Calibration of capacitive soil moisture sensor based on random forest
-
摘要:
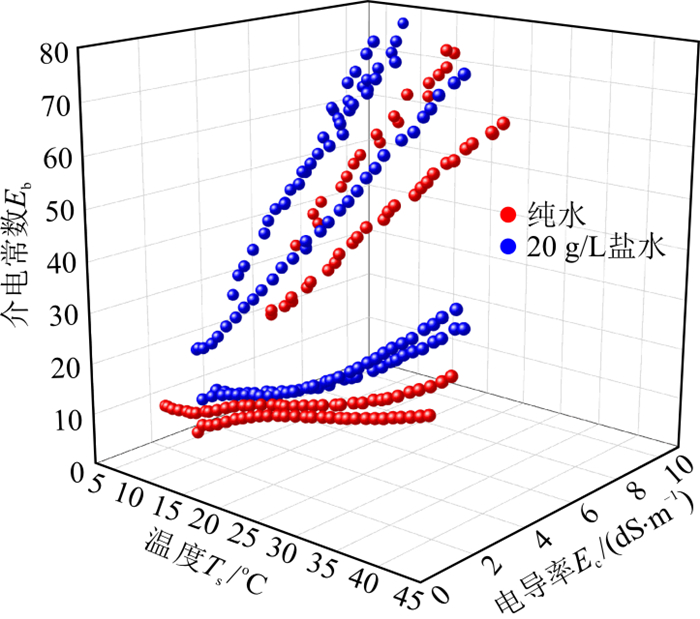
土壤含水量信息对于自然生态修复、农田灌溉管理、土体工程建设等具有重要的意义, 电容式土壤水分传感器是获取该信息的主要途径之一。为准确校准电容式土壤水分传感器(以5TE设备为例)的土壤含水量观测数据, 开展了不同温度、含盐量、土壤含水量条件下的土壤介电常数、电导率和温度观测实验, 构建了基于随机森林机器学习方法的土壤含水量估计模型。结果表明: ①变温、变含盐量情况下, 土壤介电常数受含盐量和温度影响显著, 仅基于土壤介电常数的传统土壤含水量估计模型失效; ②以电容式土壤水分传感器观测的土壤介电常数、电导率和温度数据为输入, 基于随机森林机器学习方法的土壤含水量估计模型可有效改善土壤含水量估计结果(
RMSE 为0.05 m3/m3,R 2为0.77;修正Topp公式的土壤含水量估计结果:RMSE 为0.07 m3/m3,R 2为0.54);③土壤电导率观测对土壤含水量估计最为重要, 介电常数次之, 温度最弱, 但均未达到可忽略不计的程度。研究成果可为电容式土壤水分传感器在变温、变含盐量地区的成功应用提供支撑。Abstract:Objective Soil moisture information crucial for various applications, such as natural ecological restoration, farmland irrigation management, and soil engineering construction. One of the main sensors used to obtain this information is the capacitive soil moisture sensor.
Methods To accurately calibrate the soil water content observation data of the 5TE capacitive soil water sensor, soil dielectric permittivity, electric conductivity and temperature observation experiments were carried out under different temperature, salt content and soil water content conditions. A soil water content estimation model based on the random forest machine learning method was established.
Results The results showed that: ① The soil dielectric permittivity was significantly affected by varying salinity and temperature with constant soil water content. The traditional soil water content estimation model based only on soil dielectric permittivity became invalid, ② The soil water content estimation model based on the random forest method could effectively improve the soil water content estimation with the soil dielectric permittivity, electric conductivity and temperature data as input. Random forest method obtained soil moisture estimation with
RMSE =0.05 m3/m3 andR 2=0.77, whileRMSE =0.07 m3/m3 andR 2=0.54 were obtained by the modified Topp equation, and ③ The soil electric conductivity was the most important factor for soil water content estimation, followed by the dielectric permittivity and temperature. Nevertheless, the importance of the dielectric permittivity and temperature did not reach a negligible level.Conclusion This study provides a way to support the successful application of capacitive soil moisture sensors in areas with variable temperature and salinity.
-
表 1 实验土壤基本物理特征
Table 1. Basic physical characteristics of the experimental soil
土壤类型 干容重/
(g·cm-3)含盐量/
(g·kg-1)砂粒 粉粒 黏粒 wB/% 砂质壤土 1.259 25.57 61.31 34.50 4.19 砂土 1.601 2.29 99.07 0.93 0 表 2 有效观测数据量及其属性范围
Table 2. Amount of valid observation data and their attribute ranges
数据量/组 范围 Eb Ec/(dS·m-1) Ts/℃ θ/(m3·m-3) SSC/(g·kg-1) 砂质壤土 754 2.87~79.56 0~13.21 6.5~40.1 0.007~0.468 25.57~34.30 砂土 871 2.88~79.89 0~9.2 7.0~40.2 0.005~0.333 2.29~26.52 注:Eb为介电常数;Ec为电导率;Ts为温度;θ为体积含水量;SSC为土壤全盐质量分数 -
[1] Henderson-Sellers A. Soil moisture: A critical focus for global change studies[J]. Global & Planetary Change, 1996, 13(1/4): 3-9. [2] 魏玉涛, 刘明欢, 刘可, 等. 多尺度土壤水监测研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(26): 140-145.Wei Y T, Liu M H, Liu K, et al. Progress of multi-scale soil moisture monitoring[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 37(26): 140-145(in Chinese with English abstract). [3] Yu L, Gao W, Shamshiri R R, et al. Review of research progress on soil moisture sensor technology[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2021, 14(4): 32-42. [4] Stacheder M, Koeniger F, Schuhmann R. New dielectric sensors and sensing techniques for soil and snow moisture measurements[J]. Sensors-Basel, 2009, 9(4): 2951-2967. doi: 10.3390/s90402951 [5] Selig M. Generalized equations of rheological curves for rocks[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1975, 12(11): 156. [6] Topp G C, Davis J L, Annan A P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurements in coaxial transmission lines[J]. Water Resour Research, 1980, 16(3): 574-582. doi: 10.1029/WR016i003p00574 [7] Bogena H R, Huisman J A, Oberdorster C, et al. Evaluation of a low-cost soil water content sensor for wireless network applications[J]. Journal Hydrology, 2007, 344(1/2): 32-42. [8] Wraith J M, Or D. Temperature effects on soil bulk dielectric permittivity measured by time domain reflectometry: Experimental evidence and hypothesis development[J]. Water Resources Research, 1999, 35(2): 361-369. doi: 10.1029/1998WR900006 [9] 顾惠南, 杨雷, 邓霄, 等. 电容式土壤水分检测多参数校正方法的研究[J]. 仪表技术与传感器, 2020(4): 117-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YBJS202004026.htmGu H N, Yang L, Deng X, et al. Research on multi-parameter calibration method of capacitive soil moisture detection[J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor, 2020(4): 117-123(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YBJS202004026.htm [10] Yuki K, Ryo S, Naoya M, et al. Low-cost soil moisture profile probe using thin-film capacitors and a capacitive touch sensor[J]. Sensors-Basel, 2016, 16(8): 1292. doi: 10.3390/s16081292 [11] Lekshmis S U, Singh D N, Baghini M S. A critical review of soil moisture measurement[J]. Measurement, 2014, 54: 92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2014.04.007 [12] Baón S, Ochoa J, Baón D, et al. Assessment of the combined effect of temperature and salinity on the outputs of soil dielectric sensors in coconut fiber[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(16): 6577. doi: 10.3390/su12166577 [13] Campbell C S. Response of ECH2O soil moisture sensor to temperature variation[R]. [S. l. ]: Onset Computer Corporation, 2002. [14] Jones S B, Jr J M B, Robinson D A, et al. Standardizing characterization of electromagnetic water content sensors: Part 1. Methodology[J]. Vadose Zone J., 2005, 4(4): 1048-1058. doi: 10.2136/vzj2004.0140 [15] Sun Z J, Young G D, Mcfarlane R A, et al. The effect of soil electrical conductivity on moisture determination using time-domain reflectometry in sandy soil[J]. Can. J. Soil. Sci., 2000, 80(1): 13-22. doi: 10.4141/S98-089 [16] Mcmichael B, Lascano R J. Laboratory evaluation of a commercial dielectric soil water sensor[J]. Vadose Zone J., 2003, 2(4): 650-654. doi: 10.2136/vzj2003.6500 [17] Saito T, Fujimaki H, Yasuda H, et al. Empirical temperature calibration of capacitance probes to measure soil water[J]. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2009, 73(6): 1931-1937. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2008.0128 [18] Tadaomi S, Haruyuki F, Mitsuhiro I. Calibration and simultaneous monitoring of soil water content and salinity with capacitance and four-electrode probes[J]. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 4(6): 683-692. doi: 10.3844/ajessp.2008.683.692 [19] Rosenbaum U, Huisman J A, Vrba J, et al. Correction of temperature and electrical conductivity effects on dielectric permittivity measurements with echo sensors[J]. Vadose Zone J., 2011, 10(2): 582-593. [20] Chen L P, Zhangzhong L L, Zheng W G, et al. Data-driven calibration of soil moisture sensor considering impacts of temperature: A case study on FDR sensors[J]. Sensors-Basel, 2019, 19(20): 4381-4392. [21] Moghadas D, Badorreck A. Machine learning to estimate soil moisture from geophysical measurements of electrical conductivity[J]. Near Surface Geophysics, 2019, 17(2): 181-195. [22] 马瑶, 赵江南. 机器学习方法在矿产资源定量预测应用研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 132-141. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0108Ma Y, Zhao J N. Advances in the application of machine learning methods in mineral prospectivity mapping[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 131-141(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0108 [23] Panahi M, Sadhasivam N, Pourghasemi H R, et al. Spatial prediction of groundwater potential mapping based on convolutional neural network (CNN) and support vector regression (SVR)[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 588: 125033. [24] 徐晗, 姚孔轩, 程丹仪, 等. 基于非开挖随钻检测系统与随机森林的地层岩性识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 272-280. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0039Xu H, Yao K X, Cheng D Y, et al. Stratigraphic lithology identification based on no-dig logging while drilling system and random forest[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 272-280(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0039 [25] 徐晗, 程丹仪, 徐永华, 等. 基于非开挖泥浆性能检测系统与弱监督学习的地层岩性识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 293-301. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0629Xu H, Cheng D Y, Xu Y H, et al. Stratigraphic lithology identification based on no-dig mud property detection system and weakly-supervised learning[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 293-301(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0629 [26] 李亮. 浅析石羊河下游地区水化学特征[J]. 甘肃水利水电技术, 2018, 54(8): 6-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSSJ201808002.htmLi L. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics in the lower reaches of Shiyang River[J]. Gansu Water Resources and Hydropower Technology, 2018, 54(8): 6-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSSJ201808002.htm [27] Breiman L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5-32. [28] Kizito F, Campbell C S, Campbell G S, et al. Frequency, electrical conductivity and temperature analysis of a low-cost capacitance soil moisture sensor[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2008, 352(3/4): 367-378. -





 下载:
下载: