Penner-Hahn J E, et al. Oxidation state of gold and arsenic in gold-bearing arsenian pyrite[J]. The American Mineralogist, 1999, 84(7/8): 1071-1079. [31] Abraitis P K, Pattrick R A D, Vaughan D J. Variations in the compositional, textural and electrical properties of natural pyrite: A review[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2004, 74(1/4): 41-59. [32] Savage K S, Tingle T N, O Day P A, et al. Arsenic speciation in pyrite and secondary weathering phases, Mother Lode gold district, Tuolumne County, California[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(8): 1219-1244. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00115-8 [33] Paikaray S. Arsenic geochemistry of acid mine drainage[J]. Mine Water and the Environment, 2015, 34(2): 181-196. doi: 10.1007/s10230-014-0286-4 [34] 杨阳, 唐菊兴, 吴纯能, 等. 西藏甲玛铜多金属矿床磁黄铁矿标型矿物学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2): 337-350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002008.htmYang Y, Tang J X, Wu C N, et al. Typomorphic mineralogical characteristics of pyrrhotite in Jiama Cu polymetallic deposit, Tibet, and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39(2): 337-350(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002008.htm [35] 邱红信, 张贵山, 温汉捷, 等. 攀西会理县白草钒钛磁铁矿床磁黄铁矿矿物学特征及成因[J]. 矿物学报, 2021, 41(3): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB202103003.htmQiu H X, Zhang G S, Wen H J, et al. Mineralogical characteristics and genesis of pyrrhotite in the Baicao V-Ti magnetite deposit in the Huili area of the Panzhihua-Xichang Rift[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2021, 41(3): 1-15(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB202103003.htm [36] 杨宏宇, 杨烨宇, 杨晓波, 等. 南秦岭黄龙金矿磁黄铁矿标型矿物学特征及含金性研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(3): 246-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.03.005Yang H Y, Yang Y Y, Yang X B, et al. Typomorphic mineralogy and gold-bearing property of pyrrhotite in Huanglong gold deposit, southern qinling Mountains[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2019, 28(3): 246-253(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.03.005 [37] 芮会超, 焦建刚, 靳树芳. 金川铜镍硫化物矿床磁黄铁矿矿物学特征及成因意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2017, 36(2): 501-514. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201702016.htmRui H C, Jiao J G, Jin S F. Typomorphic mineralogy and gold-bearing property of pyrrhotite in Huanglong gold deposit, southern Qinling Mountains[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2017, 36(2): 501-514(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201702016.htm [38] 叶国华, 童雄, 张杰. 含砷矿石的除砷研究进展[J]. 国外金属矿选矿, 2006, 43(3): 20-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXK200603002.htmYe G H, Tong X, Zhang J. Research progress of arsenic removal from arsenic-bearing ore[J]. Metal Ore Dressing Abroad, 2006, 43(3): 20-24(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXK200603002.htm [39] 刘金艳, 辛靖靖, 杨林恒, 等. 含砷铜矿石的生物浸出技术进展[J]. 金属矿山, 2018(3): 13-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201803003.htmLiu J Y, Xin J J, Yang L H, et al. Progress in bioleaching technology of arsenic-bearing copper ore[J]. Metal Mine, 2018(3): 13-18(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201803003.htm [40] 李艺. 广西德保铜锡矿床氧化带产出的砷酸盐矿物[J]. 广西地质, 2001, 18(1): 61-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ200101017.htmLi Y. Arsenate minerals from oxidation zone of Debao Cu-Tin deposit in Guangxi[J]. Guangxi Geology, 2001, 18(1): 61-64(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ200101017.htm [41] 戴婕, 徐金沙, 杜谷, 等. 利用扫描电镜-电子探针研究四川杨柳坪镍铜硫化物矿床铂钯的赋存状态及沉淀机制[J]. 岩矿测试, 2015, 34(2): 161-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201502001.htmDai J, Xu J S, Du G, et al. Analysis of the occurrence of platinum-palladium and precipitation mechanism by SEM and EPMA in the Ni-Cu sulphide deposits from Yangliupin, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Journal of Rock and Ore Research, 2015, 34(2): 161-168(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201502001.htm [42] 宣之强. 中国砷矿资源概述[J]. 化工矿产地质, 1998, 20(3): 8-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC803.001.htmXuan Z Q. Overview of arsenic mineral resources in China[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 1998, 20(3): 8-14(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC803.001.htm [43] 熊琼仙, 李正龙, 熊敏. 浅谈土壤中Pb~(2+)的污染及修复研究现状[J]. 广州化工, 2019, 47(17): 135-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2019.17.046Xiong Q X, Li Z L, Xiong M. Research status of pollution and remediation of Pb-(2+) in soil[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2019, 47(17): 135-137(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2019.17.046 [44] 吴攀, 刘丛强, 杨元根, 等. 矿山环境中(重)金属的释放迁移地球化学及其环境效应[J]. 矿物学报, 2001, 21(2): 213-218. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2001.02.018Wu P, Liu C Q, Yang Y G, et al. Release and transport of (heavy) metals and their environmental effect in mining activities[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2001, 21(2): 213-218(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2001.02.018 [45] Cheng H, Hu Y, Luo J, et al. Geochemical processes controlling fate and transport of arsenic in acid mine drainage (AMD) and natural systems[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165(1/3): 13-26. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jian_Luo/publication/23651861_Geochemical_processes_controlling_fate_and_transport_of_arsenic_in_acid_mine_drainage_(AMD)_and_natural_systems/links/0deec521ff1461e940000000 [46] Mielke R E, Pace D L, Porter T, et al. A critical stage in the formation of acid mine drainage: Colonization of pyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans under pH-neutral conditions[M]. Oxford, UK: [s. n.], 2003: 81-90. [47] Chen Y, Li J, Chen L, et al. Biogeochemical processes governing natural pyrite oxidation and release of acid metalliferous drainage[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(10): 5537-5545. [48] Sánchez-Andrea I, Sanz J L, Bijmans M F M, et al. Sulfate reduction at low pH to remediate acid mine drainage[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 269: 98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.032 [49] Belzile N, Chen Y, Cai M, et al. A review on pyrrhotite oxidation[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2004, 84(2): 65-76. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2004.03.003 [50] Daoud J, Karamanev D. Formation of jarosite during Fe2+ oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2006, 19(9): 960-967. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2005.10.024 [51] 李艺. 有色多金属矿山砷污染对生态环境的影响及其治理分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2008, 36(3): 256-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200803011.htmLi Y. Impacts of arsenic pollution from nonferrous multi-metal mines on ecological environment and its governance analysis[J]. Earth and Environment, 2008, 36(3): 256-260(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200803011.htm [52] Suess E, Planer-Friedrich B. Thioarsenate formation upon dissolution of orpiment and arsenopyrite[J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 89(11): 1390-1398. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.109 [53] 赵欣, 孙书堂, 谢先军. 硫代砷化合物的合成及其在地下水中的赋存特征: 以大同盆地为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(2): 131-137. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0141Zhao X, Sun S T, Xie X J. Synthesis of thioarsenate compounds and their occurrence characteristics in groundwater: A case study of Datong Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Bulletin, 2021, 40(2): 131-137(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0141 [54] Savage K S, Tingle T N, Day P A O, et al. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 39(16): 1219-1244. [55] Liu R, Wolfe A L, Dzombak D A, et al. Comparison of dissolution under oxic acid drainage conditions for eight sedimentary and hydrothermal pyrite samples[J]. Environmental Geology, 2008, 56(1): 171-182. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-1149-0 [56] 许家宁. 不同半导体类型黄铁矿电化学氧化行为研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2014.Xu J N. Study on electrochemical oxidation behavior of pyrite with different semiconductor types[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [57] Du R, Xian H, Wu X, et al. Morphology dominated rapid oxidation of framboidal pyrite[J]. Geochemical Perspectives Letters, 2021, 16: 53-58. doi: 10.7185/geochemlet.2104 [58] Mckibben M A, Barnes H L. Oxidation of pyrite in low temperature acidic solutions: Rate laws and surface textures[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1986, 50(7): 1509-1520. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(86)90325-X [59] Hu G, Dam-Johansen K, Wedel S, et al. Decomposition and oxidation of pyrite[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2006, 32(3): 295-314. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2005.11.004 [60] Savage K S, Bird D K, Ashley R P. Legacy of the California Gold Rush: Environmental geochemistry of arsenic in the southern Mother Lode Gold District[J]. International Geology Review, 2000, 42(5): 385-415. doi: 10.1080/00206810009465089 [61] 卢龙, 王汝成, 薛纪越, 等. 黄铁矿氧化速率的实验研究[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 2005, 35(5): 434-440. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200505006.htmLu L, Wang R C, Xue J Y, et al. Experimental study on oxidation rate of pyrite[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2005, 35(5): 434-440(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200505006.htm [62] Kaasalainen H, Lundberg P, Aiglsperger T, et al. Impact of declining oxygen conditions on metal(loid) release from partially oxidized waste rock[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(20): 20712-20730. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05115-z [63] 兰叶青, 周钢, 刘正华, 等. 不同条件下黄铁矿氧化行为的研究[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2000, 23(1): 81-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJNY200001020.htmLan Y Q, Zhou G, Liu Z H, et al. Pyrite oxidation under different conditions[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2000, 23(1): 81-84(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJNY200001020.htm [64] 林森, 李和平. 黄铁矿在不同pH值硫酸钠溶液中的电化学腐蚀研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(4): 526-530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.04.016Lin S, Li H P. Electrochemical corrosion of pyrite in sodium sulfate solutions with different pH[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2014, 33(4): 526-530(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.04.016 [65] 陆现彩, 李娟, 刘欢, 等. 金属硫化物微生物氧化的机制和效应[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(1): 153-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201901013.htmLu X C, Li J, Liu H, et al. Microbial oxidation of metal sulfides and its consequences[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(1): 153-163(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201901013.htm [66] St-Arnault M, Vriens B, Blaskovich R, et al. Geochemical and mineralogical assessment of reactivity in a full-scale heterogeneous waste-rock pile[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 145: 106089. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.106089 [67] 王楠, 易筱筠, 党志, 等. 酸性条件下黄铁矿氧化机制的研究[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(11): 3916-3921. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201211033.htmWang N, Yi X J, Dang Z, et al. Study on oxidation mechanism of pyrite under acidic condition[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(11): 3916-3921(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201211033.htm [68] Soler J M, Boi M, Mogollón J L, et al. The passivation of calcite by acid mine water: Column experiments with ferric sulfate and ferric chloride solutions at pH-2[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2008, 23(12): 3579-3588. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.08.011 [69] Cheng H, Hu Y, Luo J, et al. Geochemical processes controlling fate and transport of arsenic in acid mine drainage (AMD) and natural systems[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165(1/3): 13-26. [70] 李娟. 黄铁矿表生氧化及其微生物相互作用关系研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2015.Li J. Supergenic oxidation of pyrite and the study for microbial oxidation[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [71] 袁晓芳, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等. 江汉平原高砷地下水稳定碳同位素特征及其指示意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 156-163. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0008Yuan X F, Deng Y M, Du Y, et al. Characteristics of stable carbon isotopes and its implications on arsenic enrichment in shallow groundwater of the Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 156-163(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0008 [72] Ma J, Lei M, Weng L, et al. Fractions and colloidal distribution of arsenic associated with iron oxide minerals in lead-zinc mine-contaminated soils: Comparison of tailings and smelter pollution[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 227: 614-623. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.030 [73] Moore M M, Harrington-Brock K, Doerr C L. Relative genotoxic potency of arsenic and its methylated metabolites[J]. Mutat. Res., 1997, 386(3): 279-290. doi: 10.1016/S1383-5742(97)00003-3 [74] Casiot C, Morin G, Juillot F, et al. Bacterial immobilization and oxidation of arsenic in acid mine drainage (Carnoulès creek, France)[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(12): 2929-2936. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00080-0 [75] Zhu W, Young L Y, Yee N, et al. Sulfide-driven arsenic mobilization from arsenopyrite and black shale pyrite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(21): 5243-5250. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.08.006 [76] Wang J, Song J, Xie R, et al. Source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from a river in Anhui, China[J]. Environmental Forensics, 2020, 21(2): 167-175. doi: 10.1080/15275922.2020.1728439 [77] Thornburg K, Sahai N. Arsenic occurrence, mobility, and 14 retardation in sandstone and dolomite formations of the Fox River Valley, eastern Wisconsin[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(19): 5087-5094. [78] Hollibaugh J T, Budinoff C, Hollibaugh R A, et al. Sulfide oxidation coupled to arsenate reduction by a diverse microbial community in a Soda Lake[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(3): 2043-2049. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.3.2043-2049.2006 [79] Slowey A J, Johnson S B, Newville M, et al. Speciation and colloid transport of arsenic from mine tailings[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2007, 22(9): 1884-1898. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.03.053 [80] Edraki M, Baumgartl T, Mulligan D, et al. Geochemical characteristics of rehabilitated tailings and associated seepages at Kidston gold mine, Queensland, Australia[J]. International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment, 2017, 33(2): 133-147. [81] 王英旭. 矿山废水中含砷施氏矿物的环境稳定性试验研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018.Wang Y X. Experimental study on environmental stability of arsenic-bearing Schistelloite in mine wastewater[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [82] Fukushi K, Sato T, Yanase N. Solid-solution reactions in As(V) sorption by schwertmannite[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(16): 3581-3586. [83] Ying H, Feng X, Zhu M, et al. Formation and transformation of schwertmannite through direct Fe3+ hydrolysis under various geochemical conditions[J]. Environmental Science Nano, 2020, 7(8): 2385-2398. doi: 10.1039/D0EN00252F [84] 罗灿钰, 张琢, 赵华甫. 施氏矿物的矿物学特征及其除砷研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(11): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202111026.htmLuo C Y, Zhang Z, Zhao H F. The mineralogical characteristics of schwertmannite and its progress in arsenic removal[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(11): 1-14(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202111026.htm [85] Paikaray S. Environmental stability of schwertmannite: A review[J]. Mine Water and the Environment, 2020, 40: 570-586. [86] 徐诗琦. 雄黄尾矿中砷的稳定化机理及其中试研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017.Xu S Q. Study on bench and pilot-scale stabilization mechanism of arsenic in realgar railings[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese with English abstract [87] Zhu X, Wang R, Lu X, et al. Secondary minerals of weathered orpiment-realgar-bearing tailings in Shimen carbonate-type realgar mine, Changde, Central China[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2015, 109(1): 1-15. doi: 10.1007/s00710-014-0344-4 [88] Holm T R. Effects of CO32-/bicarbonate, Si, and PO43- on arsenic sorption to HFO[J]. Journal of American Water Works Association, 2002, 94(4): 174-181. doi: 10.1002/j.1551-8833.2002.tb09461.x [89] Bolanz R M, Wierzbicka-Wieczorek M, Caplovicova M, et al. Structural incorporation of As5+ into hematite[J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47(16): 9140-9147. doi: 10.1021/es305182c [90] Courtin-Nomade A, Waltzing T, Evrard C, et al. Arsenic and lead mobility: From tailing materials to the aqueous compartment[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2016, 64: 10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.11.002 [91] García-Arreola M E, Flores-Vélez L M, Loredo-Tovías M, et al. Assessment of the acid drainage neutralization capacity and the toxic metals lixiviation of tailing from Guanajuato mining district, Mexico[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(9): 355.1-355.15. [92] Moncur M C, Ptacek C J, Blowes D W, et al. Release, transport and attenuation of metals from an old tailings impoundment[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20(3): 639-659. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.09.019 [93] Klimko T, Lalinská B, Majzlan J, et al. Chemical composition of weathering products in neutral and acidic mine tailings from stibnite exploitation in Slovakia[J]. Journal of Geosciences, 2012, 56: 327-340. [94] Lottermoser B G, Ashley P M. Mobility and retention of trace elements in hardpan-cemented cassiterite tailings, north Queensland, Australia[J]. Environmental Geology, 2006, 50(6): 835-846. doi: 10.1007/s00254-006-0255-8 [95] Gieré R, Sidenko N V, Lazareva E V. The role of secondary minerals in controlling the migration of arsenic and metals from high-sulfide wastes (Berikul gold mine, Siberia)[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2003, 18(9): 1347-1359. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00055-6 [96] Nieva N E, Borgnino L, García M G. Long term metal release and acid generation in abandoned mine wastes containing metal-sulphides[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 242: 264-276. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.06.067 [97] Simon M, Ortiz I, Garcia I, et al. Pollution of soils by the toxic spill of a pyrite mine (Aznalcollar, Spain)[J]. Sci. Total Environ., 1999, 242(1/3): 105-115. [98] 朱继保, 陈繁荣, 卢龙, 等. 广东凡口Pb-Zn尾矿中重金属的表生地球化学行为及其对矿山环境修复的启示[J]. 环境科学学报, 2005, 25(3): 414-422. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2005.03.025Zhu J B, Chen F S, Lu L, et al. Heavy metal geochemistry behavior during the oxidation of the Fankou Pb-Zn minetailings in Guangdong province and the implications for environmental remediation of the mines[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 2005, 25(3): 414-422(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2005.03.025 [99] 吴英杰, 赖伟. 某铜矿尾矿处置及采空区充填协同治理实践[J]. 黄金, 2021, 42(10): 79-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ202110018.htmWu Y J, Lai W. Collaborative treatment of tailings disposal and goaf filling in a copper mine[J]. Gold, 2021, 42(10): 79-82(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ202110018.htm [100] Zhang D, Wang S, Gomez M A, et al. The long-term stability of FeⅢ-AsV coprecipitates at pH 4 and 7: Mechanisms controlling the arsenic behavior[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 374: 276-286. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.054 [101] Desbarats A J, Parsons M B, Percival J B. Arsenic mobility in mildly alkaline drainage from an orogenic lode gold deposit, Bralorne mine, British Columbia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2015, 57: 45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.11.015 -





 下载:
下载: