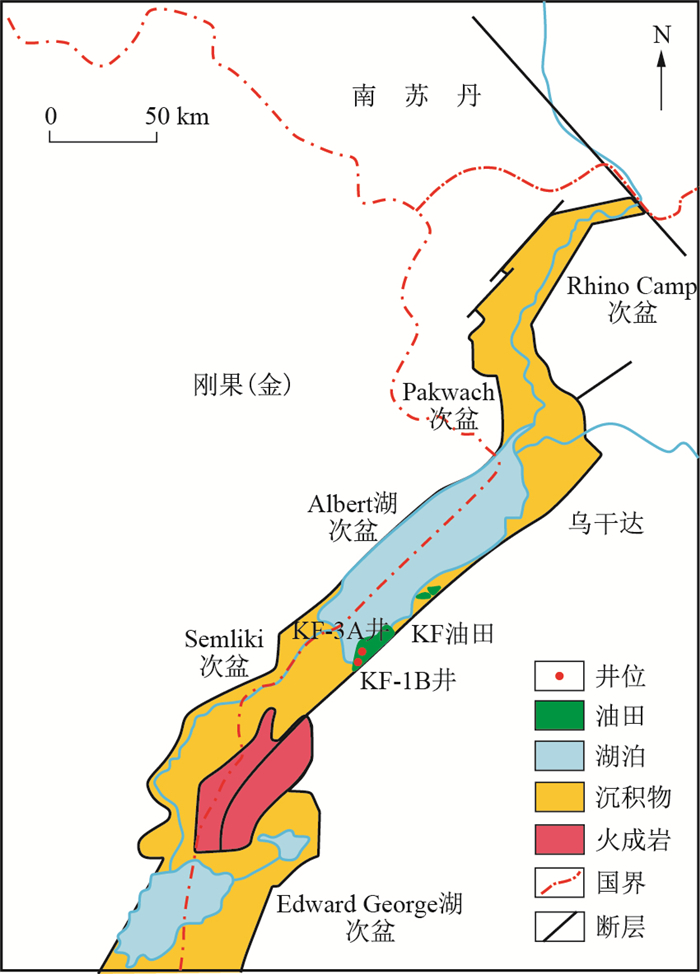
Geochemical characteristics and sedimentary environment of upper Miocene-lower Pliocene source rocks in the Albertine Basin, East African Rift Valley
-
摘要:
Albertine盆地是东非裂谷系重要的裂谷盆地, 油气资源丰富, 上中新统-下上新统烃源岩是盆地重要的生烃岩系, 目前研究相对薄弱。综合利用地质学、岩石热解、元素地球化学等资料, 对Albertine盆地上中新统和下上新统的烃源岩进行了评价, 并分析了晚中新世-早上新世时期的古环境特征。研究表明, 两套烃源岩处于成熟阶段, 但有机质丰度和类型存在差异, 下上新统烃源岩有机质丰度更高, 属于中等-好烃源岩, 干酪根类型主要是Ⅱ1~Ⅱ2型; 上中新统烃源岩有机质丰度略低, 属于差烃源岩, 干酪根主要是Ⅱ2~Ⅲ型。沉积环境是造成烃源岩差异的重要原因。晚中新世-早上新世时期, 研究区属于还原性较强的淡水湖盆, 水体逐渐加深, 气候越来越温暖, 细菌及微生物繁盛, 有机质类型变好, 同时, 湖泊生产力提高, 沉积速率有所加快, 有机质能够更有效地保存, 烃源岩的有机质丰度更高。研究结果对于Albertine盆地的油气勘探与开发具有重要的理论意义和实际意义。
-
关键词:
- 烃源岩评价 /
- 元素地球化学 /
- 沉积环境 /
- Albertine盆地 /
- 东非裂谷
Abstract:The Albertine Basin is an important rift basin in the East African Rift System, enriched in oil and gas resources. The upper Miocene to lower Pliocene hydrocarbon source rocks are important source rocks in the basin, but the research is relatively limited. In this work, we evaluate the source rocks of the upper Miocene and lower Pliocene in the Albertine Basin by integrations of geological, rock pyrolysis and elemental geochemistry data and analyses the paleoenvironmental evolutions of the late Miocene to early Pliocene. These results show that the two sets of source rocks are under the mature stage, but the abundance and type of organic matter are different. The lower Pliocene source rocks have higher organic matter abundance and belong to middle-good source rocks, yielding type Ⅱ1 -Ⅱ2 kerogen. The upper Miocene source rocks have lower organic matter abundance and belong to poor source rocks, yielding type Ⅱ2-Ⅲ kerogen. The sedimentary environment is an important controlling factor for the difference in source rocks. During the late Miocene to early Pliocene, the study area was a freshwater lake with strong reducibility, gradually increasing water depth, a warmer climate, flourishing bacteria and microorganisms, and better organic matter types. At the same time, lake productivity is elevated, the sedimentation rate is accelerated, and organic matter can be preserved more efficiently, so the abundance of organic matter in source rocks is higher.
-
图 8 Albertine盆地下上新统烃源岩稀土元素配分模式(北美页岩标准值据文献[44])
Figure 8. NASC-normalized REE patterns of the Lower Pliocene source rocks in the Albertine Basin
图 9 Albertine盆地上中新统烃源岩稀土元素配分模式(北美页岩标准值据文献[44])
Figure 9. NASC-normalized REE patterns of the upper Miocene source rock in the Albertine Basin
表 1 烃源岩成熟度与Tmax关系[15]
Table 1. Table of relation between maturity and Tmax of source rocks
Tmax/℃ 油气形成阶段 生油 凝析油 湿气 干气 Ⅰ类干酪根 437~460 450~465 460~490 > 490 Ⅱ类干酪根 435~455 447~460 455~490 > 490 Ⅲ类干酪根 432~460 445~470 460~505 > 490 -
[1] 孙和风, 姜雪, 钟锴. 阿尔伯特盆地沉降-热史演化特征分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(5): 63-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201805008.htmSun H F, Jiang X, Zhong K, et al. Analysis on subsidence-thermal history evolution characteristics of Albert Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(5): 63-70(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201805008.htm [2] 郑晨宇, 赵红岩, 邱春光, 等. 东非裂谷系Albert湖凹陷新生代构造沉降特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 162-172. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0513Zheng C Y, Zhao H Y, Qiu C G, et al. Cenozoic tectonic subsidebce characterisstics of Albert Lake Depression in East African Rift Syetem[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 162-172(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0513 [3] 温志新, 童晓光, 张光亚, 等. 东非裂谷系盆地群石油地质特征及勘探潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2012, 17(4): 60-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2012.04.010Wen Z X, Tong X G, Zhang G Y, et al. Petroleum geology features and exploration potential of basin group in East African Rift System[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2012, 17(4): 60-65(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2012.04.010 [4] 崔哿. 东非裂谷系区域构造演化与构造样式及其油气成藏特征研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.Cui G. The analysis of regional structure evolution and structural styles and its hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics in East African Rifts[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [5] 赵伟, 韩文明, 胡滨, 等. 东非裂谷Albertine地堑石油地质条件和成藏规律[J]. 四川地质学报, 2016, 36(2): 275-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2016.02.023Zhao W, Han W M, Hu B, et al. Petroleum geology and hydrocarabon accumulation in the Albertine Graben, East Africa Rift[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2016, 36(2): 275-279(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2016.02.023 [6] Njabire N. Challenges of exploring and discovering oil resources in a developing country: A case study of Uganda[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(S1): 134. [7] Gregory J W. Contributions to the physical geography of British East Africa[J]. The Geographical Journal, 1894, 4(4): 289-315. doi: 10.2307/1773534 [8] Macgregor D. History of the development of Permian-Cretaceous rifts in East Africa: A series of interpreted maps through time[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2018, 24(1): 8-20. doi: 10.1144/petgeo2016-155 [9] Yang X, Chen H, Liu J, et al. Miocene stratigraphic characteristics of semliki basin in Albertine Graben[J]. Global Geology, 2019, 22(1): 50-55. [10] Zhang X, Scholz C A. Turbidite systems of lacustrine rift basins: Examples from the Lake Kivu and Lake Albert Rifts, East Africa[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2015, 325(3): 177-191. [11] Macgregor D. History of the development of the East African Rift System: A series of interpreted maps through time[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2015, 101(1): 232-252. [12] Bosellini A. East Africa continental margins[J]. Geology, 1986, 714(1): 76-78. [13] Ebinger C J. Tectonic development of the western branch of the East Africanrift System[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(7): 885-903. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0885:TDOTWB>2.3.CO;2 [14] Karner G D, Byamumgu B R, Ebinger C J, et al. Distribution of crustalextension and regional basin architecture of the Albertine Rift System, East Africa[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(10): 1131-1150. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(00)00058-1 [15] 邬立言, 顾信章. 热解技术在我国生油岩研究中的应用[J]. 石油学报, 1986, 7(2): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB198602002.htmWu L Y, Gu X Z. The application of pyrolysis technology in the study of source rocks in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1986(2): 13-19(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB198602002.htm [16] 赵岩, 刘池洋, 张东东, 等. 宁南盆地古近纪沉积岩地球化学特征对沉积环境的反映[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(5): 27-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605004.htmZhao Y, Liu C Y, Zhang D D, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Paleogene sedimentary rocks in Ningnan Basin and their impiications for sedimentary environments[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(5): 27-33(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605004.htm [17] 申雯龙, 漆滨汶. 东海盆地丽水凹陷有效烃源岩判定及分布预测[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 77-88. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0309Shen W L, Qi B M. Defininion and distribution prediction of effective source rocks in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 77-88(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0309 [18] Roller S, Hornung J, Hinderer M, et al. Middle Miocene to Pleistocene sedimentary record of rift evolution in the southern Albert Rift(Uganda)[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2010, 99(7): 1643-1661. doi: 10.1007/s00531-010-0560-z [19] Simon B, Guillocheau F, Robin C, et al. Deformation and sedimentary evolution of the Lake Albert Rift(Uganda, East African Rift System)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 47(86): 17-37. [20] 毛小妮, 周立发, 杨甫, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘奥陶系地球化学特征与沉积环境分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2011, 30(3): 98-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201103016.htmMao X N, Zhou L F, Yang F, et al. Geochemical characteristics and its sedimentary environment significance of the Ordovician in southwest margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2011, 30(3): 98-102(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201103016.htm [21] Lennan S M, Taylor S R, Culloch M T, et al. Geochemical and Nd-Sr isotopic composition of deep-sea turbidites: Crustal evolution and plate tectonic associations[J]. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1990, 54(7): 2015-2050. [22] Floyd P A, Leveridge B E. Tectonic environment of the Devonian Gramscatho Basin, south Cornwall: Framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbiditic sandstones[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1987, 144: 531-542. [23] Cullers R L, Basu A, Suttner L J. Geochemical signature of provenance in sand-size material in soils and stream sediments near the Tobacco Root batholith, Montana[J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 70(4): 335-348. [24] Frost C D, Coombs D S. Nd isotope character of New Zealand sediments: Implications for terrane concepts and crustal evolution[J]. American Journal of Science, 1989, 289(6): 744-770. [25] 郑玉龙, 马志强, 王佰长, 等. 黑龙江省柳树河盆地始新统八虎力组油页岩元素地球化学特征及沉积环境[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(5): 689-698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201505011.htmZheng Y L, Ma Z Q, Wang B Z, et al. Geochemistry characteristics and sedimentary environment of oil shale from Eocene Bahuli Formation in Liushuhe Basin, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2015, 17(5): 689-698(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201505011.htm [26] 赵帮胜, 李荣西, 王香增, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长探区山西组泥页岩沉积地球化学特征及有机质保存条件分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(6): 103-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201606016.htmZhao B S, Li R X, Wang X Z, et al. Sedimentary envioment and preservation conditions of organic matter analysis of Shanxi Formation mud shale in Yanchang exploration area, Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(6): 103-111(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201606016.htm [27] 李浩, 陆建林, 李瑞磊, 等. 长岭断陷下白垩统湖相烃源岩形成古环境及主控因素[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(10): 1774-1786. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201710012.htmLi H, Lu J L, Li R L, et al. Generation paleoenvironment and its controlling factors of Lower Creaceous lacustrine hydrocarbon source rocks in Changling Depression, south Songliao Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(10): 1774-1786(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201710012.htm [28] 孔凡翠, 杨瑞东, 沙占江. 贵州草海赵家院子晚更新世泥炭层地球化学特征及其环境意义[J]. 地质论评, 2013, 59(4): 716-730. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201304015.htmKong F C, Yang R D, Sha Z J, Geochemical characteristics and environmental significance of Late Pleistocene peat in Zhaojiayuan, Caohai, Guizhou[J]. Geological Review, 2013, 59(4): 716-730(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201304015.htm [29] Haskin M A, Haskin L A. Rare earths in european shales: A redetermination[J]. Science, 1966, 154: 507-509. [30] Bryn J. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1): 111-129. [31] Hatch J R, Leventhal J S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian(Missourian) stark shale member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, U.S.A. [J]. Chemical Geology: Isotope Geoscience Section, 1992, 99(1/3): 65-82. [32] 王春连, 刘成林, 胡海兵, 等. 江汉盆地江陵凹陷南缘古新统沙市组四段含盐岩系沉积特征及其沉积环境意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2012, 14(2): 165-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201202004.htmWang C L, Liu C L, Hu H B, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and its environmental significance of salt-bearing strata of the Member 4 of Paleocene Shashi Formation in southern margin of Jiangling Depression, Jianghan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2012, 14(2): 165-175(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201202004.htm [33] Wignall P B, Twitchett R J. Oceanic anoxia and the end permian mass extinction[J]. Science, 1996, 272: 1155-1158. [34] 钟红利, 蒲仁海, 闫华, 等. 塔里木盆地晚古生代古盐度与古环境探讨[J]. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 42(1): 74-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201201017.htmZhong H L, Pu R H, Yan H, et al. Analysis on paleosalinity and paleoenvironment of Late Paleozoic in Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2012, 42(1): 74-81(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201201017.htm [35] 王敏芳, 黄传炎, 徐志诚, 等. 综述沉积环境中古盐度的恢复[J]. 新疆石油天然气, 2006, 2(1): 9-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY200601002.htmWang M F, Huang C Y, Xu Z C, et al. Review on paleosalinity recovery in sedimentary environment[J]. Xinjiang Oil & Gas, 2006, 2(1): 9-13(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY200601002.htm [36] 孙和风, 彭文绪, 姜雪. 断砂耦合对阿尔伯特凹陷北部转换带油气富集的控制作用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2016, 28(5): 30-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201605005.htmSun H F, Peng W X, Jiang X. Fault-sand coupling controlling effect on hydrocarbon in the northern transfer zone of Albert Sag[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2016, 28(5): 30-37(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201605005.htm [37] 林晓慧, 詹兆文, 邹艳荣, 等. 准噶尔盆地东南缘芦草沟组油页岩元素地球化学特征及沉积环境意义[J]. 地球化学, 2019, 48(1): 67-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201901006.htmLing X H, Zhan Z W, Zou Y R, et al. Element geochemical characteristics of the Lucaogou Formation oilshale in the southeastern Junggar Basin and its depositional environmental implications[J]. Geochimica, 2019, 48(1): 67-78(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201901006.htm [38] 陈慧, 解习农, 李红敬, 等. 利用古氧相和古生产力替代指标评价四川上寺剖面二叠系海相烃源岩[J]. 古地理学报, 2010, 12(3): 324-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201003011.htmChen H, Xie X N, Li H J, et al. Evaluation of the Permian marine hydrocarbon source rocks at Shangsi section in Sichuan Province using multi-proxies of paleoproductivity anf paleoredox[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2010, 12(3): 324-333(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201003011.htm [39] Schulte S, Mangelsdorf K, Rullkotter J. Organic matter preservation on the pakistan continental marginas revealed by biomarker geochemistry[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(10): 1005-1022. [40] Oliveira M R G. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution[J]. Geological Magazine, 1985, 122(6): 673-674. [41] 柏道远, 蒋启生, 李彬, 等. 湘东北冷家溪群沉积岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 1-13, 26. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0017Bai D Y, Jiang J S, Li B, et al. Geochemical and tectonic significance of sedimentary rocks in the Lengjiaxi Group in northeastern Hunan[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 1-13, 26(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0017 [42] Gromet L P, Dymek R F, Haskin L A, et al. The "North American Shale Composite": Its compilation, major and trace element characteristics[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(12): 2469-2482. [43] Haskin L A, Frey F A. Dispersed and not-so-rare earths[J]. Science, 1966, 152: 299-314. [44] 王欣欣, 郑荣才, 闫国强, 等. 基于稀土元素地球化学特征的泥岩沉积环境及物源分析: 以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长9油层组泥岩为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(9): 1387-1394.Wang X X, Zheng R C, Yan G Q, et al. The mudstone sedimentary environment and provenance analysis based on the geochemical evidence of rare earth elements: Take Chang 9 oil-bearing layer in Longdong area of Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(9): 1387-1394(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: