Effects of S2- on arsenic adsorption to river sand and its mechanisms
-
摘要:
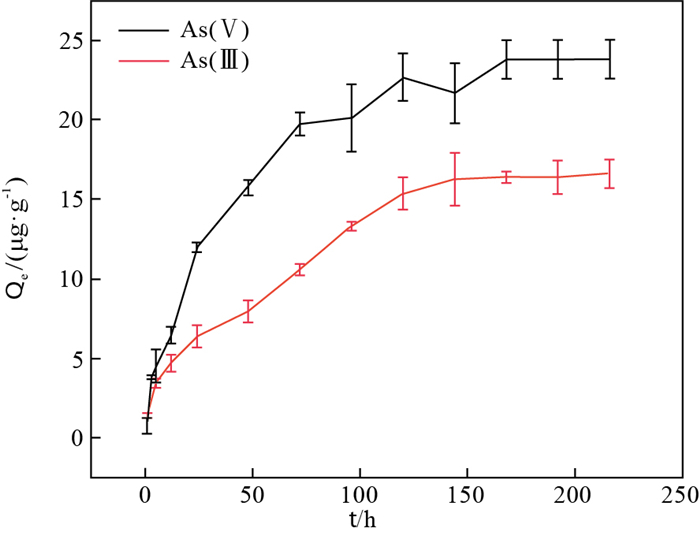
水体中S2-与砷(As)的迁移富集密切相关, 但不同含水介质中其作用机理尚不明确。为了查明潜流带中常见含水介质河砂在S2-作用下对As的吸附特征, 设计并开展了As在河砂上的吸附动力学实验, 以及S2-作用下河砂对As的吸附实验, 结合PHREEQC模拟计算, XRD、SEM-EDS、XPS和FTIR等表征测试技术, 进一步识别其作用机理。结果表明: 固液比为25 g/L情况下, 河砂对As的吸附在200 h左右达到吸附平衡, 且对As(Ⅴ)的吸附量明显高于As(Ⅲ); 随着S2-浓度的增加, 河砂对As吸附能力逐渐减弱; 模拟及表征测试结果显示, 少量As被吸附在河砂表面, 主要与其表面的Fe、Al结合, 其中As(Ⅲ)的吸附可能还与Si-O键断裂后与S2-结合形成的SiS2有关。S2-对河砂吸附As的主要影响机理为: ①S2-的加入使得溶液pH值升高、Eh值降低, 从而抑制了As的吸附; ②添加S2-条件下河砂表面的Fe、Al等能与S和As形成AlAs、AlAsO4、FeS2及Fe4As2O11等化合物, 减少了河砂表面吸附As的活性位点。研究结果有助于丰富As-S作用机理, 以及As在地下水环境中迁移过程的认识。
Abstract:Sulfur (S2-) is closely related to the migration and enrichment of arsenic (As) in the water environment, but its mechanism of action in different aqueous medium is still unclear. To determine the adsorption characteristics of As by river sand, a common aqueous medium in the hyporheic zone, under the action of S2-, the adsorption kinetics experiment of As on river sand and the adsorption experiment of As by river sand under the action of S2- are designed and carried out. Combined with simulation calculation by PHREEQC and characterization tests based on XRD, SEM-EDS, XPS and FTIR, the mechanism of action is further identified. The results show that the adsorption of As by river sand reaches adsorption equilibrium at approximately 200 h and the adsorption capacity of As(Ⅴ) is significantly higher than that of As(Ⅲ) at the solid-to-liquid ratio of 25 g/L; with increasing S2- concentration, the adsorption capacity of river sand to As decreases gradually. The simulation and characterization test results show that a small amount of As is adsorbed on the surface of river sandandis mainly combined with Fe and Al on its surface. The adsorption of As (Ⅲ) may also be related to SiS2 that is formed after the fracture of the Si-O bondwith S2-. The main influence mechanism of S2- on the adsorption of As by river sand is as follows: ① the addition of S2- increases the pH of the solution and decreases Eh, thus inhibiting the adsorption of As; ②under the condition of adding S2-, Fe and Al on the surface of river sand can form compounds such as AlAs, AlAsO4, FeS2 and Fe4As2O11 with S and As, which reduces the active sites of As adsorption on the surface of river sand.
-
Key words:
- sulfur /
- river sand /
- characterization /
- influence mechanism
-
表 1 河砂主要成分
Table 1. Main composition of river sand
成分 SiO2 Al2O3 K2O Fe2O3 CaO TiO2 MgO Na2O MnO wB/% 90.69 5.91 1.62 1.51 0.32 0.17 0.15 0.14 0.06 表 2 不同ρ(S2-)条件下反应前后溶液的pH和Eh对比
Table 2. Comparison of pH and Eh before and after the reaction at different S2- concentrations
初始ρ(S2-)/(mg·L-1) 0.1 1.0 5.0 20.0 As(Ⅲ) 反应前pH 7.58 9.91 10.09 11.01 反应后pH 6.77 7.23 6.96 9.64 反应前Eh/mV -256.40 -316.90 -338.90 -398.50 反应后Eh/mV 223.90 174.00 115.60 -191.30 As(Ⅴ) 反应前pH 7.22 9.24 10.28 11.01 反应后pH 6.57 7.15 7.38 9.76 反应前Eh/mV -283.40 -343.50 -375.10 -401.70 反应后Eh/mV 243.93 46.93 47.6 -195.93 表 3 PHREEQC模拟中选取部分矿物饱和指数结果
Table 3. Selected mineral saturation index results in the PHREEQC simulation
反应体系 ρ(S2-)/(mg·L-1) As2O3 As2O5 As2S3 AsS S 饱和指数SI S2--As(Ⅲ) 0.1 -8.52 -44.05 -5.56 -1.62 -5.22 1.0 -9.62 -45.73 -12.03 -3.81 -7.92 5.0 -9.89 -46.7 -9.85 -3.56 -6.97 20.0 -11.59 -48.26 -16.68 -25.12 -8.46 S2--As(Ⅴ) 0.1 -8.74 -35.38 -59.22 -21.76 -18.58 1.0 -9.03 -44.51 -8.87 -2.82 -6.13 5.0 -10.24 -46.14 -12.81 -4.23 -7.25 20.0 -11.60 -47.82 -16.71 -19.57 -8.25 -
[1] 刘碧君, 吴丰昌, 邓秋静, 等. 锡矿山矿区和贵阳市人发中锑、砷和汞的污染特征[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(3): 907-912. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.03.047Liu B J, Wu F C, Deng Q J, et al. Pollution characteristics of antimony, arsenic and mercury in human hair at Xikuangshan antimony mining area and Guiyang City, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(3): 907-912(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.03.047 [2] Jain C K, Ali I. Arsenic: Occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques[J]. Water Research, 2000, 34(17): 4304-4312. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00182-2 [3] 张玉玺, 向小平, 张英, 等. 云南阳宗海砷的分布与来源[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(11): 3768-3777. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201211013.htmZhang Y X, Xiang X P, Zhang Y, et al. Distribution and sources of arsenic in Yangzonghai Lake, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(11): 3768-3777(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201211013.htm [4] De Zuane J. Handbook of drinking water quality: Standards and controls[M]. [S.I. ]: [s. n. ], 1990. [5] Nath K J, Majumber A. Arsenic in groundwater: Methodology for removal, in measurement and mitigation strategies for arsenic in drinking water at the field level[M]. [S.I. ]: Outcome of a workshop, 1998: 21-30. [6] 潘茂华, 朱志良. 自然环境中砷的迁移转化研究进展[J]. 化学通报, 2013, 76(5): 399-404. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXTB201305004.htmPan M H, Zhu Z L. Progress of investigations on transformation and distribution of arsenic in natural environment[J]. Chemistry, 2013, 76(5): 399-404(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXTB201305004.htm [7] Streat M, Hellgardt K, Newton N L R. Hydrous ferric oxide as an adsorbent in water treatment: Part 3, Batch and mini-column adsorption of arsenic, phosphorus, fluorine and cadmium ions[J]. Process Safety & Environmental Protection, 2008, 186(1): 21-30. [8] Farquhar M L, Charnock J M, Livens F R, et al. Mechanisms of arsenic uptake from aqueous solution by interaction with goethite, lepidocrocite, mackinawite, and pyrite: An X-Ray absorption spectroscopy study[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(8): 1757-1762. [9] Guo H M, Liu C, Lu H, et al. Pathways of coupled arsenic and iron cycling in high arsenic groundwater of the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia, China: An iron isotope approach[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 112: 130-145. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.02.031 [10] McArthur J M, Banerjee D M, Hudson-Edwards K A, et al. Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water: The example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2004, 19(8): 1255-1293. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.02.001 [11] Pi K, Wang Y, Postma D, et al. Vertical variability of arsenic concentrations under the control of iron-sulfur-arsenic interactions in reducing aquifer systems[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 561: 200-210. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.03.049 [12] Wolthers M, Charlet L, Linde P, et al. Surface chemistry of disordered mackinawite(FeS)[J]. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(14): 3469-3481. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.01.027 [13] Xie X J, Liu Y Q, Pi K F, et al. In situ Fe-sulfide coating for arsenic removal under reducing conditions[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 534: 42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.12.057 [14] Kirk M F, Holm T R, Park J, et al. Bacterial sulfate reduction limits natural arsenic contamination in groundwater[J]. Geology, 2004, 32(11): 953-956. doi: 10.1130/G20842.1 [15] 郭华明, 郭琦, 贾永锋, 等. 中国不同区域高砷地下水化学特征及形成过程[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2013, 35(3): 83-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.03.008Guo H M, Guo Q, Jia Y F, et al. Chemical characteristics and geochemical processes of high arsenic groundwater in different regions of China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2013, 35(3): 83-96(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.03.008 [16] 袁翰卿, 李巧, 陶洪飞, 等. 新疆奎屯河流域地下水砷富集因素[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(2): 247-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202002027.htmYuan H Q, Li Q, Tao H F, et al. Groundwater arsenic enrichment factors of Kuitun River basin, Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(2): 247-253(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202002027.htm [17] 罗艳丽, 李晶, 蒋平安, 等. 新疆奎屯原生高砷地下水的分布、类型及成因分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(8): 2897-2903. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201708010.htmLuo Y L, Li J, Jiang P A, et al. Distribution, classificationandcause analysis of geogenic high-arsenic groundwater in Kuitun, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(8): 2897-2903(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201708010.htm [18] Liu Z, Zhuang Z, Yu Y, et al. Arsenic transfer and accumulation in the soil-rice system with sulfur application and different water managements[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 269(5): 128772. [19] 王焰新, 苏春利, 谢先军, 等. 大同盆地地下水砷异常及其成因研究[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(3): 771-780. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.033Wang Y X, Su C L, Xie X J, et al. The genesis of high arsenic groundwater: A case study in Datong Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(3): 771-780(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.033 [20] 严志弦. 硫化物的水解[J]. 化学世界, 1952(7): 11-13, 22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXSS195207002.htmYan Z X. Hydrolysis of sulfides[J]. Chemical World, 1952(7): 11-13, 22(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXSS195207002.htm [21] 许嘉琳, 杨居荣, 荆红卫. 砷污染土壤的作物效应及其影响因素[J]. 土壤, 1996(2): 85-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA602.007.htmXu J L, Yang J R, Jing H W. Crop effect of arsenic contaminated soil and its influencing factors[J]. Soils, 1996(2): 85-89(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA602.007.htm [22] Smedley P, Kinniburgh D. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2002, 17(5): 517-568. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5 [23] 陈辉, 单慧媚, 彭三曦, 等. 不同水化学因素对砷在河砂上的吸附影响研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(7): 2727-2739. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202107023.htm [24] 苏春利, Win H, 王焰新, 等. 大同盆地砷中毒病区沉积物中砷的吸附行为和影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2009, 28(3): 120-126.Su C L, Win H, Wang Y X, et al. Arsenic adsorption behavior and influence factors in sediments of endemic arsenism diseased areas from Datong Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2009, 28(3): 120-126(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] 曹文庚, 董秋瑶, 谭俊, 等. 河套盆地晚更新世以来黄河改道对高砷地下水分布的控制机制[J]. 南水北调与水利科技: 中英文, 2021, 19(1): 140-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD202101014.htmCao W G, Dong Q Y, Tan J, et al. The mechanism of Yellow River diversion in controlling high arsenic groundwater distribution since the Late Pleistocene[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science&Technology, 2021, 19(1): 140-150(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD202101014.htm [26] 段艳华. 浅层地下水系统中砷富集的季节性变化与机理研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2016.Duan Y H. Seasonal variations of groundwater arsenic concentration in shallow aquifers at Jianghan Plain[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [27] 邓娅敏. 河套盆地西部高砷地下水系统中的地球化学过程研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2008.Deng Y M. Geochemical processes of high arsenic groundwater system at western Hetao Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2008(in Chinese with English abstract). [28] O'Day P A, Vlassopoulos D, Root R, et al. The influence of sulfur and iron on dissolved arsenic concentrations in the shallow subsurface under changing redox conditions[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(38): 13703-13708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402775101 [29] 王建燕, 张传巧, 陈静, 等. 新型铁铜锰复合氧化物颗粒吸附剂As(Ⅲ)吸附行为与机制研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(8): 2575-2585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201908014.htmWang J Y, Zhang C Q, Chen J, et al. The adsorption of As(Ⅲ) on a novel granular Fe-Cu-Mn trimetal oxide (GFCM): Behavior and mechanism[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(8): 2575-2585(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201908014.htm [30] 吴雅静, 王华伟, 孙英杰, 等. 原位形成生物铁锰氧化物对砷(Ⅲ/Ⅴ)的去除效果与机制[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(2): 526-535. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202102023.htmWu Y J, Wang H W, Sun Y J, et al. Removal efficiency and mechanism of arsenic(Ⅲ/V) by in-situ generated biogenic Fe-Mn oxides[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(2): 526-535(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202102023.htm [31] 马淼, 黄玉代, 郭勇, 等. 白烟灰的物相分析及酸浸脱砷工艺[J]. 应用化学, 2015, 32(10): 1208-1214. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2015.10.150012Ma M, Huang Y D, Guo Y, et al. Determination of speciation in white ashand acid leaching arsenic removal technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2015, 32(10): 1208-1214(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2015.10.150012 [32] Kim E, Batchelor B. Macroscopic and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic investigation of interactions of arsenic with synthesized pyrite[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(8): 2899. [33] 李娜, 孙竹梅, 阮福辉, 等. 三氯化铁除砷(Ⅲ)机理[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(7): 2224-2228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.07.033Li N, Sun Z M, Run F H, et al. Mechanism of removing arsenic(Ш) with ferric chloride[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(7): 2224-2228(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.07.033 [34] 陈和生, 孙振亚, 邵景昌. 八种不同来源二氧化硅的红外光谱特征研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2011, 30(4): 934-937. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201104040.htmChen H S, Sun Z Y, Shao J C. Investigation on FT-R spectroscopy for eight different sources of SiO2[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Cera Mix Society, 2011, 30(4): 934-937(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201104040.htm [35] 董静兰, 耿晓, 高正阳, 等. 飞灰中的缺陷位SiO2对痕量元素As的吸附机理[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2018, 46(11): 1401-1408. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.11.015Dong J L, Geng X, Gao Z Y, et al. Adsorption mechanism of trace As on the defect sites of SiO2 in fly ash[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2018, 46(11): 1401-1408(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.11.015 [36] Bostick B C, Fendorf S. Arsenite sorption on troilite (FeS) and pyrite (FeS2)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 167(5): 909-921. [37] Wolthers M, Charlet L, Weijden C, et al. Arsenic mobility in the ambient sulfidic environment: Sorption of arsenic(V) and arsenic(Ⅲ) onto disordered mackinawite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(14): 3483-3492. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.03.003 [38] 田飞翔, 郑天亮, 李琦, 等. 江汉平原第四系沉积物中砷的垂向分布规律及其对地下水中砷浓度的影响[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3): 226-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803030.htmTian F X, Zheng T L, Li Q, et al. Vertical distribution of arsenic in Quaternary sediments and its impacts on arsenic contentin multi-level aquifers from Jianghan Plain[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(3): 226-234(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803030.htm [39] Grossl P R, Eick M, Sparks D L, et al. Arsenate and chromate retention mechanisms on goethite: 2. Kinetic evaluation using a pressure-jump relaxation technique[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1997, 31(2): 321-326. [40] 甘义群, 王焰新, 段艳华, 等. 江汉平原高砷地下水监测场砷的动态变化特征分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4): 37-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404006.htmGan Y Q, Wang Y X, Duan Y H, et al. Dynamic changes of groundwater arsenic concentration in the monitoringfield site, Jianghan Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4): 37-49(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404006.htm [41] 黄爽兵, Emilie E, 王焰新. 高砷含水层沉积物矿物学特征及砷的活化[J]. 矿物岩石, 2012, 32(4): 7-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201204002.htmHuang S B, Emilie E, Wang Y X. Mineralogical characteristics of sediments and arsenic mobilization in the aquifer, Jianhan Plain[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Prtrology, 2012, 32(4): 7-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201204002.htm [42] 郭华明, 倪萍, 贾永锋, 等. 原生高砷地下水的类型、化学特征及成因[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404002.htmGuo H M, Ni P, Jia Y F, et al. Types, chemical characteristics and genesis of geogenic high-arsenic groundwater in the world[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4): 1-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404002.htm [43] 江湛如, 汤媛媛, 李冰玉, 等. 磁性海藻酸铁介孔碳微球的合成及对水体中砷的去除[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(6): 2382-2392. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201806031.htmJiang Z R, Tang Y Y, Li B Y, et al. Synthesis of magnetic alginate mesoporous carbon for the removal of As fromwater solution[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(6): 2382-2392(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201806031.htm [44] 柳亚清, 谢先军, 皮坤福, 等. 水流场及水化学过程对地下水中砷富集的影响[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(3): 185-190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2015.03.020Liu Y Q, Xie X J, Pi K F, et al. Effects of groundwater flowing and hydrochemical processes on the arsenic enrichmenting groundwater system[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(3): 185-190(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2015.03.020 -





 下载:
下载: