Genetic mechanism and permeability evaluation of low contrast oil reservoirs in M Oilfield of Wushi Sag
-
摘要:
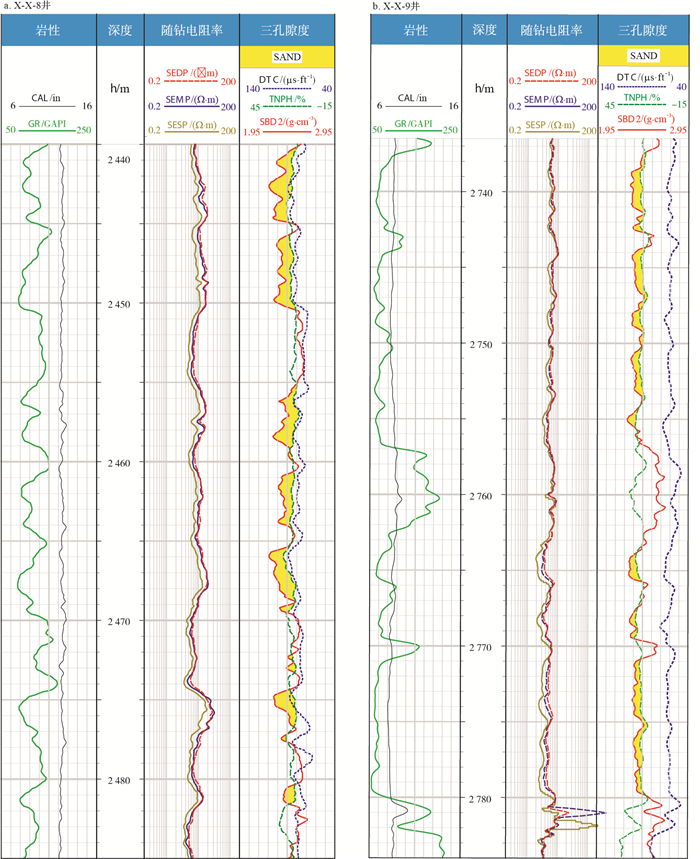
乌石凹陷M油田主力油组砂体规模较大, 岩性主要为含砾中粗砂岩和砂砾岩, 其次为细砂岩。砂砾岩油层由于受特殊沉积和成岩作用影响, 浅层油层表现为高阻特征, 中深层部分油层电阻率与水层相差不大, 为测井流体性质识别及渗透率定量评价带来较大困难。以核磁、压汞、铸体薄片等实验资料为基础, 从微观研究高阻油层与低对比度油层储层特征的差异, 并且将储层按粒间孔、混合孔、铸模孔分为3类, 建立了M油田储层类型划分标准及渗透率预测模型。结果表明: 孔隙结构的复杂性造成的高束缚水饱和度是导致区域低对比度油层形成的主要原因; 储层分类后渗透率计算精度明显提高, 为油田开发方案的制定与实施及钻后评价奠定了坚实的基础。
Abstract:The sandstone body of the main oil layer of M oilfield in Wushi Sag is large, and the lithology is mainly gravelly medium-coarse sandstone and sandy conglomerate, followed by fine sandstone.Due to the influence of special sedimentation and diagenesis, the shallow buried oil layer shows the characteristics of high resistivity, while the resistivities of some middle and deep buried oil layers are very close with that of the water layers, which brings great difficulties to the well logging based identification of fluid properties and quantitative evaluation of permeability.Based on the experimental data of NMR, mercury injection and cast thin sections, this paper analyzed the difference in reservoir characteristics between high resistivity reservoirs and low contrast reservoirs from the microscopic view.Then, based on the pore types (intergranular pores, mixed pores and mold pores), the resevoirs were diveded into three types, and the reservoir type classification standard were established. At last, the reservoir type-based permeability estimation models were proposed.The results show that the high irreducible water saturation caused by the complexity of pore structure is the main reason of the low contrast reservoirs. The accuracy of the estimated permeability is significantly improved after reservoir classification, which lays a solid foundation for the formulation and implementation of the oilfield development plan and post drilling evaluation.
-
Key words:
- low contrast reservoir /
- genetic mechanism /
- permeability /
- pore type /
- Wushi Sag1
-
-
[1] 刘冲, 朱定军, 苏文辉, 等. 乌石凹陷流沙港组成岩作用及其孔隙演化[J]. 地质与资源, 2013, 22(5): 426-430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2013.05.015Liu C, Zhu D J, Su W H, et al. Diagenesis and pore evolution of the Liushagang formation in wushi sag[J]. Geology and resources, 2013, 22(5): 426-430(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2013.05.015 [2] 曾小明, 邹明生, 张辉, 等. 北部湾盆地乌石凹陷东区流沙港组三段储层物性主控因素及分布规律[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(6): 757-764. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201606009.htmZeng X M, Zou M S, Zhang H, et al. Main controls on the distribution of the 3rd member of Liushagang Formation in eastern Wushi Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(6): 757-764(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201606009.htm [3] 彭志春, 杨丽, 汪新光, 等. 北部湾盆地乌石17-X油田流沙港组三段砂砾岩储层物性主控因素研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(10): 6-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.10.002Peng Z C, Yang L, Wang X G, et al. The key control factors study on glutenite physical property of Liushagang Ⅲ, Wushi 17-X oil field of Beibu Gulf Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(10): 6-11(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.10.002 [4] 吴金龙, 孙建孟, 朱家俊, 等. 济阳坳陷低阻油层微观成因机理的宏观地质控制因素研究[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 30(3): 22-25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-5870.2006.03.005Wu J L, Sun J M, Zhu J J, et al. Study on macro-geologic control genesis of micro-geological causes in low-resistivity oil layer of Jiyang Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2006, 30(3): 22-25(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-5870.2006.03.005 [5] 王丽, 袁伟, 丁磊, 等. 基于常规测井资料的储层流体识别方法[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2): 241-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802033.htmWang L, Yuan W, Ding L, et al. Reservoir fluid identification based on normal logging data[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(3): 241-245(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802033.htm [6] Archie G E. The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics[J]. Petroleum Transactions, AIME, 1942, 146: 54-62. doi: 10.2118/942054-G [7] Adrian C, Claudine D, Etienne B. Pore microgeometry analysis in low-resistivity sandstone reservoirs[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2002, 35(3/4): 205-232. [8] 于红岩, 李洪奇, 郭兵, 等. 基于成因机理的低阻油层精细评价方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2012, 42(2): 335-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201202008.htmYu H Y, Li H Q, Guo B, et al. Low-resistivity oil layers fine evaluation approaches based on mechanism[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(2): 335-343(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201202008.htm [9] 骆玉虎, 何胜林, 谭伟, 等. 北部湾盆地砂砾岩低阻油层成因及饱和度计算方法[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 33-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906006.htmLuo Y H, He S L, Tan W, et al. Genetic mechanism and saturation calculation method of low resistivity sandy conglomerate oil layers in Beibu Gulf Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 33-41(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906006.htm [10] 黄月银, 姚光庆, 成涛, 等. 文昌13-1/2油田珠江一段细粒储层沉积相及低阻油层性质[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(2): 161-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201602033.htmHuang Y Y, Yao G Q, Cheng T, et al. Geological origin and genesis of low-resistivity oil layers in Wenchang13-1/2 Oilfield[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(2): 161-168(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201602033.htm [11] 张爱华. 辽河油区低阻油气层成因机理及研究思路[J]. 特种油气藏, 2004, 11(6): 37-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2004.06.011Zhang A H. Genetic mechanism and study method for low resistivity reservoirs in Liaohe oil Province[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2004, 11(6): 37-39(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2004.06.011 [12] 游瑜春, 刘伟兴, 谭振华, 等. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷低阻油气层成因研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(6): 941-944. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200906018.htmYou Y C, Liu W X, Tan Z H, et al. Genesis of low-resistivity reservoirs in Qintong Sag, Subei Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(6): 941-944(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200906018.htm [13] 王伟, 宋渊娟, 黄静, 等. 利用高压压汞实验研究致密砂岩孔喉结构分形特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 22-30. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0402Wan W, Song Y J, Huang J, et al. Fractal characteristics of pore-throat structure in tight sandstones using high-pressure mercury intrusion porosimetry[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 22-30(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0402 [14] 汪新光, 张冲, 张辉, 等. 基于微观孔隙结构的低渗透砂岩储层分类评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 93-103. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0429Wang X G, Zhang C, Zhang H, et al. Classification and evaluation of low-permeability sand reservoir based on micro-pore structure[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 93-103(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0429 [15] Wang J M, Zhang S. Pore structure differences of the extra-low permeability sandstone reservoirs and the causes of low resistivity oil layers: A case study of Block Yanwumao in the middle of Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(2): 273-280. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30030-2 [16] Lai J, Wang G W, Wang Z Y, et al. A review on pore structure characterization in tight sandstones[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 177: 436-457. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.12.003 [17] 王赛英, 赵冠军, 张萍, 等. 低阻油层形成机理及测井识别方法研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2010, 17(4): 10-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201004002.htmWang S Y, Zhao G J, Zhang P, et al. Formation mechanism and logging identification of low resistivity reservoirs[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2010, 17(4): 10-14(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201004002.htm [18] 张冲, 张超谟, 张占松, 等. 低渗透砂砾岩储层饱和度测井评价方法及其应用: 以王府断陷小城子地区登娄库组储层为例[J]. 西安石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 31(2): 11-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201602002.htmZhang C, Zhang C M, Zhang Z S, et al. Calculation method of water saturation of low-permeability gluteniter eservoir and its application: Taking the reservoir of Denglouku Formation in Xiaochengzi area, Wangfu Fault[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 31(2): 11-17(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201602002.htm [19] 陈杰, 周改英, 赵喜亮, 等. 储层岩石孔隙结构特征研究方法综述[J]. 特种油气藏, 2005, 12(4): 11-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ200504002.htmChen J, Zhou G Y, Zhao X L, et al. Overview of study methods of reservoir rock pore structure[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2005, 12(4): 11-14(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ200504002.htm [20] 赵新伟, 许红. 基于微焦X-CT的碳酸盐岩孔隙结构精细表征[J]. 特种油气藏, 2016, 23(1): 127-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201601029.htmZhao X W, Xu H. Microfocus X-CT based fine characterization of carbonate pore texture[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2016, 23(1): 127-131(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201601029.htm [21] 朱林奇, 张冲, 何小菊, 等. 基于动态孔隙结构效率的核磁共振测井预测渗透率方法[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2015, 36(5): 607-611. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201505022.htmZhu L Q, Zhang C, He X J, et al. NMR logging permeability prediction method based on dynamic pore structure efficiency[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2015, 36(5): 607-611(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201505022.htm [22] 秦瑞宝, 张磊, 周改英. 潜山油田裂缝孔隙度和渗透率测井评价新方法[J]. 中国海上油气, 2015, 27(3): 31-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201503005.htmQin R B, Zhang L, Zhou G Y. A new logging method for evaluating fracture porosity and permeability in buried hill oil fields[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2015, 27(3), 31-37(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201503005.htm [23] 宋子齐, 杨红刚, 孙颖, 等. 利用岩石物理相分类研究特低渗透储层参数建模[J]. 断块油气田, 2010, 17(7): 672-677. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201006009.htmSong Z Q, Yang H G, Sun Y, et al. Study on parametric modeling of ultra-low permeability reservoir with petrophysicalfaciesclassification[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2010, 17(7): 672-677(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201006009.htm [24] 石玉江, 张海涛, 侯雨庭, 等. 基于岩石物理相分类的测井储层参数精细解释建模[J]. 测井技术, 2005, 29(4): 328-332. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200504013.htmShi Y J, Zhang H T, Hou Y T, et al. The fine logging interpretation method based on petrophysical faces[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2005, 29(4): 328-332(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200504013.htm [25] 景成, 宋子齐, 蒲春生, 等. 基于岩石物理相分类确定致密气储层渗透率: 以苏里格东区致密气储层渗透率研究为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2013, 28(6), 3222-3230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201306049.htmJing C, Song Z Q, Pu C S, et al. Refined permeability of tight gas reservoir based on petrophysical facies classification: Taking the study of tight gas reservoir permeability in the eastern of Sulige for an example[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2013, 28(6), 3222-3230(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201306049.htm [26] Swanson B F. Asimple correlation between permeability and capillary pressure[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1981, 67(11): 2498-2503. -





 下载:
下载: